NPB101: Neurophysiology Part 2
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CNS: Brain and Spinal Cord
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Disclaimer PNS here would be Parasympathetic Nervous System
PNS: Parasympathetic Nervous System
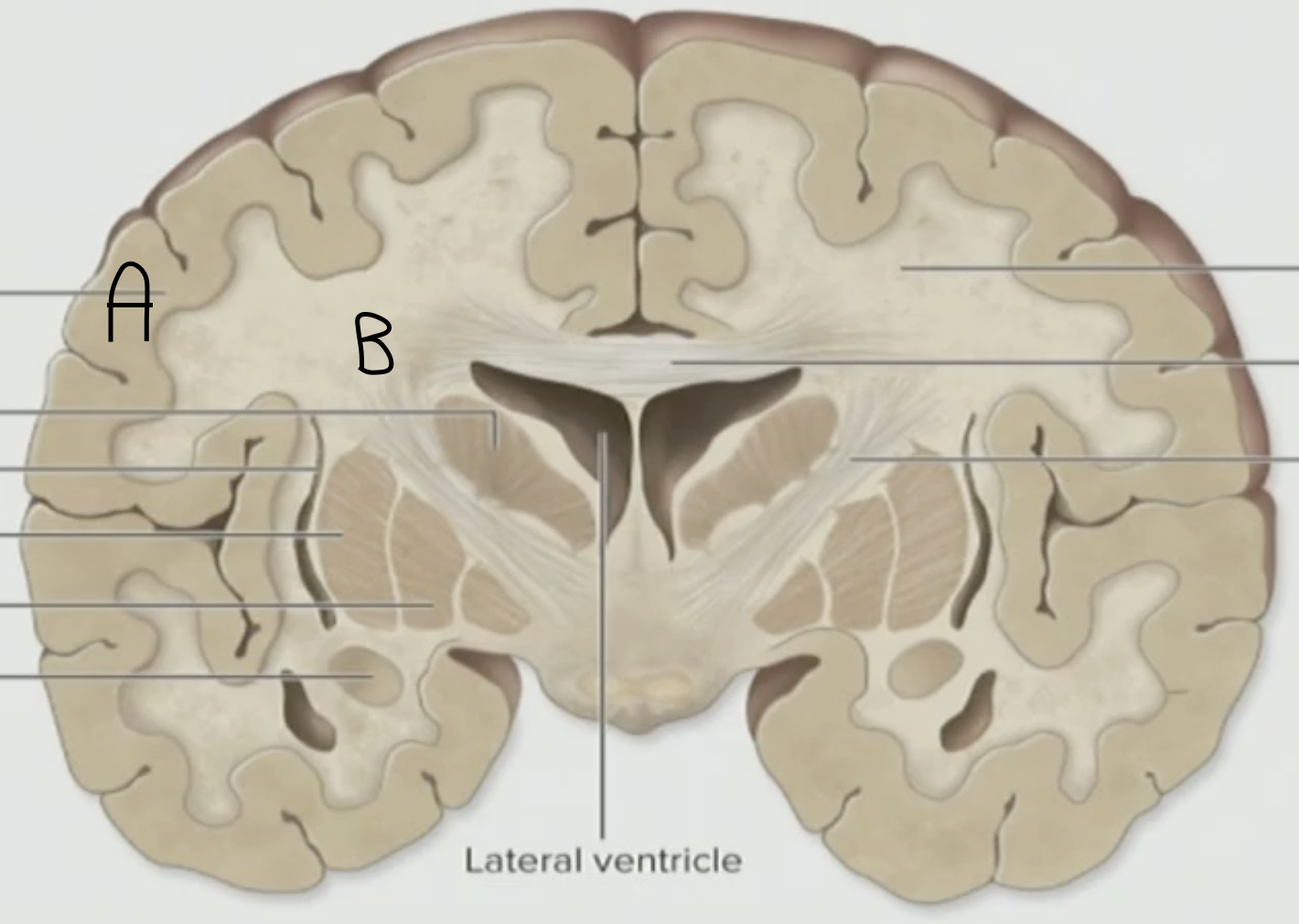
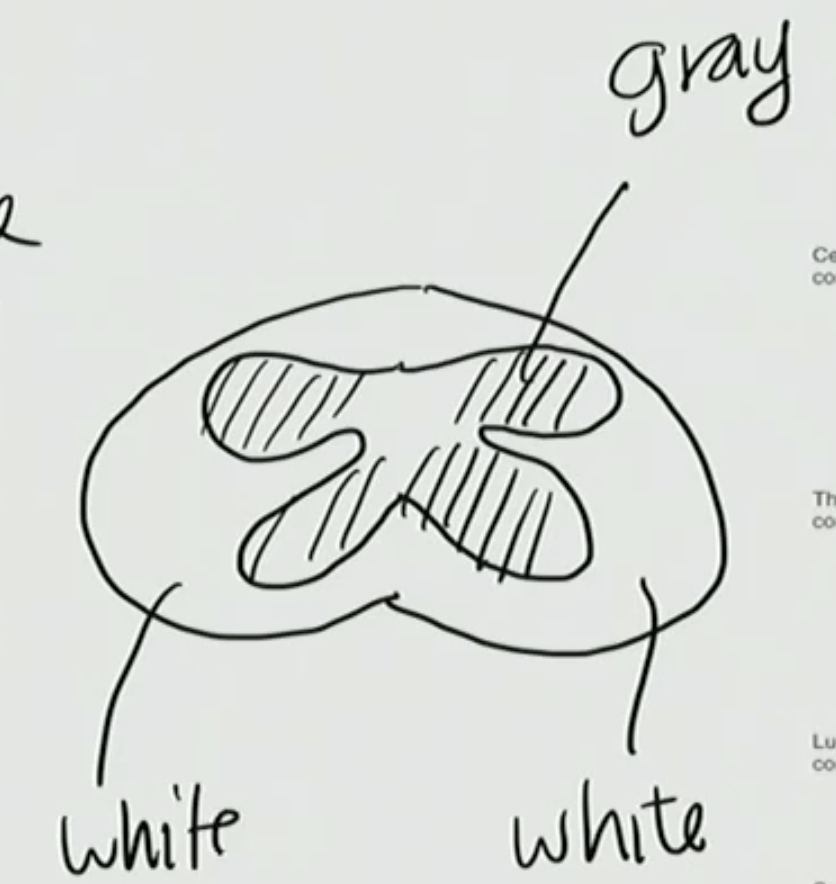
Which is the Gray Matter, A or B
A
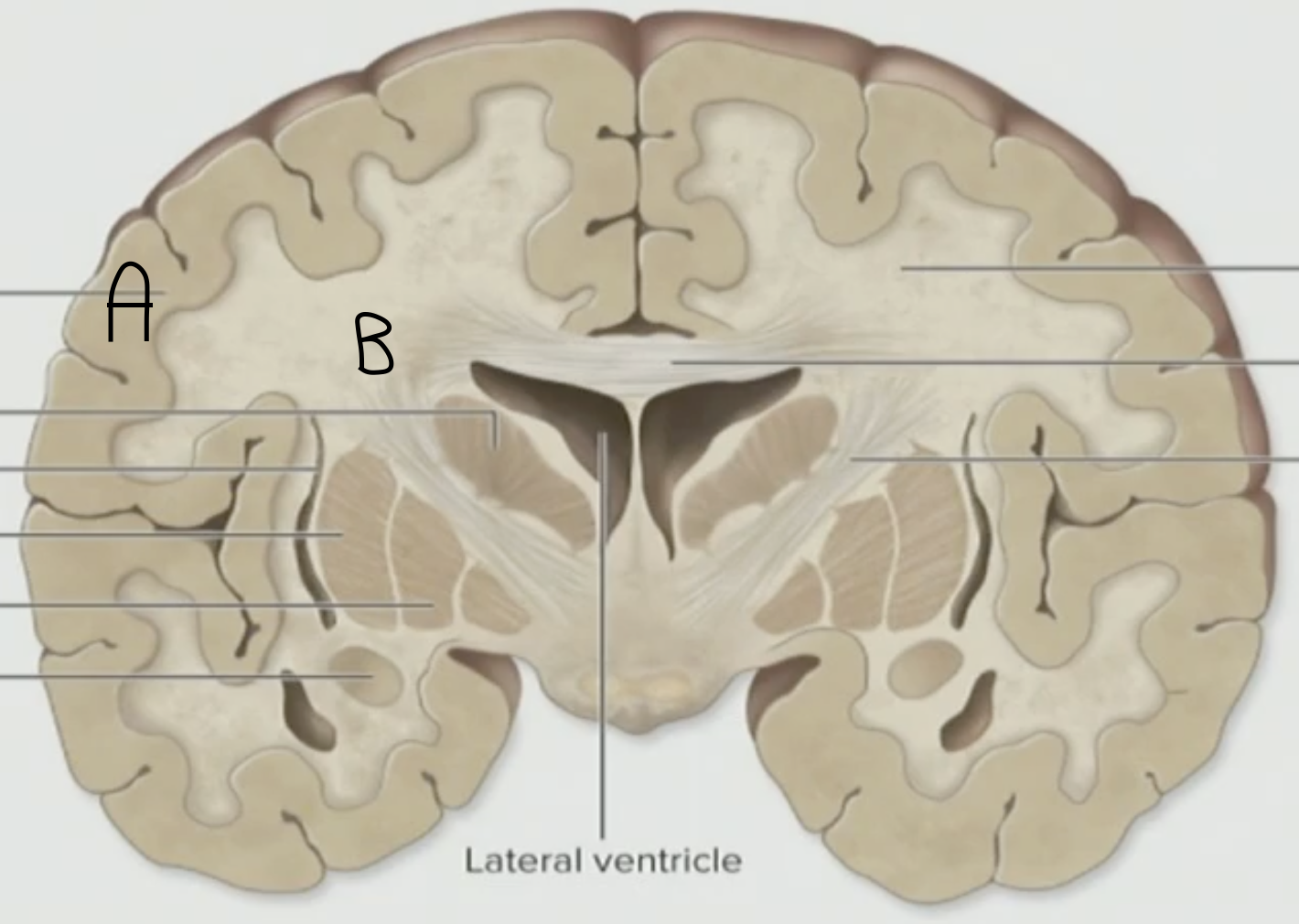
Which is the White Matter, A or B
B
