hemostasis & blood clotting
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
coagulation / clotting
the normal, protective process whereby blood changes from a liquid to solid or semi-solid state in response to vascular injury
may result in hemostasis
hemostasis
the cessation of blood loss from a vascular injury
thrombosis
a pathologic process in which blood clots form inside blood vessels
fibrinolysis
breakdown of the blood clot
part of hemostasis
breaks down the fibrin meshwork
plasma
the liquid portion of the blood
CAN clot (contains all clotting factors)
serum
the liquid portion left over after blood has clotted
CANNOT clot
events of blood coagulation (hemostasis)
1. vasoconstriction
2. platelet activation
3. formation of fibrin meshwork
4. fibrinolysis
vasoconstriction
limits blood flow to the site of injury
primary hemostasis
platelet activation
forms a platelet plug
adhesion (to subendothelium), aggregation, secretion
secondary hemostasis
formation of the fibrin meshwork by coagulation cascade
binds blood cells together
forms hemostatic plug
clot dissolution (fibrinolysis)
removes clots during wound healing
one step in the thrombolysis
thrombocytes (platelets)
derived from megakaryocytes in bone marrow; small, discoid, enucleated cell fragments
doesn't divide
lifespan: 7 - 10 days
contains glycogen & mitochondria (can perform aerobic metabolism)
open canalicular system
invaginatons of plasma membrane increase surface area available for clotting reactions
alpha granules
contain PROTIENS to be secreted upon activation (e.g. some coagulation proteins like thrombin, fibrinogen, von Willebrand factor)
dense ganules
contain SMALL MOLECULES to be secreted upon activation
e.g. ADP, serotonin, Ca2+
microtubules (actin/myosin network)
maintain discoid shape and mediate morphological changes upon activation
e.g. extension of pseudopodia
activated platelets
dramatically change their shape
change their surface properties (become sticky for adhesion)
secrete contents of their granules
platelet activation process
adhesion
aggregation
secretion of granule content
adhesion
multiple interactions between platelet membrane glycoproteins (GPs) and components of the denuded subendothelium
initial trigger of activation
binding of GP1b to collagen via von Willebrand factor (vWF)
