Surgical Nursing Exam 2 +terms +instruments
1/222
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
223 Terms
ur/o
urine, urinary tract
-tomy
incision
-rrhexis
rupture
-pathy
disease
cauter/o
heat, burn
tom/o
to cut, slice
edema
swelling
-oma
tumor
lith/o
stone
trich/o
hair
-itis
inflammation
post
after, behind
megaly
enlargement
-cide
killing
y, -esis
condition
-logy
study of
-cision
cutting
an-, a-
without, non
-ectomy
removal
-centesis
surgical puncture
pro-, pre-
before, in front of
rrhagia, rrhage
bursting forth
plasty
surgical repair
viscer/o
internal organs
-tocia
birth, labor
-rrhaphy
suture
-scopy
visual examination
-desis
binding, fixation
dys-
bad, painful
electr/o
electricity
-osis
abnormal condition, increase
-pexy
fixation (of an organ)
Dx
diagnosis
Fx
fracture
Hx
history
Tx
treatment
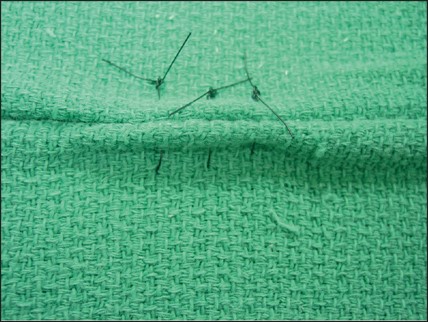
name of pattern
vertical mattress

name of pattern
simple interrupted
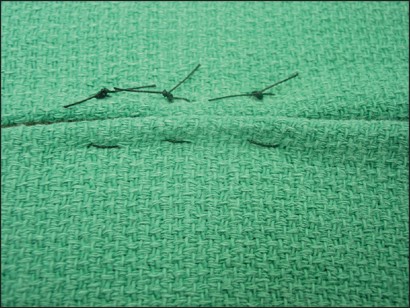
name of pattern
horizontal mattress
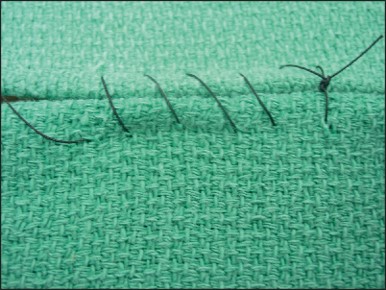
name of pattern
simple continuous

name of pattern
cruciate
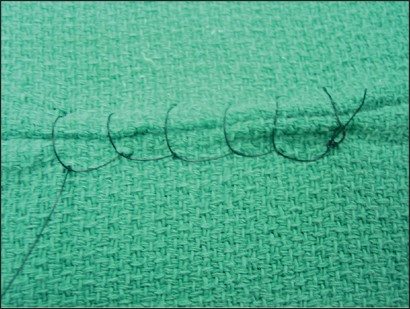
name of pattern
fords interlocking
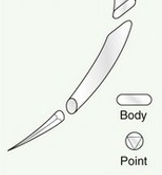
name of suture needle
taper cut
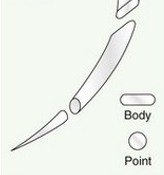
name of suture needle
taper point
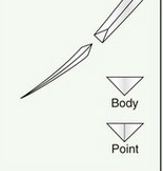
name of suture needle
reverse cutting

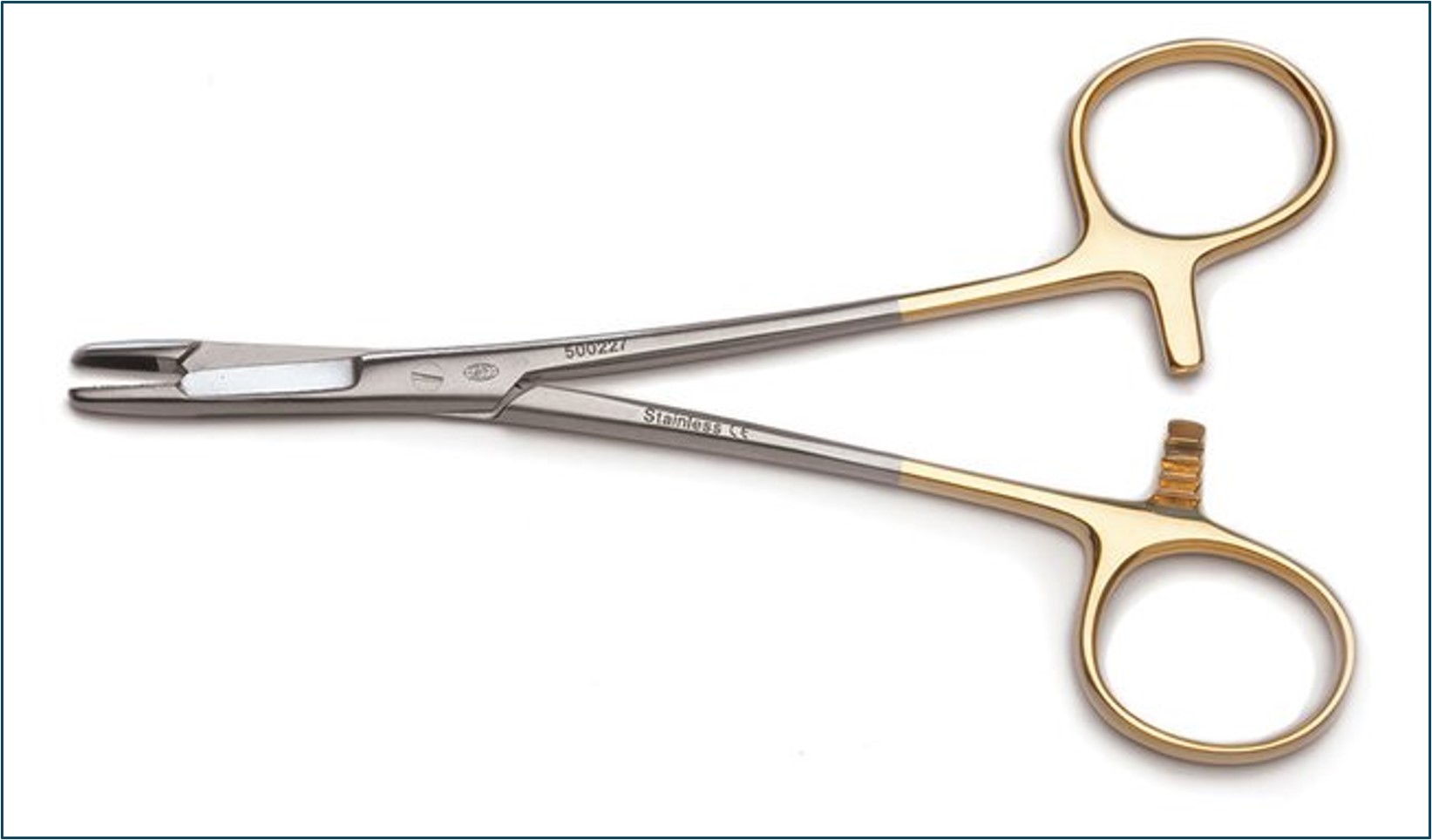
name of instrument
adson thumb tissue forceps
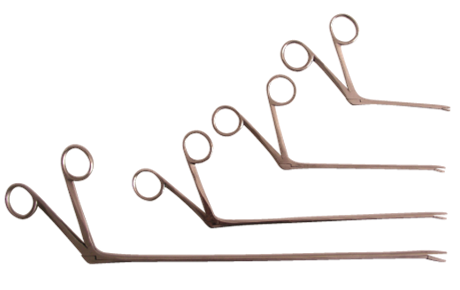
