EKG rhythms & TX
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
sinus bradycardia and how to treat
less than 60 bpm
treat with atropine; if atropine is ineffective, transcutanoues pacemaker
possible dopamine or epi
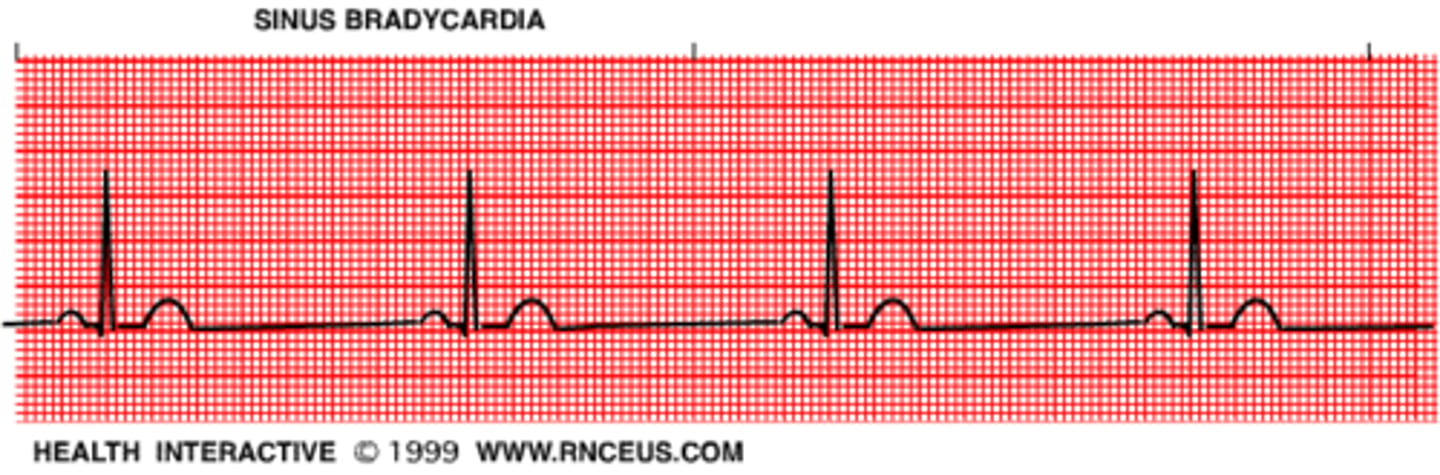
what causes bradycardia
vagal stimulation
CCB like nifedipine and amioradone
-lols
hypoxia
sinus tachycardia and how to treat
greater than 100bpm, reduced CO and low BP
-vagal maneuvers
-adenosine
- Bb and CCB
-cardioversion if drugs dont work
-treat cause of tachy
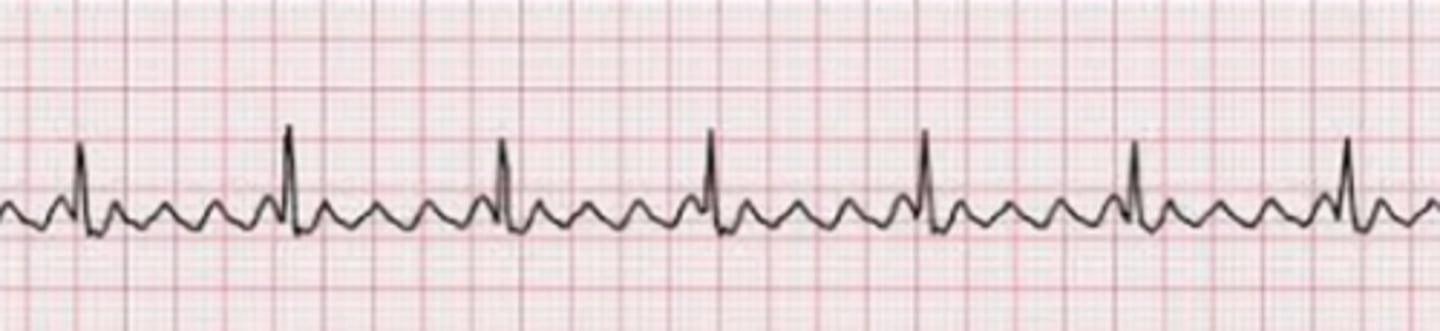
types of negative inotropes
beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic medicines
atrial flutter and how to treat
regular rhythm
treat with
-cardioversion
-antiarrhythmic
-anticoags
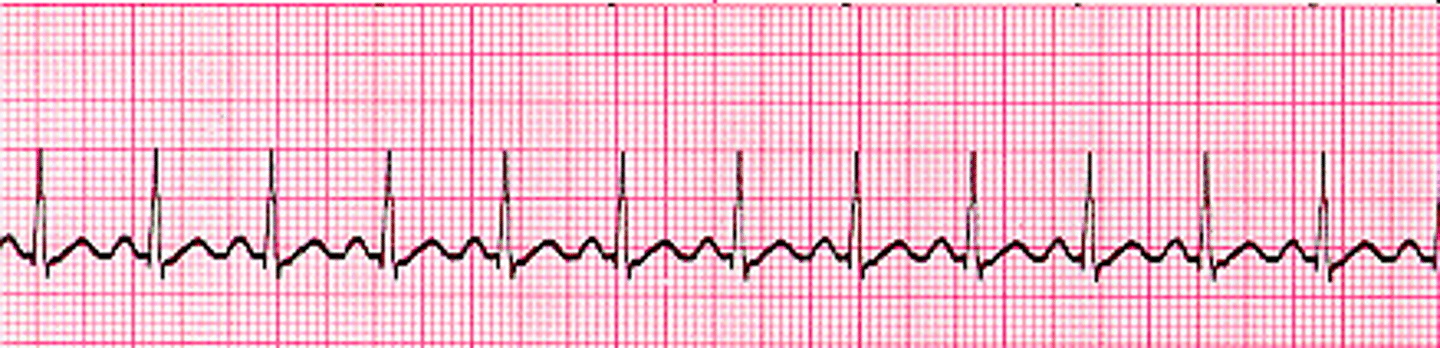
atrial fibrillation
rapid, irregular, ineffective contractions of the atrium
no P wave, PR cant be measured
treat with cardioversion, arrhythmic and anti coags, digoxin
how does someone with Afib present
SOB
HYPOTN
clots
what causes Afib
age
Htn
diabetes
obesity
heart disease
smoking
MI
heart fx
heart diseases
how to treat Afib in ot who are hemodynamically unstable
BB THEN CARDIOVERSION
