CNS 7 - Somatic Senses
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
4 somatic senses
touch, temperature, proprioception, and nociception
Proprioception
awareness of the position of body parts relative to each other
Nociception
detects tissue damage or the threat of it, and is perceived as pain or itch.
Somatosensory receptor cells are…
all neurons
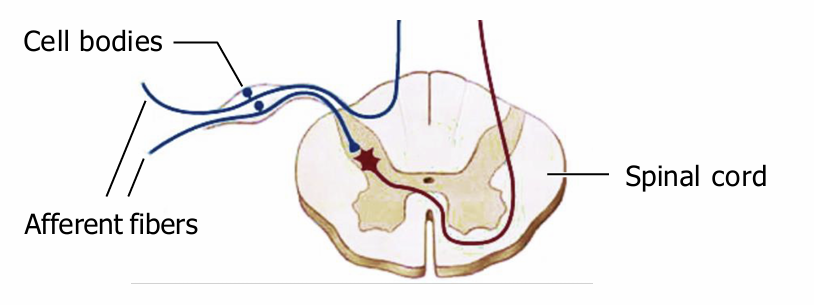
Receptors for somatic sensation below the chin have their cell bodies in the…
dorsal root ganglia
Receptors for the head have their cell bodies in the
brain
Nerve endings
parts of these neurons that transduce touch, pressure etc
in the tips of their fibers, in the skin and viscera.
Epidermis
outer layer of skin — has free nerve endings
Free nerve endings
detect mechanical stimuli, temperature, and chemicals
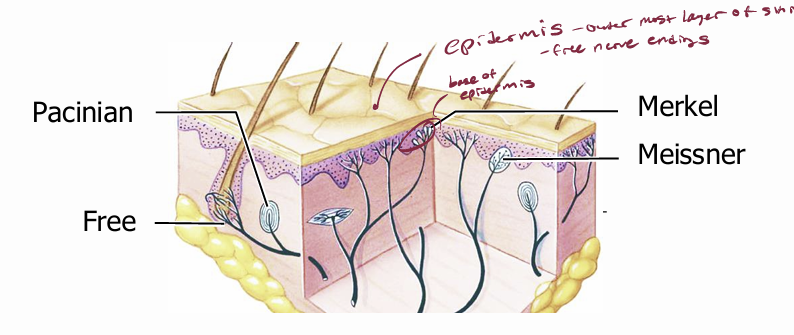
Merkel receptors (merkel disks)
mechanoreceptor nerve endings in contact with specialized epithelial cells called Merkel cells
detect fine pressure, steady pressure. concentrated at fingertips
very sensitive to deformation of the skin
more tonic than phasic,
i.e. they send a sustained message as long as the deformation persists.
Signal contact
Encapsulated receptors (e.g. Meissner and Pacinian corpuscles)
mechanoreceptors sheathed in connective tissue
At the bottom of the epidermis are saucer shaped…
Merkel disks
Most mechanoreceptors are…
phasic
Given a sustained, constant stimulus, the nerve ending’s membrane depolarizes but then returns to baseline in ~3 ms
registers changes — not steady levels
At the top of the dermis are egg shaped
Meissner corpuscles (meiser, money)
Meissner corpuscles
mainly in the tongue and hairless skin — erogenous zones, palms and fingertips
detect sideways shearing, as when you stroke a surface or lift something with your fingertips
phasic - sense changes in shear (rather than sustained pressure)
Deep in the dermis are onion-shaped…
Pacinian corpuscles
Pacinian corpuscles
They can sense tiny displacements (10 μm) if the motion is quick
nerve endings are sheathed in many layers.
phasic - they respond strongly to vibration and other fast-changing stimuli
Receptors are not uniformly distributed over the body surface
Palms, fingertips, and lips are the foveas of the somatosensory system
they have more densely packed receptors, and therefore higher acuity, than other areas.