name of instrument
alligator forceps
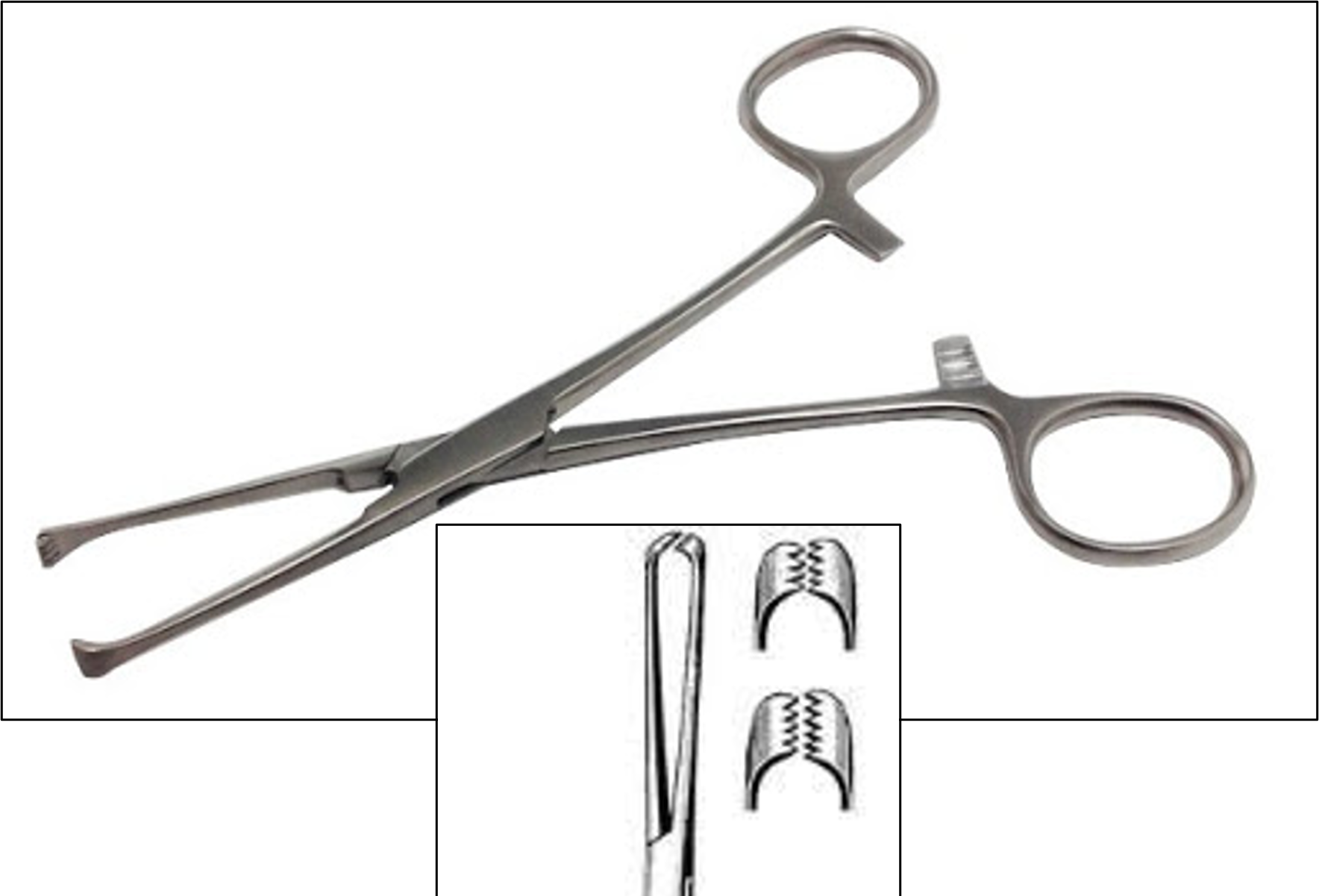
name of instrument
allis tissue forceps
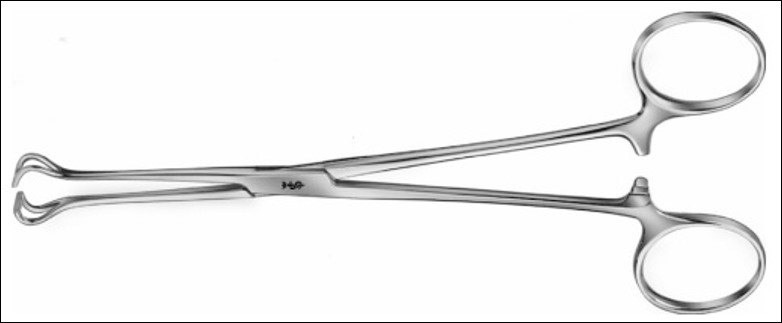
name of instrument
babcock clamps
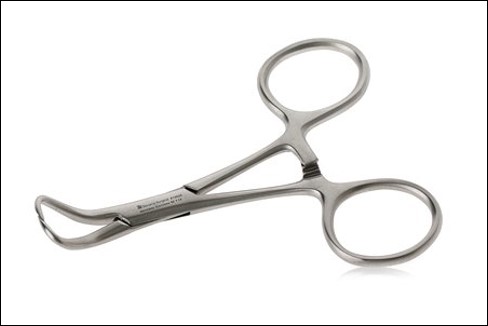
name of instrument
backhaus towel clamps
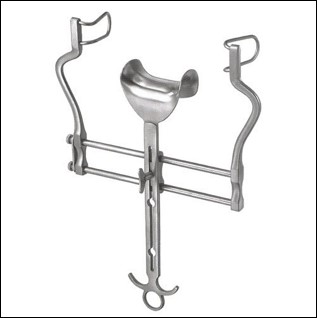
name of instrument
belfour retractor
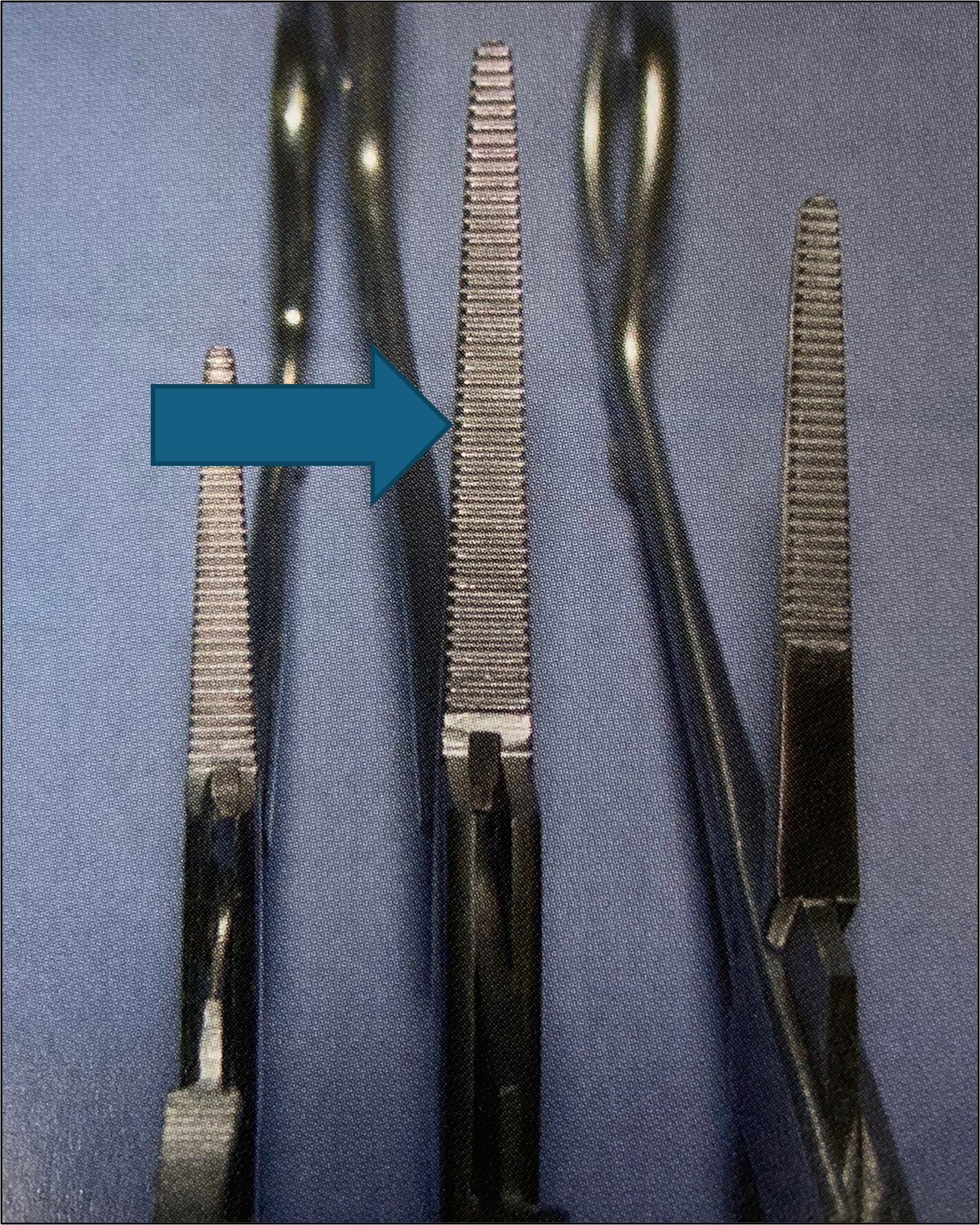
name of instrument
crile forcep hemostats
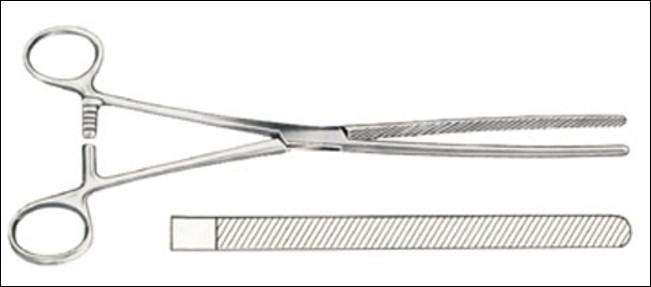
name of instrument
doyen clamp

name of instrument
dressing thumb tissue forcep
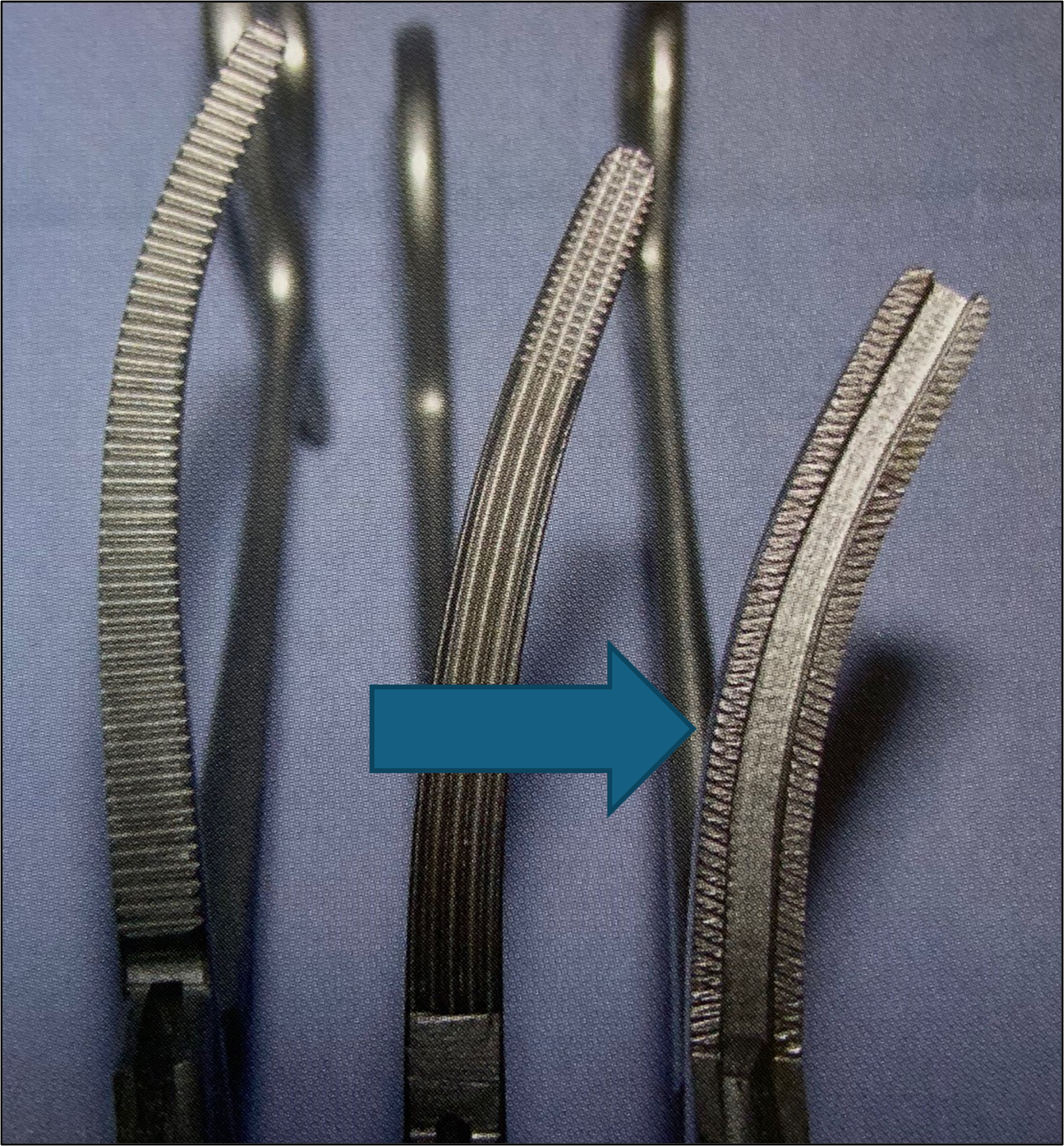
name of instrument
ferguson angiotribe hemostats
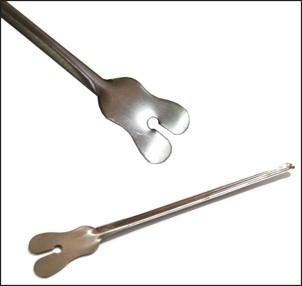
name of instrument
groove director
