IMED1001 - Integumentary Anatomy (Skin)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
(Prefix) A-
- absence of
- e.g avascular means no blood vessels
Stratum
a layer or series of layers
Connective Tissue Abbreviation
CT
Integumentary System
comprised of:
- skin
- sweat glands
- sebaceous glands
- hair follicles
- nails
Skin
- Weighs 4-5kg
- 1.5 to 4mm thick (from thin to thick skin)
Composed of:
1. Epidermis: most superficial layer, shed 50,000 cells per minute
2. Dermis: bulk of the skin volume, rests on hypodermis
Epidermis
Five distinct layers:
1. Stratum basale (deepest)
2. Stratum spinosum
3. Stratum granulosum
4. Stratum lucidum (only in thick skin)
5. Stratum corneum (most superficial)
- It is avascular
- Melanocytes, dendritic cells and tactile cells in the deeper layers
- epidermis constantly regenerates
Stratum basale
- deepest layer of epidermis
- one row continuously active mitotic cells
Stratum spinosum
- a layer of the epidermis that provides strength and flexibility to the skin
- several layer keratinocytes joined by desmosomes
Stratum granulosum
a layer of the epidermis that marks the transition between the deeper, metabolically active strata and the dead cells of the more superficial strata
Stratum lucidium
only in thick skin,
Stratum corneum
- most superficial, dead cells, anucleate, cells filled with keratin
Thick vs Thin Skin
- Corneum (horn) layer is much thicker in thick skin
- Thick has stratum lucidum, thin does not
- Thick has no hair follicles, no sebaceous glands
Dermis
- between epidermis and hypodermis
- composed of connective tissue
- contains blood vessels, lympathic vessels and nerves
FORMED OF:
1. Papillary Layer (areolar CT, capillaries, sensory nerve endings)
2. Reticular Layers (dense irregular CT (collagen and elastin fibres) sebaceous and sweat glands, surrounds hair follicle, blood vessels
fibroblasts produce collagen and elastin
Hypodermis
- subcutaneous CT, usually quite fatty (stores energy and insulating)
- not part of the skin, however anchors skin to underlying bones and fascia (muscle); provides passage for nerves, vessels and lymphatics in transit
- protects your body from external harm
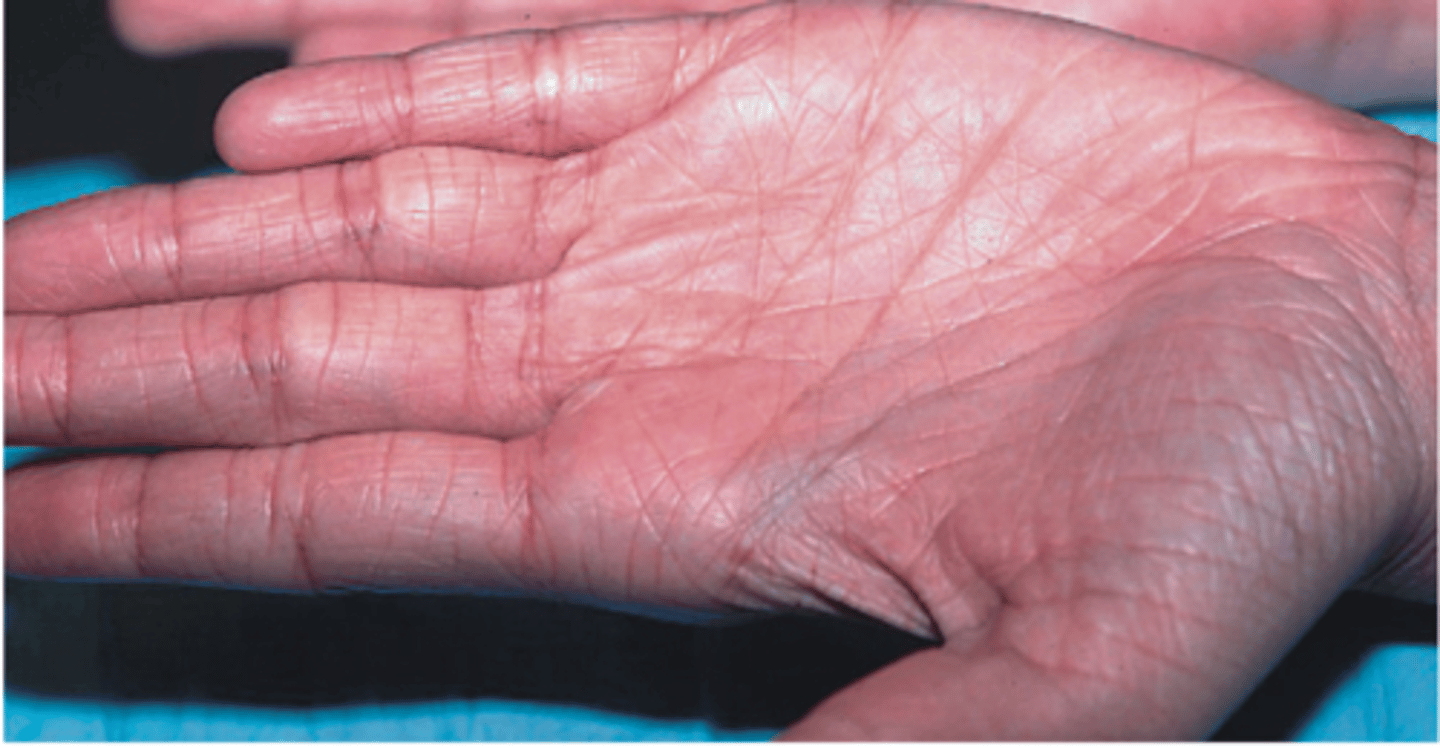
Flexure Markings
- skin marking
- dermal folds at or near joints
- dermis tightly secured to deeper structures
- joint movements create deep creases
- visible on hand writs, digits, toes, soles of feet
Skin Markings (Striae and Blister)
STRIAE:
- silvery white, pink, red, dark-blue or black
- "Stretch marks"
- stretching that causes tear in the dermis
BLISTER:
- from acute, short term trauma
- fluid filled pocket accumulating between epidermal and dermal layers
Skin and Hair Colour
3 pigments contribute to skin colour:
1. Melanin:
- only pigment made in skin (also determines hair colour). Produced by melanocytes. Protects DNA in nuclei of keratinocytes. Production increases with sun exposure. Accumulates in moles and freckles. Type and ratio of melanin secreted is either Eumelanin (brown and black forms, equatorial) or Peomelanin (yellow-red forms; northern migration)
2. Carotene (yellow-orange):
- Accumulates in stratum corneum, most visible palms and soles
- Can be converted to Vitamin A for visual and epidermal health
3. Haemoglobin (pinkish-red):
- Skin translucency differs
- Noticeable in people with fair skin
Appendages of the Skin
Derivatives of the epidermis:
- hair and hair follicles
- nails
- sweat glands
- sebaceous glands
Hair
- hair is a sensory structure
- epidermal invagination found in dermis and hypodermis
- most skin is covered in thinner Vellus hair
- scalp is terminal hair
- Absent from palmar/plantar surfaces of hands/feet, lips
- Hair shaft anchored at its root, which has a bulb
