ASA 101
1/152
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
When sailing, always be aware of the wind’s ______ and ______.
Speed and direction
The desirable force generated by the wind moving across a sail is called ______.
Lift
The direction relative to the wind in which the sailboat cannot sail is called the _____ _____ _____.
No sail zone
Sailboats can reach an upwind destination by sailing a ______ course.
Zigzag
The point of sail at the edge of the no-sail zone is called _____ _____.
Close hauled
A boat sailing across the wind is said to be ______.
Reaching
Sailing straight downwind is called _____.
Running
As the sailboat’s direction changes relative to the wind, so should the sail’s _____ to the wind be adjusted.
Angle (or trim)
The combination of the true wind and the wind created by the boat’s motion (that we feel on the boat) is called the _____ wind.
Apparent
The _____ is an underwater fin fixed on the bottom of the sailboat that provide stability and lateral resistance.
Keel
The sailboat’s direction through the water is controlled by the _____, which can be turned by means of either a _____ or a _____ _____.
Rudder, tiller, steering wheel
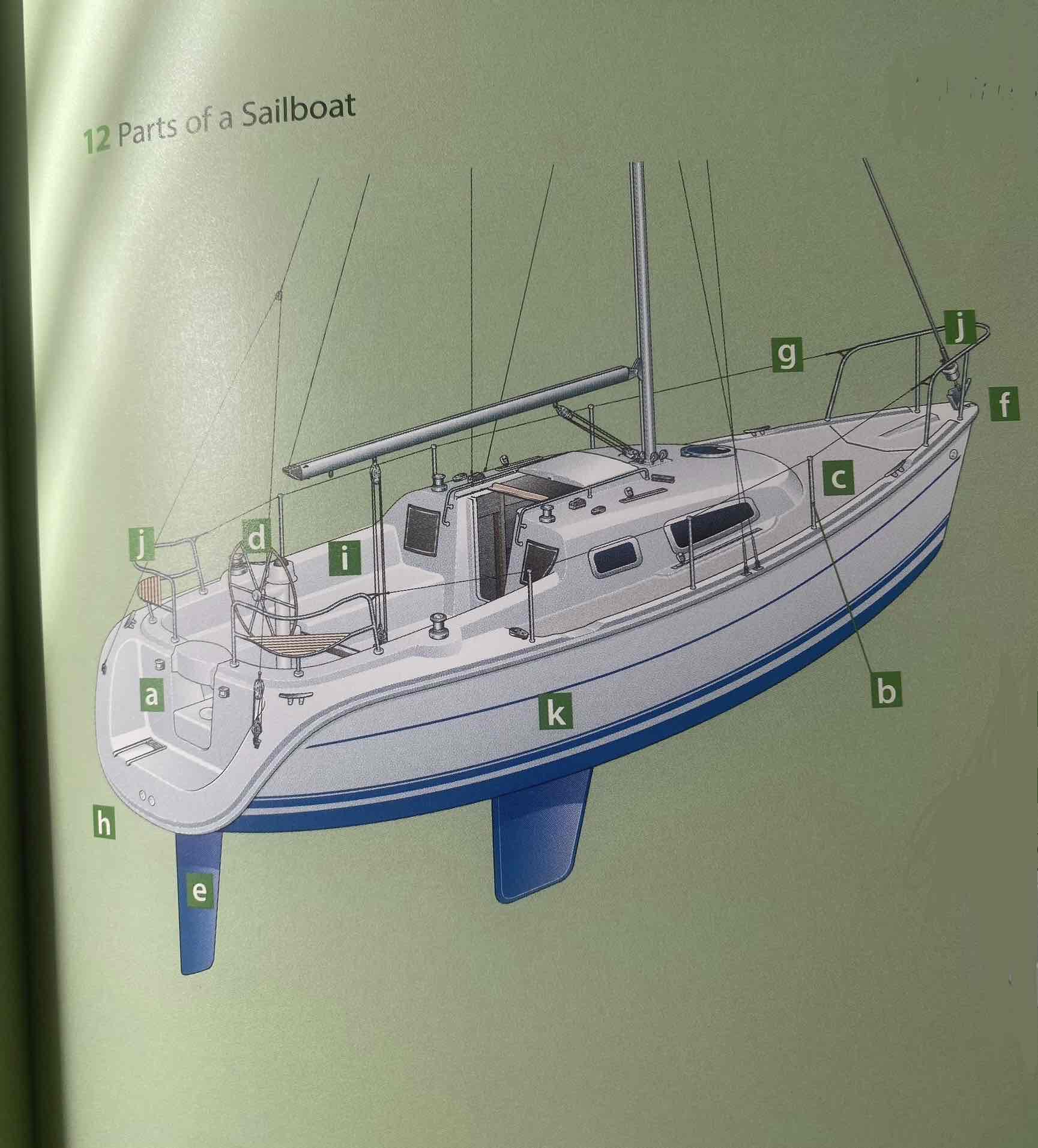
Identify the hull.
K
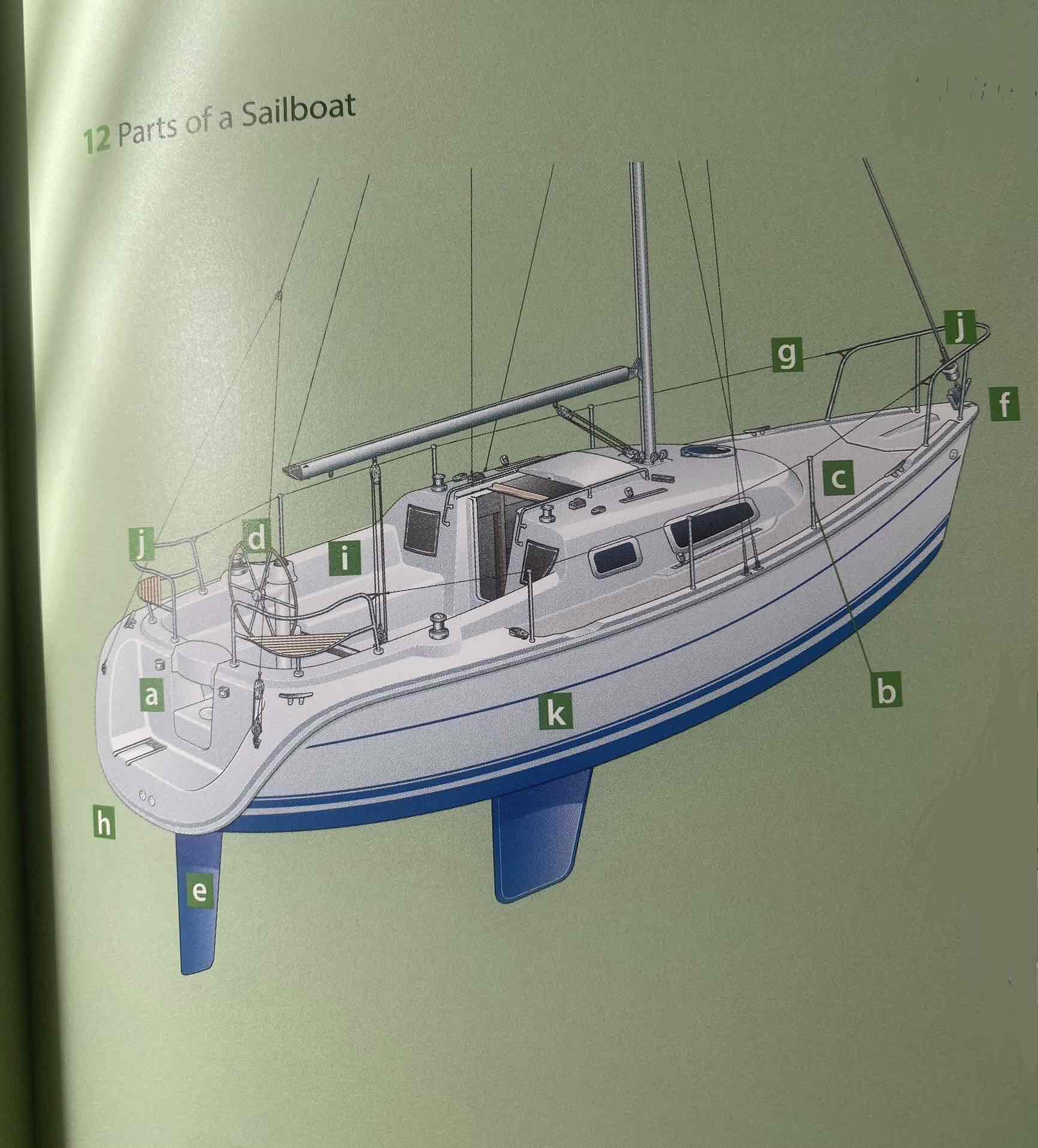
Identify the deck.
C

Identify the cockpit.
I
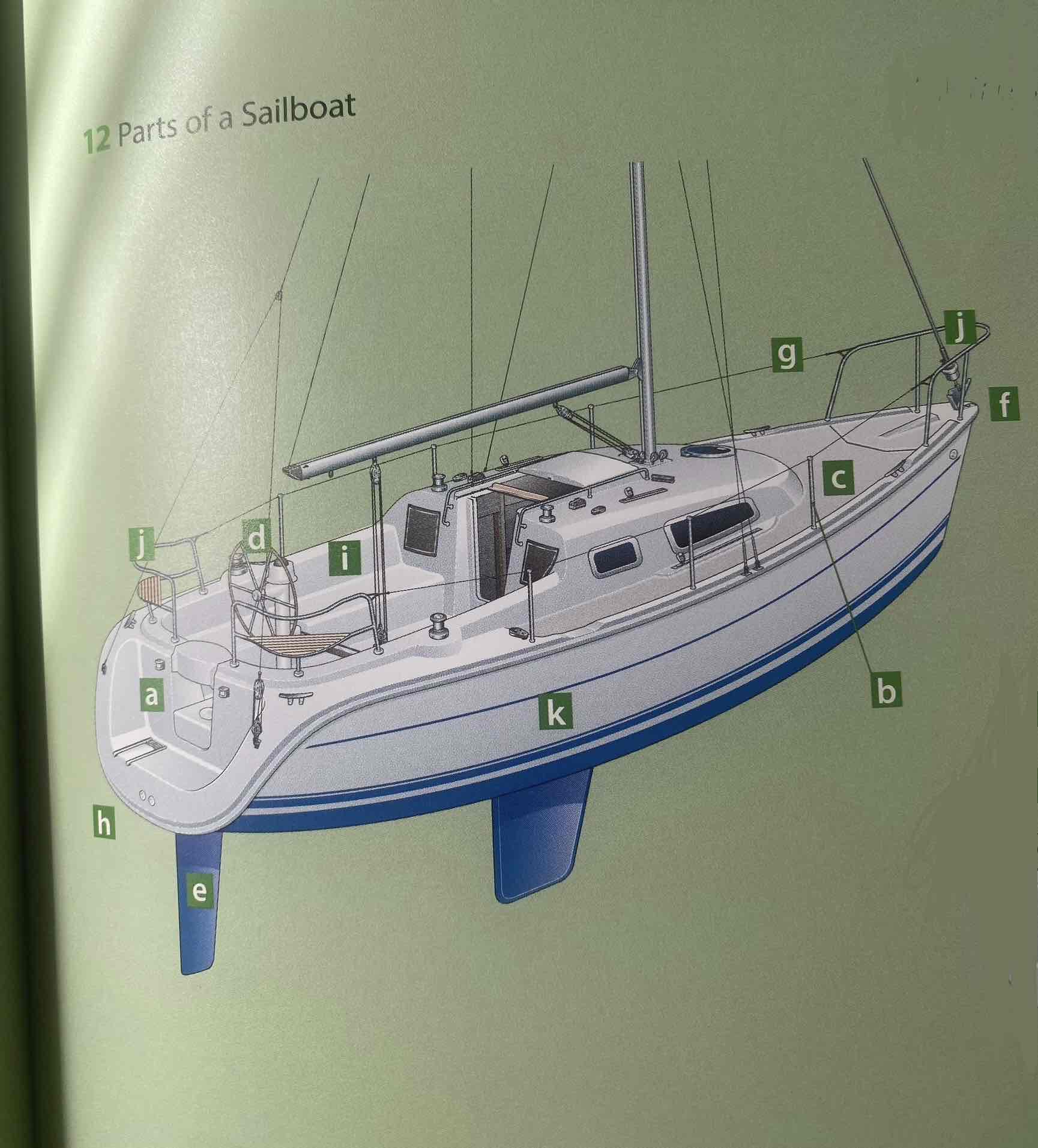
Identity the transom.
A

Identify the bow.
F
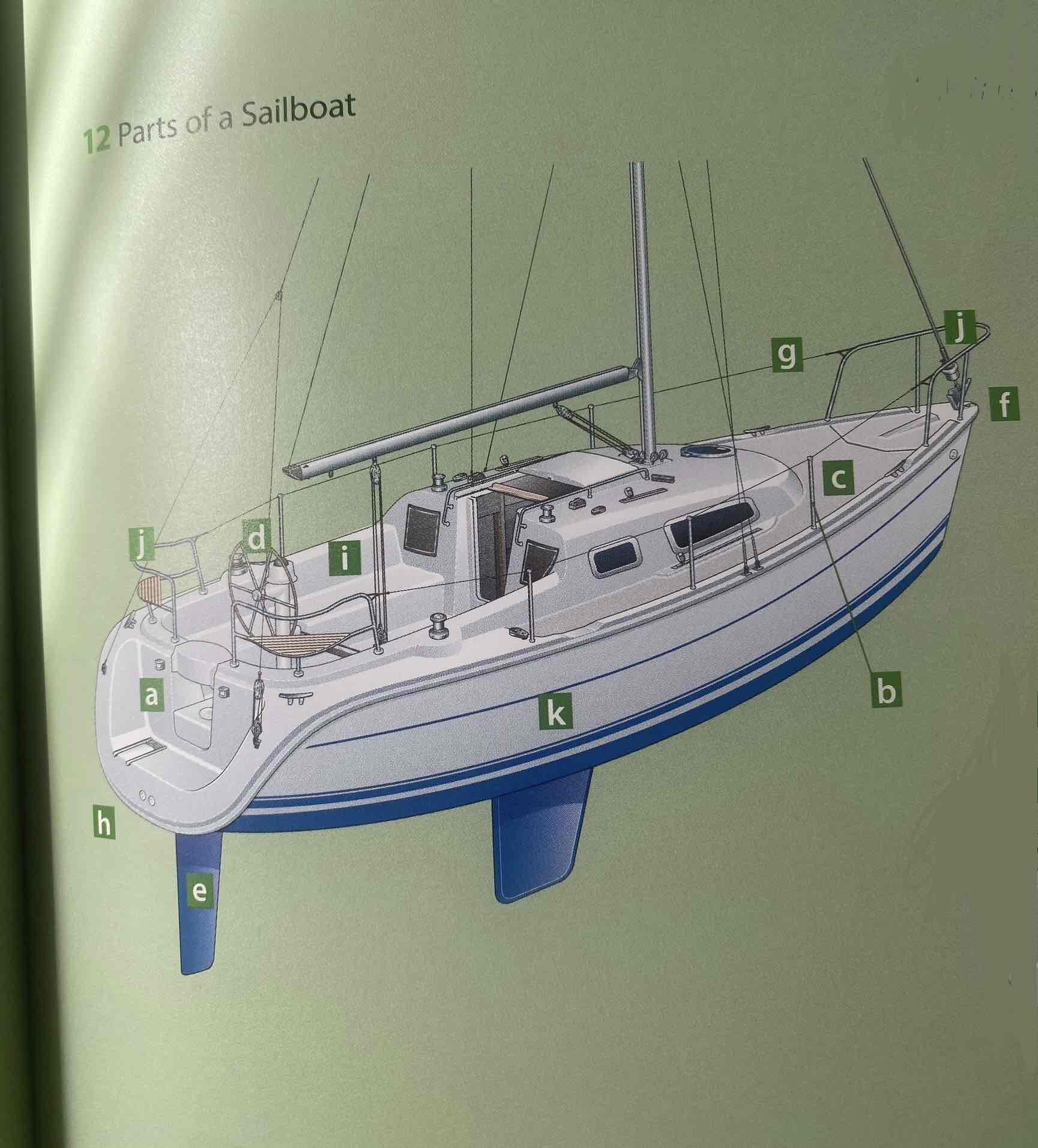
Identify the stern.
H

Identify the rudder.