SVT / Afib with RVR
heart is beating so fast, you cant see a rhythm
treat with vagal maneuvers, amiodarone, adenosine then cardioversion
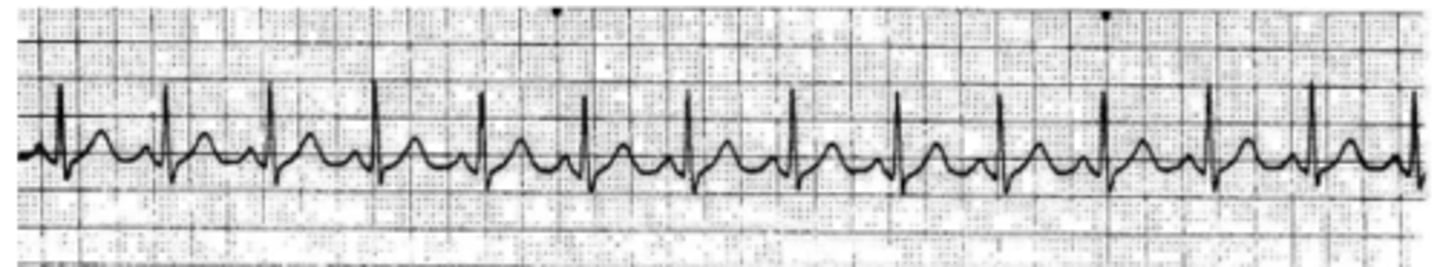
what happens in a SVT
p waves are not identifiable
pt is unstable
signs in pt with SVT
SOB
hypoxic
change in VS
PAC/PVC
Premature atrial/ventricular contraction
seen with tachy
-usually regular with caffeine
- treat if symptoms are present or >6 a minute
-can turn into vtach
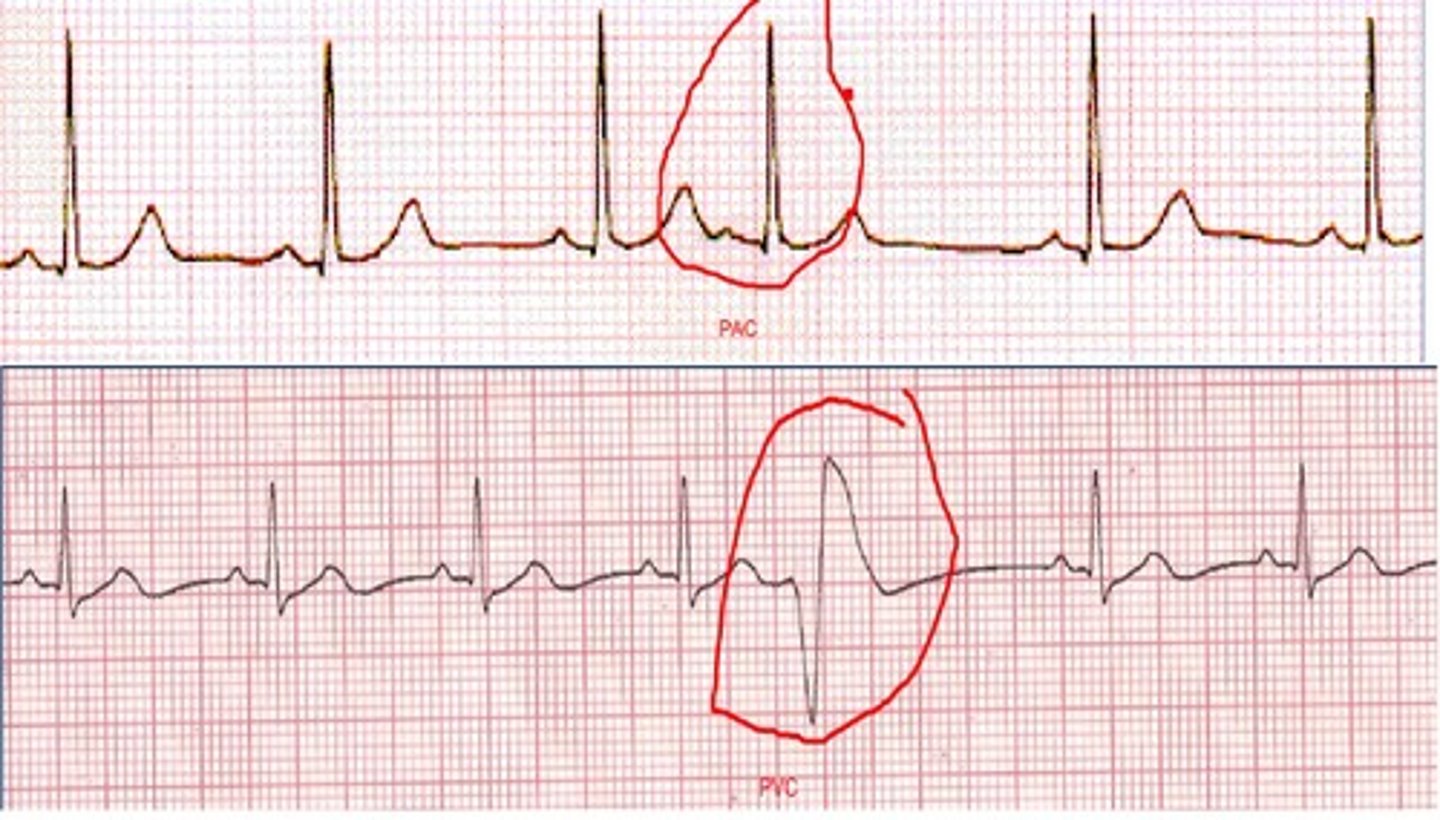
what happens in a PAC/PVC
hidden P wave
-atrias and ventricles contract at the same time
ways to treat PVC/PAC