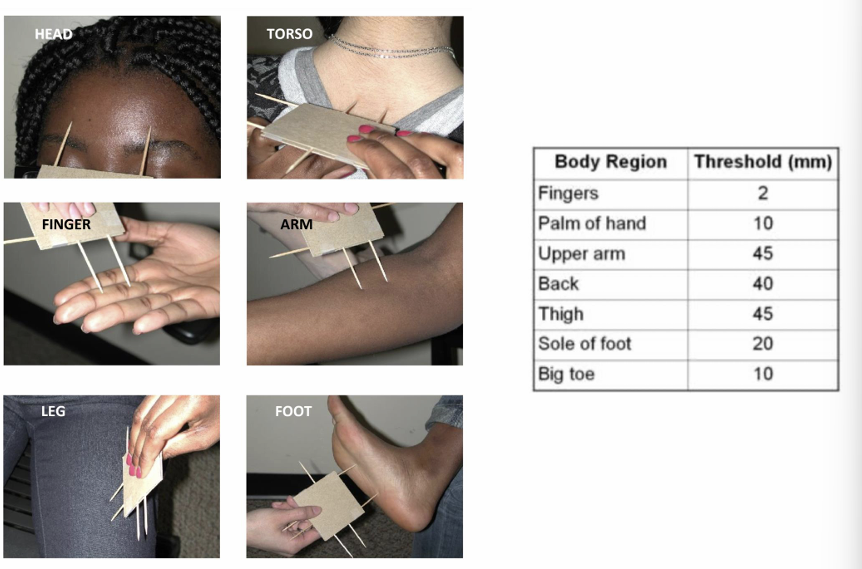
Acuity test of 2-point discrimination
if your skin is touched at 2 places simultaneously, can you tell whether there are one or 2 contact points?
On your lips and fingertips you can distinguish points 2–4 mm apart, but on your calves you need 40 mm
Thermoreceptors are…
free nerve endings
Cold receptors
respond maximally at ~30°C (which is well below body temperature)
phasic-tonic
why we get used to cold lake
Warm Receptors
respond at ~45°C
phasic-tonic
why we get used to hot bath
Pain receptor activation temperature
Above 45°C
paradoxical cold
a hot object, touched briefly, may feel cold
We have more cold receptors than warm, and few thermoreceptors in total
as few as 1000 fibers may carry temperature information up the spinal cord to the brain (precise localization isn’t crucial for temperature)
Nociceptors
free nerve endings that respond to noxious (harmful) stimuli
Some respond to damaging mechanical stimuli, others to damaging heat or chemicals
Some respond to chemicals released from damaged cells (K+, histamine, prostaglandins) or to serotonin released by platelets in response to injury
Somatosensory afferents fall into 2 groups
small and large
Somatosensory afferents
Carry signals from sensory receptors to the CNS
The small fibers
C and Aδ (A-delta) — come mainly from free nerve endings
C fibers
unmyelinated, and conduct spikes at speeds up to 2 m/s. — slower
Aδ’fibers
thicker than C’s, myelinated, and conduct at up to 30 m/s — faster
Large fibers — Aβ (A-beta),
come from Merkel disks or encapsulated mechanoreceptors such as Meissner or Pacinian corpuscles
myelinated, and conduct at 70 m/s.
Large and small fibers project differently
Large fibers turn upward on reaching the spinal cord, and run ipsilaterally up to the medulla in tracts called the dorsal columns.