E
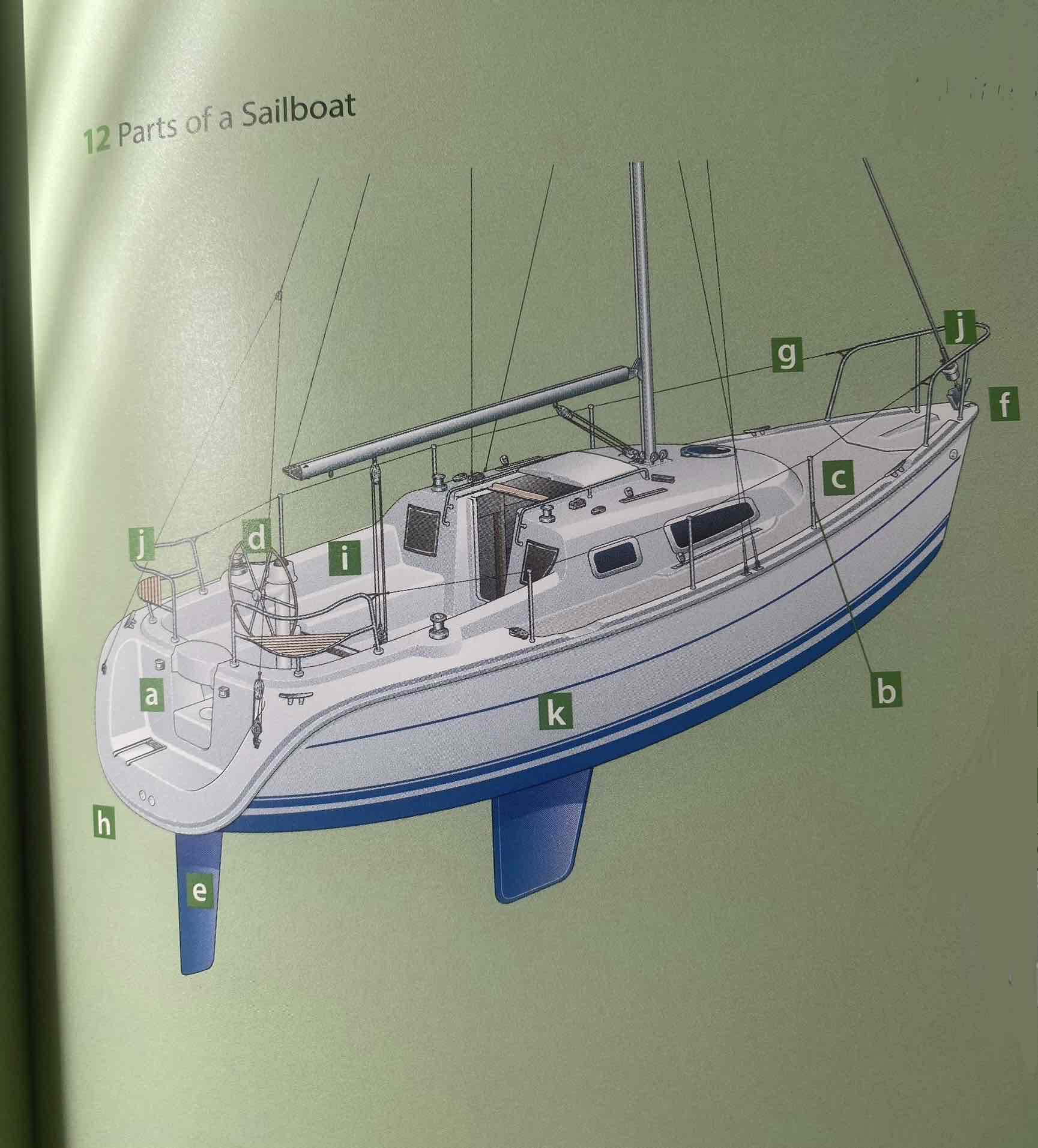
Identify the helm (tiller or wheel).
D

Identify the lifeline.
G
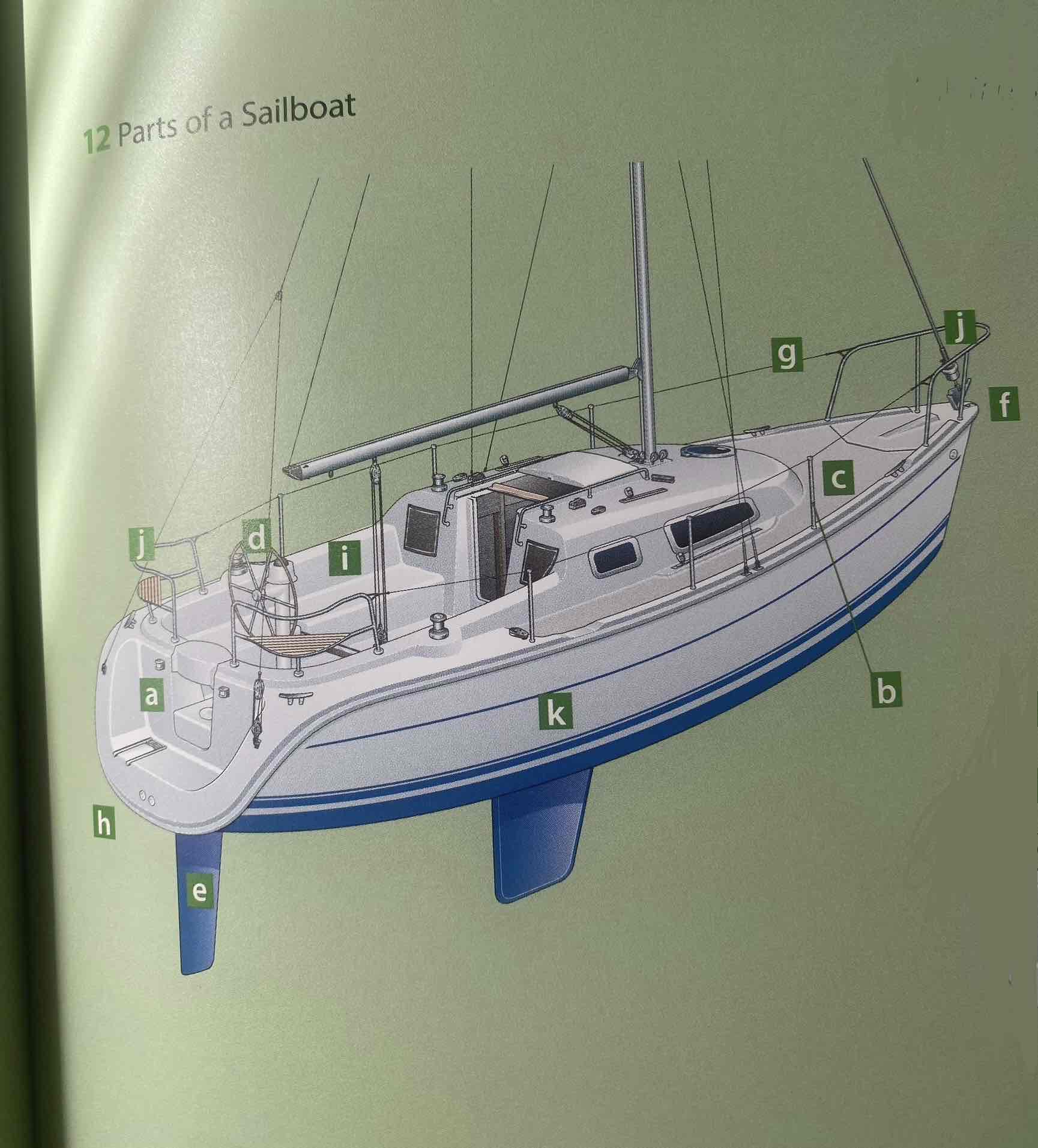
Identify the pulpit.
J

Identify the mast.
D
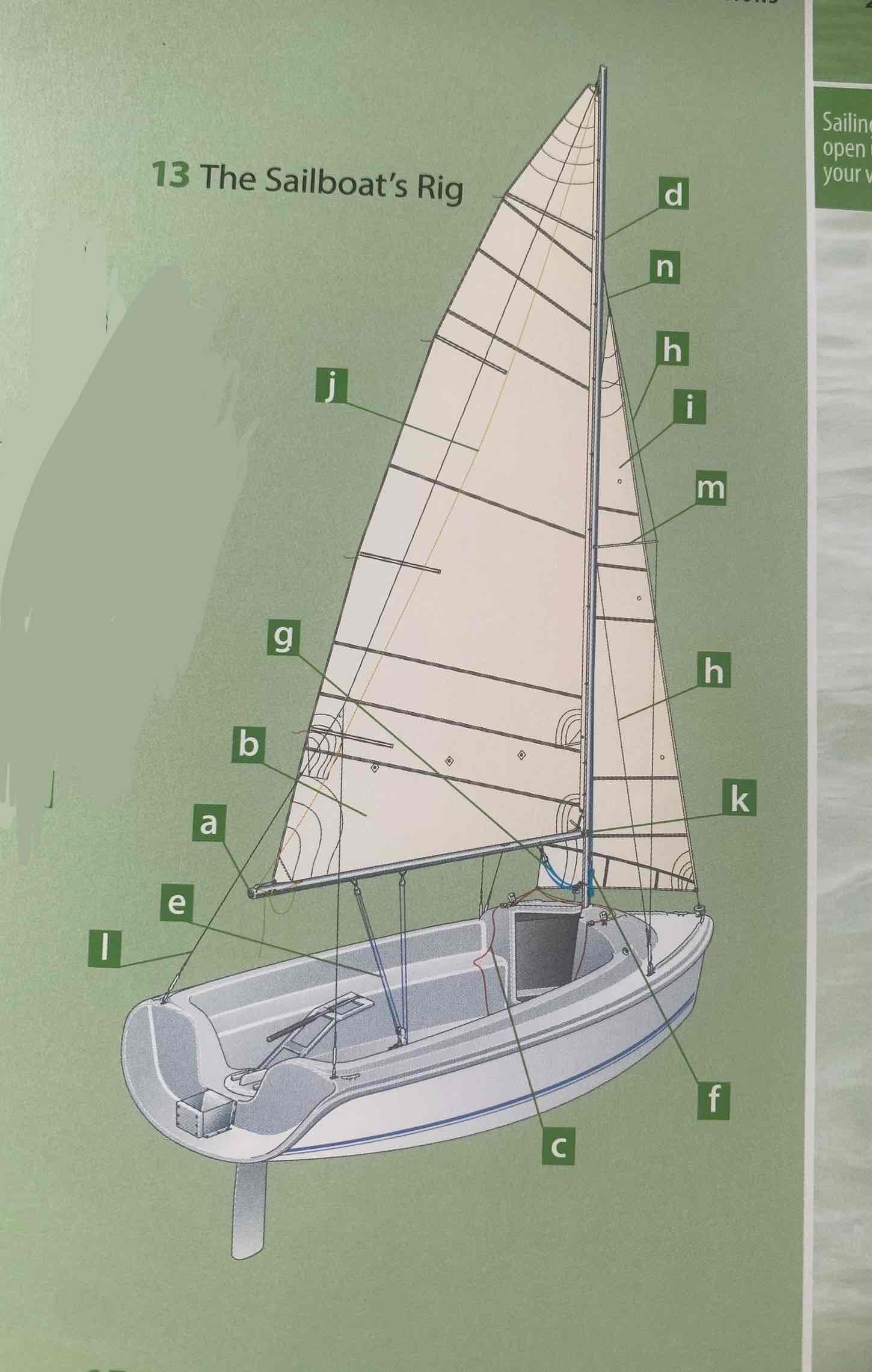
Identity the boom.
A
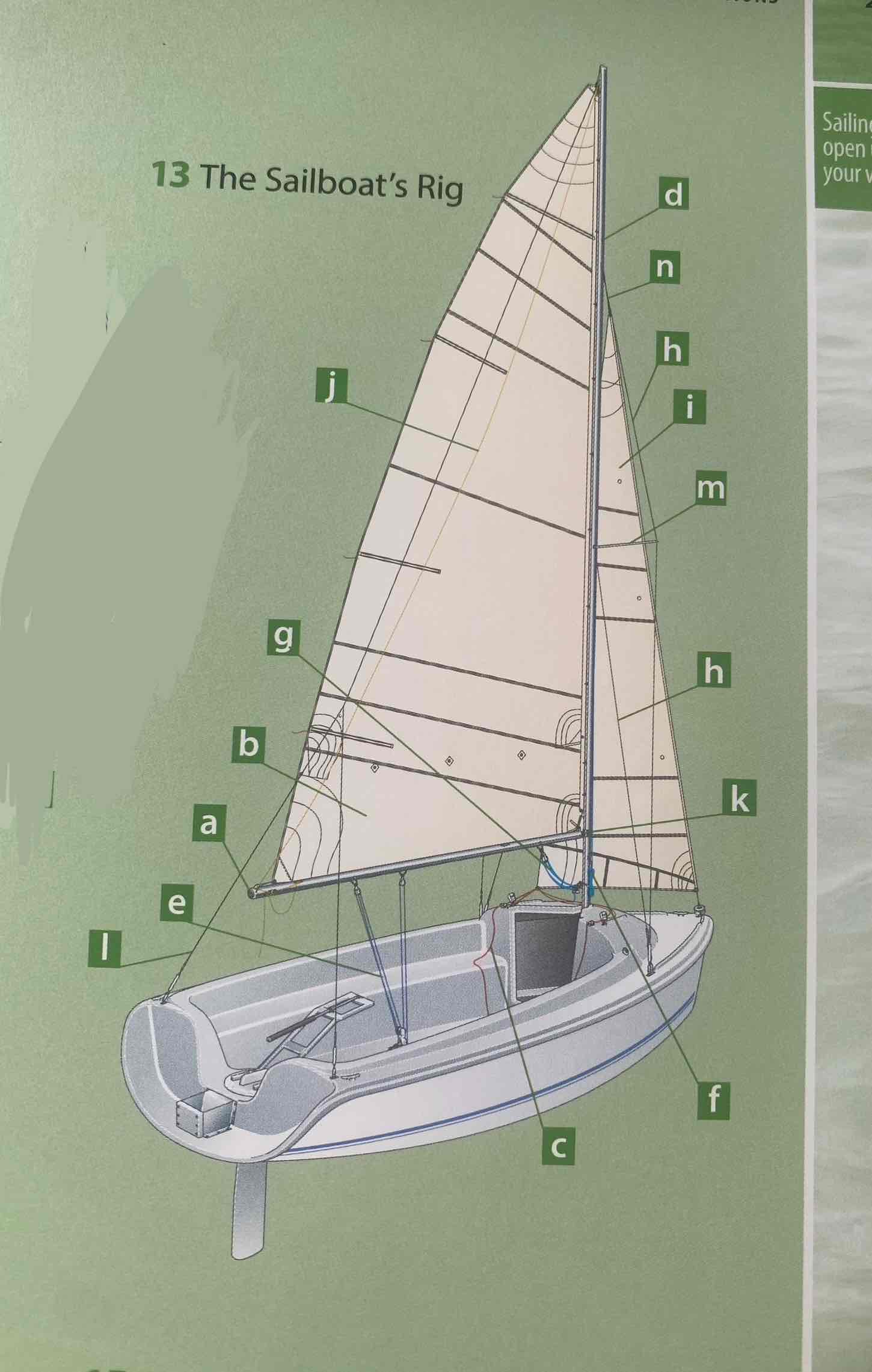
Identify the gooseneck.