What is the largest part of the forebrain?
Cerebrum or Cerebral Hemispheres
Why is the Cerebrum super wrinkly
Because we have to cram in a bunch of cells/tissue
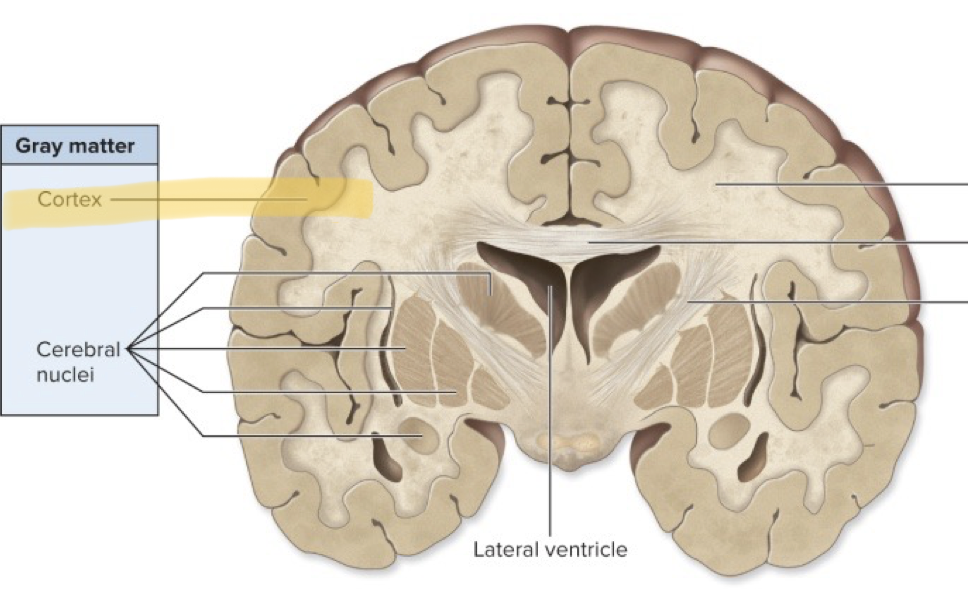
What does the Cerebral Cortex do?