Small fibers synapse directly or via interneurons on motoneurons (for reflex responses) or on dorsal-horn neurons whose axons cross the midline and run in the spinothalamic tracts, in the lateral part of the cord, between the dorsal and ventral horns
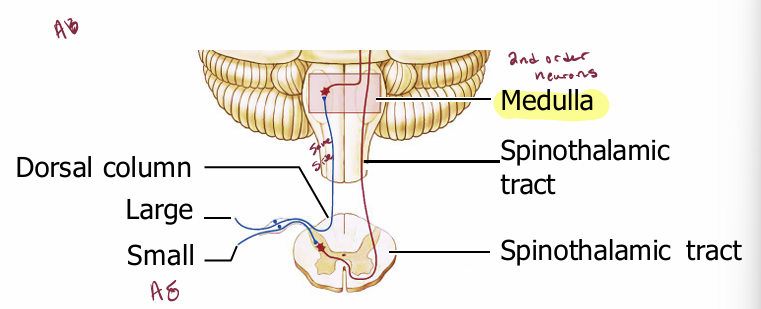
This anatomy reflects the fibers’ different functions
Large fibers provide feedback to…
the brain, especially to motor cortex, as it manipulates objects. Their information has to travel a long way (up to the brain) quickly — complex
Small fibers evoke simple responses…
to specific stimuli: withdrawing from pain, brushing away a bug, thermoregulatory and sexual responses. Many of these tasks can be handled in the spinal cord, without immediate input from the brain.
Signals travel via
thalamus to cortex
Signals from the spinal cord travel via the…
ventroposterolateral (VPL) nucleus of the thalamus.
pass to the primary somatosensory cortex, S1
Signals from the head travel via the…
ventroposteromedial nucleus (VPM)
pass to the primary somatosensory cortex, S1
Primary somatosensory cortex is somatotopic
Neighboring areas of skin project to neighboring cells in cortex, so S1 is a map of the contralateral body surface
map is distorted, as areas of high sensitivity and acuity (such as hands and lips) get a lot of cortical space, just as the foveas do in the visual system
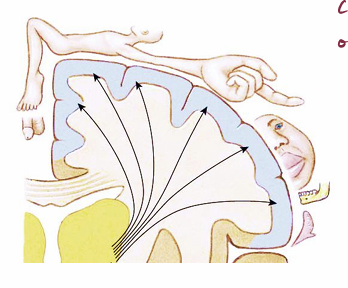
Somatotopic
cortex contains map of the body’s surface
Primary somatosensory cortex (S1) location
Parietal Lobe
lateral inhibition
enhances spatial differences, i.e. edges
There is lateral inhibition among somatosensory fibers
If you step into a very hot bath, most discomfort is felt ay the line formed by the water surface around your leg, because that is the temperature edge — bc of lateral inhibition
somatosensory version of the Chevreul illusion
TRP
transient receptor potential (TRP) channels
Many nociceptors have ion channels of the TRP type
eg: TRPV1 channels—vanilloid receptors: respond to damaging heat and to chemicals, including the capsaicin in chili peppers
TRPM8 channels respond to cold and to menthol
Nociceptive signals
report damage or danger, and evoke pain or itch
congenital analgesia
cannot feel pain
people with this usually die before they are 20, because of injury and infection
2 types of pain
fast and slow
e.g. when you stub your toe, you feel an immediate sharp pain, followed ~1 s later by a duller sensation
Fast pain is carried by…
Aδ fibers
slow pain is carried by…
C fibers
reason for the 2 types is likely that pain evokes 2 distinct responses:
quick withdrawal and prolonged immobilization
quick withdrawal
to get away from the painful thing
prolonged immobilization
(to promote healing)
Nociceptive signals evoke responses from the…
CNS
Nociceptive signals trigger withdrawal
e.g. pulling your hand back from a hot stove.