K
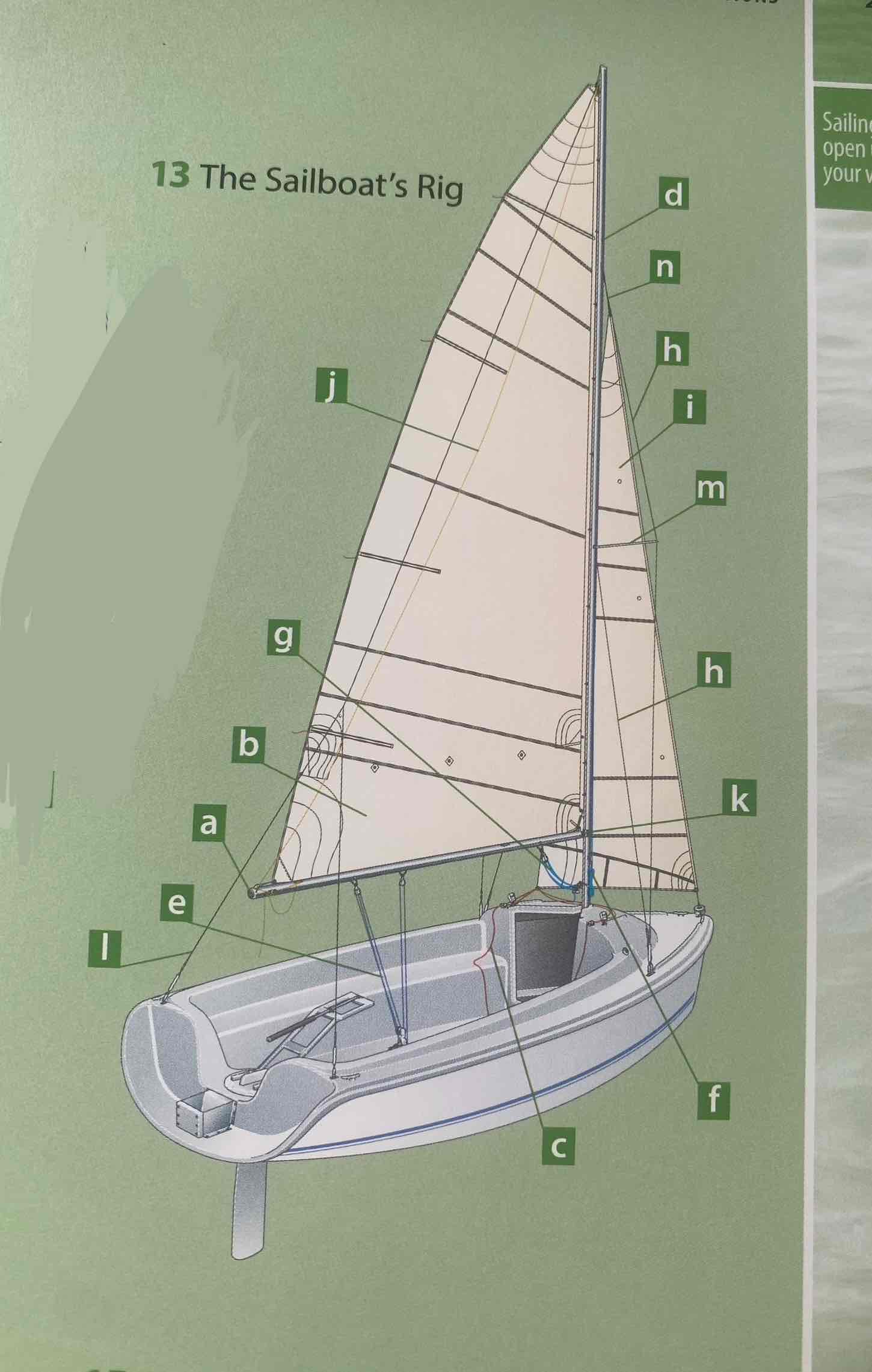
Identify the spreader.
M
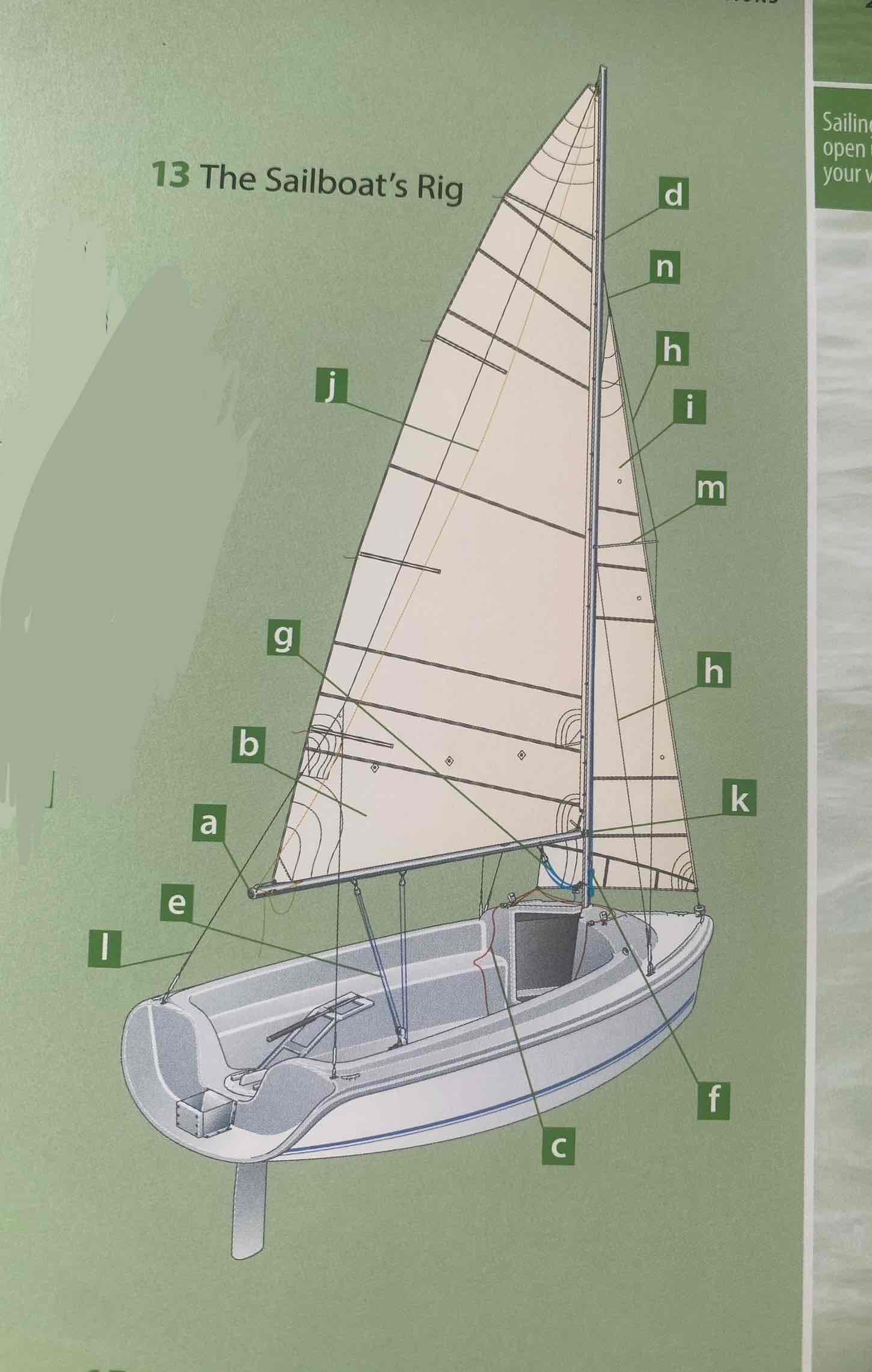
Identify the shroud.
H
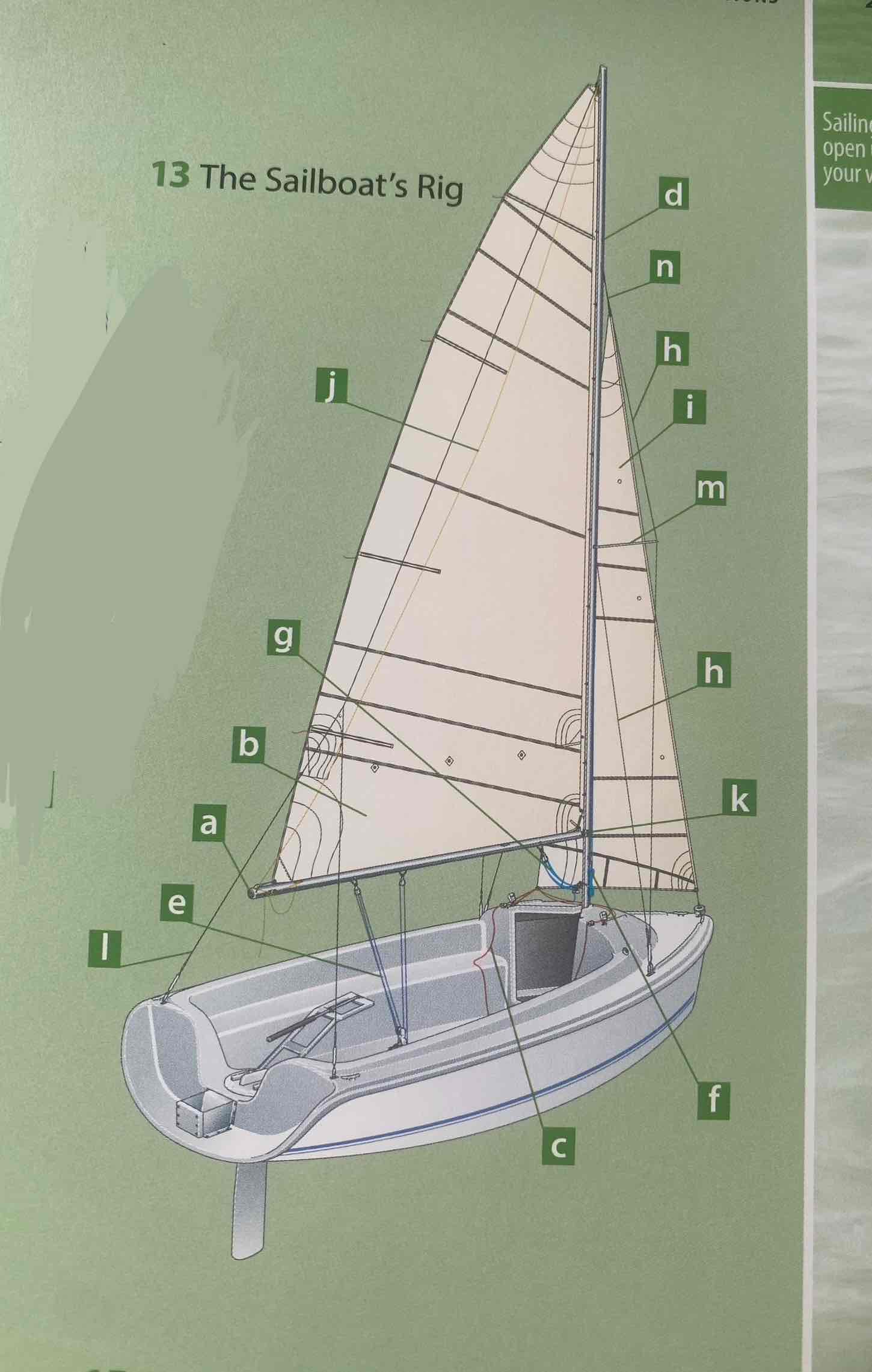
Identity the headstay/forestay.
N
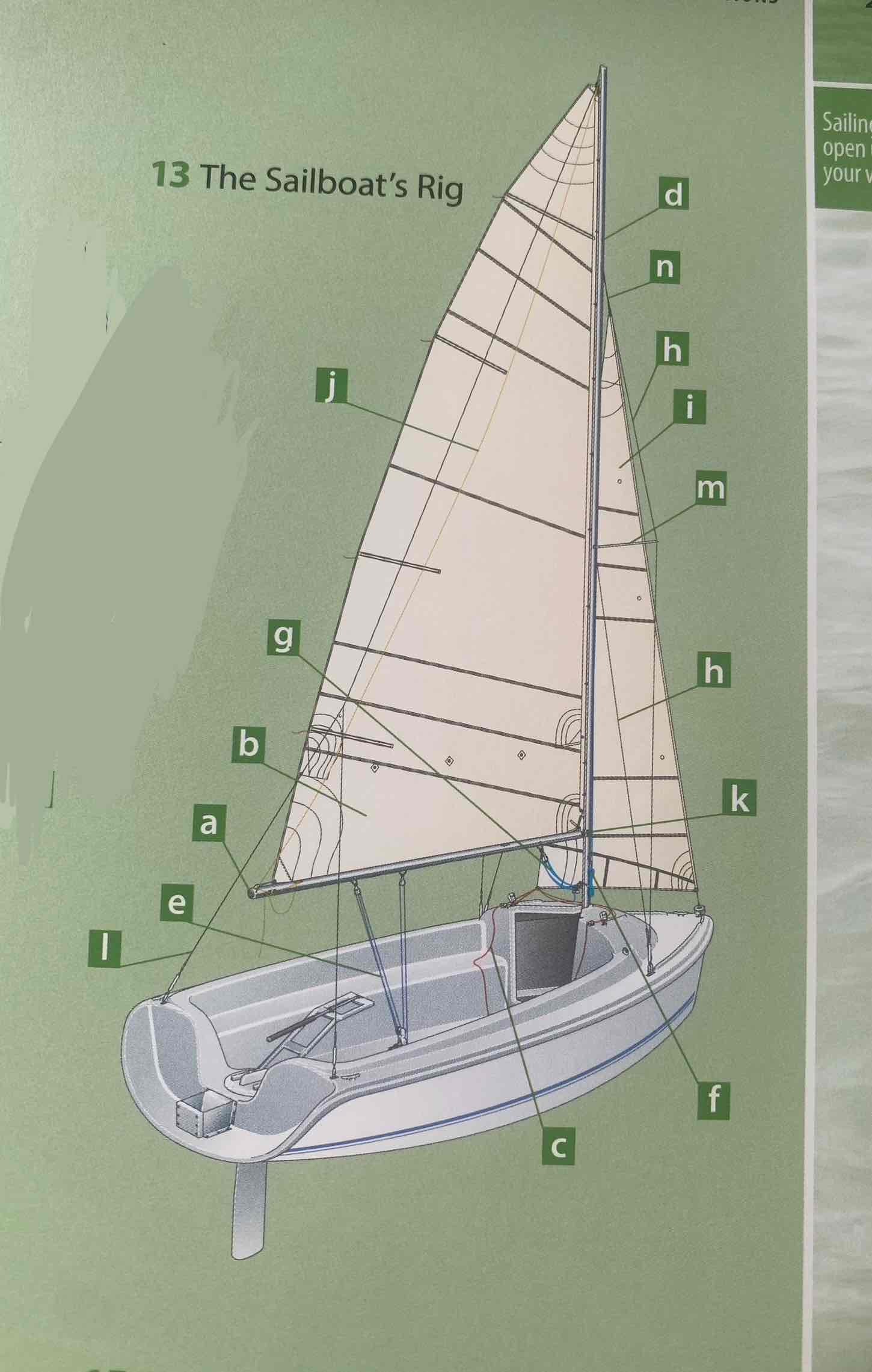
Identify the backstay.
L
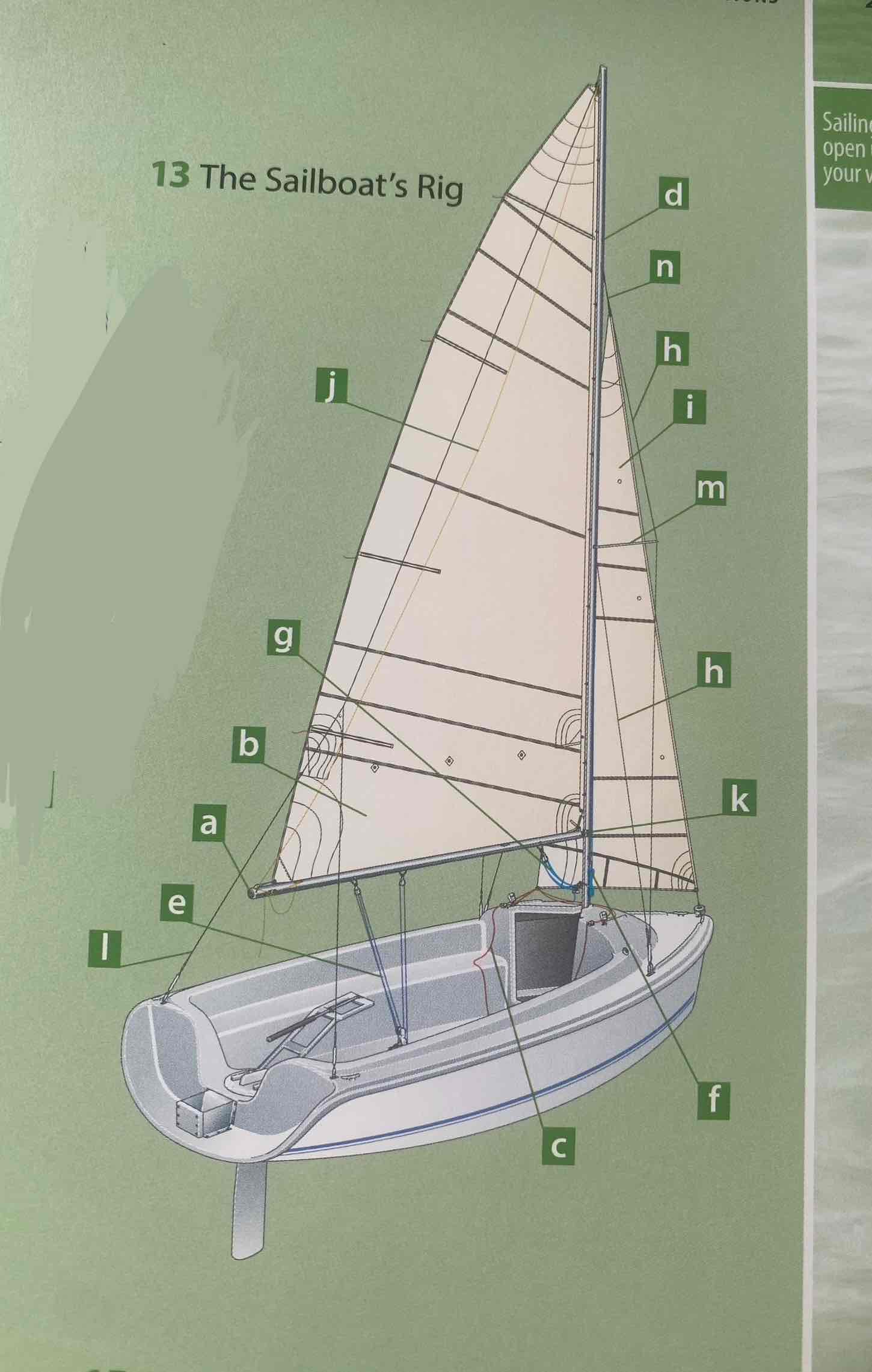
Identify the mainsail.