The cerebral Cortex has higher cognitive function (memories, language, decision making, coordinating motor activities)
The cerebrum cortex contains what two matters?
Gray & White Matter
What is the outermost layer of the Cerebral Hemisphere?
Gray Matter
T/F: Axonal Projections are in Gray Matter
False, Axonal Projections are in White Matter, as they are mainly made up of axons
T/F: The cerebrum corrects movement
False, Yes the Cerebrum coordinates movement, but that’s not correcting movement
The ___ sits atop ____ matter.
cortex, white
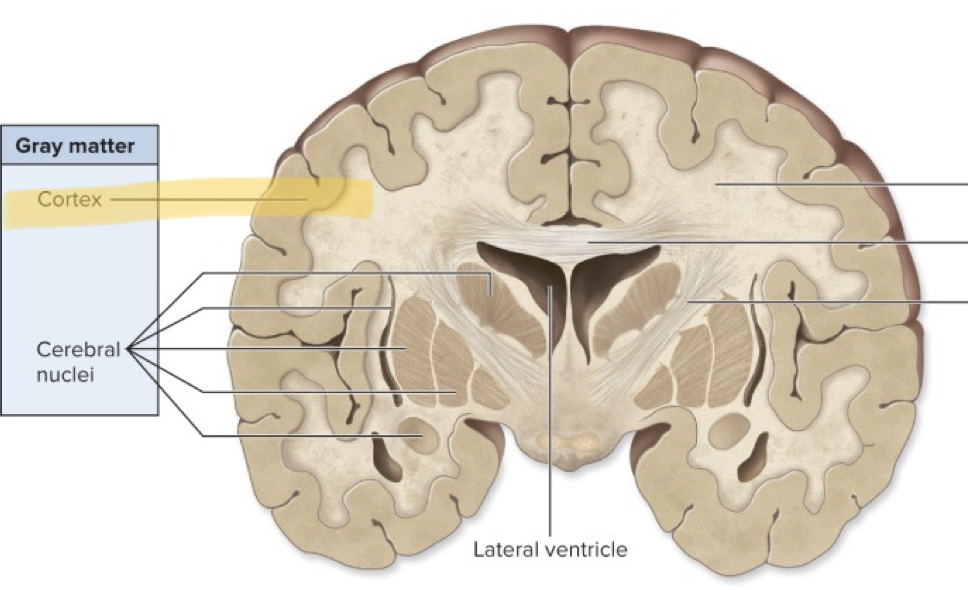
The Cortex contains ___ lobes
a. 1
b. 3
c. 6
d. 2
e. 5
e. 5
What are the Cortex 5 lobes?
Frontal, Temporal, Occipital, Parietal, Insular
The frontal cortex is strongly associated with:
a. Sensory functions
b. Motor functions
c. Only involuntary reflexes
d. Purely visual processing
b. Motor functions
The frontal cortex can do what traits?
Motor functions
Decision making
Planning for voluntary movement
Personality Traits
Coordination of complex movements
The Parietal lobe is associated with the ___ cortex
Somatosensory
What does the Somatosensory/Parietal lobe do?