Spinal reflex
doesn’t need immediate input from the brain
Nociceptive signals also reach the limbic system and hypothalamus
causing emotional distress, nausea, vomiting, and sweating
Descending pathways through the thalamus can…
can block nociceptive cells in the spinal cord,
in emergencies where survival depends on ignoring pain
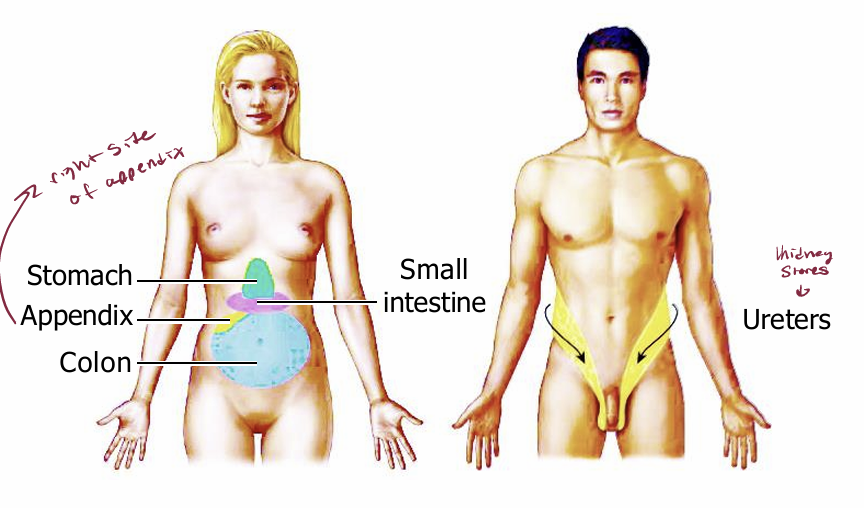
Referred Pain
Pain in an internal organ is often felt on the body surface
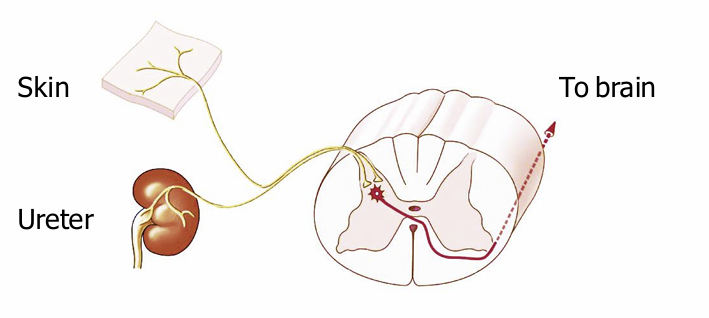
Nociceptors from different locations converge on a single…
ascending tract
when that tract sends signals to the brain, the brain doesn’t know where the stimulus came from
As pain is more common in skin than in internal organs…
the brain assumes the problem is on the body surface
Pains from different organs are referred to different regions on the body surface
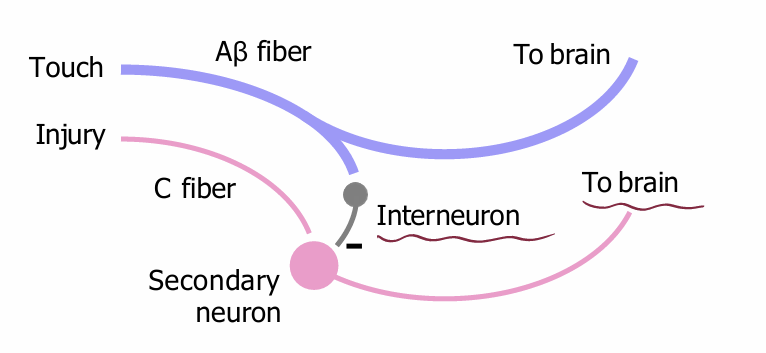
Pain can be gated by…
Aβ activity
In the dorsal horn, C fibers contact secondary neurons.
'Those secondaries are inhibited by Aβ fibers via interneurons.
Aβ’s can block or dampen pain signals, e.g. if you rub a sore shoulder, it feels better
Analgesics
Drugs that relieve pain
Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin)
inhibits prostaglandins and inflammation and slows transmission of pain signals.
Opioids
(such as morphine and codeine) decrease transmitter release from primary sensory neurons and postsynaptically inhibit secondary sensory neurons.
Body’s natural painkillers
Endorphins, enkephalins and dynorphins