B
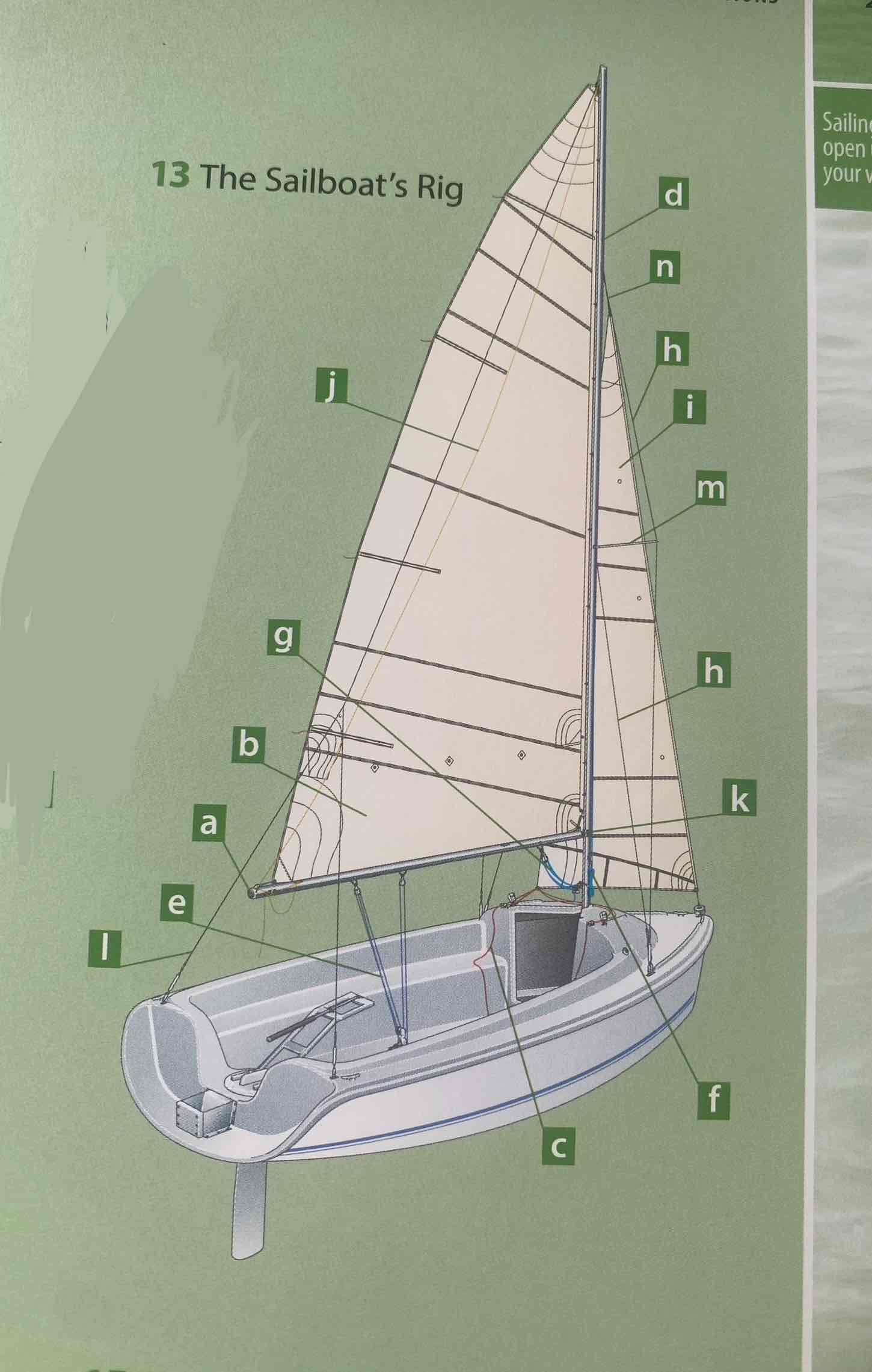
Identify the headsail/jib.
I
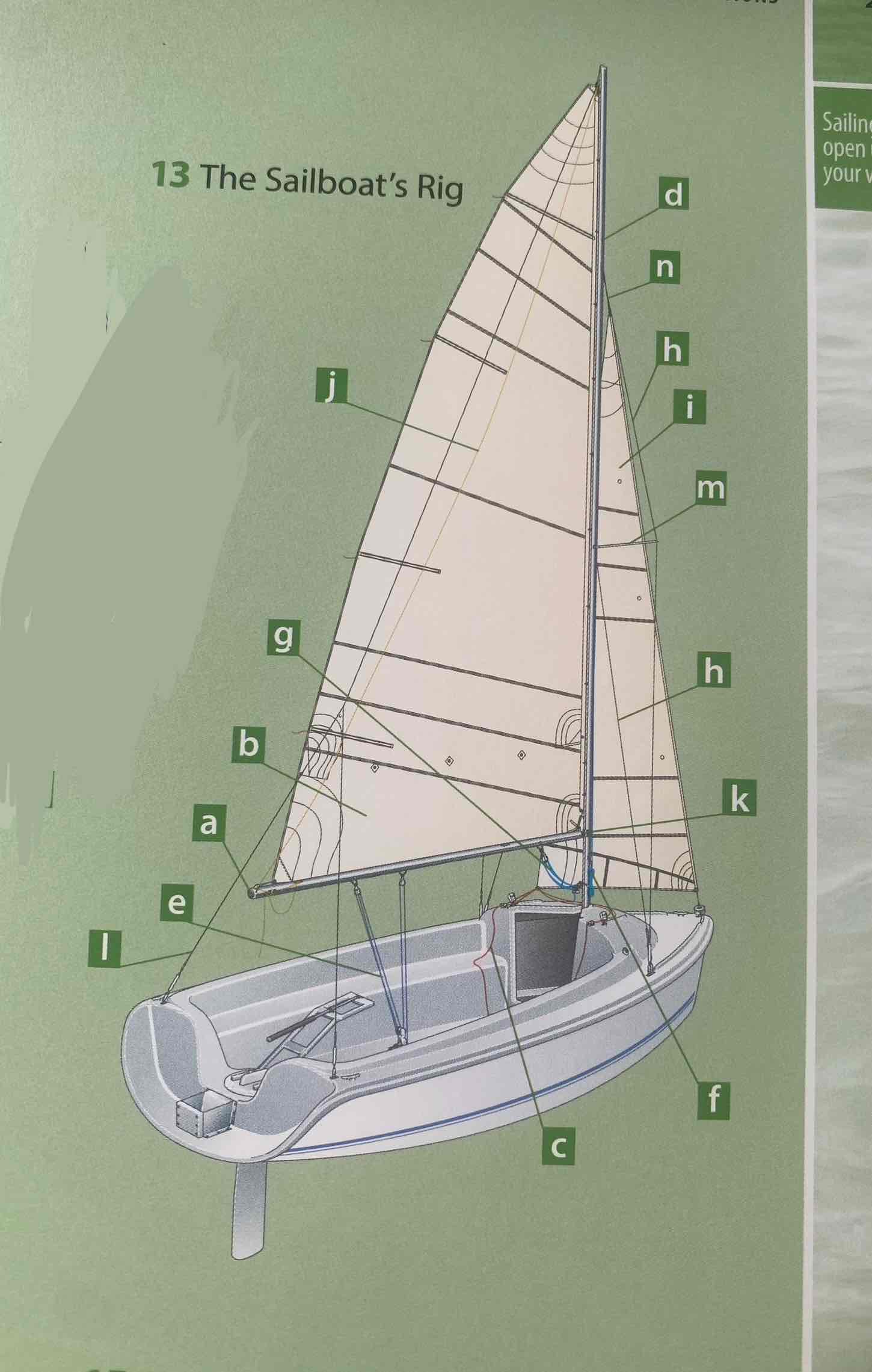
Identify the halyard.
F
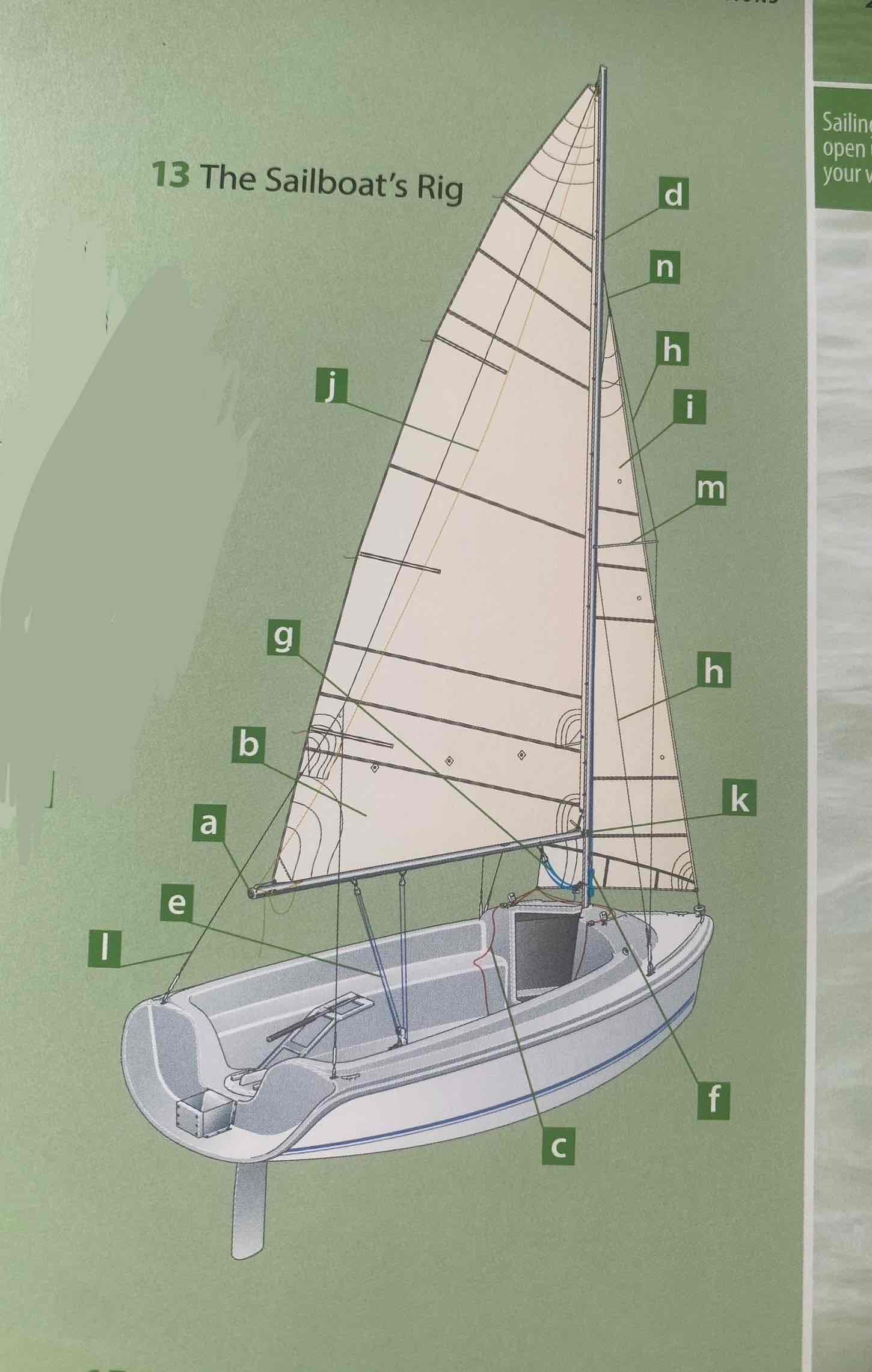
Identify the mainsheet.
E
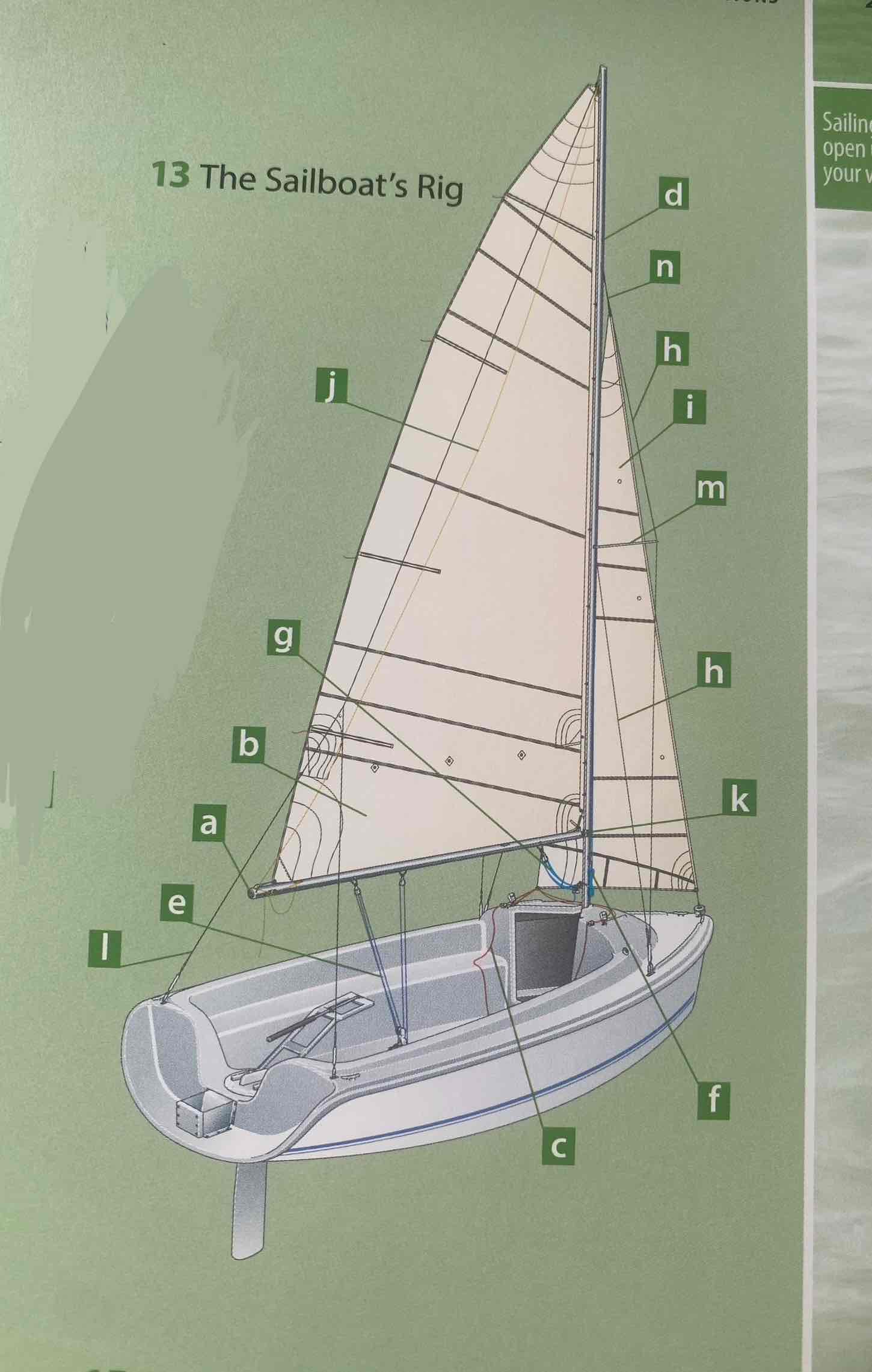
Identify the jibsheet.
