5. Microbial Metabolism: Catabolism and Anabolism Overview
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Metabolism
Biochemical reactions within an organism's cells.
-ultimate function is to reproduce the organism
what are the purposes of studying metabolism?
occurs in all living cells, used in microbiology to identify organisms, possible basis for treatment
Catabolism
Breakdown of large molecules into smaller ones. -releases energy (exergonic), stored as ATP
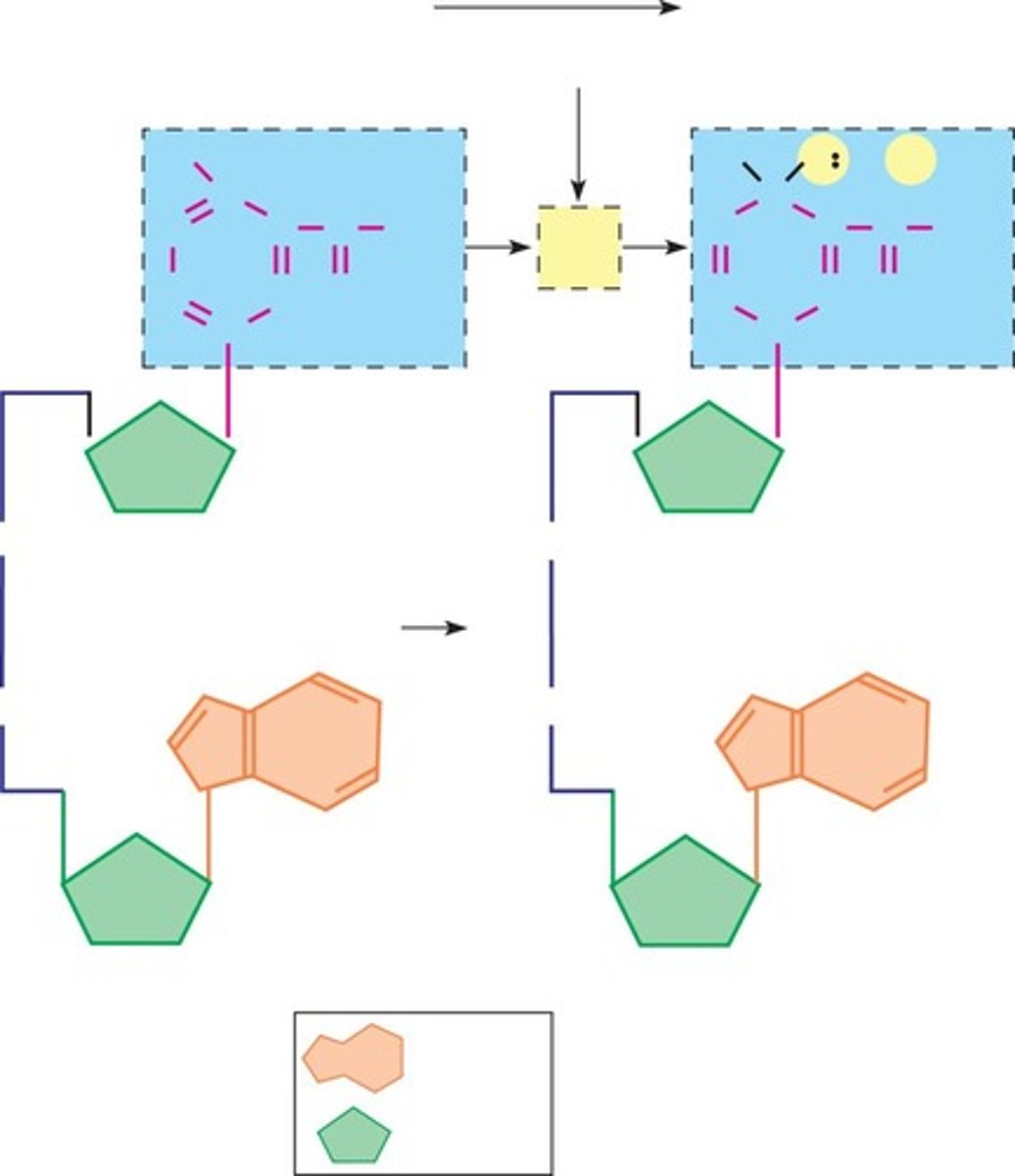
Anabolism
Synthesis of large molecules from small ones. -requires energy (endergonic)
Exergonic
Reactions that release energy, often stored as ATP.