Processes Sensory information coming from the body (touch, pain)
The Occipital Lobe does ___ output
visual
The Insular functions with ___, _____, _______
taste, emotion, self awareness
Lateralized
stronger or specialized in one hemisphere
What is a Lateralized Function?
speech production
The Basal Nuclei/Ganglia
suppress unwanted movement & initiates intended movements
Our hands aren’t shaking normally because the ___ ____ is (suppressing/initiating)____ the movement
Basal Ganglia, suppressing
Patients w/ Parkinson’s are given a ___ precursor to (exhibit/inhibit) _____ a movement
dopamine, exhibit
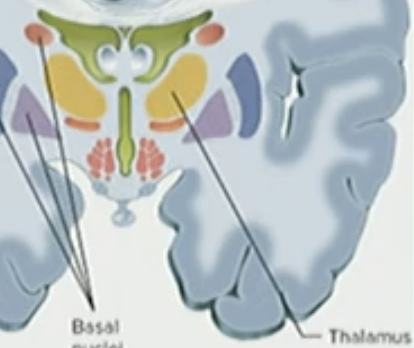
Thalamus
where we have sensory information, touch, pain, info, visual, auditory
T/F: The Thalamus is NOT a relay center for all sensory info
False, the thalamus is a relay center for all sensory info
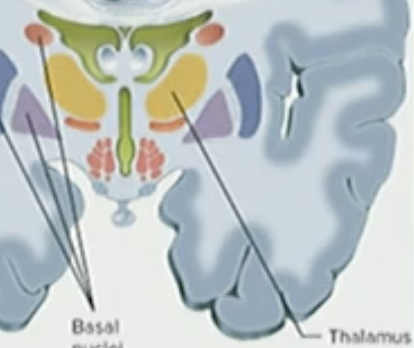
____ & ____ doesn’t communicate with the thalamus
Olfactory & taste
The thalamus filters out ____
noise (non-coding, not important)
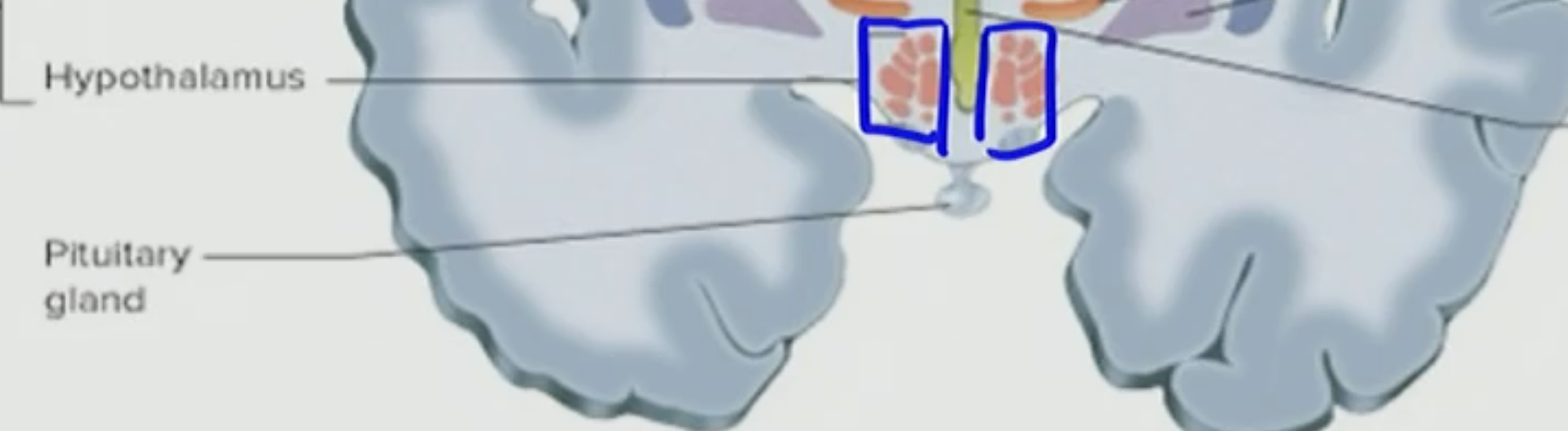
Hypothalamus
homeostatically regulates the body when there is a change in body temp, regulates sleep and wake, its a central controller
If there is a change in our body temp ___ homeostatically regulates it
hypothalamus
T/F: The Hypothalamus regulates only sleep
False the Hypothalamus regulates both sleep and wake
Brainstem
controls homeostatic reflexes
The Brainstem is involved in which of the following functions?