-reduce alcohol and caffeine
-reduce stress
-stop smoking
- correct hypokalemia
beta blocker may be prescribed
Vtach
tombstones, 3 PVC in a row
-can be pulseless or pulse
-asses for pulse first
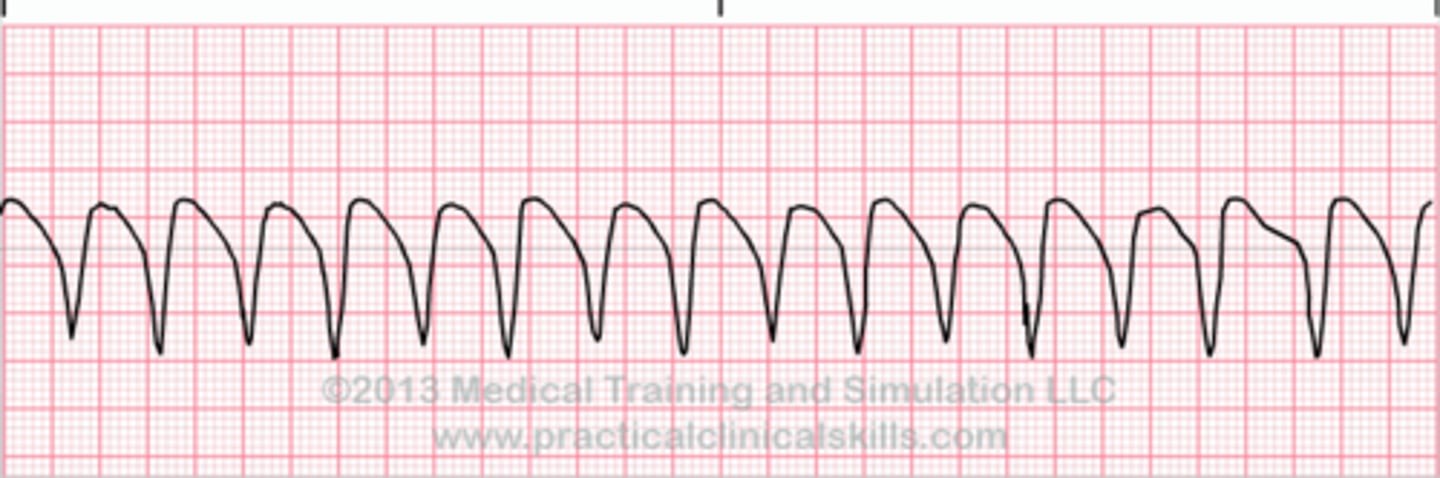
what to do if theres a pulse/ not in VTach
pulse: slow HR or cardiovert, ECG, amiorodone, lidocaine
no pulse: CPR and defib
Vfib
-lethal arrhythmia where there is uncoordinated quivering of the ventricles
start CPR and defib
amioradine and epi
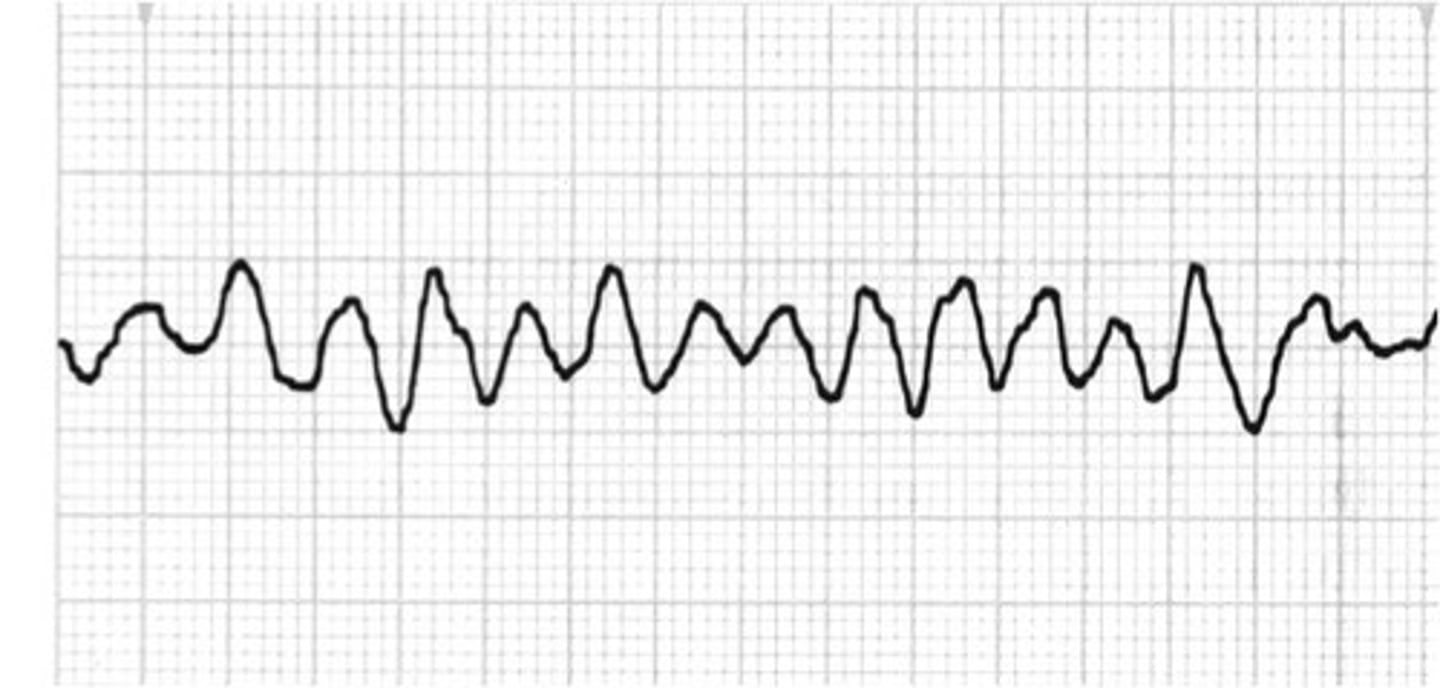
cause of Vfib
CAD
MI
what you need in pt with VFIB
-continuous VS monitoring