binding of GP1a to collagen directly
Bernard-Soulier syndrome
autosomal recessive deficiency of GP1b (defective primary hemostasis)
macrothrombocytopenia, easy bruising, heavy and prolonged bleeding
affects platelet adhesion
platelet aggregation
activated platelets adhere to other activated platelets
mediated by:
adhesive receptors GPIIb/GPIIIa (integrins) on the platelet membrane that bind to fibrinogen
fibrinogen forms a bridge between activated platelets
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia
autosomal recessive deficiency of GPIIb/GPIIIa (defective primary hemostasis)
easy bruising, heavy prolonged bleeding
affects platelet aggregation
Plavix (clopidogrel)
antithrombotic drug that inhibits platelet aggregation by interfering with GPIIb/GPIIIa
secretion
upon activation, platelets release a number of substances stored in granules
dense bodies: ADP, serotonin, Ca2+
alpha granules: vWF, fibrinogen, coagulation cascade proteins
ADP, serotonin, Ca2+
secreted from dense bodies upon platelet activation
adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
secreted from dense bodies: platelet activator
serotonin
secreted from dense bodies: vasoconstrictor
calcium (Ca2+)
secreted from dense bodies: activator of coagulation cascade (necessary for secondary hemostasis)
acts as signal to other platelets to activate eicosanoid production
vWF, fibrinogen, coagulation cascade proteins
secreted from alpha granules upon platelet activation
fibrinogen
promotes platelet aggregation & converted to fibrin to form mesh
coagulation cascade proteins
i.e. prothrombin & thrombin (acts as activator of platelets + key role in coagulation cascade)
most other clotting proteins are produced by the liver and released into blood
von Willebrand factor (vWF)
a large multimeric glycoprotein (polymer up to 80 polypeptides) synthesized only in endothelial cells & megakaryocytes
found in subendothelial matrix, in circulation, & in platelet alpha granules
promotes adhesion of platelets to subendothelium to initiate activation
stabilizes clotting factor VIII in circulation (forms complex with Factor VIII in circulation)
von Willebrand disease (vWD)
caused by mutations in vWF gene encoding vWF
~ 1 in 100 people have defect in vWF (majority subclinical)
~ 1 in 8000 have clinical diagnosis (more common than hemophilia A)
