Urinalysis Clin path2
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Physical urinalysis
gross evaluation, USG determination
Chemical urinalysis
dipstick reagent pad analysis, ictotest, UP:UC
Microscopic urinalysis
evaluation of sediment
For best results of urinalysis?
analyze within 30 minutes
Urine is expected to be clear in all healthy animals except what species?
horses
True or false: You can use the dipstick to determine specific gravity
false
What is reliable on the urine dipstick?
protein, glucose, ketones, pH, bilirubin, hemoprotein
Carnivores have increased protein catabolism which makes their urine pH more?
acidic (6-7.5)
Ruminants have decreased protein catabolism which makes their urine pH more?
alkaline (7.5-8.5)
Infection with urease-producing bacteria results in _ of the urine?
alkalinization
What can cause a false positive for urine protein?
very alkaline urine or some cleaning agents
Always interpret proteinuria in the context of?
USG
True or false: some glucose can be in the urine
False
Glucose is efficiently reabsorbed in the?
proximal tubule
Glucosuria is present if?
renal threshold is exceeded
False positive for glucose
contamination with cleaning agents
False decreases or negative for glucose
Vit C, ketones, cold urine
What is the most common cause of glucosuria?
hyperglycemia
What can cause hyperglycemic glucosuria?
diabetes mellitus, severe pancreatitis, hyperadrenocorticism, severe stress/excitement, iatrogenic
What can cause normoglycemic glucosuria?
previous transient episode of hyperglycemia, or renal tubular defect
If the normoglycemic glucosuria is due to renal tubular defect what is a cause of this?
gentamycin toxicity
What ketones does the dipstick detect?
acetone and acetoacetate
What ketone is produced in the largest quantity?
B-hydroxybutyrate
When are ketone bodies produced
negative energy balance (starvation or inability to use carbohydrates-lack of insulin)
What can cause false positives for ketones?
pigmented urine
True or false: ketones can be present in urine of healthy animals
false
Which comes first, ketonuria or ketonemia?
ketonuria
True or false: heme in the urine is a very sensitive test
true
Positive heme test in urinalysis could be?
hematuria, hemoglobinuria, myoglobinuria
hematuria
RBCs in sediment, normal plasma color
Hemoglobinuria
red, clean supernatant, no RBCs in sediment, red plasma, evidence of anemia on CBC
myoglobinuria
red brown supernatant, no RBCs in sediment, plasma normal clear, increased CK and AST
True or false: bilirubin can be seen in concentrated urine
true
1+ bilirubin is common in what species?
dogs
Bilirubinuria is always significant in what species?
cats, horses, cattle
positive reaction of urine bilirubin means what?
conjugated bilirubin is in urine
What causes a false decrease in bilirubin
exposure to UV light (keep urine in the dark prior to analysis!)
How many RBCs are considered normal in urine sediment?
<5
How many WBCs are acceptable in urine sediment?