C
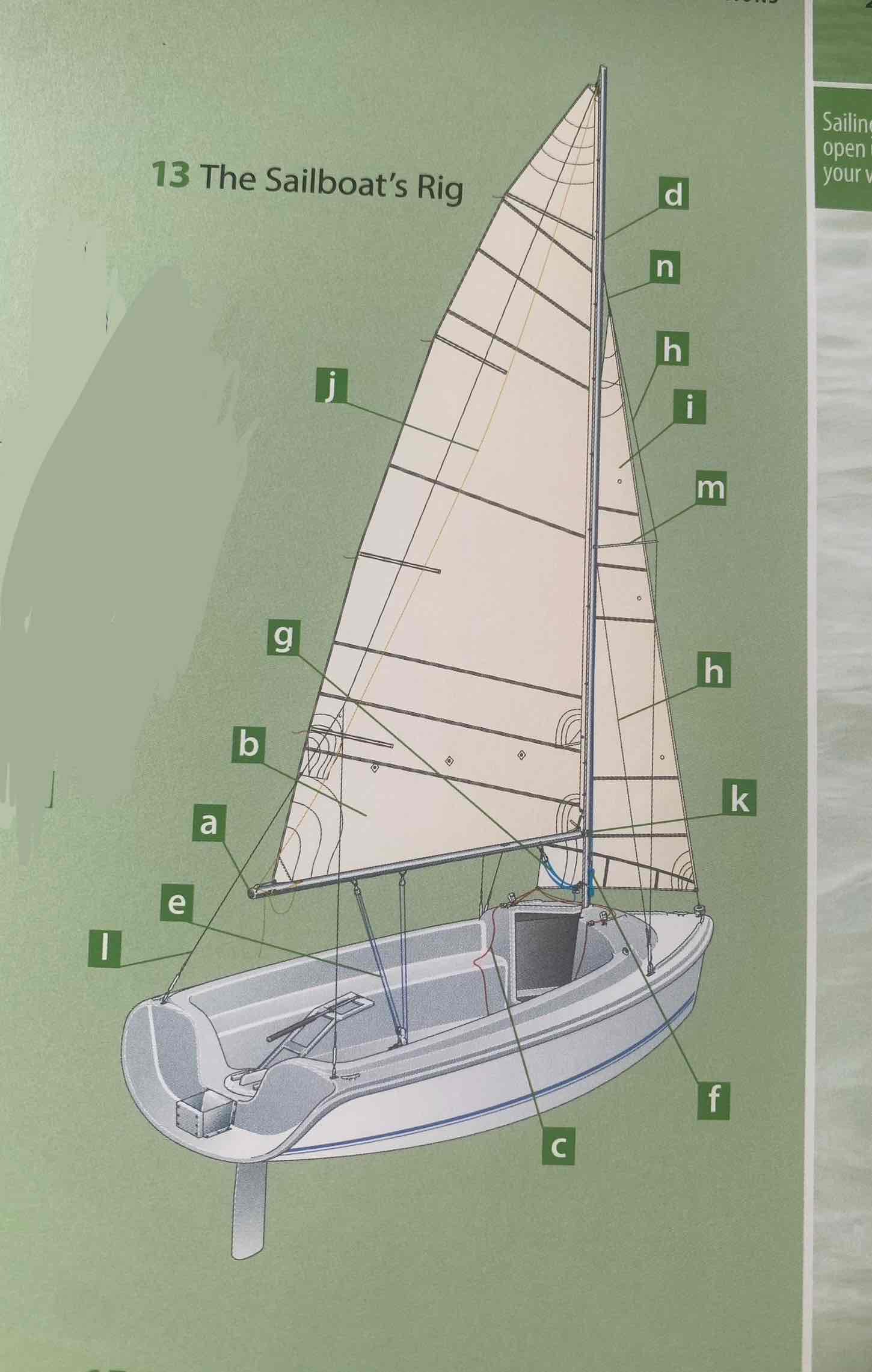
Identity the boom vang.
G
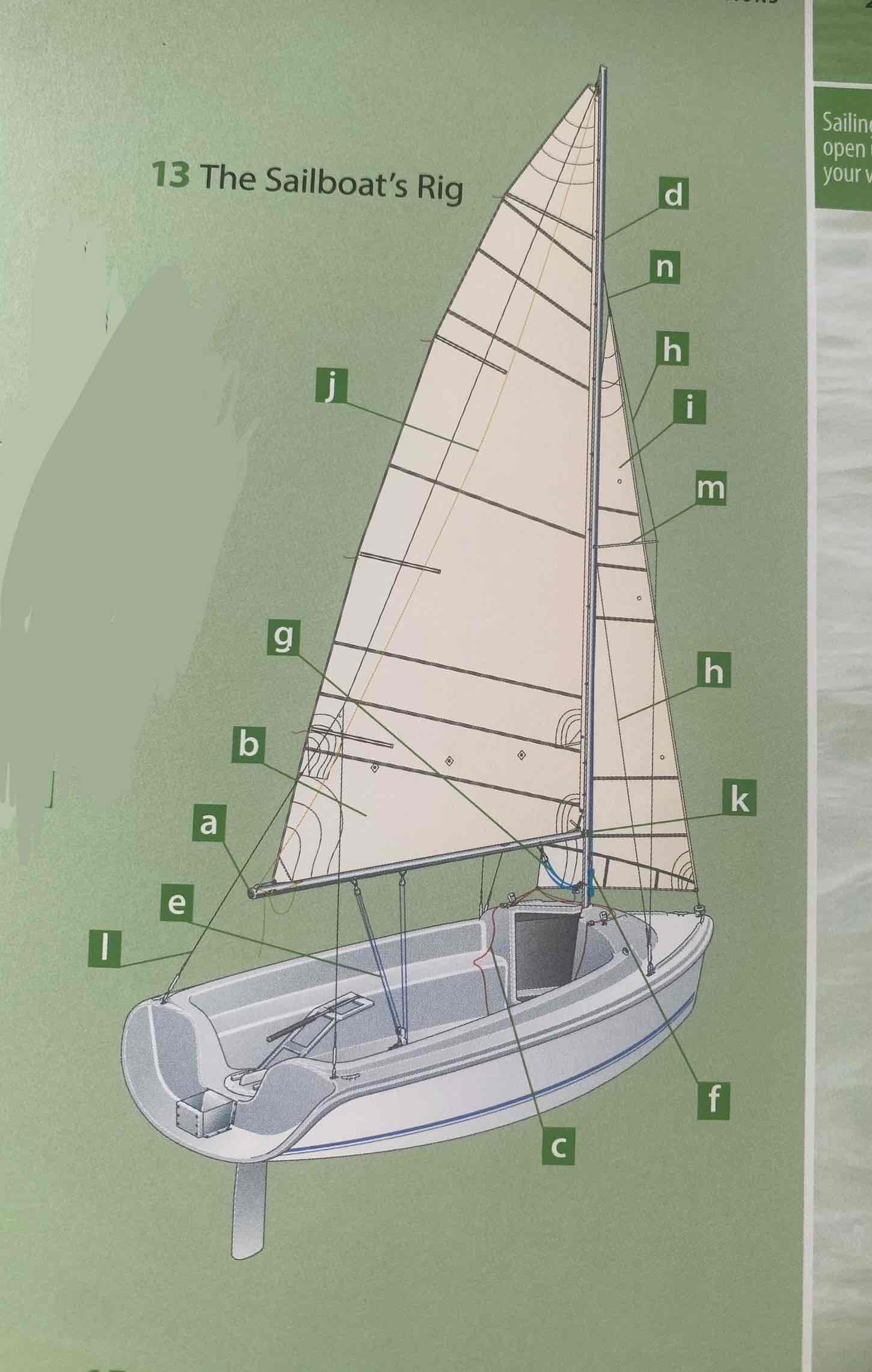
Identify the boom topping lift.
J
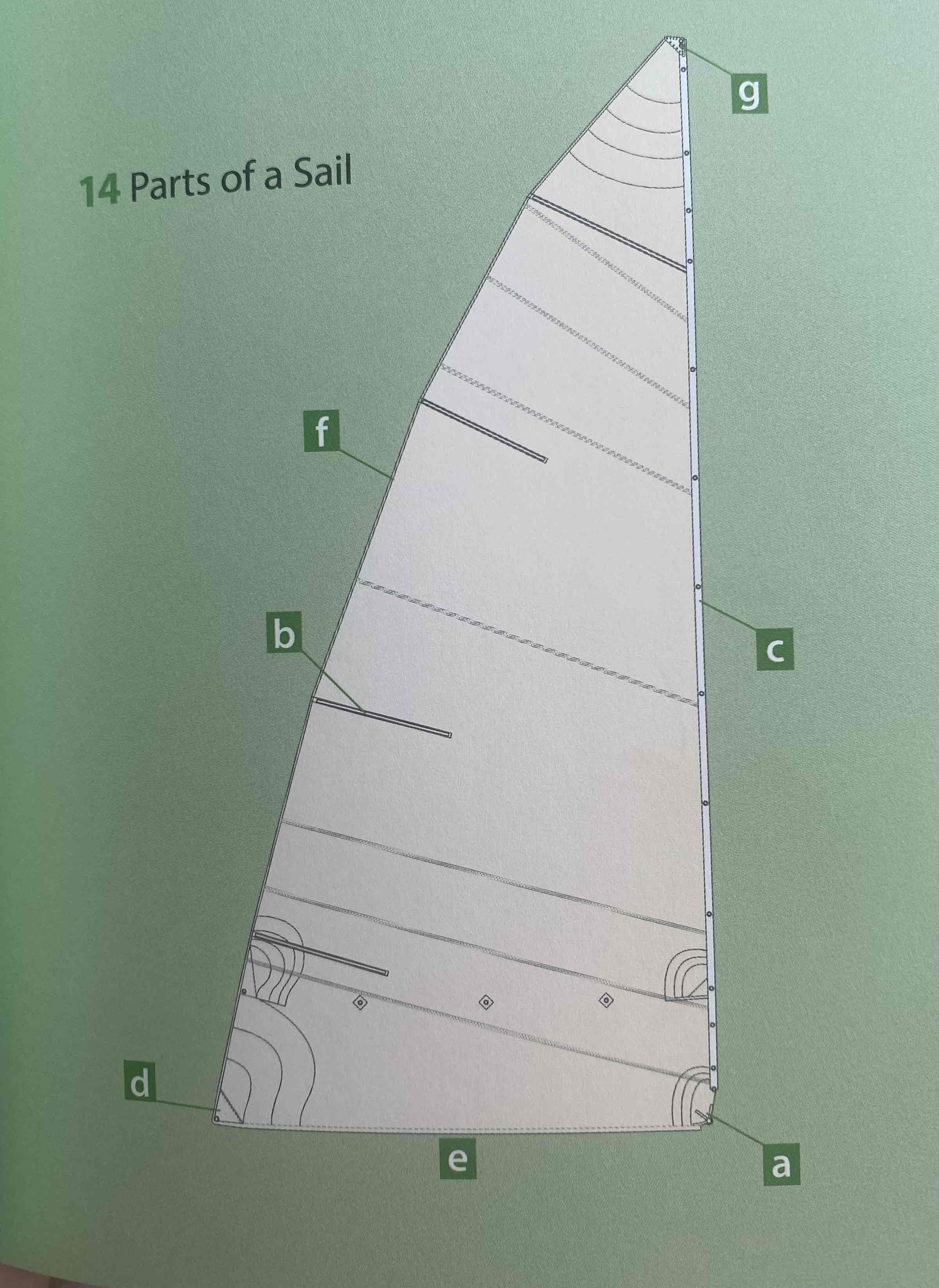
Identify the head.
G
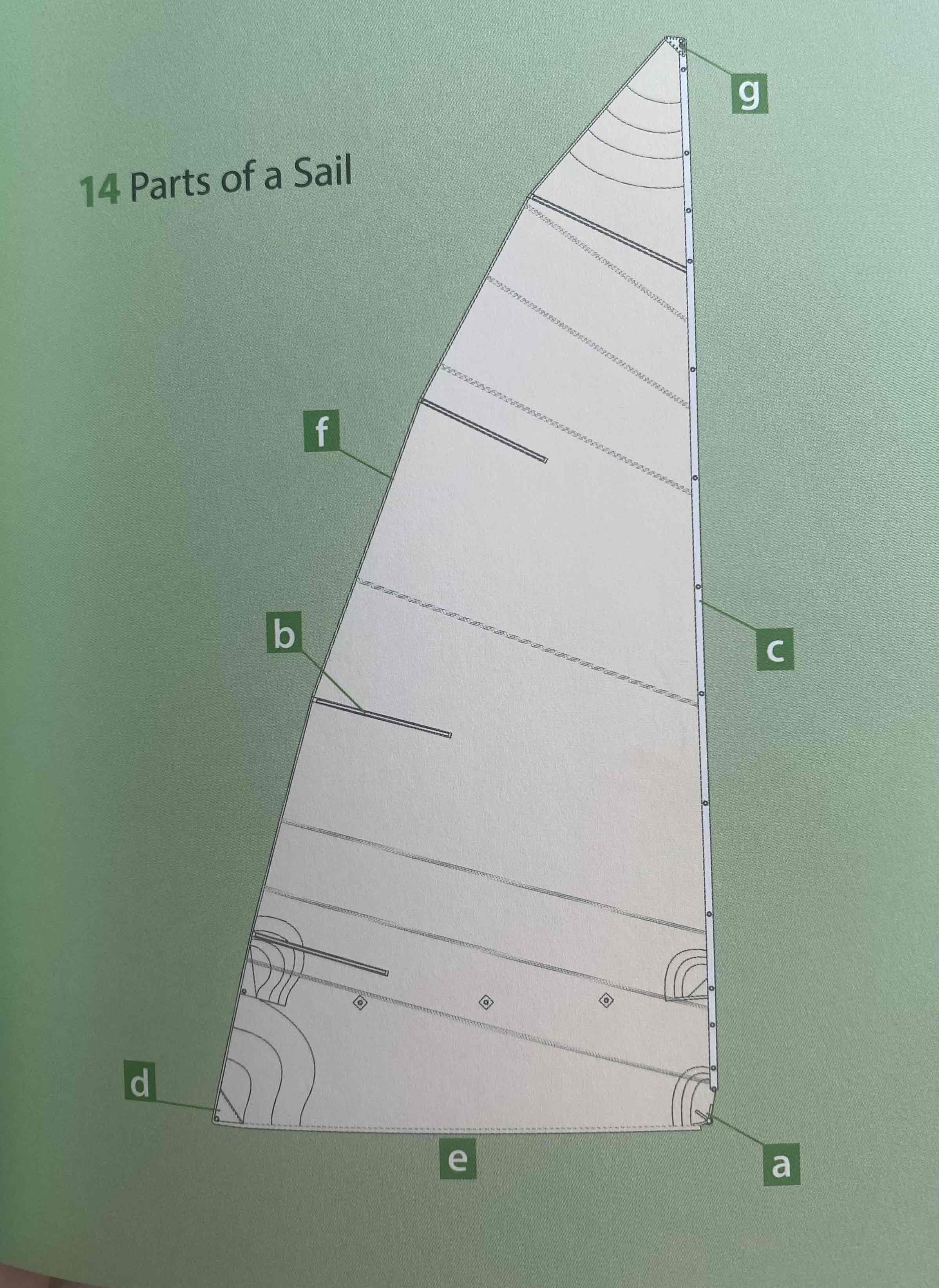
Identify the tack.