-2 IV access
PEA rhythm
lethal rhythm with no pulse
CPR and epi
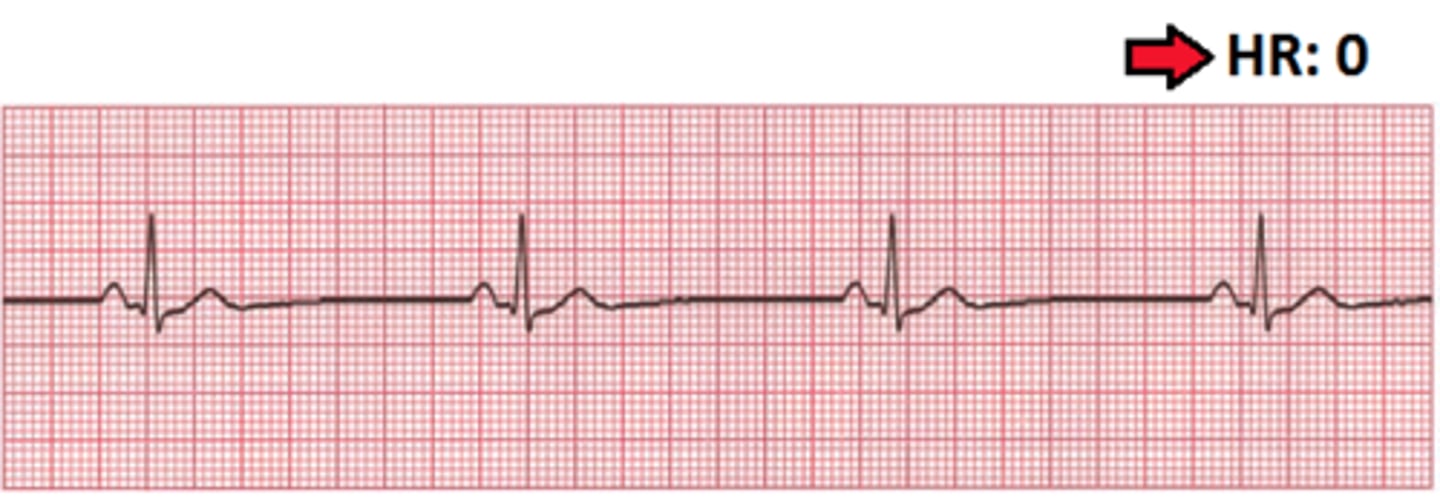
Asystole
flat line that is lethal
CPR and Epi
Atrial Problems
A flutter
A fib
SVT
PAC
RVR
ventricular problems
Vtach
Vfib
PEA
Asystole
PVC
RVR
what rhythms dont you defib for
PEA and Asystole
which ones do you defib for
Vtach and Vfib
what is the electrical cardiac function
SA & AV nodes
what is the mechanical cardiac function
heart moving
what is the P wave
atrial depolarization (contraction)
a P wave longer than 0.2 indicates
heart block
What happens in the QRS complex/ R wave?