Endergonic
Reactions that require energy input, supplied by ATP.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, energy currency of cells. (stored in phosphate bonds)
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ATP generation via electron transport chain.
redox
shuffling of electrons
redox reaction
A chemical reaction involving the transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another; also called oxidation-reduction reaction.
coenzyme
something that an enzyme needs in order to do its job, assists in enzyme-catalyzed reactions by carrying chemical groups, electrons, or atoms from one molecule to another.
phosphorylation
The metabolic process of introducing a phosphate group into an organic molecule.
substrate-level phosphorylation
transfers a phosphate group from a phosphorylated substrate (a molecule that already has a phosphate group attached) to ADP during glycolysis and Krebs.
substrate
the specific molecule that an enzyme acts on during a chemical reaction.
Photophosphorylation
Conversion of sunlight energy into ATP.
Oxidation
Loss of electrons or hydrogens in reactions.
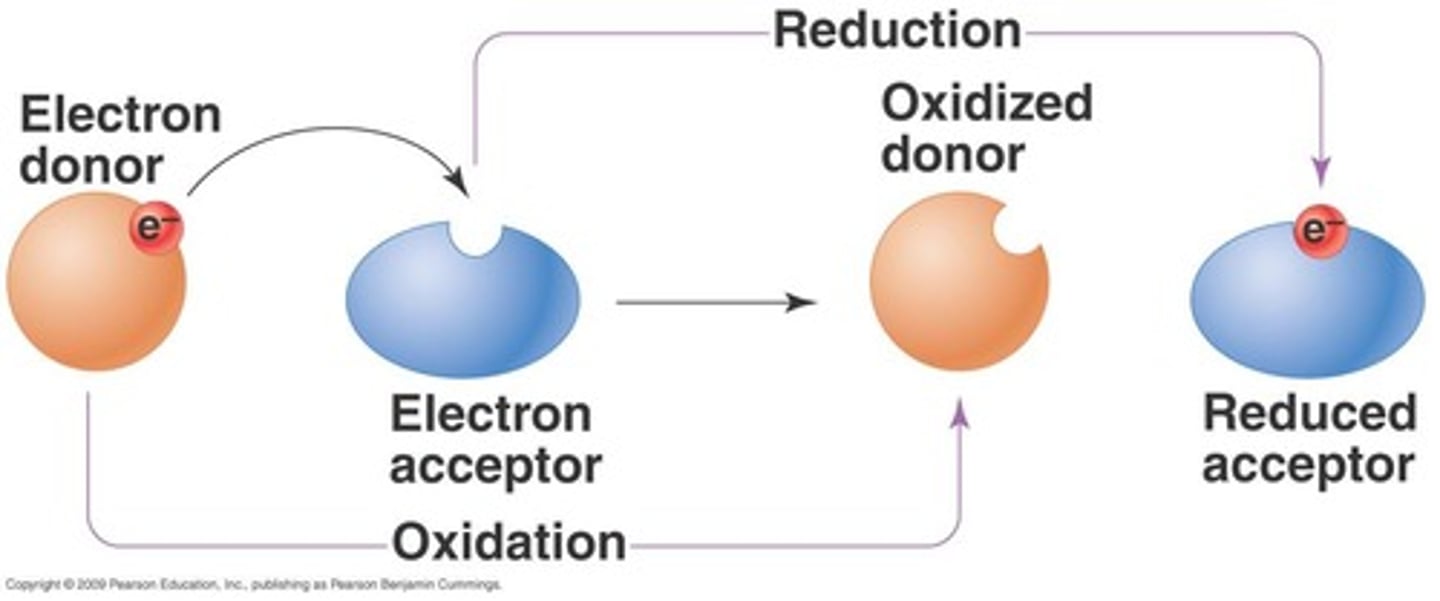
Reduction
Gain of electrons or hydrogens in reactions.