(Select all that apply)
A. Breathing
B. Sleep regulation
C. Voluntary muscle movement
D. Heart rate control
E. Alertness
F. Visual processing
G. Motor Coordination
A, B, D, E, G
The ____ is in the hindbrain
brainstem
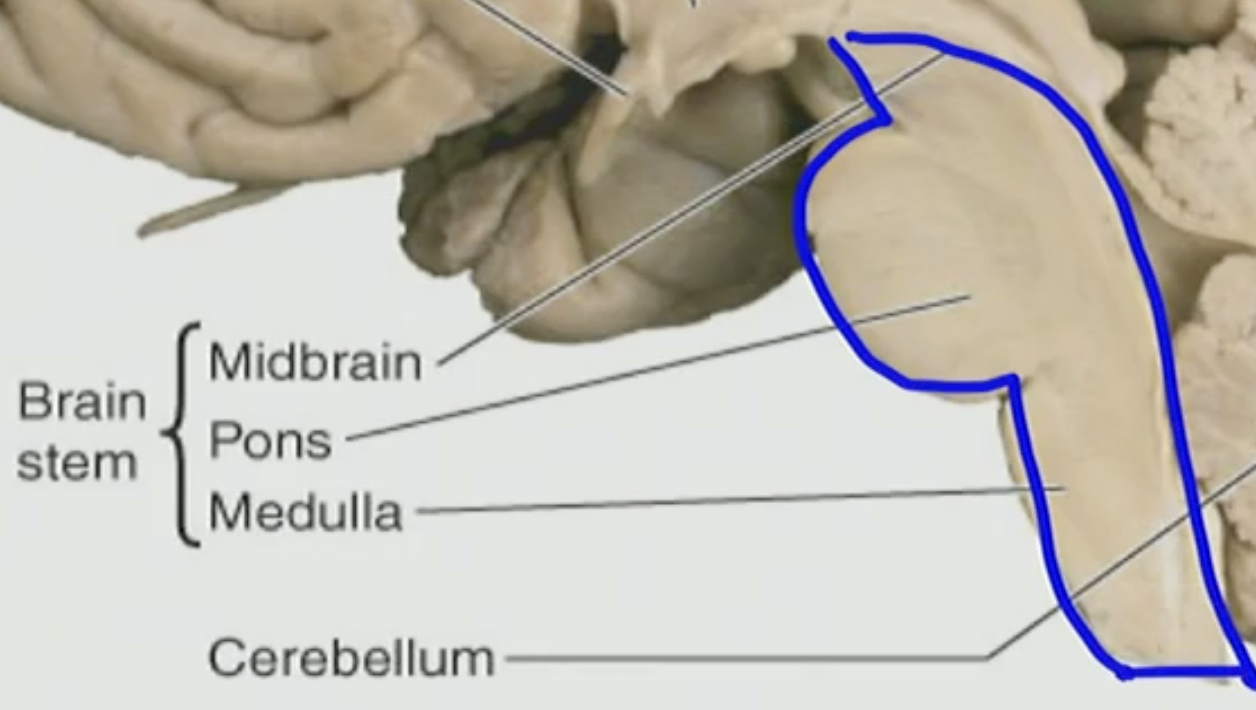
The ____ is the most ancient part of our brain.
brainstem
The brain stem is made up of ___ distinctive regions
a. 3
b. 5
c. 2
d. 4
2
What are the 2 distinctive regions in the Hindbrain?