A
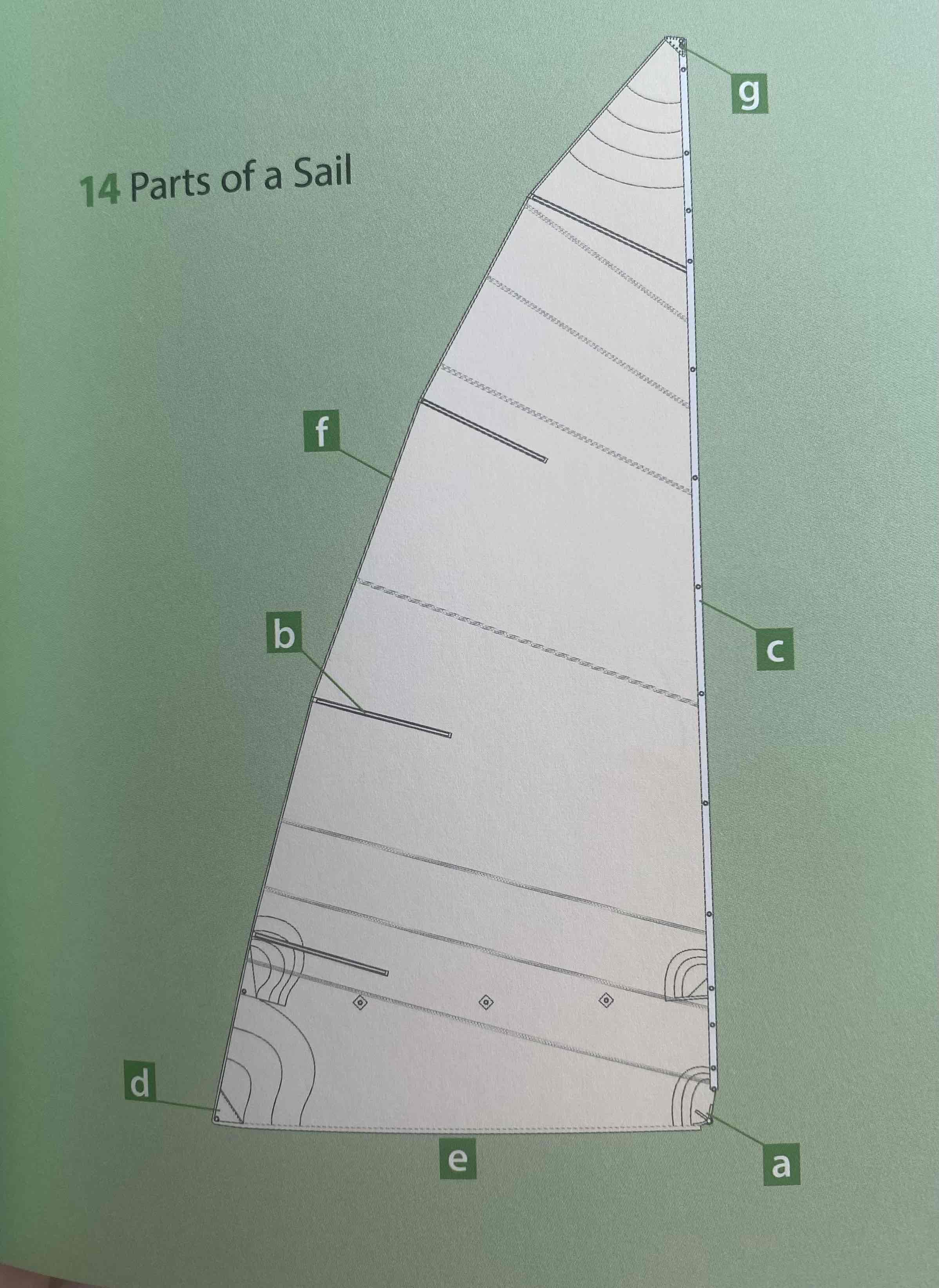
Identify the clew.
D
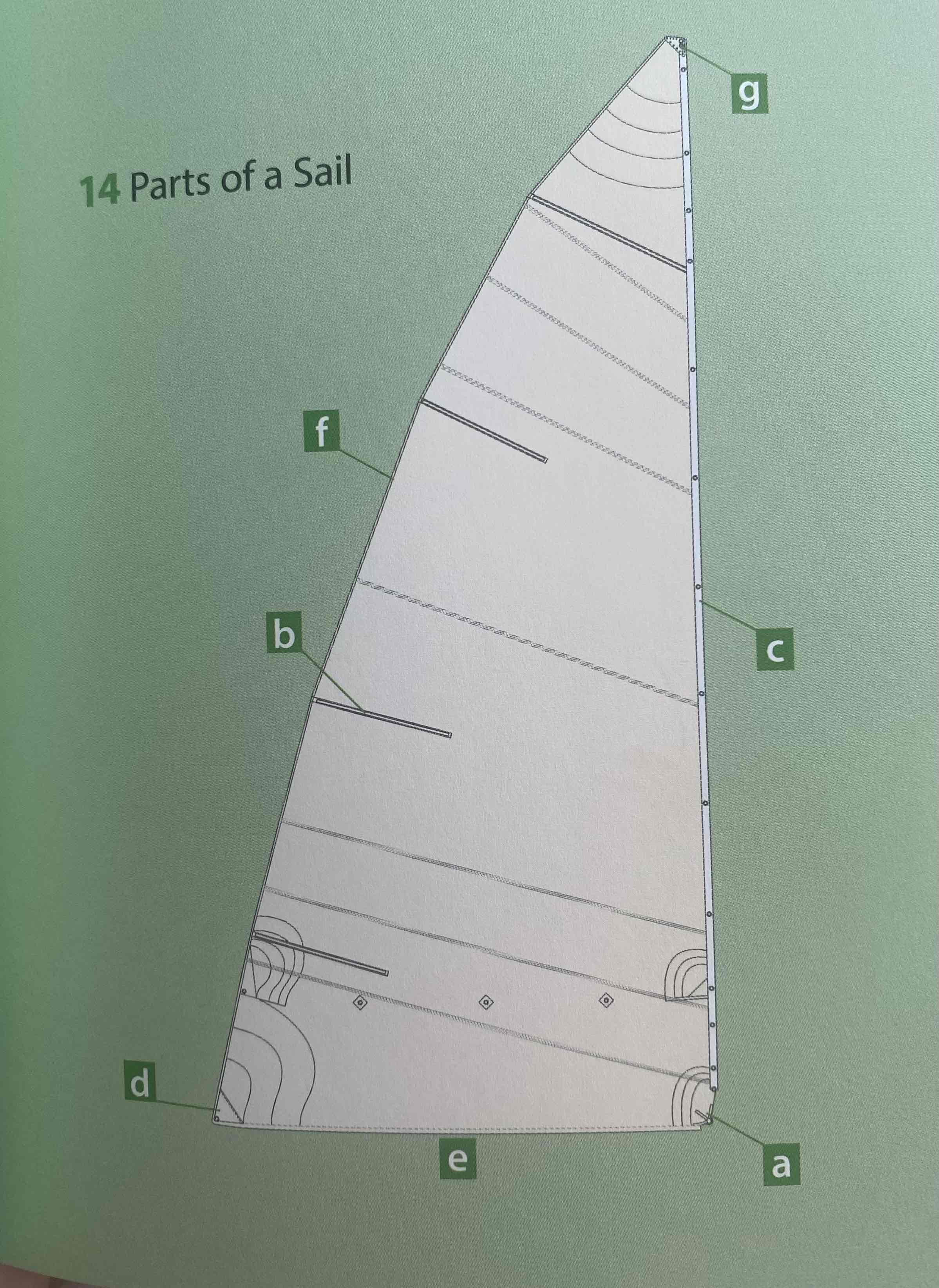
Identify the luff.
C
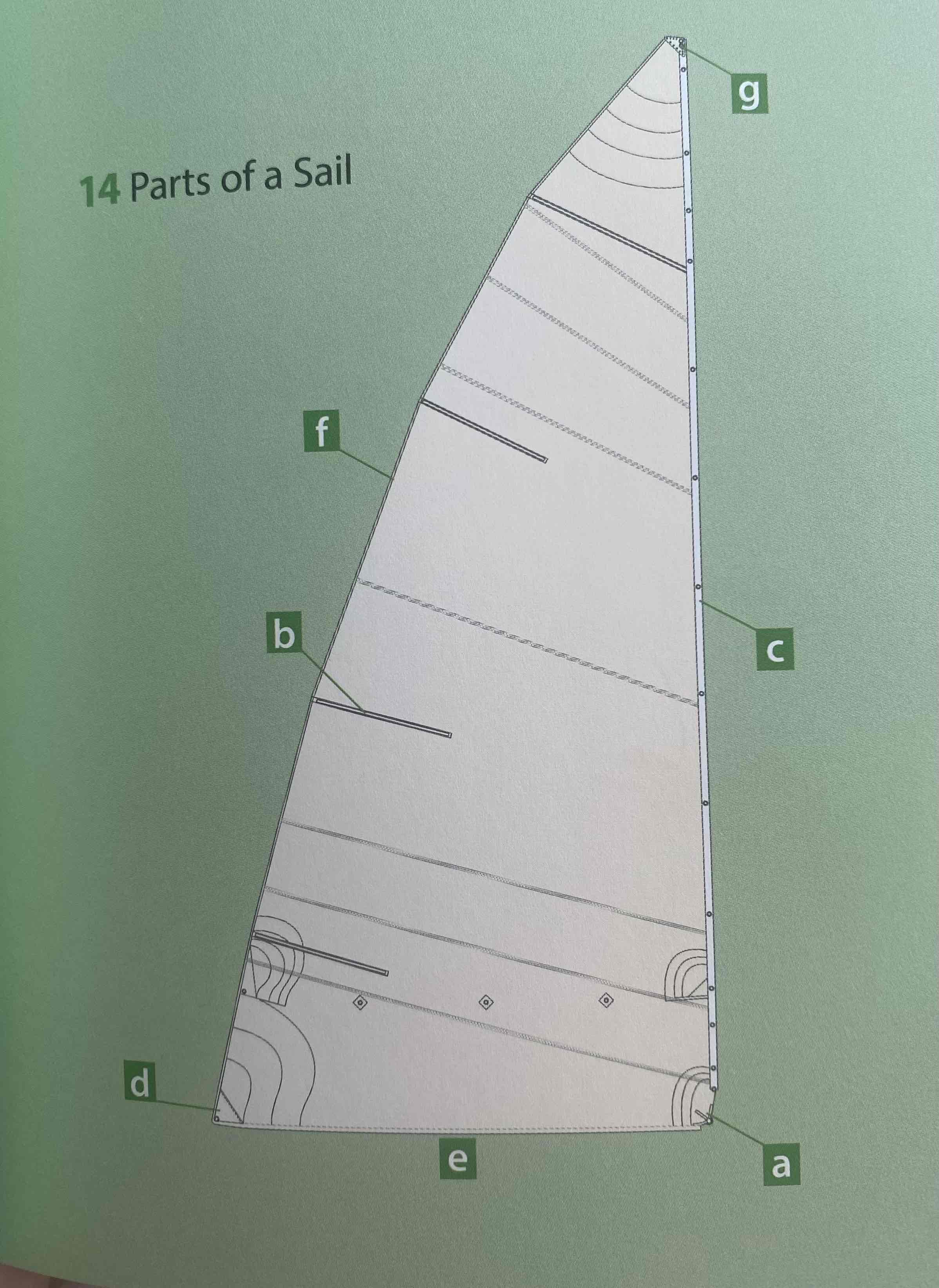
Identify the leech.
F
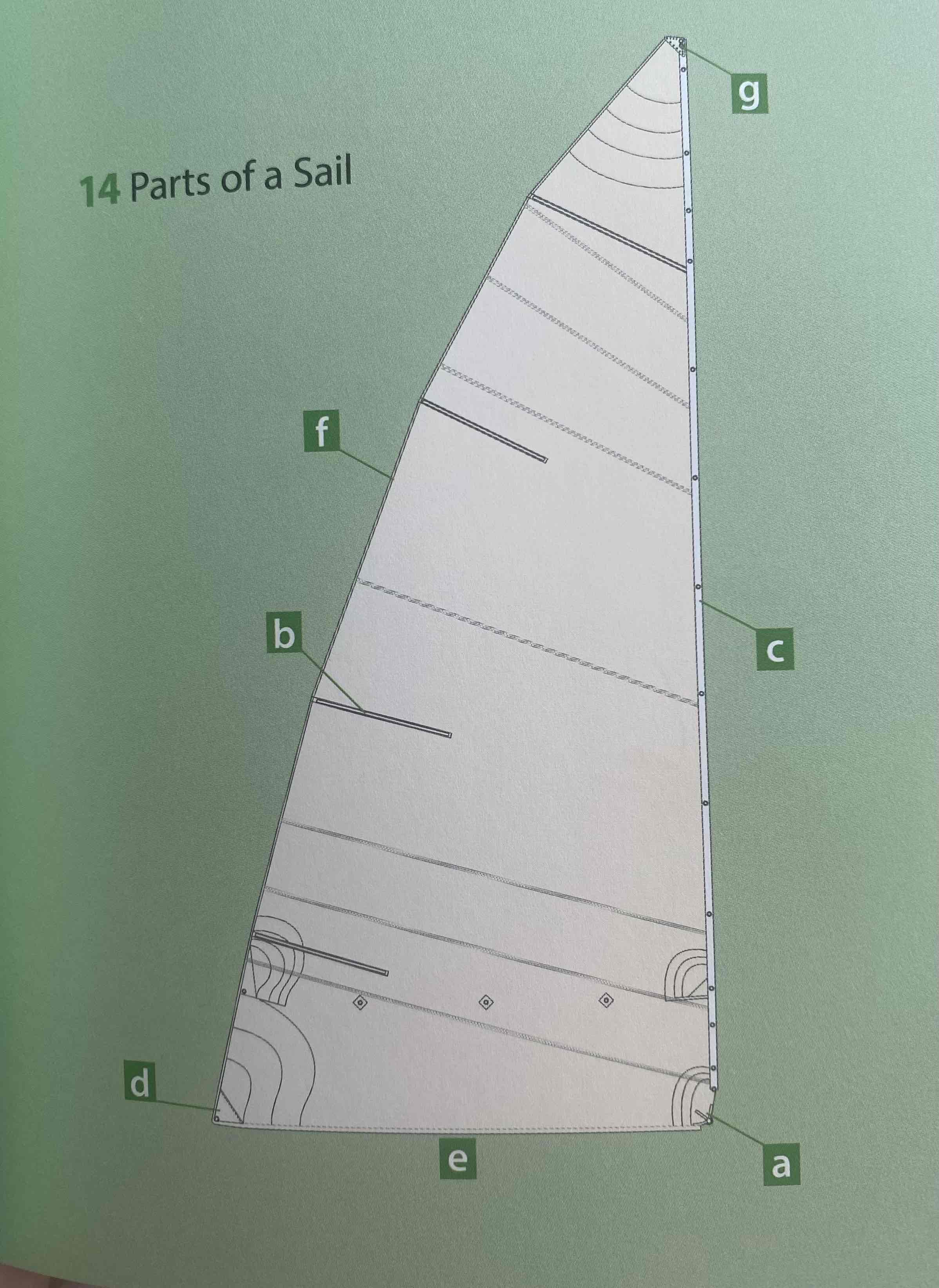
Identify the foot.
E
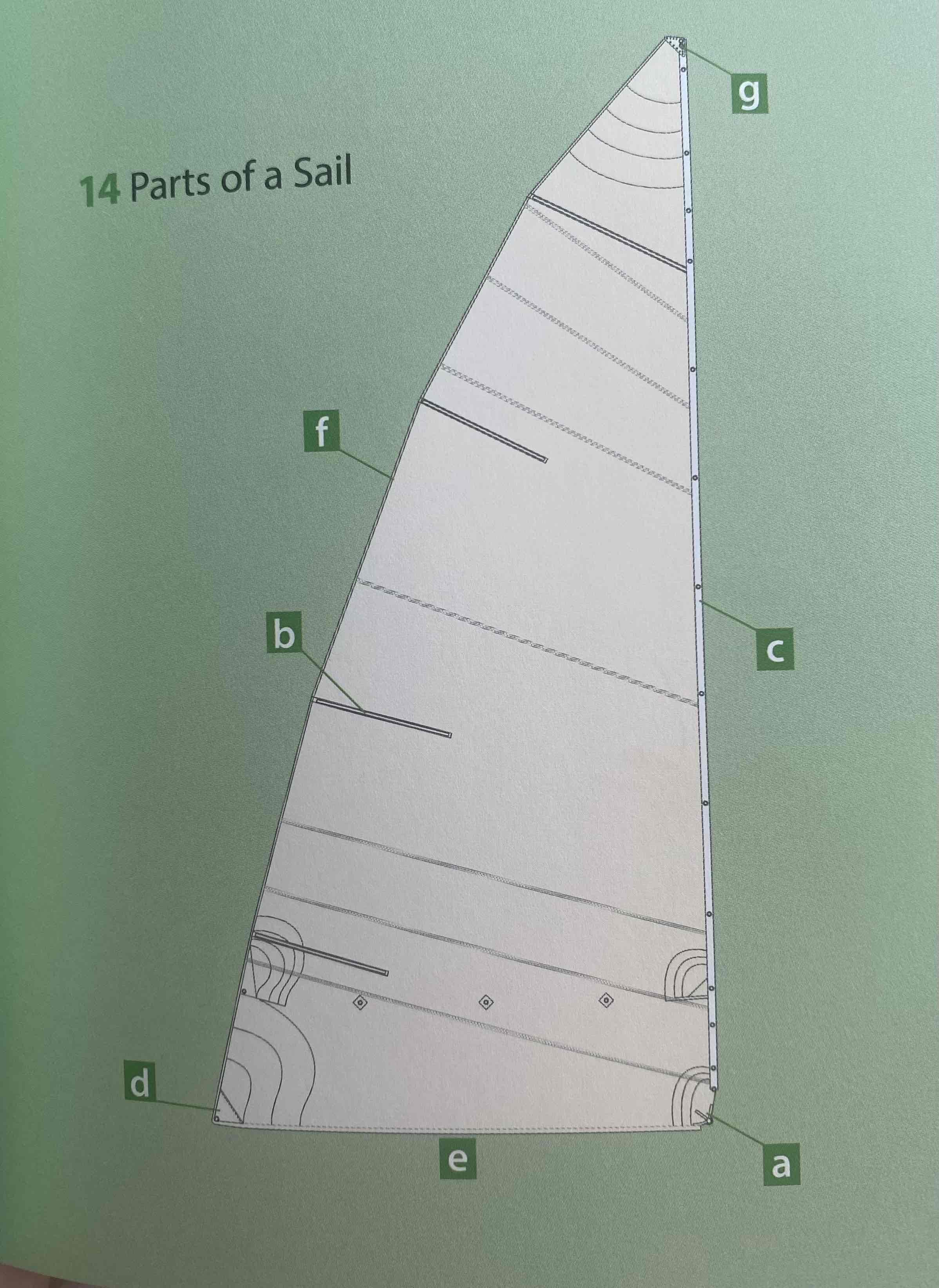
Identify the batten.