<5
Increased WBCs in urine indicates
pyuria
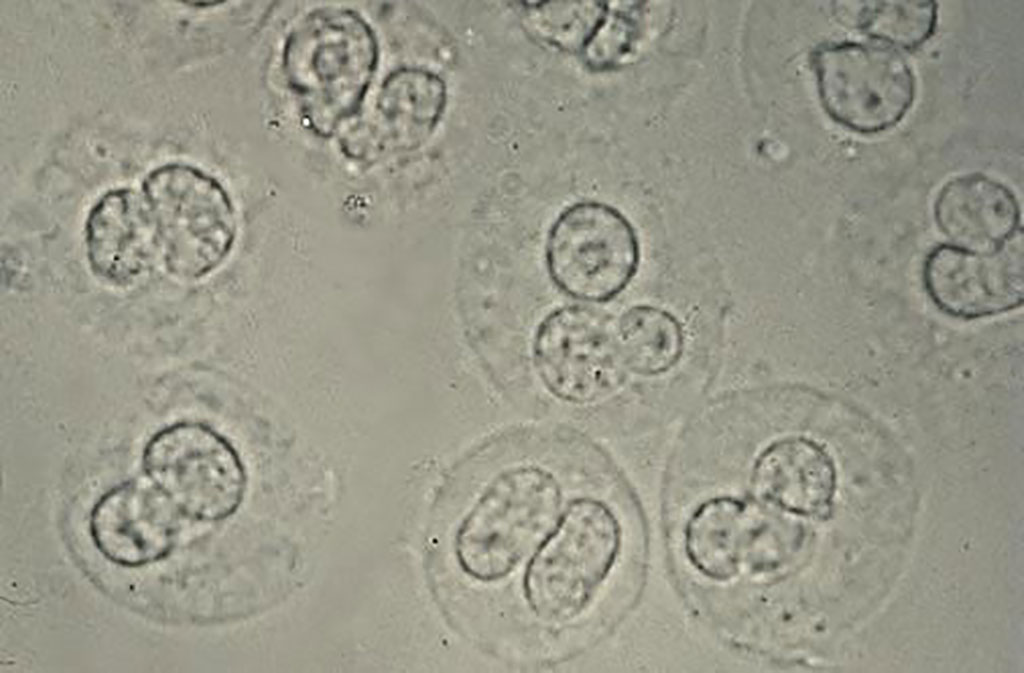
What is in the urine sediment
wbcs
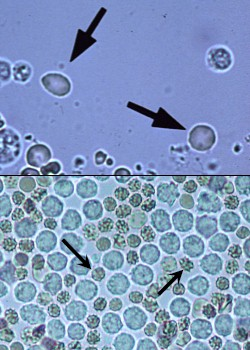
What is in the urine sediment
rbcs
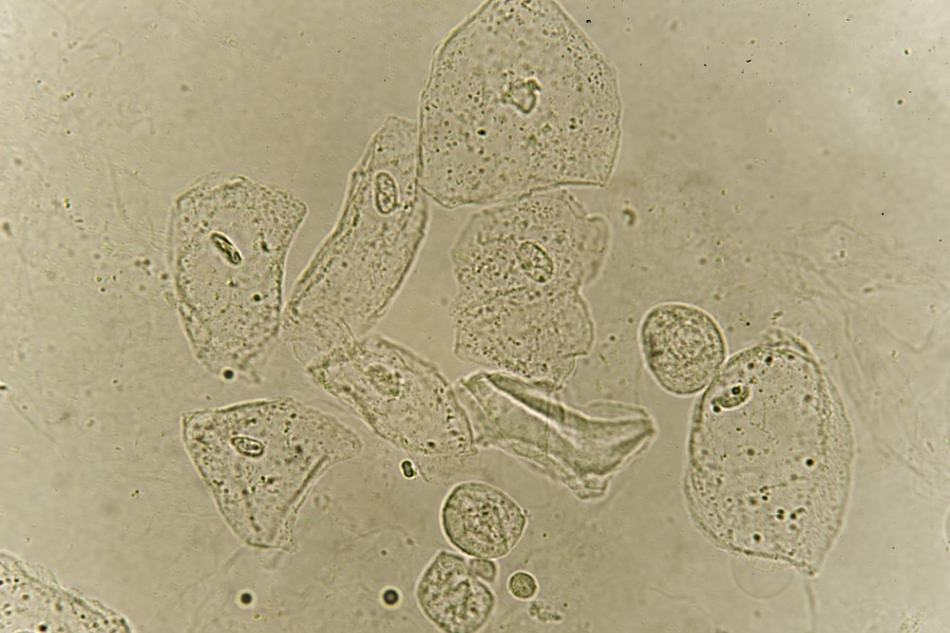
What is in the urine sediment?