a. Thalamus and hypothalamus
b. Pons and medulla oblongata
c. Midbrain and pons
d. Cerebrum and cerebellum
b. Pons(Pontine) and medulla oblongata
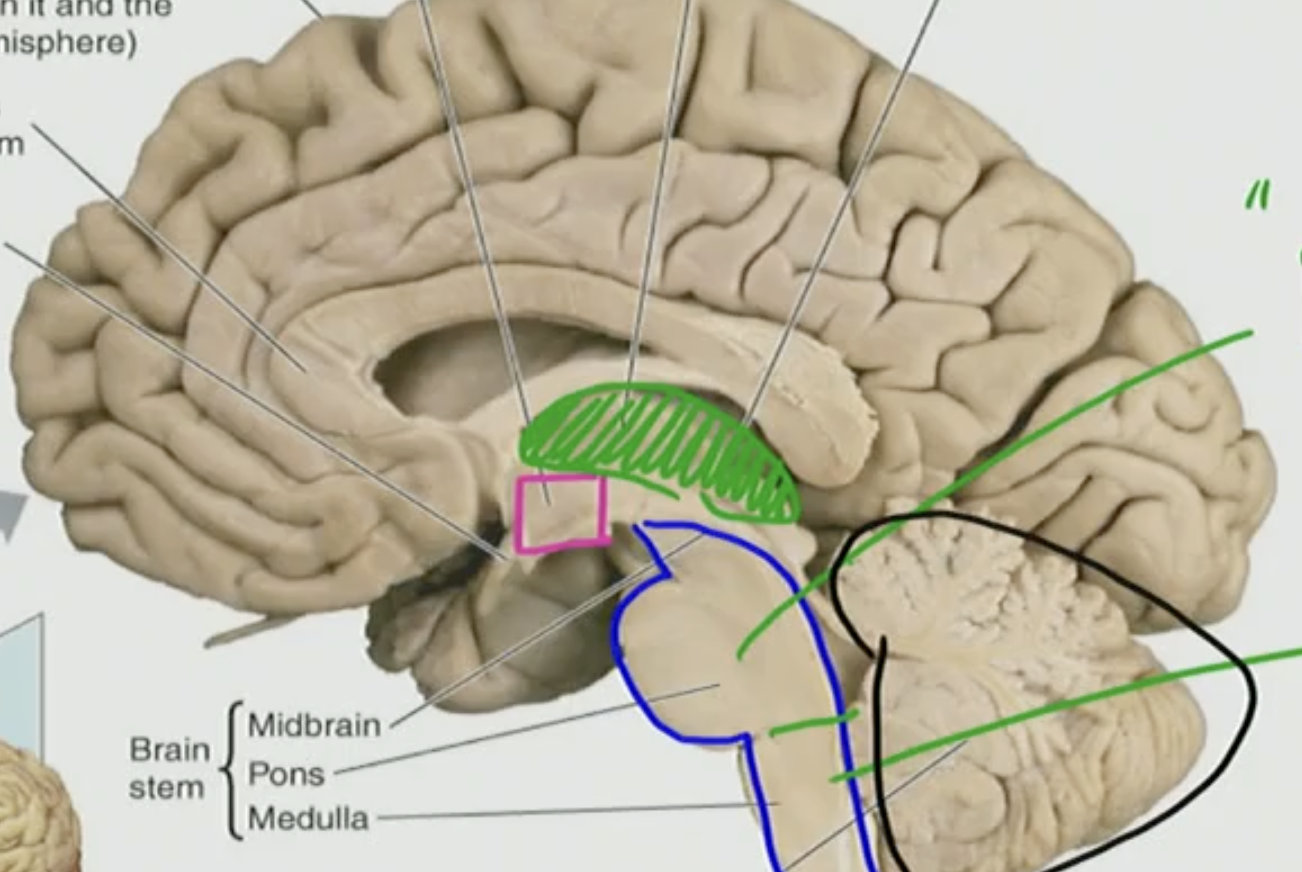
The black outlined triangle is the?