B

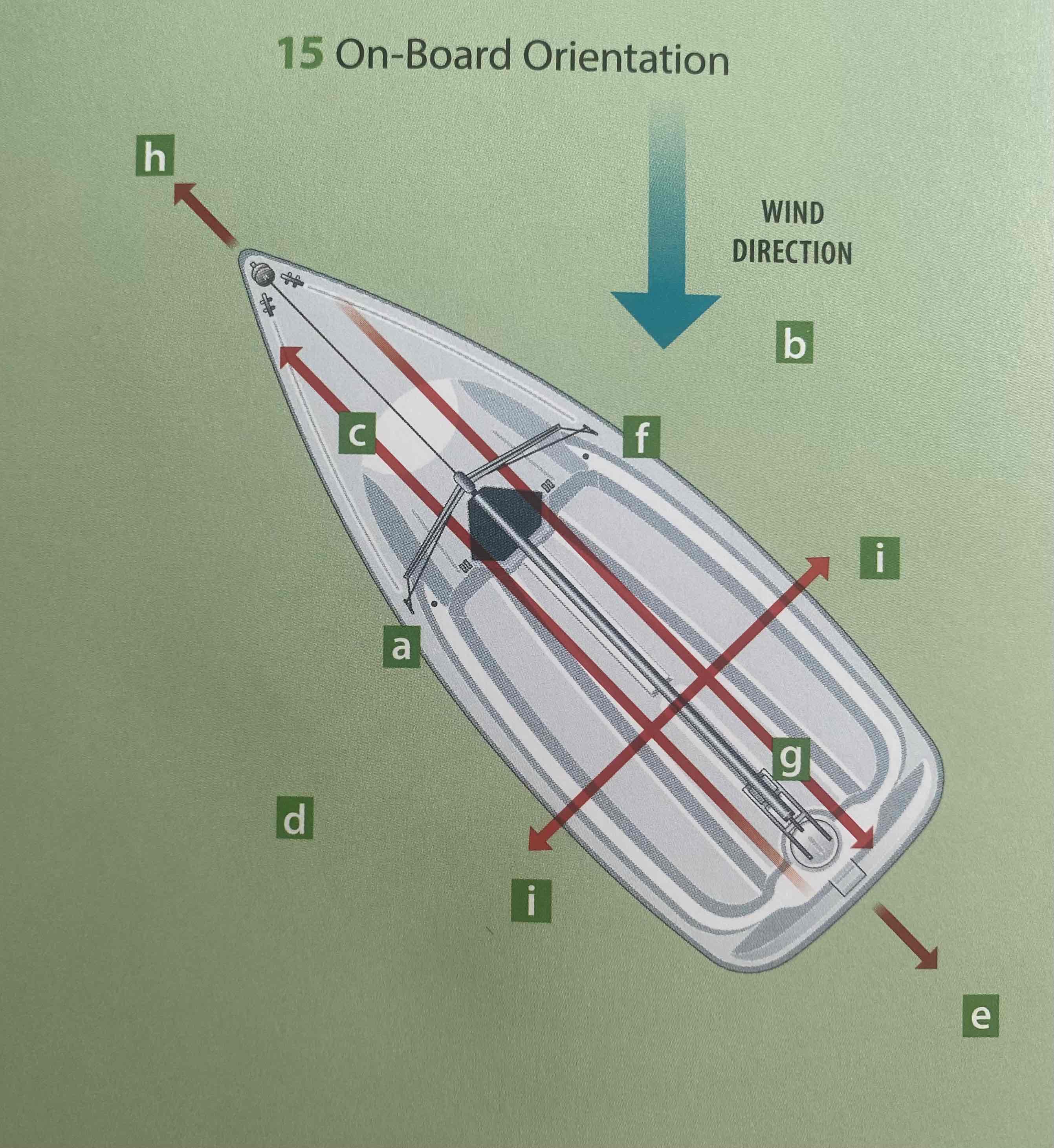
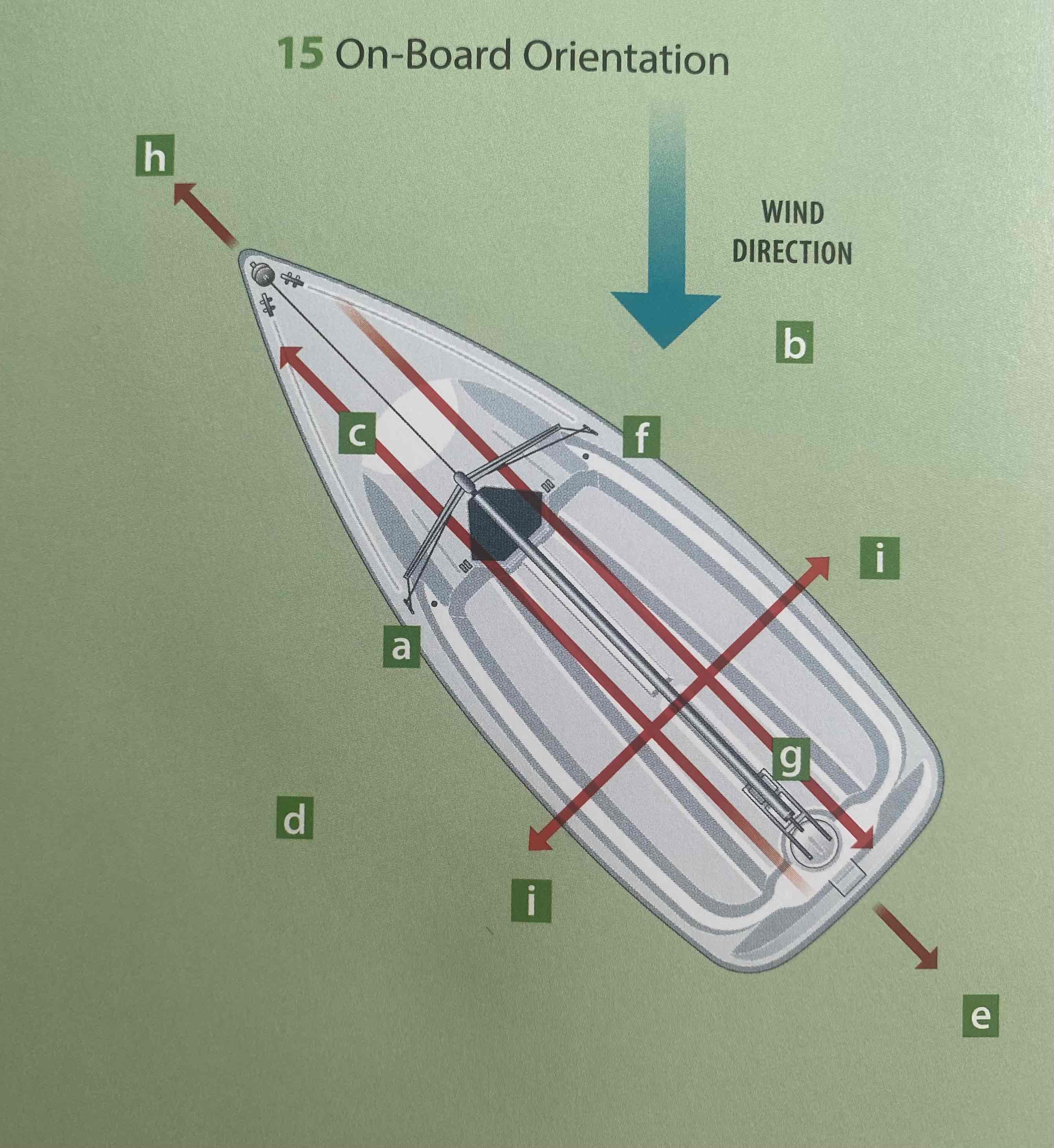
Identify the port.
A
Identify the starboard.
F
Identify the forward.
C
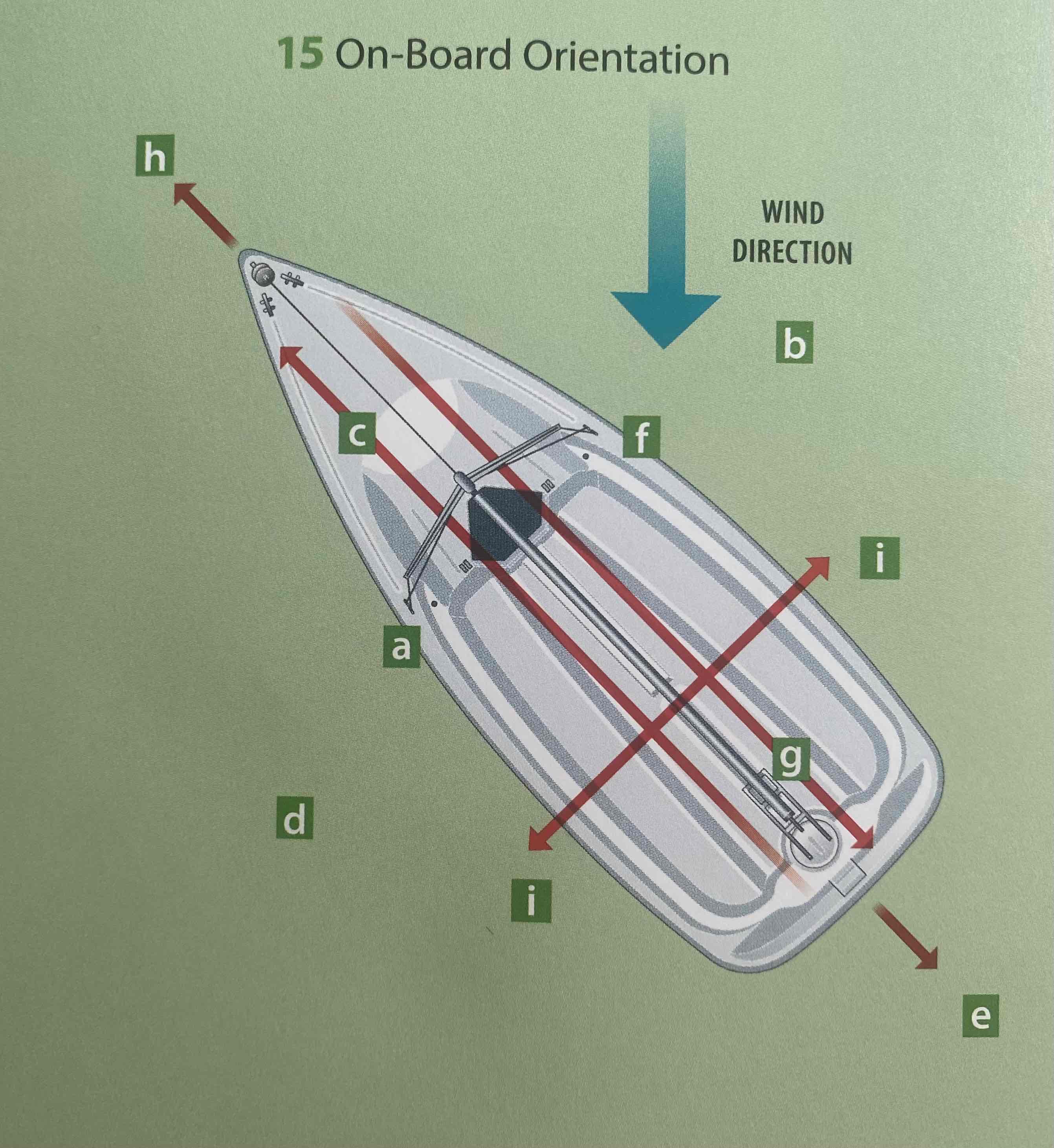
Identify the aft.
G
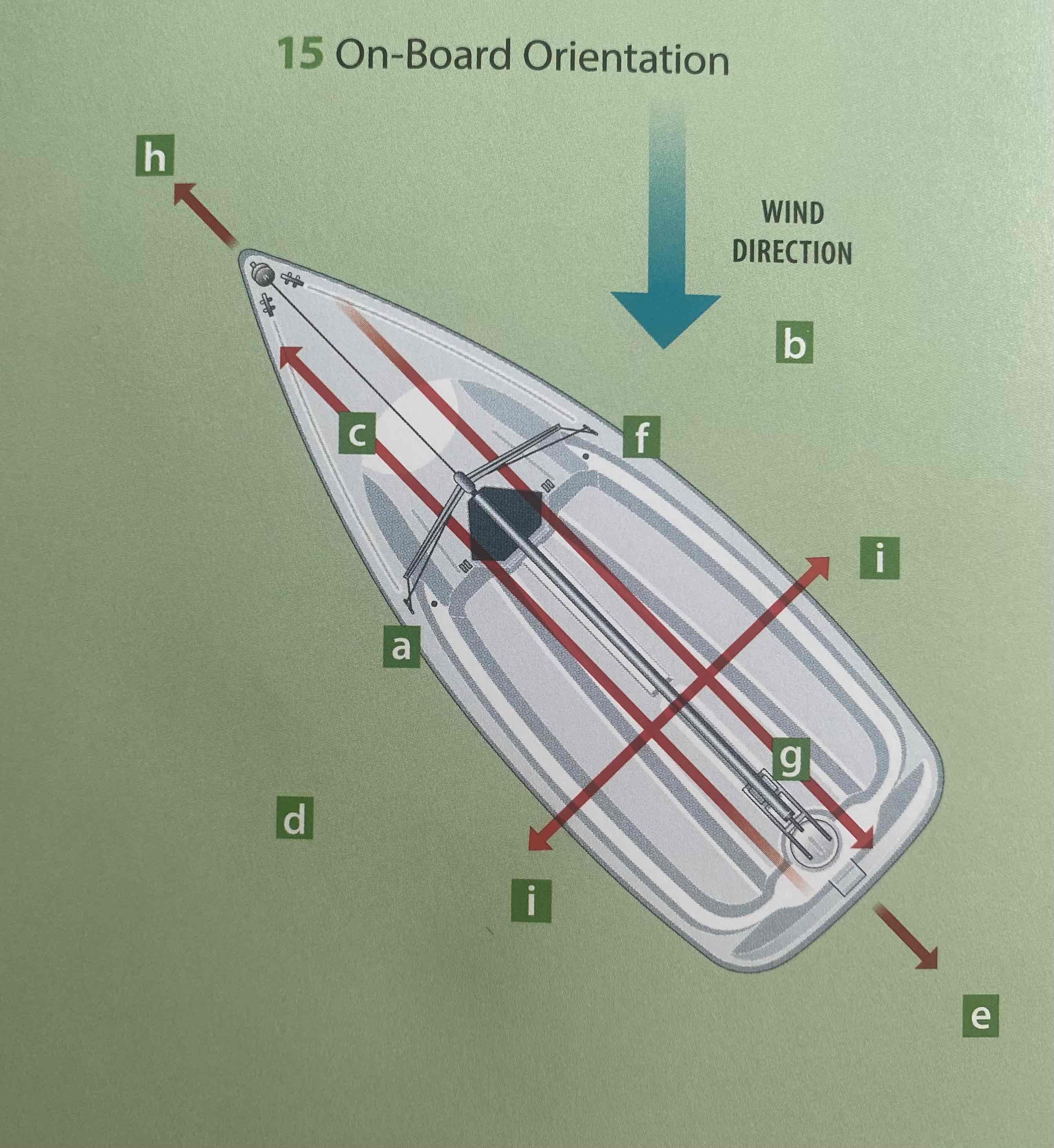
Identify the ahead.