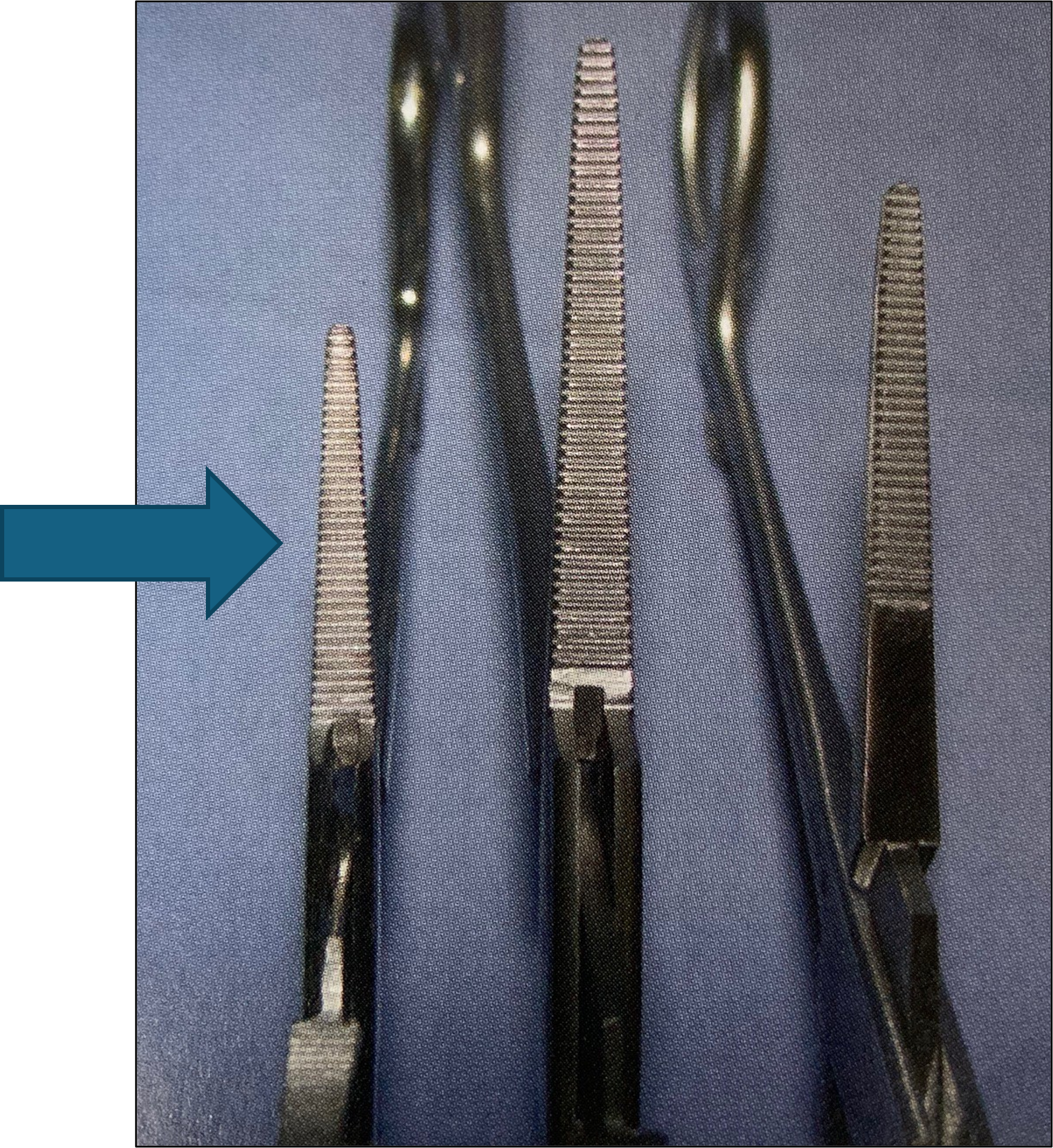
name of instrument
halstead mosquito forceps
name of instrument
kelly forceps hemostats
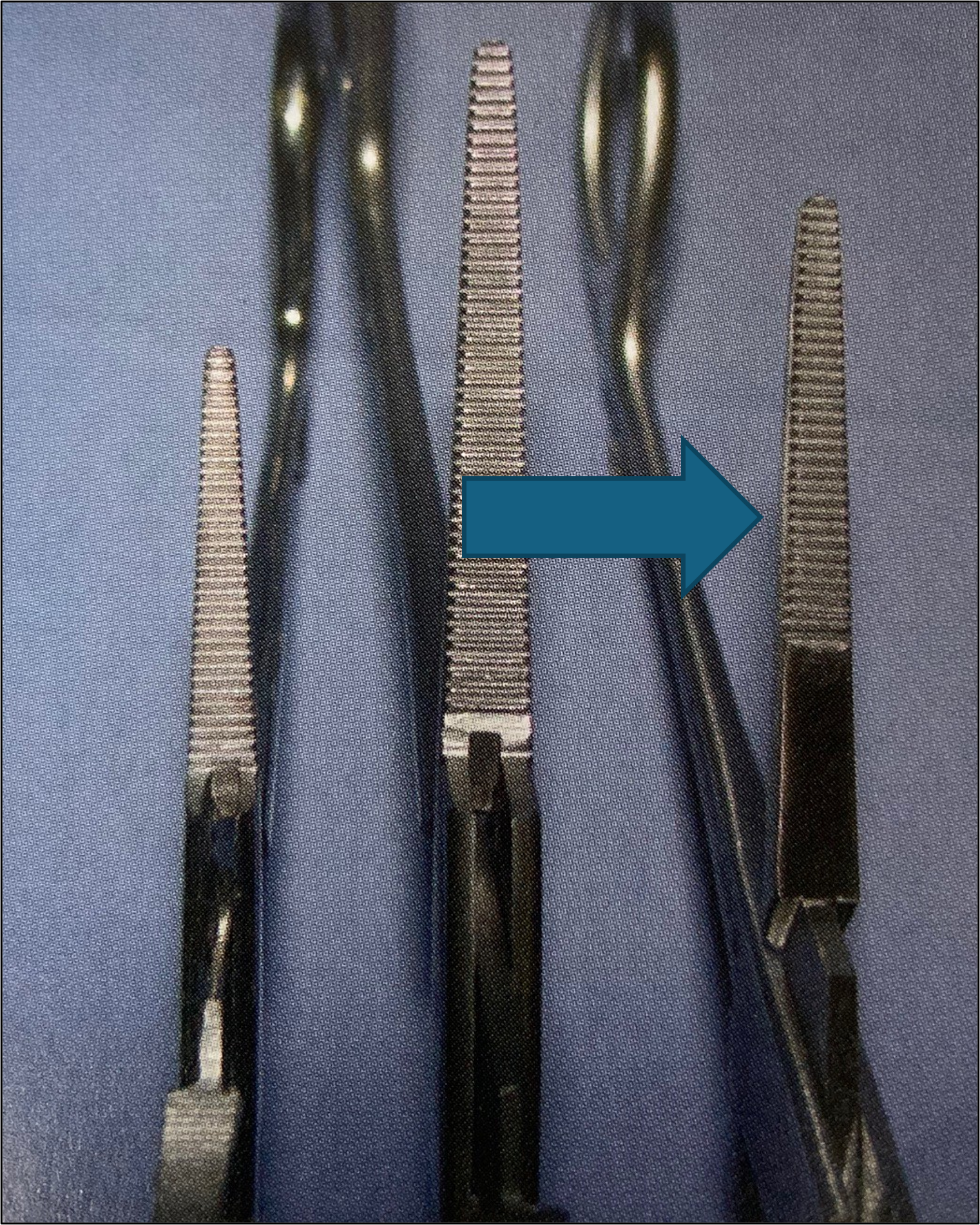
name of instrument
lorna edna towel clamps

name of instrument
mayo needle holder
name of instrument
mayo scissor

name of instrument
metzenbaum scissor

name of instrument
needle rack
name of instrument
olsen hegar needle scissor combo
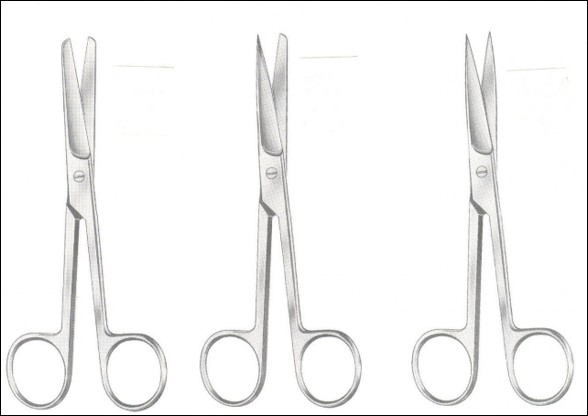
name of instrument
operating scissor
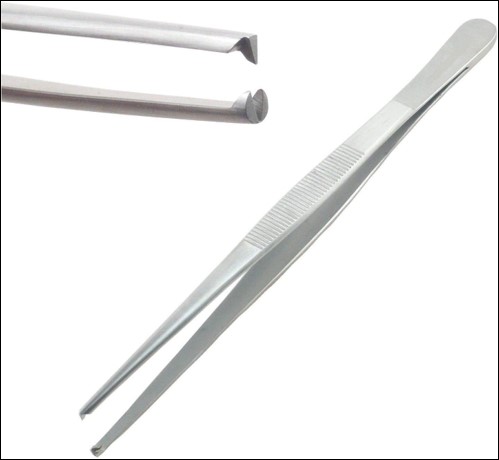

name of instrument
rat tooth thumb tissue forceps
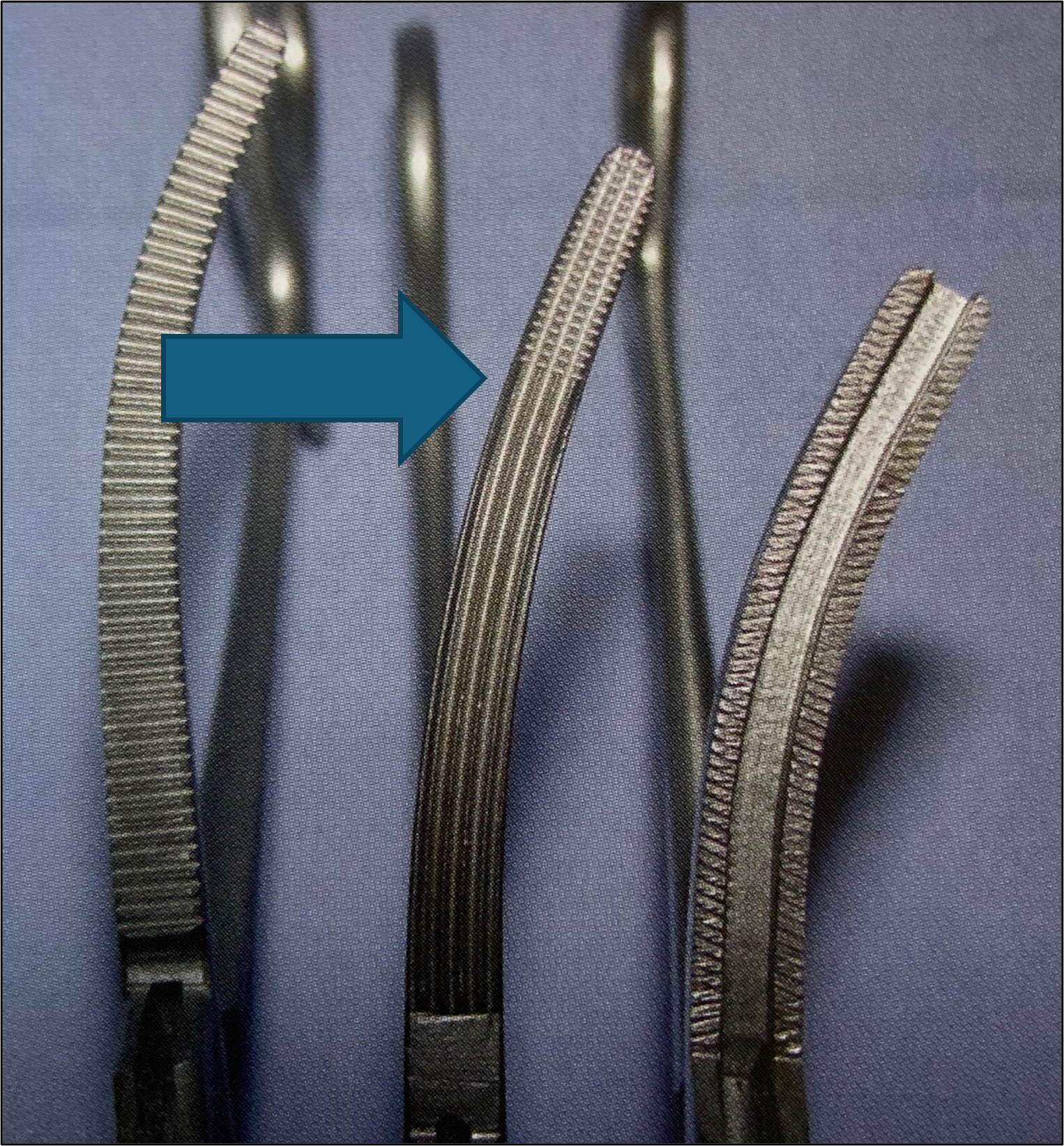
name of instrument
rochester carmalt forceps
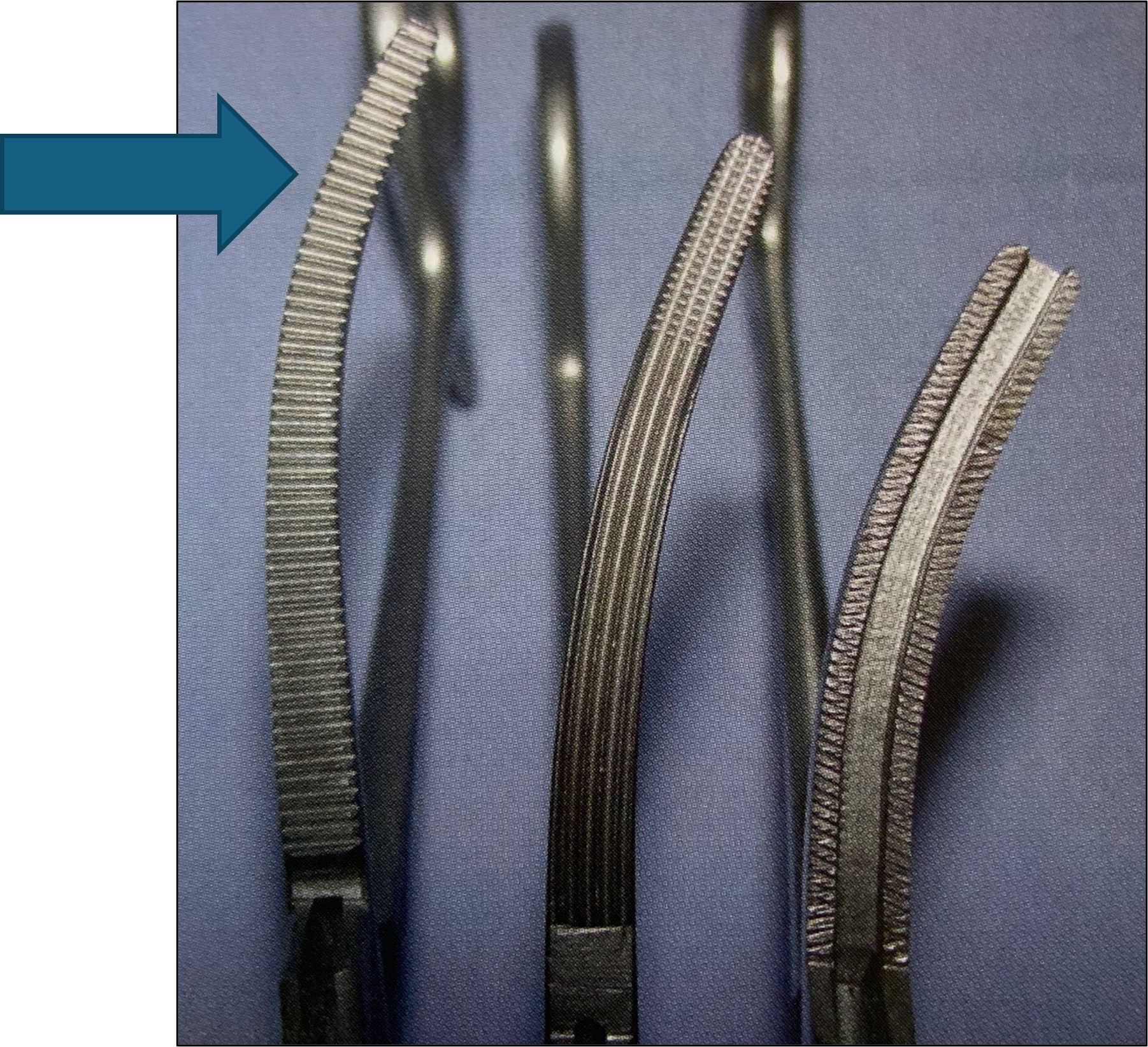
name of instrument
rochester pean forceps
name of instrument
