Biology - Immunity
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is an antigen
Foreign protein that triggers immune response
What is an antibody
A protein specific to an antigen, released by B cells
Outline phagocytosis
pathogen recognized by phagocyte because it’s foreign (and its antigens bind to complementary receptors on phagocyte)
pathogen is engulfed by endocytosis
vesicle fuses with pathogen and then lysosome containing enzymes
so the enzyme hydrolyses & destroys pathogen and then it is released via exocytosis
phagocyte become antigen presenting
Explain how the release of antibodies stimulates the process of phagocytosis (2)
antibodies bind to antigens
which causes clumping / attracts phagocytes
How does vaccination work?
vaccine contains antigen from pathogen
Macrophage presents antigen on its surface
T helper cell with complementary receptor binds to antigen
T helper cell stimulates B cells to undergo mitosis and differentiate into plasma and memory cells
memory cells differentiate into plasma cells upon second exposure and secrete antibodies which destroy antigens
Describe how B-lymphocytes respond when they are stimulated by antigens
B lymphocyte engulfs antigen and becomes antigen presenting
T helper cell with complementary receptor binds to antigen
T helper cell stimulates B lymphocyte to undergo mitosis and make plasma cells which can secrete antibodies and memory cells which can differentiate into plasma cells and secrete antibodies upon re-exposure to pathogen
Suggest why it is advisable for people to be vaccinated against influenza every year
Influenza mutates so its antigens change
So influenza antibodies need replacing
Describe cell-meditated immunity
T helper cell with complementary receptor binds to antigen on antigen presenting cell
T cell clones by mitosis to:
stimulate phagocytosis and mitosis of B cells, and activate cytotoxic T cells and become memory cells
How are monoclonal antibodies made ?
Why are they called monoclonal ?
mouse injected with vaccine
B cells are collected and fused with tumor cells
forms hybridoma and then antibodies are collected
Monoclonal → antibody made from single group of identical B cells
Give two ways pathogens might cause disease when they enter the body
release toxins
kill cells
Why are antibodies specific ?
It has specific primary structure meaning its tertiary structure is also specific so it is only complementary to one antigen
Describe the replication of HIV
HIV’s attachment proteins bind to host helper T cell
RNA & reverse transcriptase enters cell
reverse transcriptase makes single complementary DNA strand from RNA
Viral protein produced
Virus assembled and released
Describe how HIV is replicated once inside helper T cells