most common congenital bleeding disorder
autosome dominant or recessive: allelic heterogeneity
symptoms:
considerable clinical heterogeneity due to allelic heterogeneity
3 clinical types with subtypes
bleeding diathesis due to defective platelet adhesion
easy & excessive bleeding following injury, easy bruising, heavy or prolonged menstruation
in severe cases, there is a secondary Factor VIII deficiency
can lead to hemophilia A misdiagnosis
thromboxanes
a member of eicosanoid family of lipids
following platelet activation
phospholipase A2 (PLA2) is activated
PLA2 cleaves arachidonic acid from membrane phospholipids
arachidonic acid is converted to intermediary prostaglandins by cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes
prostaglandins are → — A2
thromboxane A2
a potent activator of platelets and promotes vasoconstriction
aspirin
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID)
(suicide inhibitor) of COX1 & COX2
platelet inhibitor (antithrombotic = inhibits production of thromboxane A2)
collagen, vWF
platelet activating signals: subendothelial molecules exposed to endothelial damage
platelet activating signals (via positive feedback)
ADP: activator signal
fibrinogen: bridge between GPIIb/GPIIIa mediating platelet aggregation
vWF: needed for adhesion to subendothelium
thromboxane A2: activator
thrombin: activator
platelet activating factor (PAF): a phospholipid hormone
phosphatidylserine
membrane phospholipid
exposed to outer leaflet of activated platelet (similar to apoptosis)
provides a surface for clotting cascade: acts as cofactor
extrinsic pathway
activated by external stimuli (e.g. blunt trauma)
injury → VII + TF → VII to VIIa → TF:VIIa→ TF:VIIa + X → Xa
the BLUE pathway
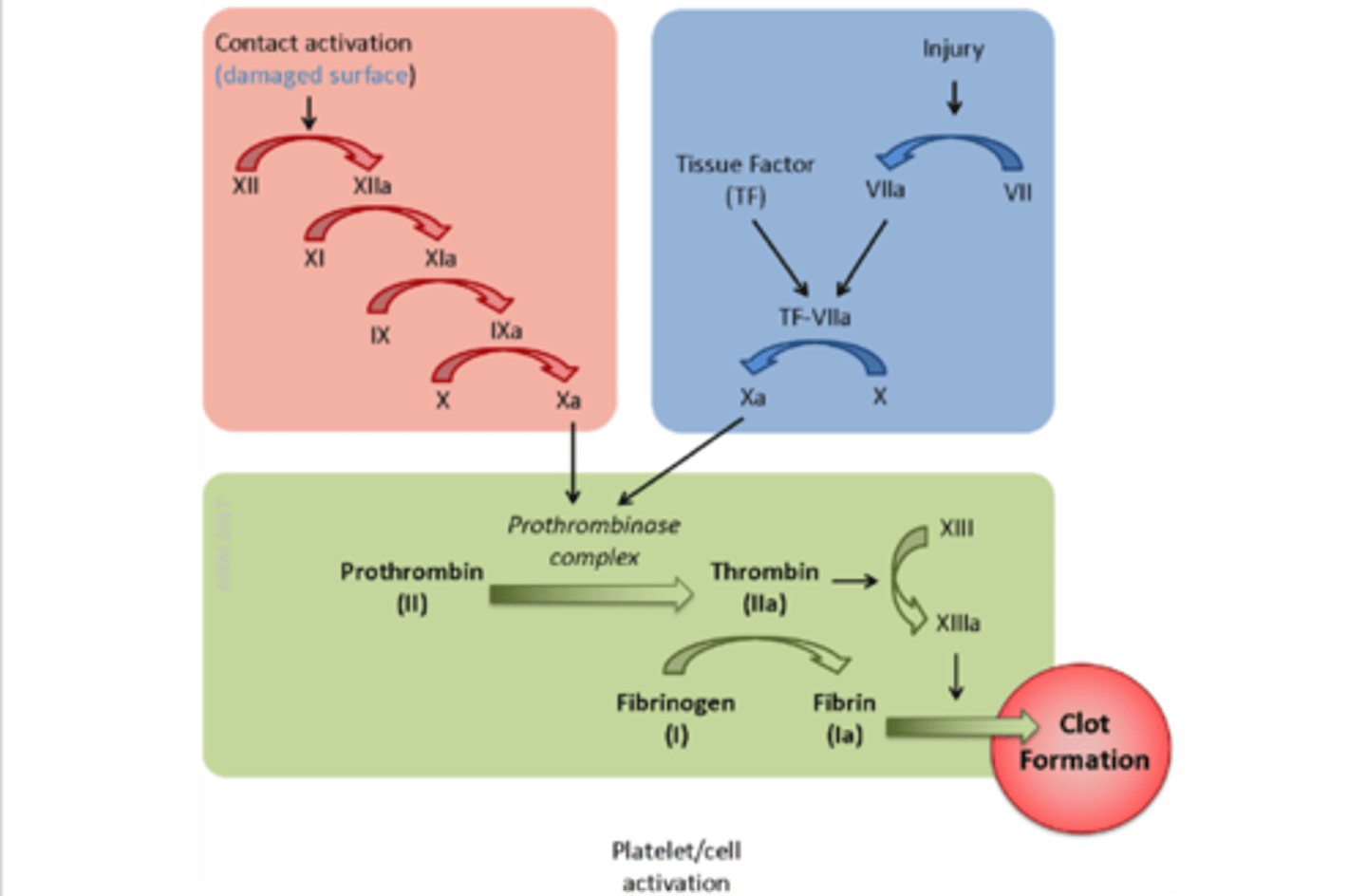
intrinsic pathway
activated by internal stimuli (e.g. clotting in a test tube)
surface contact → XII to XIIa → XIIa + XI→ XIa + IX → IXa + X→ Xa
the RED pathway
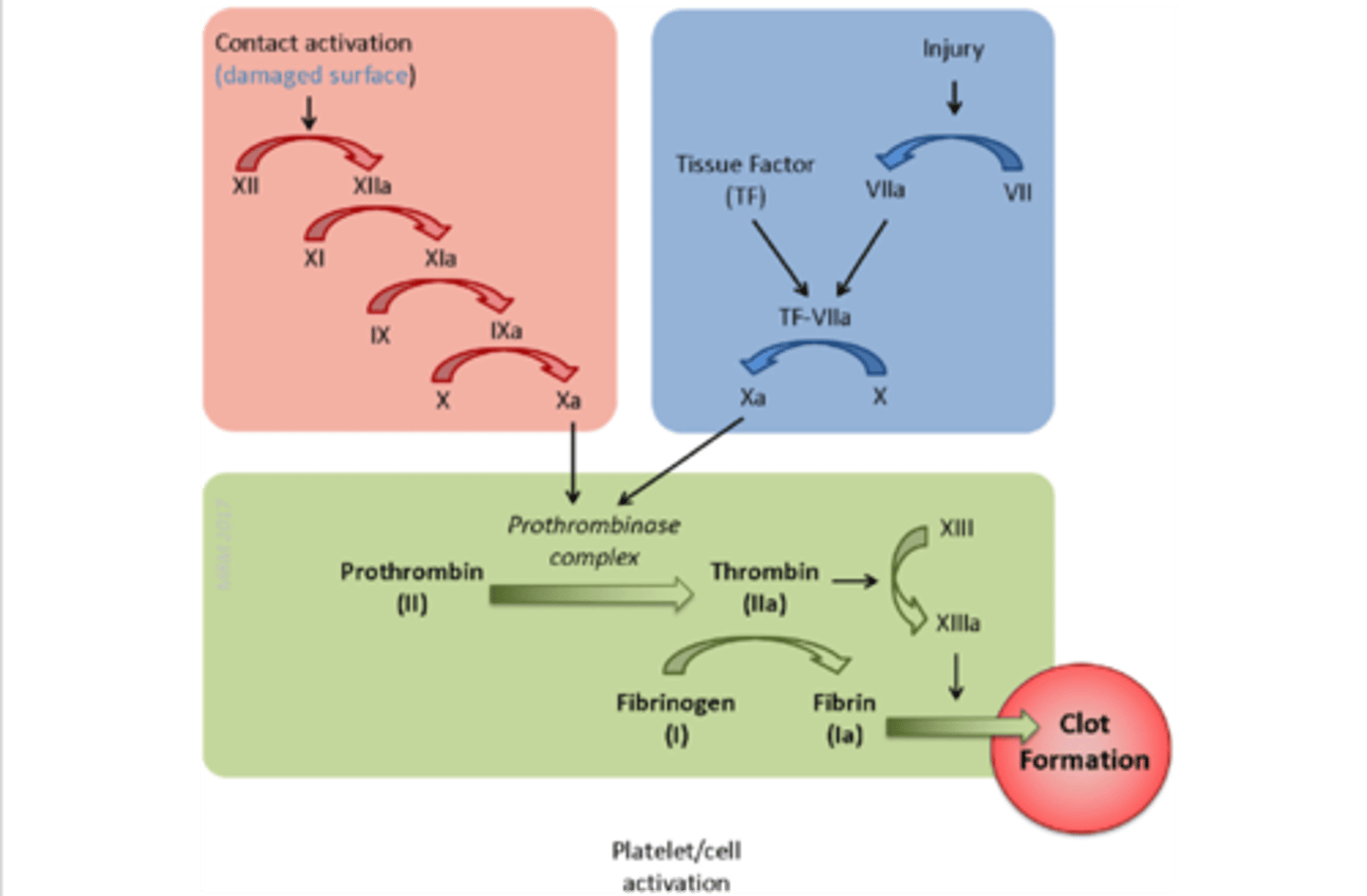
Factor X
initiates the common pathway
convergence of the intrinsic & extrinsic pathway
activation of thrombin & production of fibrin
zymogen
most clotting factors are synthesized in the liver & secreted into the plasma in their — (precursor) form
available to be quickly activated
phospholipid (PL), calcium (Ca2+)