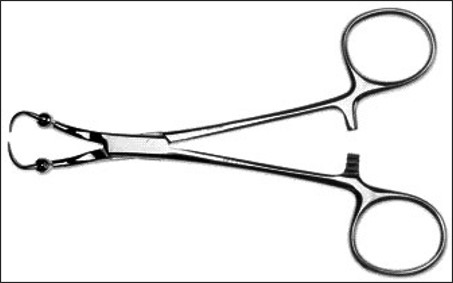
roeder towel clamps
name of instrument
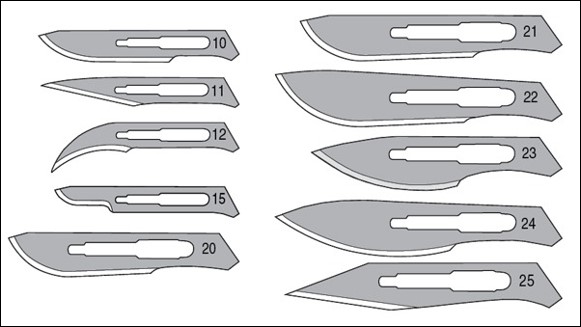
scalpel blade
name of instrument
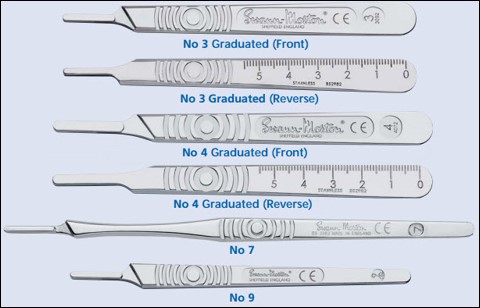
scalpel handle

name of instrument
snook spay hook
name of instrument
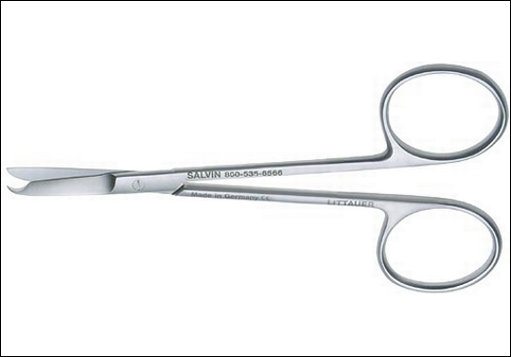
suture scissorname of instrument
what is asepsis
removal or prevention of harmful microorganisms to keep the environment clean for surgery
what does sterile mean
free from all living microorganisms, including spores
what is the surgical environment expected to be
aseptic
why is asepsis important in surgery
prevents infections in patients by reducing exposure to microorganisms
what is a sterile field
any area covered with a sterile barrier such as a drape, gown, table cover, or patient area