RNA converted into DNA using reverse transcriptase
DNA inserted into T helper cell
DNA transcribed into mRNA
mRNA is translated into new viral proteins
What is herd immunity
Vaccinating a large amount of the population so most of the people are immune and the virus can’t spread
Difference between active and passive immunity
Active is long term because antibodies are produced in response to antigen while passive is short term because antibodies given are broken down
Active can take time to work while passive is fast acting
Active involves memory cells while passive doesn’t
Active involves antibodies from plasma cells while passive involves antibodies from outside source
how do cytotoxic t cells work
kills abnormal or infected cells
produces perforin which makes pores in cell surface membrane which kills cells
explain active immunity
memory cells differentiate into plasma cells rapidly to release lots of antibodies quickly upon exposure to same pathogen
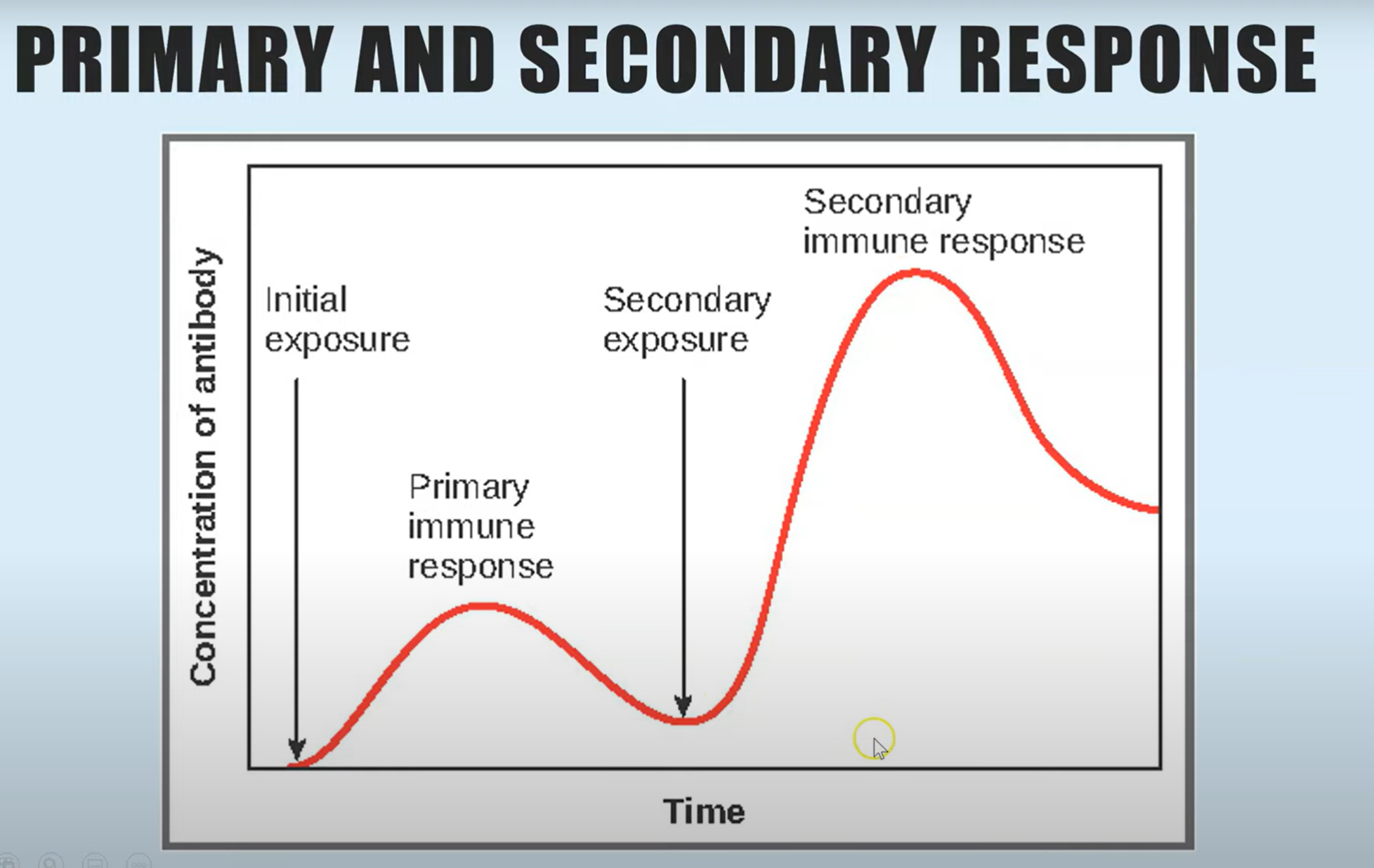
describe and explain differences between primary and secondary response
primary response releases less antibodies slower because there’s not many B cells that can make antibody complementary to antigen
it takes time to locate B cells with specific antibodies to antigens and then for them to be activated and undergo mitosis
secondary response is immediate and produces more antibodies faster because memory cells differentiate quickly into plasma cells which release lots of antibodies rapidly upon second exposure to pathogen
describe the structure of an antibody antigen complex
antibodies are flexible and so can bind to many antigens which help attract phagocytes so they destroy pathogens easier
antibodies have different antigen binding sites because different primary structures create specific tertiary structures
how to identify non-self cells
pathogen
organ transplant
toxins
abnormal cells
what is AIDS
viruses replicate in helper T cells and kill them
immune system cant properly function since B cells cant be stimulated
no antibodies produced
person is vulnerable to infections
how does the pregancy ELISA test work
First mobile antibody, complementary to hCG antigen being tested has colour dye attached to it (application area)
Second antibody, complementary to hCG antigen is immobilised (test zone, shows positive result)
Third antibody, complementary to first antibody is immobilised (control)
ELISA test
Add first antibody complementary to antigen to base of beaker
Wash to remove unbound antibodies
Add second antibody, complementary to first, which contains enzyme
Wash to remove unbound antibodies
Add colourless substrate which produces coloured solution in presence of enzyme
Antigen is present if colour changes