OIL RIG//LEO says GER
Acronym for Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain.
NAD+
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, accepts electrons. (oxidized)
-two sets of: a nitrogenous base, phosphate, sugar
NADH
Reduced form of NAD+, carries electrons.
FAD
Flavine adenine dinucleotide, another electron carrier. (oxidized)
FADH2
Reduced form of FAD, carries electrons.
Cofactors
Non-protein molecules aiding enzyme function.
Active Site
Region on enzyme where substrates bind. (similar to the substrate shape)
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up reactions.
Secondary Structure
Local folding patterns in proteins, like alpha-helices.
Tertiary Structure
Overall 3D shape of a single polypeptide.
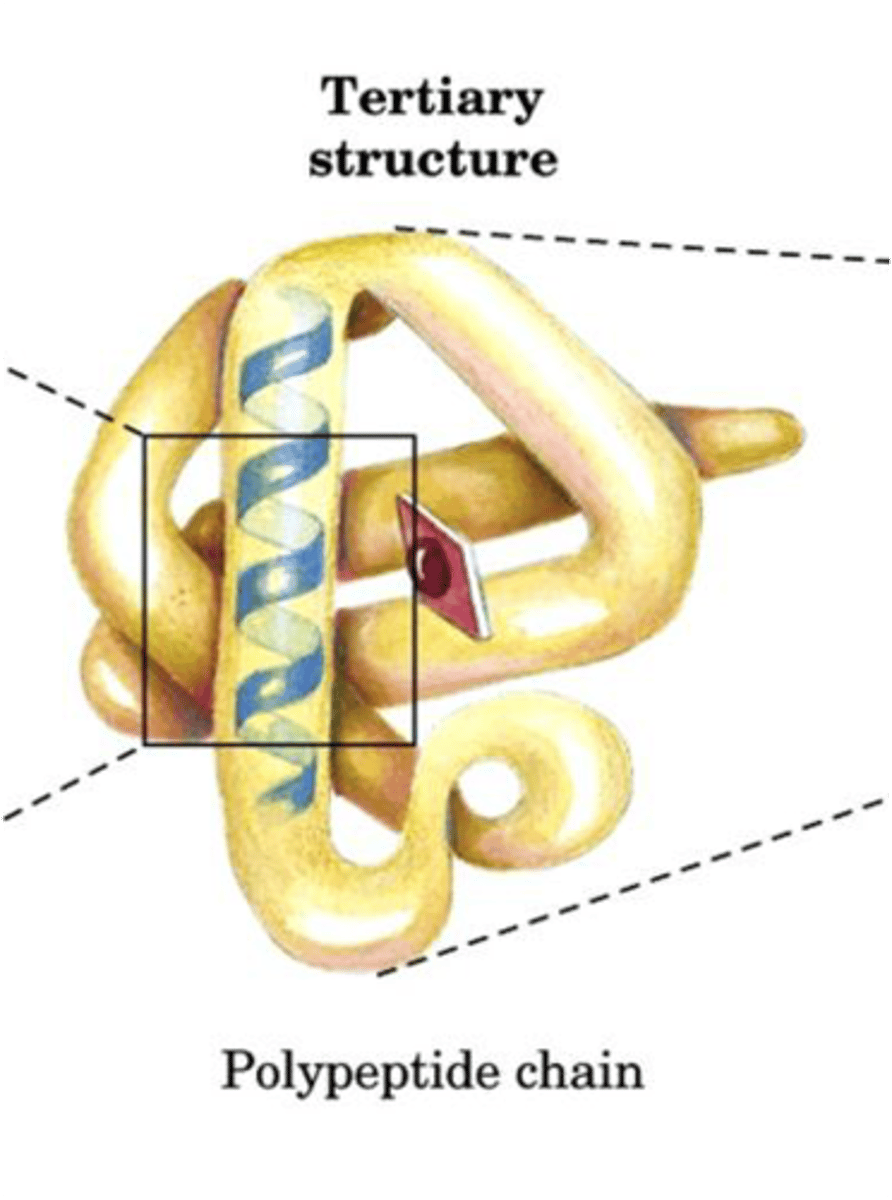
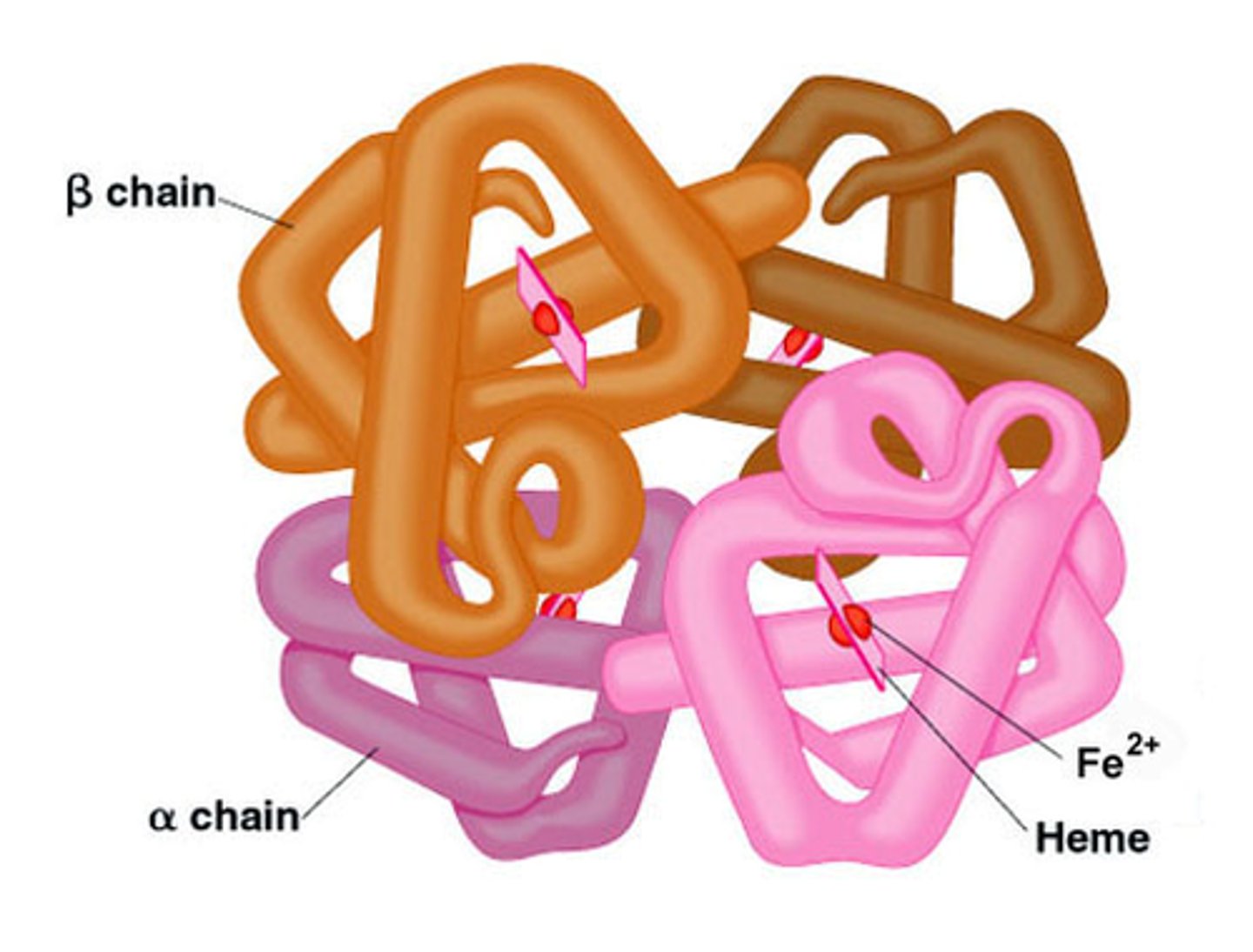
Quaternary Structure
Complex of multiple polypeptides in proteins.
endoenzymes
(also called intracellular enzymes) are enzymes that function inside the cell where they are produced.
exoenzymes
enzymes secreted by a cell into the external environment to perform their function outside the cell
Glycolysis
First step in glucose metabolism, producing pyruvate.