Epithelial Cells
What two ways to collect urine samples may have some bacteria contaminant?
voided and catheterized
What urine collection method should never have bacteria in it?
cystocentesis
True or false: centrifugation of urine concentrates bacteria
false
Struvite crystals
colorless, 3D prism-like crystals, "coffin lids"
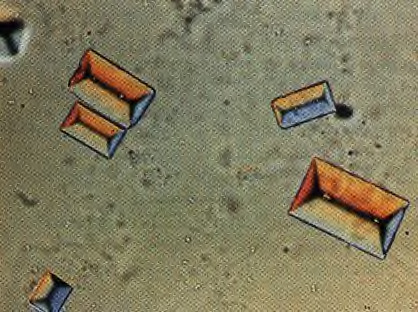
True or false: struvite crystals can be seen in urine of healthy animals
true
What are struvite crystals made of?
magnesium ammonium phosphate or triple phosphate
What pH of urine do struvite crystals prefer?
neutral to alkaline
What predisposes the animal to having struvite crystals and urolithiasis?
bacterial cystitis (increases pH)
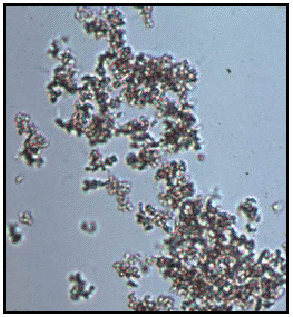
Amorphous crystals
grain-like precipitate material

Calcium oxalate dihydrate crystals
colorless squares with corners connected by central X
True or false: calcium oxalate dihydrate crystals can be seen in healthy animals
true
What pH can you see calcium oxalate dihydrate crystlas?
any
Where do calcium oxalate dihydrate crystals develop?
in stored urine
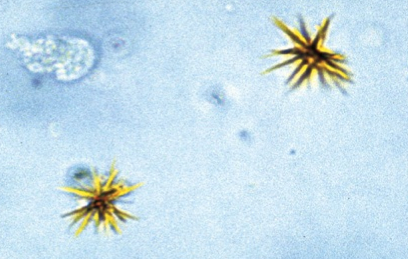
Bilirubin crystals
fine needle-like crystallin structure
True or false: bilirubin crystals can be seen normally in concentrated dog urine
true
True or false: bilirubin crystals can be seen normally in cats, horses, and cattle
False, always pathologically significant
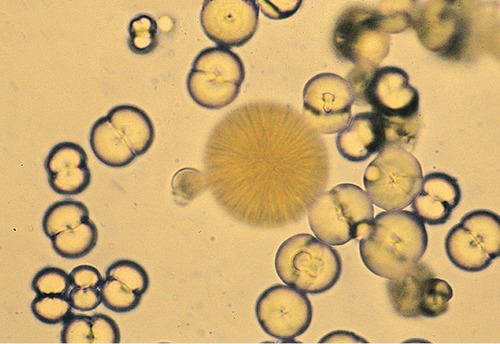
Calcium carbonate
large, yellow-brown or colorless spheroids with radial striations or dumbbell shaped
What species is calcium carbonate normal in ?
horses, rabbits, guinea pigs, goats
If you see calcium carbonate in a dog or cat that has signs of renal disease what might it be?
melamine-cyanuric acid crystals (2004 toxic food products outbreak)
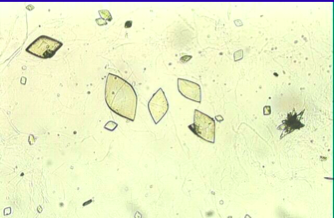
What are these?
uric acid crystals
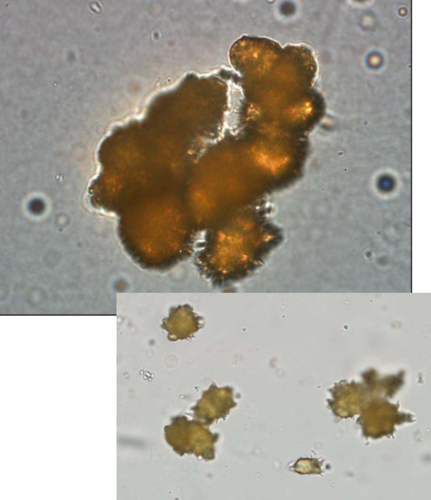
What is this?
ammonium urate/biurate
Urate crystals (both uric acid and ammonium urate/biurate) can be seen when?
portosystemic shunts and other hepatic diseases where hyperammonemia exists
What breeds of dogs get urate crystals?