ventricular depolarization and atrial repolarization
what happens in T wave?
ventricular repolarization
what interval needs to short
QT; long means poor perfusion
QRS interval should be how long
less than 0.12
PR interval should be how long
0.12-0.20
QT interval should be how long
less than 0.40
anything more means ventricle cant relax
electrode placement
cloud over grass, smoke over fire
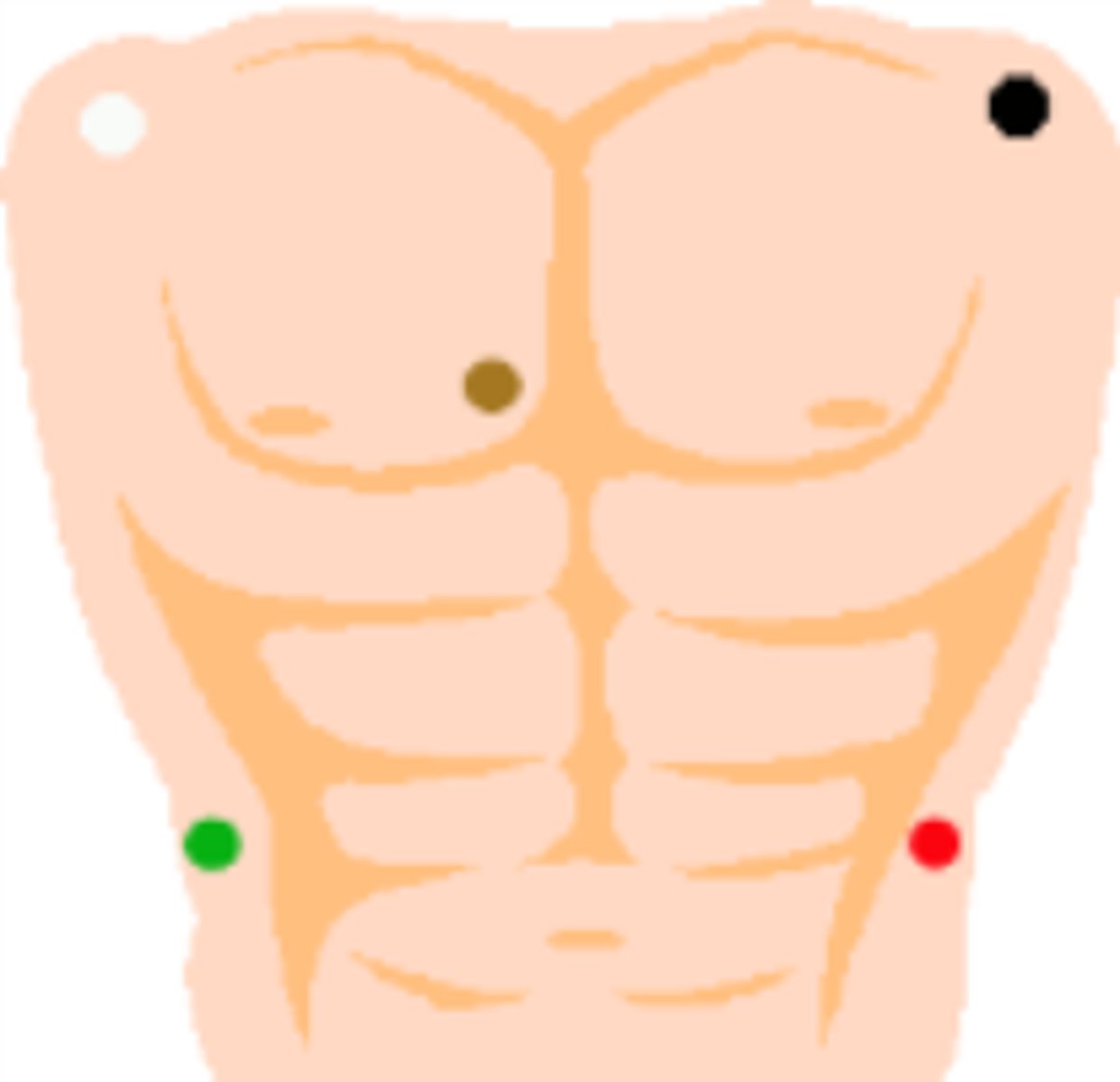
What is a 12 lead ECG?