Krebs Cycle
Series of reactions generating ATP and electron carriers.
Respiratory Chain
Final stage of cellular respiration, producing ATP.
Fermentation
an anaerobic metabolic process (does not require oxygen) in which microorganisms break down organic compounds (like glucose) to produce energy (ATP), along with byproducts like acids, alcohols, or gases.
what's the main purpose of fermentation?
To reoxidize the electron carriers to serve as coenzymes in glycolysis
Active enzymes
Enzymes that are currently catalyzing reactions.
Inactive enzymes
Enzymes that are not currently catalyzing reactions.
Substrate
Molecule upon which an enzyme acts.
Constitutive enzymes
Enzymes produced continuously at constant levels.
Regulated enzymes
act like traffic signals in metabolism — ensuring that pathways run only when needed, and not too fast or too slow.
down regulated enzymes
an enzyme whose activity or production is decreased in response to certain signals or conditions.(saving energy)
Activation energy
Energy required to initiate a chemical reaction.
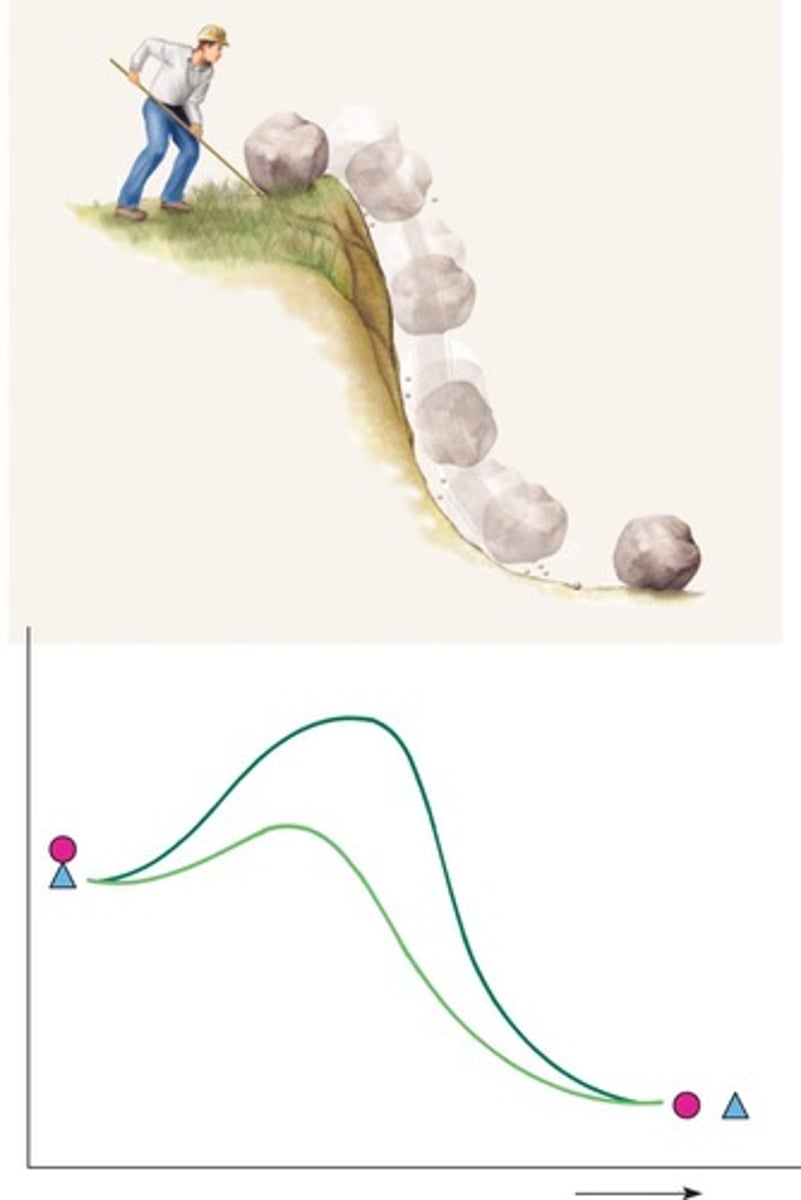
Exergonic reactions
Reactions that release energy, typically catabolic. (hydrolysis)
Endergonic reactions
Reactions that consume energy, typically anabolic. (dehydration)
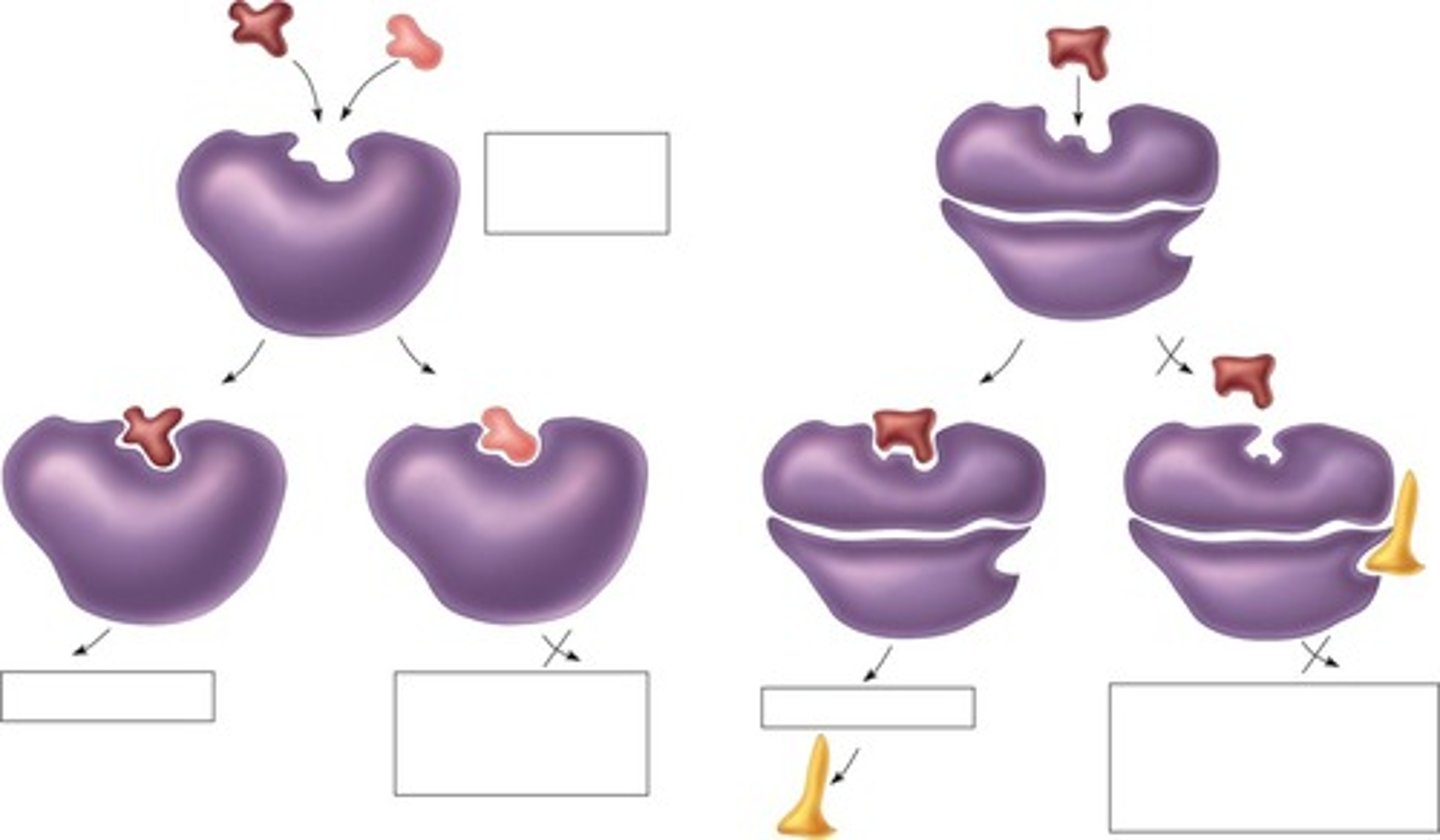
Competitive inhibition
Inhibition where substrate and inhibitor compete for active site.