what is surgical conscience
commitment of surgical staff to follow strict aseptic technique and and report any contamination immediately
what should be done if aseptic technique is broken
must be reported, corrected, and re-sterilized if possible to prevent infection
who promotes aseptic and sterile techniques in the OR
AORN
AORN
association of periOperative Registered Nurses
what parts of the surgical gown are sterile
the chest to the sterile field level and sleeves from 2 inches above the elbow to cuff
what parts of the surgical gown are not sterile
neckline, shoulders, cuff tops, lower portion, and back of the gown
what is the purpose of sterile drapes
act as barriers that prevent microorganisms from passing between sterile and non-sterile areas
what is strike-through contamination
when fluid soaks through a sterile drape, making it contaminated
what should you do with a wet drape
consider it contaminated and replace immediately
how should sterile packs be opened
on clean surface, opening the far flap first, then sides, then nearest flap last
why should you never reach over a sterile field
risk contamination from clothing to skin
what happens when opening fluid bottles for surgery
once opened, the cap is contaminated, and unused fluid must be discarded
how should surgical personnel move around the sterile field
move face-to-face or back-to-back to avoid contamination
what is endogenous contamination
contamination that comes from the patient’s own body (skin or internal infection)
what is exogenous contamination
contamination from outside sources (surgical team or environment)
how can exogenous contamination be controlled
maintain a clean surgical suite and limit traffic
what should be worn in the surgical area to maintain asepsis
fresh scrubs, mask, head cover, clean shoes
why can’t street clothes be worn in surgery
they can carry dirt, bacteria and other contaminats
how should scrub suits be cleaned
launder in the hospital (not at home
why are bouffant caps preferred over skullcaps
they fully cover all hair on head and neck
when should masks be changed
frequently, whenever they become damp and soiled
what should you do if you need to cough or sneeze while masked
step back from the sterile field (not away)