Ten electrodes are placed on the chest and extremities.
Provides 12 different perspectives of electrical activity in the heart
what are arrhythmias
irregular heart rhythms that can sometimes produce symptoms
what does arrhytmias do to the heart
increase the risk of clots
what to assess in those with arrhythmias/dysrhytmias
-otc medications
-s/s of decreased CO
-s/s of fluid retention
-V/S and auscultation
interventions for arrhythmias
stabilize
manage symptoms
manage anxiety
what characterizes a regular rhythm
equal distance between each R wave
p wave
Tall tented T waves
hyperkalemia
types of rhythm tx
ACLS algorithm
cardioversion
defib
pacemaker
ICD
what is the ACLS algorithm
CPR and oxygen
epi
shock
what is a ZOLL
..
what is cardioversion for
used for Vtach with pulse
-SVT
-torsades
-Afib
A flutter
when do you use cardioversion
when amiordadone for Afib, flutter and RVR
or adenosine dont work for SVT
how does cardioversion work
shocks on R wave at 120-200J to reset rhythm
elective procedure that needs consent
sedation
emergency supply for cardioversion
cardiac monitor
ambu bag
suction
intubation
meds and elective cardioversion
no digoxin fir 48 hours
anticoagulants few weeks before
what is Defib used for
when pt has no pulse and are in vtach or vfib; emergency
360J
what to know about Defib
uses ZOLL to shock back into any rhythm
does not need to sync with electrical activity
shcok done every 2 minutes between CPR cycle
what is given after unsuccessful defib
Epi
what does a pacemaker do
Maintains a normal heart beat rhythm in bradycardia and heart blocks; needs to sense and send
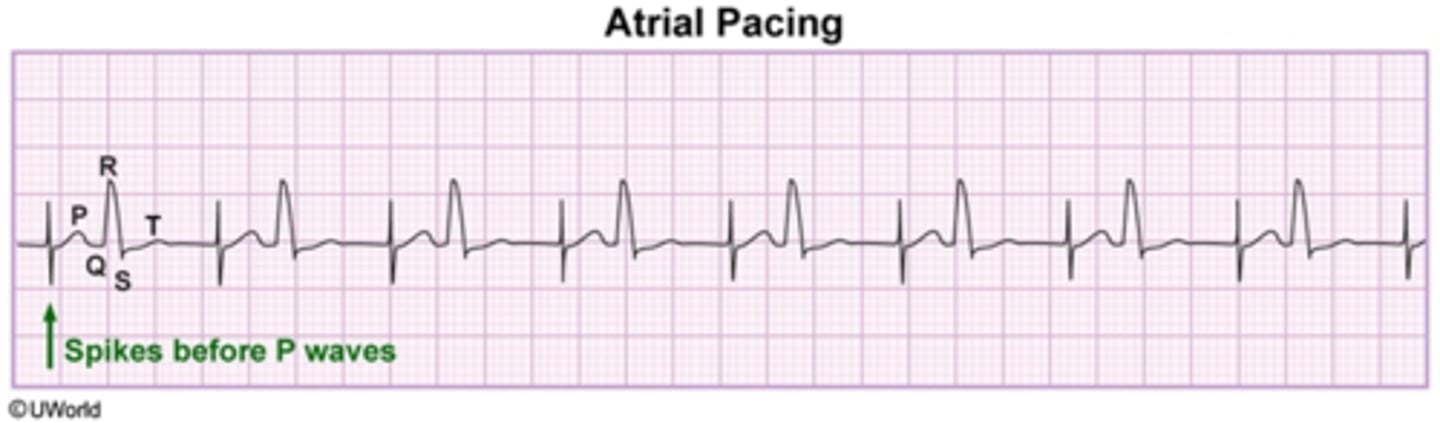
atrial paced
spike before P wave
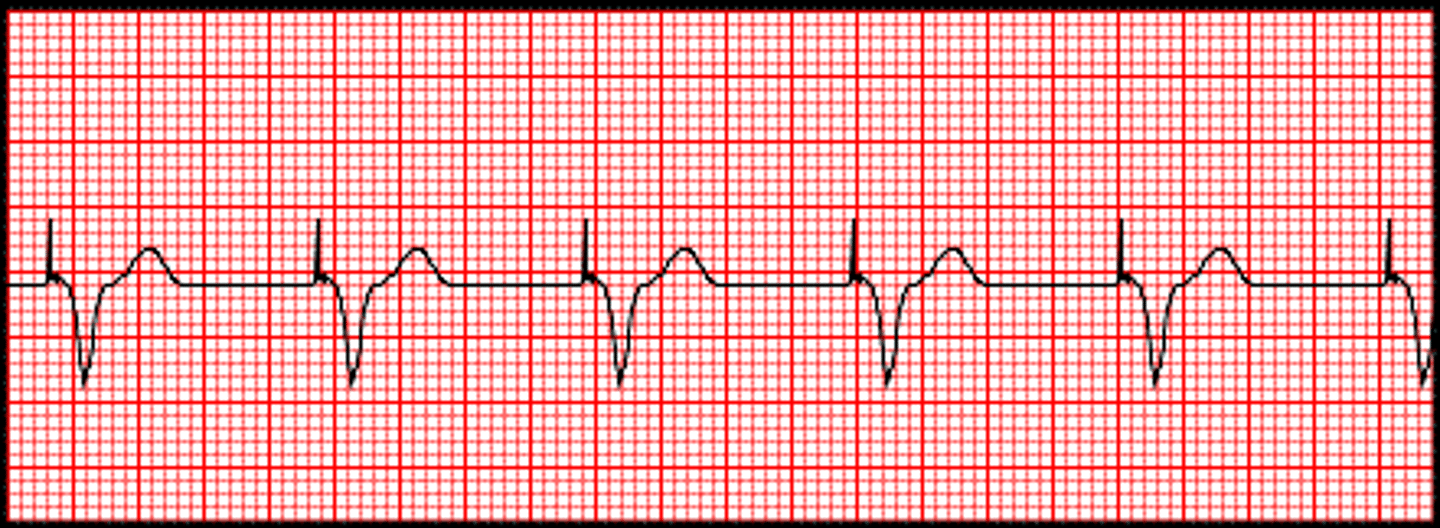