most steps in the coagulation cascade happen on a membrane and require — & —
clotting reaction activation
a SERINE protease binds to its protein cofactor on a membrane surface
protease cuts a peptide bond in zymogen (substrate) releasing the active form
products catalyze the next proteolytic step in the cascade
cofactors accelerate clotting 10000-fold
common pathway
the GREEN pathway
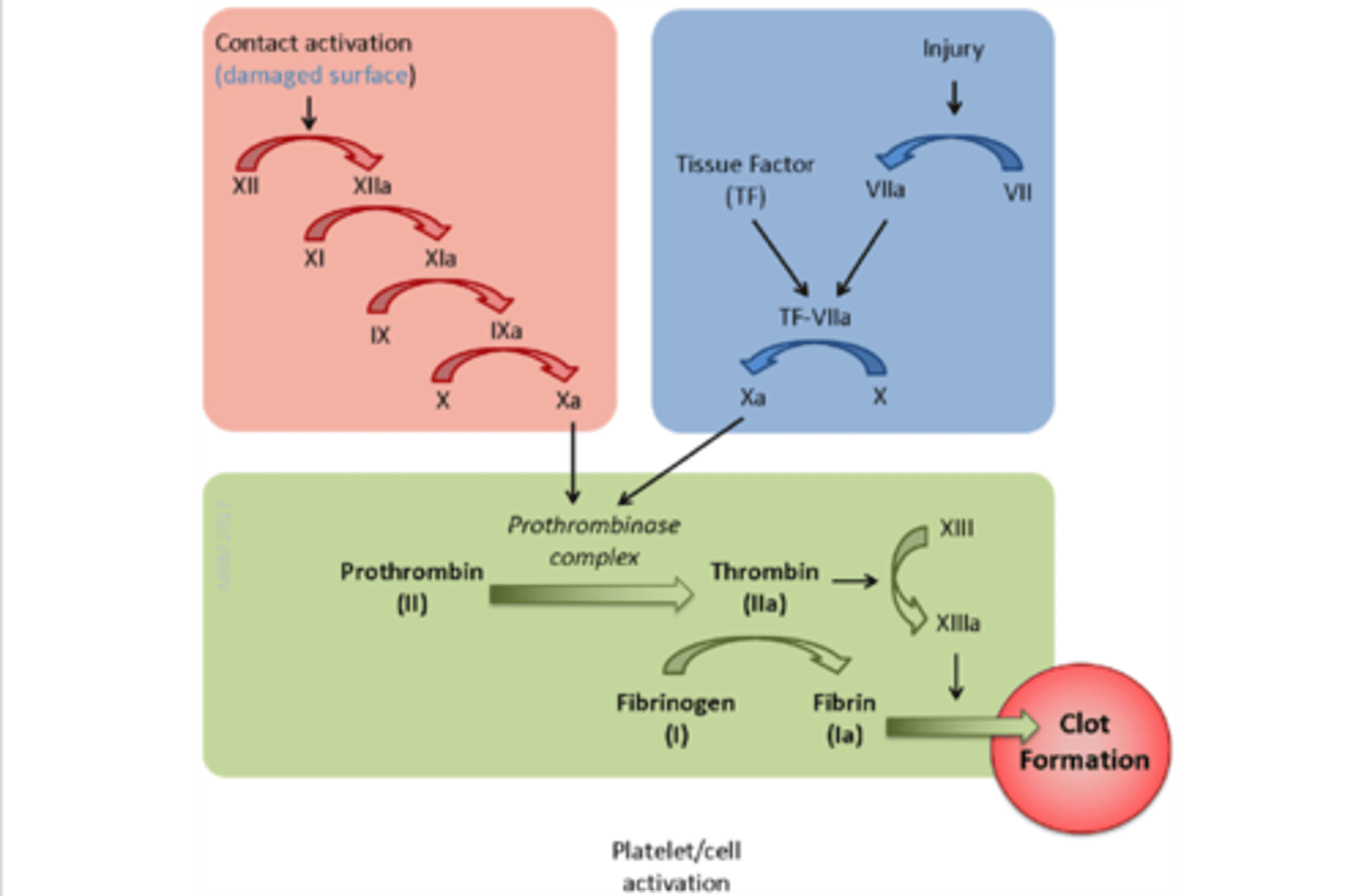
tissue factor (factor III)
exposed upon damage to endothelium; required for initiation of the extrinsic pathway in response to vascular trauma
a cell-surface protein found in cells in subendothelium (similar to vWF)
cofactor for FACTOR VIIa
factor VIIa
acts on the membrane surface & requires the following cofactors:
phospholipid (PL)
Ca2+
TF (required for activity)
activates X (extrinsic pathway) & IX (intrinsic pathway)
factor VII
binds to tissue factor & autocatalyzes its activation to VIIa
fibrinogen
composed of 1 triple-helices of α, β, & γ chains joined at N-termini = 6 chains total per molecule
N-terminal ends are highly negatively charged (prevents aggregation by repulsion)
thrombin
cleaves the N-termini of fibrinogen
soft clot
aggregation of of fibrin
hard clot
covalent cross-linking by Factor XIIIa stabilizes the firbin clot
factor XIIIa
transglutaminase = catalyzes a transamination between gln & lys in neighboring fibrin monomers (hard clot)
only enzyme of the clotting cascade that is NOT a serine protease
creates a strong 3-D network resistant to mechanical and proteolytic damage
traps aggregating platelets forming the clot (hemostatic plug)
bleeding time
evaluation of platelet function
standardized small incisions are made in the arm
time for bleeding to stop is measured
poor reproducibility and invasive; largely replaced
platelet aggregometry
in vitro evaluation of platelet function
platelets are isolated in plasma and activated with ADP (or another platelet activator)
time for platelets to aggregate is measured (normal range varies by lab)
prothrombin time (PT)
evaluation of EXTRINSIC clotting cascade activity (including common pathway)
clotting of plasma is induced by addition of tissue factor (TF)
clotting factors required: I (fibrinogen), II (prothrombin), V, VII, X
time for plasma to clot is measured (normal = 10 - 13 secs)
partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
evaluation of INTRINSIC clotting cascade activity (including common pathway)
clotting of plasma is induced by addition of silica (or other activator of intrinsic pathway)
clotting factors required: I (fibrinogen), II (prothrombin), V, VIII, IX, X, XI, XII
time for plasma to clot is measured (normal = 30 - 50 secs)
hemophilia A
gene: F8 (due to unequal crossing over between inverted repeats which results in an inversion = null mutation)
protein: factor VIII
incidence: 1 in 4000 male births
hemophilia B
also called Christmas disease after the patient
gene: F9 (due to unequal crossing over between inverted repeats which results in an inversion = null mutation)
protein: factor IX
incidence: 1 in 20000 male births
hemophilia A/B
X-linked bleeding disorder caused by the deficiency of clotting factors
symptoms:
spontaneous bleeding in joints and skeletal muscles
arthritis
prolonged bleeding
labs:
bleeding test: normal
PTT: prolonged
PT: normal
treatment:
recombinant clotting factors now available; administered by IV
anticoagulant
proteins which prevent clotting beyond the injured area
antithrombin
serpin (serine protease inhibitor) = irreversibly inactivates serine proteases
one of the most important anticoagulant
protein-inhibitor complexes are removed from the circulation by the liver
factor Xa, thrombin
the main targets of antithrombin is — & —
heparin
a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) that is used as an anticoagulant
stimulated antithrombin
17000-fold antithrombin activation for Xa substrate
9000-fold antithrombin activation for thrombin substrate
injected therefore accelerates inactivation of Xa & thrombin
treatment for venous thrombosis
fondaparinux (F)
a pentasaccharide related to Low-Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH) & more specific than High-Molecular Weight Heparin (HMWH)
specific inhibitor of Xa
antithrombogenic
endothelial cell surfaces are —
thrombomodulin
located on endothelial cell surface that binds to thrombin
thrombin substrate specificity changes
activation of PROTEIN C
protein C
activated by thrombomodulin from endothelial cells
activated protein C (APC)
forms a complex with PROTEIN S
proteolytically destroy Factors Va & VIIIa
inhibits the clotting cascade
protein S
forms a complex with activated protein C (APC)