inhibit
to block
Non-competitive inhibition
Inhibition where inhibitor binds elsewhere (not at site), altering enzyme function. (reducing or stopping)
Feedback inhibition
Process where end product inhibits an earlier step.
Optimum temperature
Temperature at which enzyme activity is highest.
Denatured enzymes
Enzymes that lose structure and functionality due to conditions.
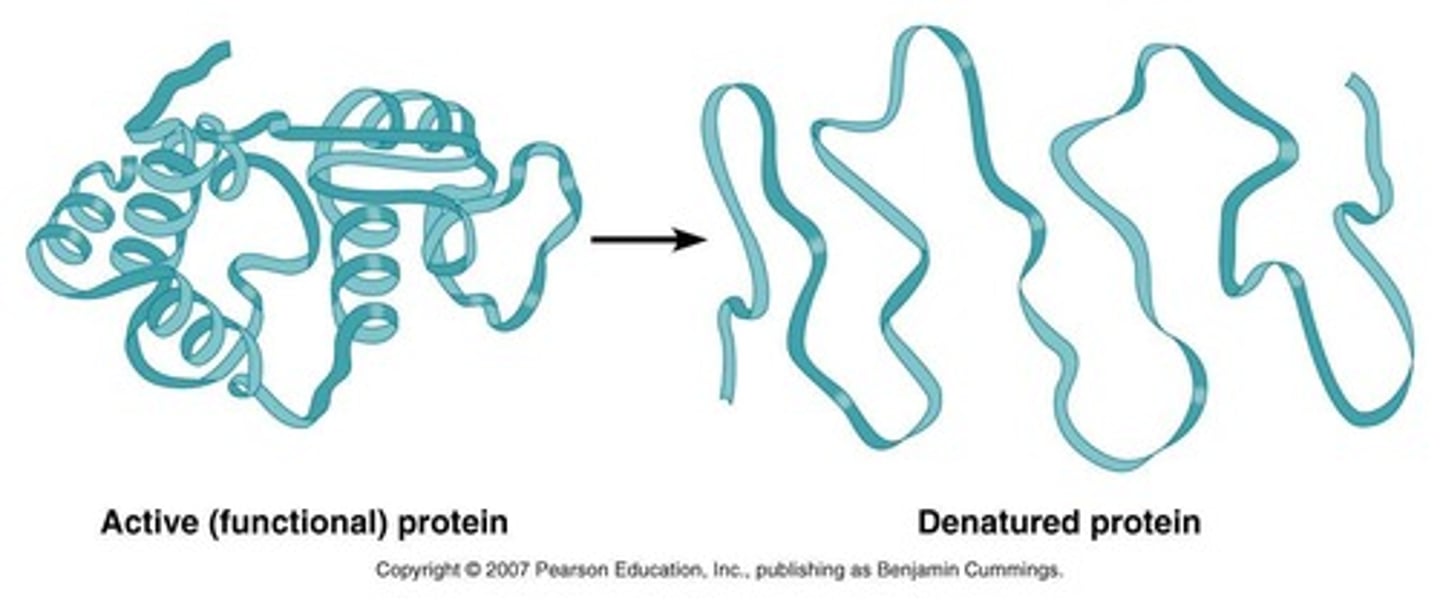
Optimum pH
pH level at which enzyme activity peaks.
Substrate concentration
Amount of substrate available for enzyme reactions.
Aerobic respiration
Respiration using oxygen as the final electron acceptor.
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration using an inorganic molecule other than oxygen.
Glycosidic bond
Bond formed between two monosaccharides during dehydration.
Peptide bond
Bond formed between amino acids during protein synthesis.
Phosphoenolpyruvate
Final glycolysis intermediate before pyruvate.