ventricular paced
spike before QRS
first letter on pacemaker
location of pacing
- atria, ventricular or dual
second letter on pacemaker
chamber being sensed; atria,ventricular or dual
third letter on pacemaker
mode of pacing
-inhibited meaning when heart dont work , triggered meaning when there is an intrinsic heart avtivity or both
transcutaneous pacing
temporary pacing that is accomplished through the application of two large external electrodes
considerations for transcutaneous pacing
erythema and burns
consent
monitor RR
what is an ICD
monitors rhythm continuously, shocks heart when it is in vtach or vfib
sends multiple shocks and if unsuccesful, device performs cardioversion and defb
nurse post op for ICD
check settings to make sure it is set to what is ordered
bleeding or infection
xray to rule out pneumo
ICD precautions
-wear ID bracelet
-manufacturer ID card
-dont use metal detector
-avoid large stereos
-chain saws
-car engines
- old cellphones
-MRI
-no battery pacls
tx for sinus bradycardia
Atropine, pacemaker
tx for SVT
vagal maneuvers --> adenosine--> cardioversion
Adenosine
Antiarrhythmic with short life; needs to be a psuh med
what rhythms do you give epi for
asystole
PEA
pulseless Vtach
V fib
complications for pacemaker
Infection
Hematoma formation
Hemothorax
Vtach
dislocation of lead placed
hiccuping
rare: cardiac tamponade
how is malfunction of pacemaker signified
ECG
brasycardia
cardiac conduction surgery
procedure done when Vtach is unresponsive to meds and cannot be cardioverted or paced
types of cardiac condcution surgery
ablation
endocardial resection
endocardial isolation
types of unstable rhythms
svt and rvr with hypotension
lack of QRS complex
asystole