AP Chem Unit 9: Thermodynamics and Electrochemistry
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
_______ is the heat absorbed or released by a system during a constant-pressure process.
Enthalpy
________ is a measure of the randomness in a system.
Entropy
What does thermodynamically favorable mean?
Spontaneuous
TRUE OR FALSE: Temperature and pressure can affect spontaneity.
True
𝜟S means
Entropy (final-initial)
The entropy of the universe ______ in any spontaneous processes.
increases
Entropy increases with the ______ of motion of molecules.
freedom
Entropy of a system increases for processes where:
gases form from either solids or liquids.
liquids or solutions form from solids.
the number of gas molecules increases during a chemical reaction.
The entropy of a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero is
0
What are the factors that increase entropy?
an increase in volume (more possible positions).
an increase in temperature (greater distribution of molecular speed).
an increase in the number of atoms/molecules (more degrees of freedom).
If 𝜟G is negative, then the forward reaction is _____
spontaneous
If 𝜟G is 0, the system is…
at equilibrium
If 𝜟G is positive, then the reaction is ________ , but spontaneous in the _____ direction
nonspontaneous; reverse
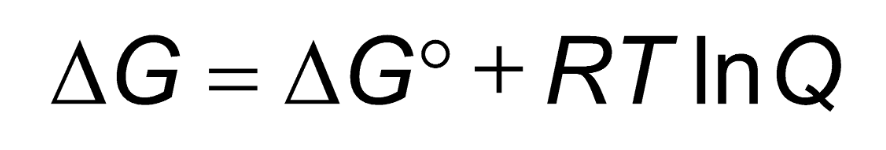
In this equation, how is Q calculated?
[products]/[reactants]
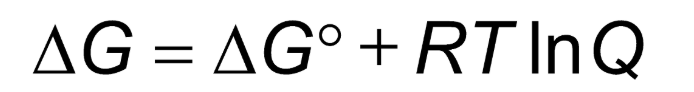
If Q = K, the equilibrium constant, then…
the reaction is at equilibrium
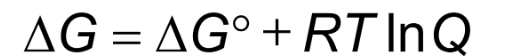
If Q < K, the equilibrium constant, then
the reaction shifts right to form products
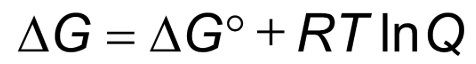
If Q > K, the equilibrium constant, then
the reaction shifts left to form reactants
What does thermodynamically favored mean?
It means the reaction is spontaneous and that the products are favored at equilibrium.
What does thermodynamically favored mean in terms of Gibbs and the equilibrium constant (K)?
𝛥G < 0, K > 1
Electrochemistry is the study of the relationships between _____ and ______ ______. It includes the study of both spontaneous and nonspontaneous processes.
electricity; chemical reactions
What is a voltaic (galvanic) cell?
an electrochemical cell in which an electric current is generated from spontaneous oxidation–reduction reactions
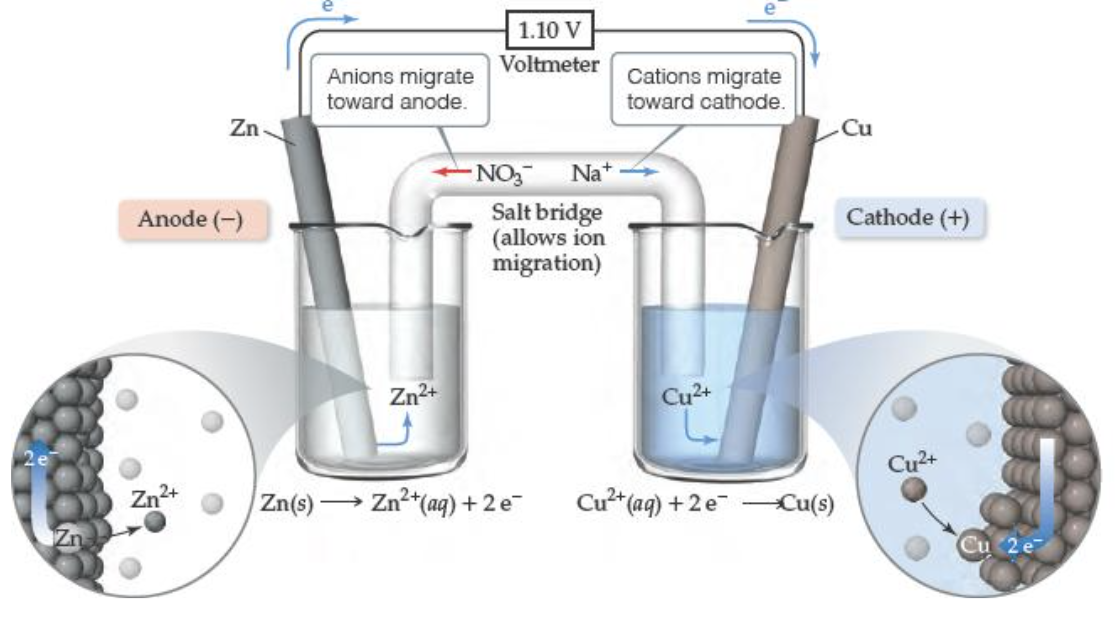
What is an electrolytic cell?
The electrolytic cell has an anode (positive) and a cathode (negative) connected to a voltage source. The electrons flow from the anode to the cathode via the voltage source. Allows nonspontaneous reactions to occur.
What is the Nernst equation used for?
Finding cell potential under nonstandard conditions
Spontaneous redox reactions produce a _____ cell potential, or electromotive force.
positive
The more positive the value of the E°red the greater the tendency for _____ under standard conditions
reduction
The more negative the value of the E°red the greater the tendency for _____ under standard conditions
oxidation
What is E°red?
Standard reduction potential