Pyruvate
End product of glycolysis, enters Krebs cycle.
Net Yield of ATP
2 ATP produced from one glucose in glycolysis.
carbohydrate catabolism
the breakdown of carbohydrate molecules, especially (oxidize) glucose, to extract energy.
aerobic reaction
C6H12O6+6O2→6CO2+6H2O+ 38ATP
anaerobic reaction
6CO2+6H2O+ 38ATP----C6H12O6+6O2
cellular respiration
the process by which cells break down glucose (or other food molecules) to release energy in the form of ATP the cell's energy currency.
what are the 3 stages of cellular respiration?
1. synthesis of acetyl-CoA
2. krebs cycle
3. final series of redox reactions (electron transport chain)
Synthesis of Acetyl-CoA
Preparation step for Krebs cycle from pyruvate. (2acetyl-CoA go in, 2CO2 and 2 pyruvate come out)
Krebs Cycle in cellular respiration
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into CO2 in a series of energy-extracting reactions
Electron Transport Chain
Final stage of cellular respiration, produces ATP via oxidative phosphorylation
oxidative phosphorylation
The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain; the third major stage of cellular respiration.
holoenzyme
enzyme with its cofactor
kinase
transfers some phosphates and results in ATP and pyruvate
Total ATP from Glucose
Net 2 ATP from glycolysis, 4 ATP from Krebs.
Metabolic Products of Glucose
6 CO2 produced from one glucose during respiration.
intermediate
in-between molecule in a pathway
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
a chain of steps where electrons are passed from one molecule to another, and each step releases energy, which is used to make ATP.
Proton Gradient
a difference in proton concentration across a membrane, and it's used by cells to make ATP. (oxidative)
-Potential energy created by protons across a membrane.
:Proton gradient → ATP synthase → ATP production (oxidative phosphorylation).
ATP Synthase
Enzyme that synthesizes ATP using proton gradient.
what is the final electron acceptor in the Electron Transport Chain (ETC).
molecular oxygen (forms water-reduction) "aerobic respiration"
where does aerobic respiration occur in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Occurs in the bacterial plasma membrane (in prokaryotes) and the mitochondria (in eukaryotes).
Theoretical ATP Yield
Maximum ATP produced during cellular respiration: 38 ATP.
Terminal Electron Acceptors
the final molecule that receives electrons at the end of the electron transport chain (ETC) during respiration.
carrier molecules
a protein that functions in transport of molecules across a membrane
what are the 4 categories of carrier molecules?
Flavoproteins
Ubiquinones
Metal-containing proteins
Cytochromes
Chemiosmosis
using a proton gradient to power ATP production through ATP synthase. (oxidative phosphorylation)
Flavoproteins
Carrier molecules in ETC containing flavin groups.
Ubiquinones
Mobile electron carriers in the electron transport chain.
Metal-containing Proteins
Proteins that facilitate electron transfer in ETC.
Cytochromes
Heme-containing proteins involved in electron transport.
Proton Pumping
Movement of protons out of the cell during ETC.
what's the order of best efficient to least in ATP production in cellular respiration?
aerobic, anaerobic, fermentation
O2 as Electron Acceptor
Best acceptor, yielding largest proton gradient.
Amphibolism
when a metabolic pathway can work in both directions, it can be used for breaking down molecules (catabolism) and for building up molecules (anabolism).
Inorganic Molecules as Acceptors
Less efficient than O2; examples include nitrate.
Gluconeogenesis
the process of making glucose from non-carbohydrate sources; literally means "new glucose formation."
Weak Proton Gradient
Generated during anaerobic respiration, yielding less ATP.
Strong Proton Gradient
Generated during aerobic respiration, yielding maximum ATP.
Metabolic Water Formation
Final product of electron transport involving O2.
ATP Production Mechanism
Protons entering ATP synthase drive ATP formation.
ATP Yield
Total of 36-38 ATP produced per glucose molecule.
Organic Electron Acceptor
Molecule like pyruvate accepting electrons in fermentation.
Facultative Anaerobes
Organisms that can switch between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism.