RD 1 Lecture 1 (8/20)
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
184 Terms
What does the term dentition refer to?
all of the the teeth in the mouth
What are homodonts?
Animals that have all the same teeth in their dentition
All teeth are exactly the same
What is the typical anatomical shape of homodont dentition?
conical and interdigitate
What are heterodonts?
mammals that have teeth of different types/classes
How many classes of teeth are in the human permanent dentition?
four
How many classes of teeth are in the human primary dentition?
three
What is another word for primary?
deciduous
What is a monophyodont?
has one set of teeth
ex. beluga whale, dolphin
What is a Polyphyodont?
has an endless succession of teeth
constantly exfoliated and replaced
ex. sharks, frogs
What is a diphyodont?
has two sets of teeth
ex. humans
what is another term for permanent?
secondary
succedaneous (besides premolars)
What are the two types of dentition that humans have?
Diphyodont and Heterodont
What is the top arch of teeth called?
Maxillary arch
What is the lower arch of teeth called?
Mandibular arch
What else can the arches be divided into?
quadrants
What age is the primary/deciduous dentition normally found?
2-6 years
What are the classes of teeth that the primary dentition has?
incisors, canines, and molars
How many teeth are in the entire primary dentition?
20
By what age is the primary dentition usually shed?
12 or 13
What is the formula used to represent the teeth in the primary dentition?
I 2/2, C 1/1, M 2/2
How many teeth are in the secondary/permanent/succedaneous dentition?
32
What are the classes of teeth in the permanent dentition?
incisors, canines, premolars, molars
What is a key difference between the primary and permanent dentition?
Only permanent has premolars
What is the formula that can be used for the permanent dentition?
I 2/2, C 1/1, PM 2/2, M 3/3
Which dentition are the anterior teeth present in?
both primary and permanent
What are the anterior teeth?
incisors and canines
What are the posterior teeth?
premolars and molars
Which teeth are present only in the permanent/not in the primary dentition?
premolars
What is the universal numbering system?
1-32 secondary, A-T primary
What is the FDI numbering system
• PERMANENT DENTITION
1 = maxillary, right quadrant
2 = maxillary, left quadrant
3 = mandibular, left quadrant
4 = mandibular, right quadrant
• PRIMARY DENTITION
5 = maxillary, right quadrant
6 = maxillary, left quadrant
7 = mandibular, left quadrant
8 = mandibular, right quadrant
The second number starts at midline and go back the quad (1-8 perm, 1-5 prim)
What is the palmer system?
uses a bracket for each quad and 1-8 or number (A-E) starting at midline and going back
What are the four tissues of the tooth
enamel, dentin, cementum, and pulp
What tooth tissues are calcified?
enamel and dentin
What tooth tissues are relatively hard and in what order?
enamel > dentin > cementum
what are the only visible tooth tissues?
enamel and cementum
What is the hardest substance in the body? (herder than bone)
enamel
What is the composition of enamel?
95% calcium hydroxyapatite (calcified) and 5% water and enamel matrix
What does the enamel develop from?
enamel organ (ectoderm)
What is enamel the product of?
specialized epithelial cells called ameloblasts
What does cementum look like?
dull yellow
external layer of root
How thick is the cementum on the tooth root?
very thin
What is the composition of cementum?
65% calcium hydroxyapatite (mineralized and calcified) and 35% organic matter (collagen fibers)
What is cementum about as hard as?
Bone
softer than enamel!
Where does the cementum develop from?
dental sac (mesoderm)
What is the cementum produced by?
cells called cementoblasts
What does dentin look like?
hard(sticky) yellowish tissue
What is dentin composed of?
70% calcium hydroxyapatite, ~18% organic matter (collagen fibers), and water
How hard is dentin?
harder than cementum but softer and less brittle than enamel
Where does dentin develop from?
embryonic dental papilla (mesoderm)
what cells form the dentin?
odontoblasts
What is the softest tooth tissue?
pulp
what is pulp?
connective tissue in the cavity or space in the center of the crown and root called the pulp cavity
What does the pulp contain?
rich supply of blood vessels and nerves
what is the coronal portion of the pulp called?
pulp chamber
what is the root portion of the pulp called?
pulp canal or root canal
what is the pulp cavity surrounded by?
dentin
where is the only spot the pulp cavity is not surrounded
root tip (apex) called apical foramen
where do nerves and blood vessels enter the pulp?
apical foramina
what is the only way pulp is visible (like dentin)
xrays or sectioned tooth
where does the pulp develop from?
dental papilla (mesoderm)
What is the anatomical crown?
part of the tooth (in the mouth or handheld) normally covered by an enamel layer
What is the anatomical root?
part of a tooth covered by cementum
What is the clinical crown?
amount of tooth visible in the oral cavity
What is the clinical root?
amount of tooth that is not visible since it is covered with gingiva (gum tissue)
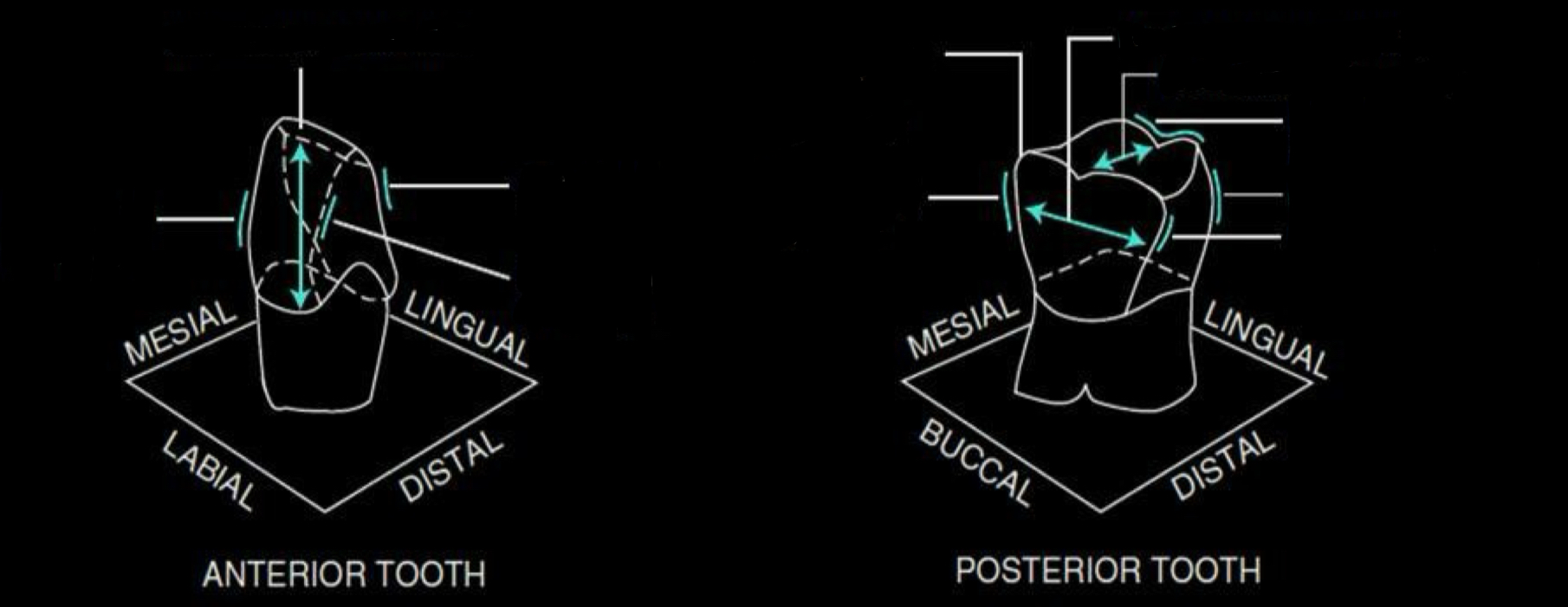
What is the facial surface?
surface of a tooth in the mouth resting against or next to the cheeks or lips
can be used for all teeth
posterier facial surface can also be called
buccal
anterior facial surface can also be called
labial
what is the lingual surface?
surface of a maxillary or mandibular tooth nearest the tongue
in the maxillary the lingual surface can also be called
palatal
on posterior teeth the chewing surface is called
occlusal
on anterior teeth the chewing surface is called
incisal edge or ridge
what are proximal surfaces
sides of a tooth generally next to an adjacent tooth
where is the mesial
close to the midline
where is the distal
surface further away from the midline
what is an exception to the fact that a mesial of one tooth touches a distal of the tooth next to it?
central incisors (mesial to mesial) and last tooth in back
proximal surfaces are not
naturally cleaned by the action of the cheeks, lips and tongue
what surfaces are usually more slef-cleaning?
facial and lingual
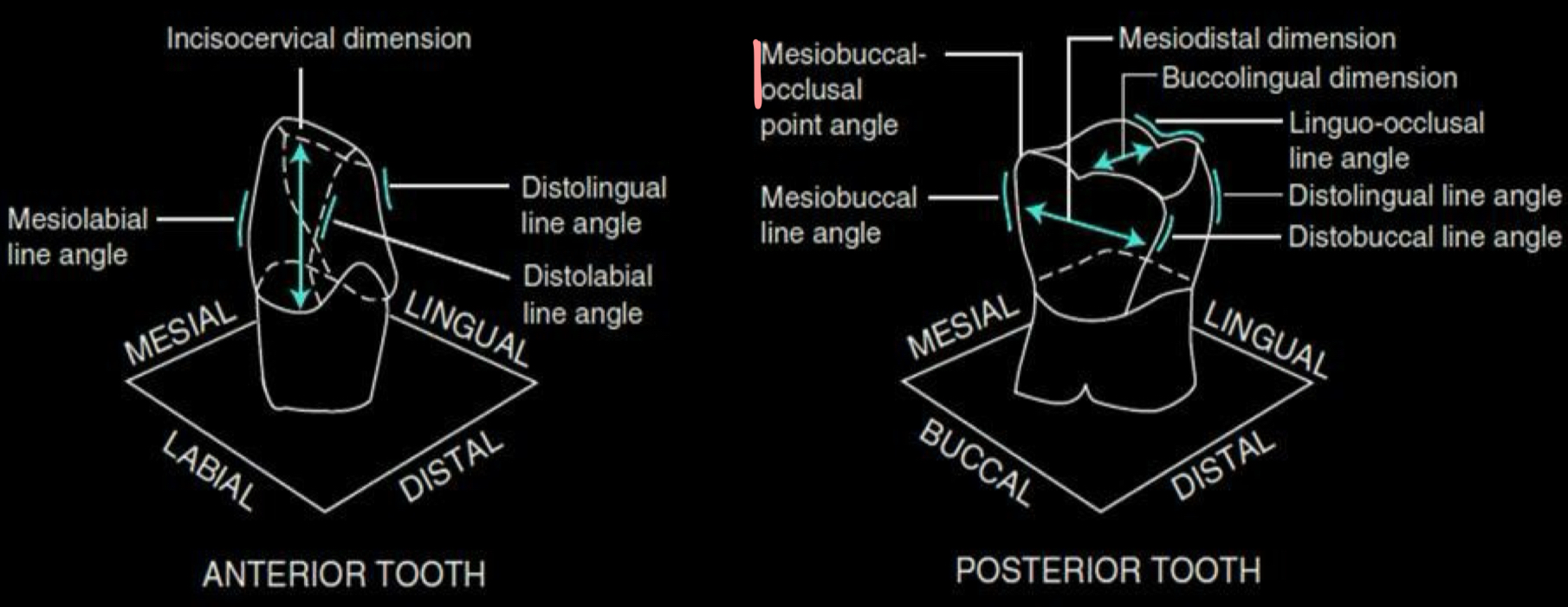
What is a line angle?
junction line where two tooth surfaces meet
what is the guideline to combining terms for line angles?
mesial → distal → facial → lingual → occlusal or incisal
what are point angle?
junctions of three tooth surfaces at a point
To describe a dimension of a tooth, for example, the length of an incisor crown from the incisal edge to the cervical line is called
incisocervically
Label the line and point angles
a tooth can be divided into
thirds
divide the tooth crown into the following thirds (horizontally from any side)
cervical, middle, and occlusal (or incisal)
horizontal lines can divide the root into thirds
cervical, middle, and apical (toward the root tip or apex)
tooth from the facial (or lingual) surface, vertical lines can be used to divide the crown or root into
mesial, middle, and distal thirds
tooth from the proximal (mesial or distal) surface, vertical lines can be used to divide the crown or root into
facial, middle, and lingual thirds
tooth from the occlusal (or incisal) surface, lines running mesiodistally can be used to divide the crown into
facial, middle, and lingual
lines running faciolingually can be used to divide the tooth into
mesial, middle and distal thirds
Root-to-crown ratios for teeth are normally
>1.00
why is it significant to know root-to-crown ratios?
A tooth with a small root-to-crown ratio (closer to 1) is not the best choice for attaching and supporting false teeth
morphological structures can be divided into two broad sections based on:
1. Elevations & Ridges
2. Depressions & Grooves
Elevations =
rounded
ridges =
linear
what is a cusp?
pyramidal elevation or peak
where are cusps located?
occlusal surfaces of molars and premolars, and on the incisal edges of canines
how many cusp ridges does each cusp have?
four, converge towards the cusp tip
(rounded pyramid)
cusps are named based on
location on tooth
On a two-cusped premolar, the two cusps are named
after the surface adjacent to each cusp: buccal or lingual
On a four-cusped molar, the four cusps are named
after the adjacent line angles: mesiobuccal, distobuccal, mesiolingual, and distolingual