The Cerebellum
The Cerebellum is made up of __#__ hemispheres and is functionally divided into __#__ parts
2, 3
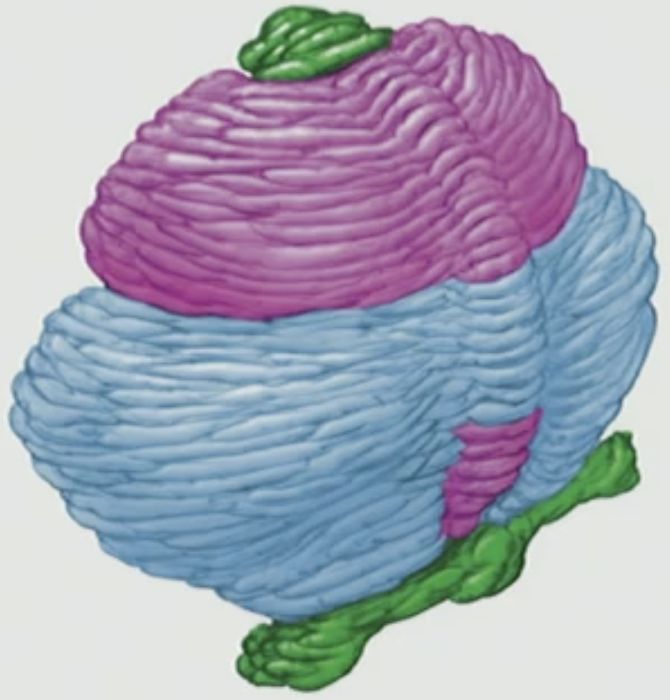
What are the three parts in the Cerebellum
Cerebrocerebellum, Spinocerebellum, Vestibulocerebellum
Cerebrocerebellum
Stores all motor memories (riding bike, dance, musical instrument)
Spinocerebellum
coordination of voluntary movement
where our body is in space
regulates muscle tone
Vestibulocerebellum
receives output from the eyes and vestibular system for Balance
tells us where we are relative to the planet & gravity
The _____ & _____ parts help us coordinate our activities
Spinocerebellum & Vestibulocerebellum
The ___ & the ____ parts will mess up if intoxicated while doing the Field Sobriety Test because you can’t control your ____
Spinocerebellum & Vestibulocerebellum, muscles
The Spinal Cord runs along our ____
back
What will we see inside our spinal cord?
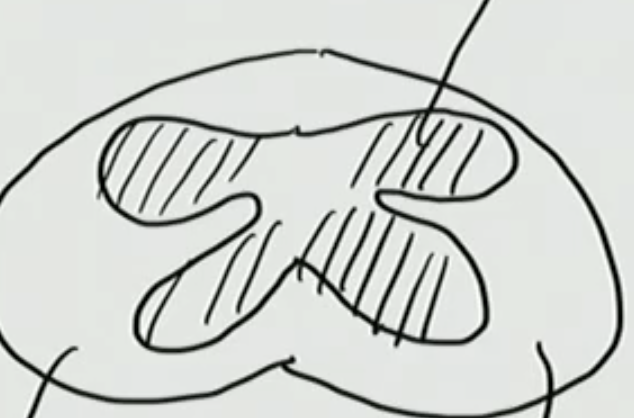
Our Spinal Cord is consumed of ___ & ____ matter
White & Gray
Dorsal
towards the spine
Ventral
toward belly
Interneuron
does processing within gray matter
T/F: In Gray matter there are primarily composed of axons
False, Gray matter is composed of bodies of neurons and white matter is composed of axons
T/F: In white matter the axons only project one way
False, in white matter the axons can project towards the brain or downward to spinal cord
The Spinal Nerves contain efferent ____ & afferent ___
efferent axons & afferent sensory processes/neuronal pathways
White matter contains ___ axons
efferent
Gray Matter contains _____
afferent sensory/processes