Dalmatians and English Bulldogs
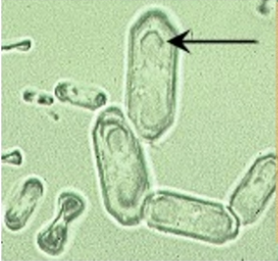
Calcium oxalate monohydrate
hemp seed, dumbbell shaped or flat, six-sided form (fense pickets)
True or false you can see calcium oxalate monohydrate in health
true
What species would you especially expect to see calcium oxalate monohydrate?
healthy horses and rabbits
What is a pathological cause of calcium oxalate monohydrate?
ethylene glycol poisoning and hypercalciuria (chocolate toxicosis)

Cystine crystals
flat, colorless, hexagonal, with equal or unequal sides. often aggregate in layers
Cystine crystals are seen in what pH of urine?
acidic
What causes some animals to have the tubular inability to reabsorb cystine and cause them to have cystine crystals?
inherited sex linked metabolic abnormality (avoid breeding these animals!)
Casts form where?
distal tubules and collecting ducts
What are casts composed of mainly?
Tamm-Horsefall mucoprotein
Hyaline casts are made of
protein only
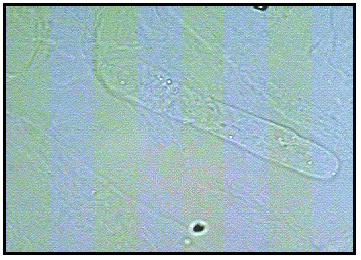
Hyaline casts
rounded ends and parallel sides (often cigar shaped)
True or false: some hyaline casts may be seen in healthy animals
true
If you see hyaline casts in high numbers it is associated with
proteinuria (especially glomerular proteinuria)
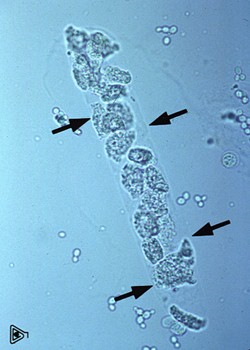
Epithelial cell casts
desquamation from renal tubules, cast is shed shortly after being formed, cells appear intact
What do epithelial cell casts indicate?
renal disease, ischemia, infarction, nephrotoxicity
True or false: some epithelial cell casts can be seen in a healthy patient
false
What cast is the earliest indicator of renal tubular cell injury when drugs are potentially damaging the kidney?
epithelial cell casts
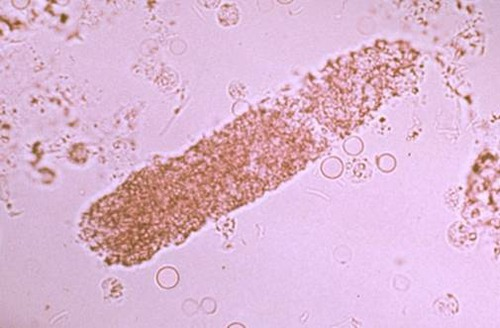
Granular casts
degenerated cellular casts
True or false: granular casts can be seen in a healthy patient
true
What do large numbers of granular casts indicate?
tubular degeneration consistent with nephritis, nephrotoxin, infection, protein losing nephropathy
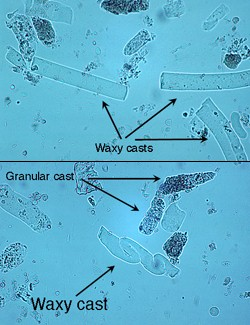
Waxy casts
long standing granular casts, with sharp squared off ends, smooth consistency, but more refractile than hyaline casts
What do waxy casts indicate
chronic tubular lesions
True or false waxy casts can be seen in a healthy patient?
false
Waxy casts are often associated with
severe renal disease like glomerulonephritis and amyloidosis
Casts do NOT correlate with of disease
severity
Large number of casts always indicates?
active generalized renal disease
Casts are shed _
intermittently
The lack of casts DOES NOT _ renal disease
rule out