- hair cells become keratinised in their lower 1/3, above this they're dead
- bulb cells connected to a papilla for blood supply
STRUCTURE:
- nerve fibres surround the hair and papilla
- erector pili (means hair) muscles: smooth muscle, hence autonomic control
Nail
- hard plates of keratin
- dorsal surface of tips of fingers and toes (phalanges)
Epidermal Derivatives
Glands
- Merocrine (means partial separate): exocrine glands that uses exocytosis (salivary glands; some sweat glands)
- Apocrine (means separates away): cell surface breaks off, moves away (sweat glands (odorous))
- Holocrine (means whole separates): whole cell broken into components (sebaceous glands around hairs)
Sweat Glands
1. Merocrine (or Eccrine, means excrete):
- excrete sweat onto skin surface
- most numerous on the foot soles, palms and forehead
- sweat gland number set from birth, but not all remain active
- Thermoregulation: evaporation of sweat = cooling
2. Apocrine sweat glands (excrete into terminal hair follicles in Axillary and Anogenital areas)
- Sweat with a little bit of fat in it (pheromones, smell is byproduct of bacterial activity)
- largely confined to axillary and perineal regions
- dont play a thermoregulatory role
Holocrine Glands
Sebaceous Glands:
- excrete sebum (oily lipids) into hair follicle (few exceptions including nipples)
- Acinar appearance (means grape or berry) (like a sac of cells)
- Sebocytes closes to the duct explode, releasing sebum around hair follicle
- secretion from sebaceous glands greatly increases at puberty
Skin Functions (7 of them)
Seven functions of the skin:
1. Absorption
2. Protection
3. Sense Organ
4. Thermoregulation
5. Communication
6. Vitamin Production
7. Excretion
Pneumonic to rmbr: A Pale Skin Turns Crimson Very Easily
1. Absorption (Skin Function)
- certain vitamins (lipophillic), drugs (e.g hydrocortisone cream), gases (O2 and CO2)
- properly utilised for transdermal drug delivery
2. Protection (Skin Function)
- Chemical barrier: low pH retards bacterial multiplication, sebum and defensins kill bacteria; melanin defence against UV damage
- Physical barrier: Keratin and glycolipids block water and water-soluble substances (can be penetrated by above mentioned substances, poison ivy and heavy metals)
- Biological barriers: Resident WBCs (dendritic cells and macrophages recognise foreign antigens). UV radiation converted to heat (protects DNA)
3. Sense Organ (Skin Function)
Cutaneous (skin) sensory receptors (nervous system) detect temperature, touch, pain (general senses)
4. Thermoregulation (Skin Function)
- temperature regulation through sweating and blood vessel vasodilation and vasoconstriction
- Insensible perspiration: passive vapour diffusion of water through the epidermis. Occurs most constantly due to evaporative loss from the epithelial cells
- Sensible perspiration: occur at ambient temperatures above 32C, when sweat glands (merocrine) release sweat to cool the body
5. Communication (Skin Function)
- sensory receptors communicate information to the central nervous system (brain). Skin is also very expressive
6. Vitamin Production (Skin Function)
- UV stimulates synthesis of a vitamin D precursor (vitamin D is essential nutrient that helps regulate calcium metabolism and promotes bone mineralisation)
7. Excretion
nitrogenous wastes and salts via sweat
Skin Cancers
- most tumours are benign (not cancerous) and do not metastasize (spread)
- Risk factors: overexposure to UV radiation and frequent irritation of the skin
3 main types:
1. Basal cell carcinoma (a): stratum basale cells slowly invading the dermis and hypodermis
2. Squamous cell carcinoma (b) - keratinocytes of stratum spinosum
3. Melanoma (c) - melanocytes proliferation
Summary of the topic
ALL INFO ON SLIDE 35 of Integumentary System Slides