not a serine protease
factor V Leiden
most common cause of hypercoagulability in Caucasians
autosomal semi-dominant
a point mutation in factor V near the APC cleavage site
resistant to proteolysis by activated protein C (APC) = more likely to stay active in endothelial cell surfaces
heterozygotes have 6 - 8 fold increased risk for deep-vein thrombosis
homozygotes have 30 - 60 fold increased risk for deep-vein thrombosis
plasmin
a serine protease that degrade fibrin clots
circulates in the plasma as an inactive zymogen
free — is immediately inactivated by anti- —
plasminogen
zymogen of plasmin
- activated by tissue-type — activator (tPA) & urinary-type — activator (uPA; urokinase)
antithrombogenic agents
prostacyclin (PLI2) + nitric oxide (NO)- inhibits adhesion and aggregation
thrombomodulin & heparan sulfate (heparin-like)
tissue factor inhibitor
plasminogen activator (tPA)
vitamin K dependent carboxylation
γ carboxylation of glutamate residues
carboxyl groups chelate Ca2+ which forms a bridge to membrane phospholipids (necessary for localization of clotting factors @ cell surface )
vitamin K
is oxidized in the carboxylase reaction
must be recycled by a 2-step reduction
factor II (prothrombin), VII, IX, X, protein C, protein S
factors that undergo vitamin K-dependent gamma carboxylation of glutamate residues (via vitamin K dependent carboxylase)
coumarin (warfarin)
antagonize vitamin K-dependent gamma carboxylation of several clotting factors = competitive inhibitor
has to be controlled so that only partial inhibition of the carboxylation is achieved to prevent bleeding complications
action can be reversed by administration of vitamin K
being replaced by direct inhibitors
plasminogen activator (PA)
used to treat myocardial infarction & stroke
promote dissolution of thrombi by locally activating plasminogen to plasmin
indications: myocardial infarctions, ischemic stroke, pulmonary embolism (only in severe cases)
Activase
thrombolytic- tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA)
action cannot be reversed by administration of vitamin K
Abbokinase
thrombolytic- urinary-type plasminogen activator (uPA; urokinase)
action cannot be reversed by administration of vitamin K
Streptase
thrombolytic- streptokinase
action cannot be reversed by administration of vitamin K