H
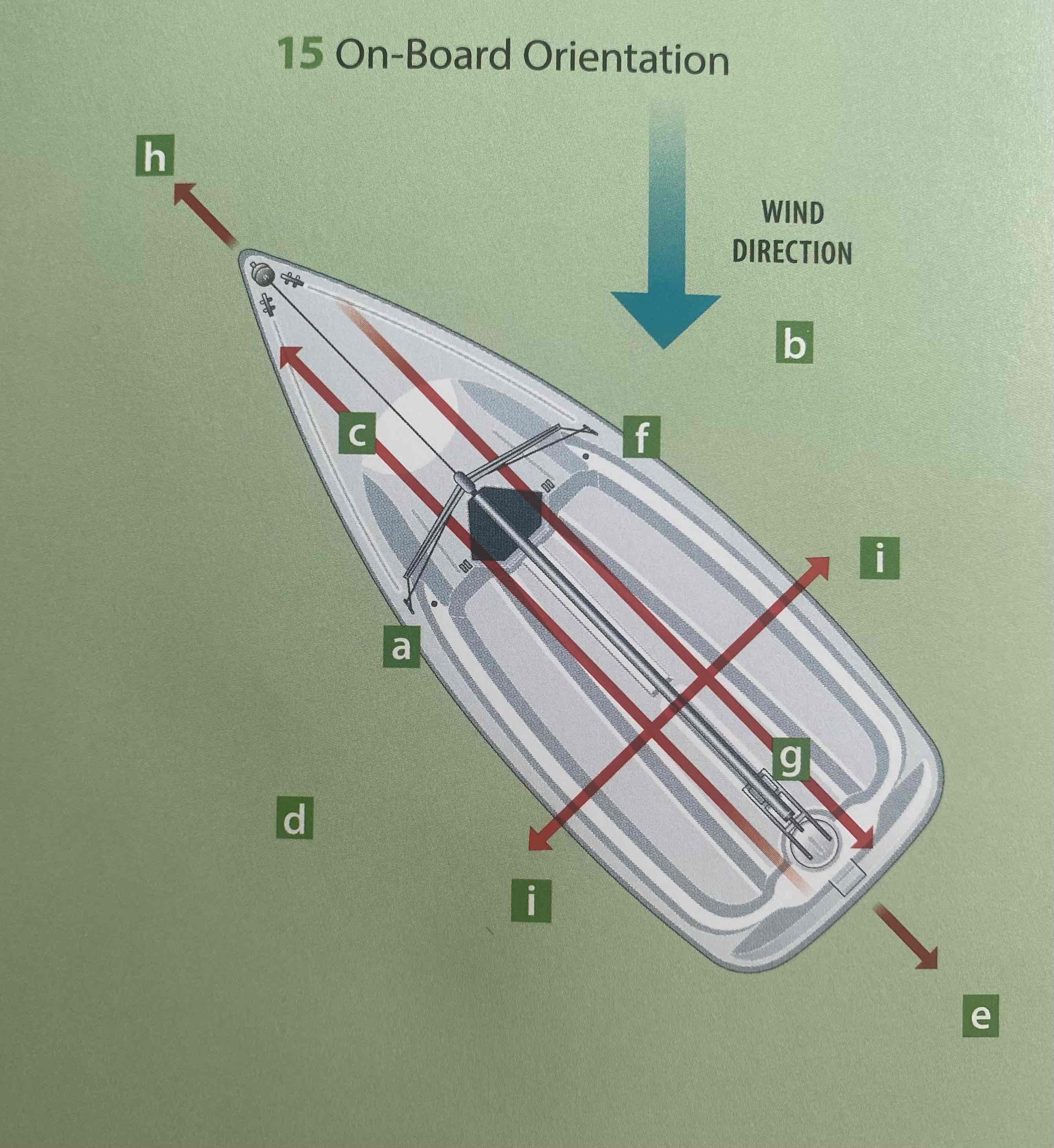
Identify the abeam.
I
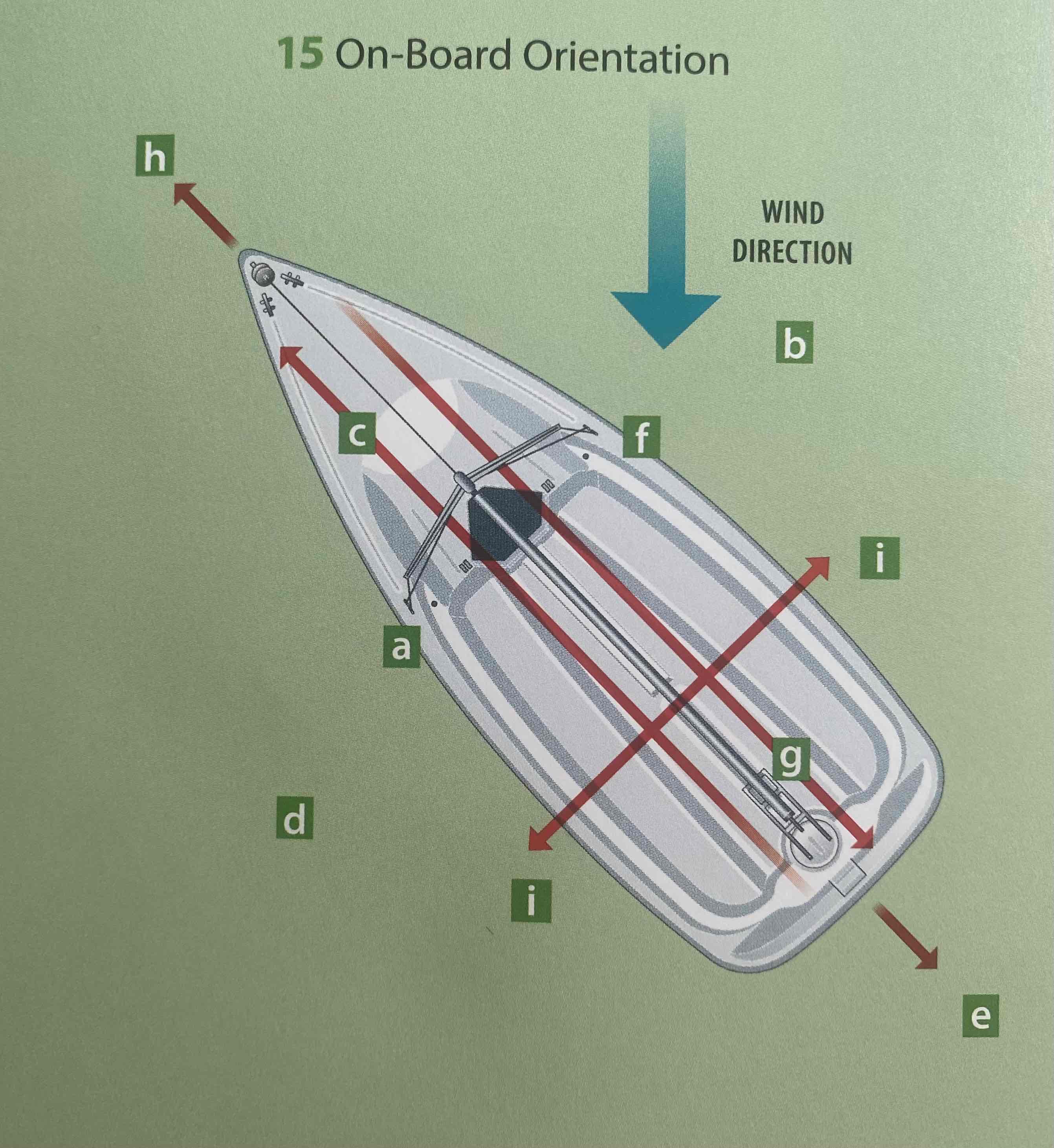
Identify the astern.
E
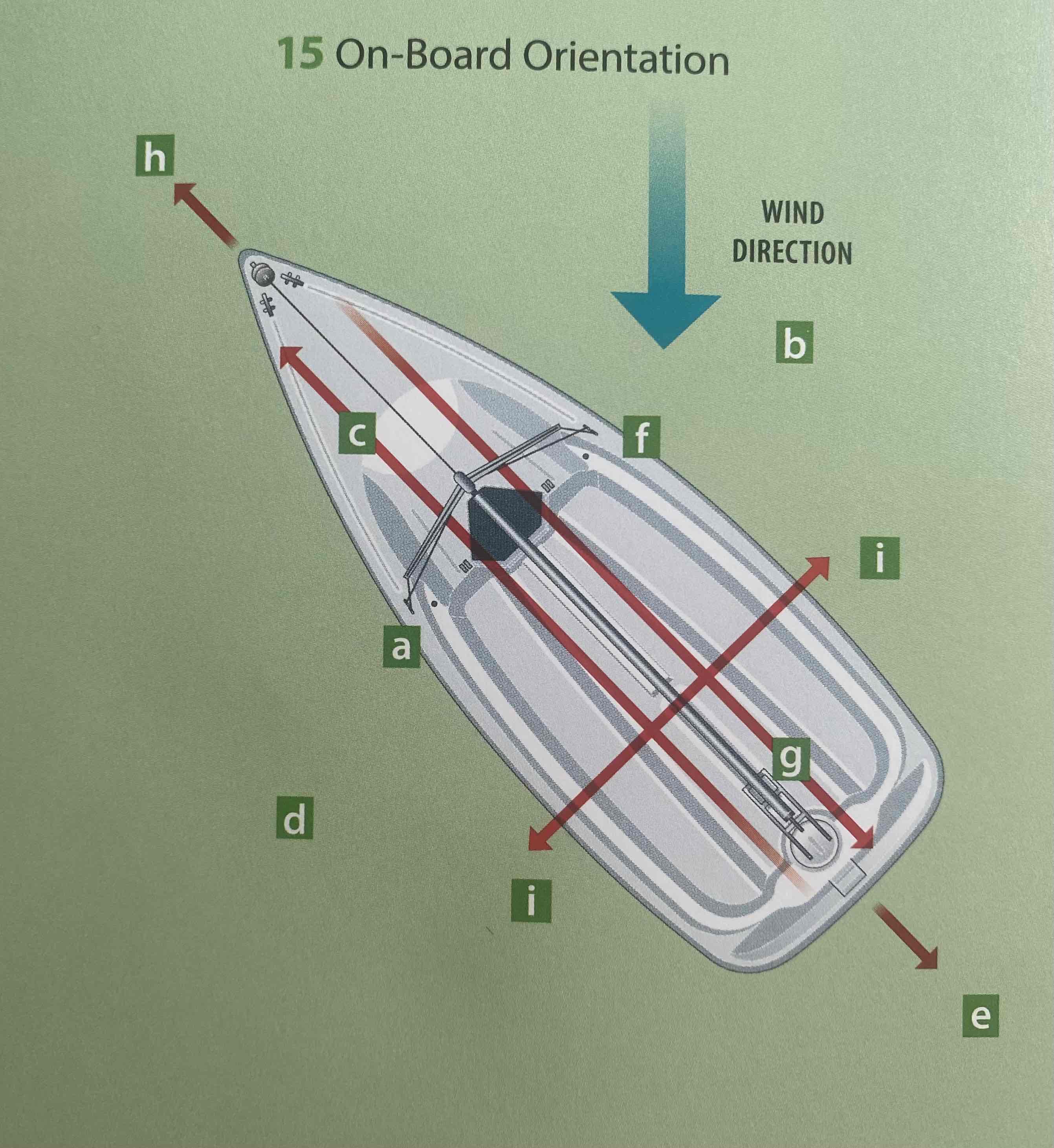
Identify the windward.
B
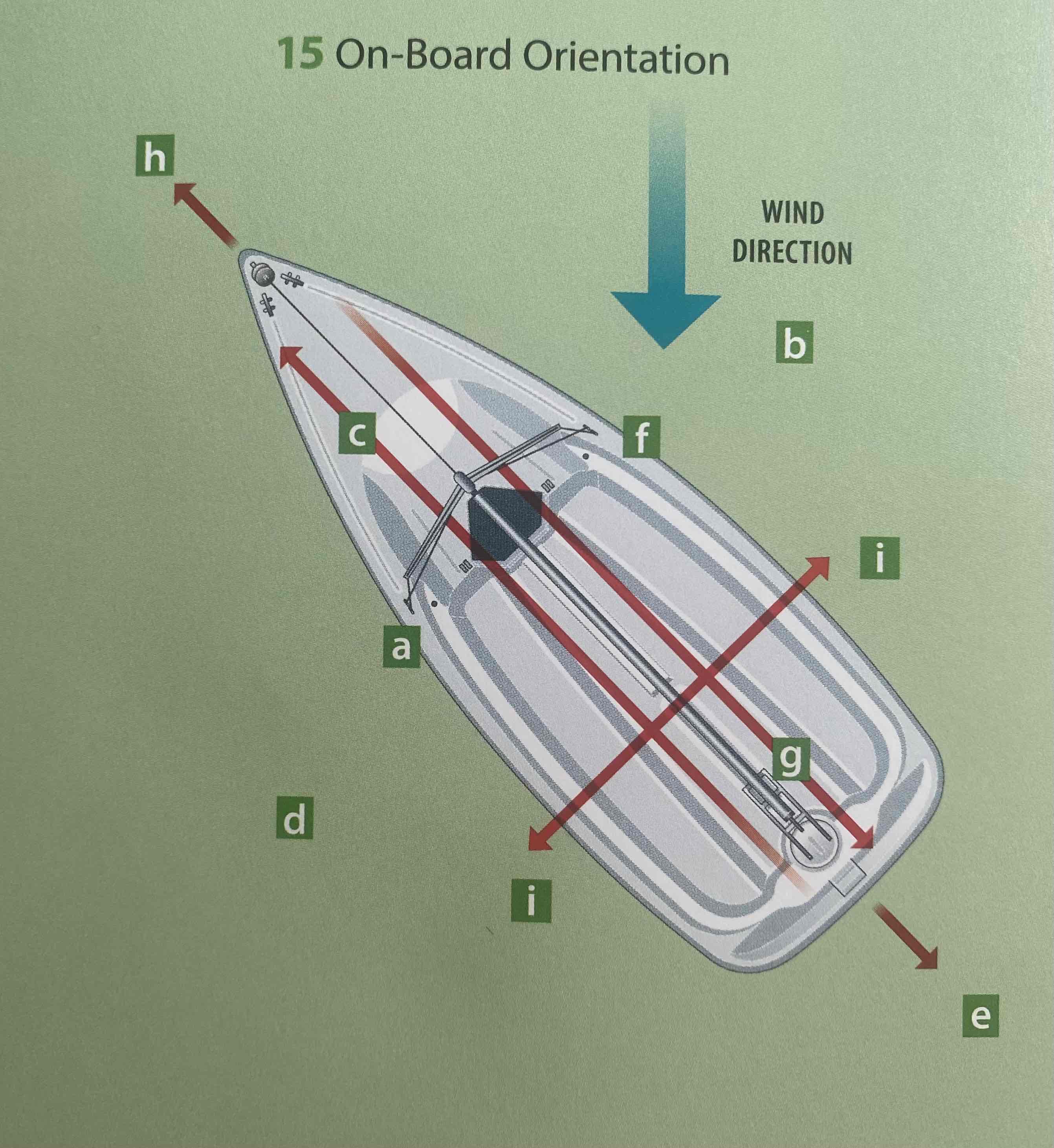
Identify the leeward.
D
The mainsail should be raised when the sailboat is oriented _____ to _____.
Head to wind
When turning the boat toward the wind, the sails should be _______ in.
Trimmed
When turning the boat away from the wind, the sails should be _______ out.
Eased
“Fluttering” sails are said to be _____.
Luffing
The best way to steer the boat on a straight course is to look toward the _____ and pick a _____ to steer toward.
Shore, landmark
When you turn the bow of the boat toward the wind you are ______ ______.
Heading up
When you turn the bow of the boat away from the wind you are ______ ______.
Bearing away
The “golden rule” of sail trim is: “when in ______, let it ______”.
Doubt, out
When the boat is stopped, pointed toward the wind with the sails luffing, it is said to be ______ ______.
In irons

Which illustration shows a boat in irons/no-sail zone?
F

Which illustration shows a boat close-hauled?
C

Which illustration shows a boat in close reach?
A

Which illustration shows a boat in beam reach?
E

Which illustration shows a boat in broad reach?
B

Which illustration shows a boat running?
D
When the wind is blowing on the port side, the boat is said to be sailing on a _____ _____.
Port tack
When the wind is blowing on the starboard side, the boat is said to be sailing in a _____ _____.
Starboard tack
Turning the boat so the bow passes through the wind, bringing the wind to blow onto the opposite side of the boat, is called _____.
Tacking
Changing tacks by turning the boat so its stern passed through the wind is called _____.
Jibing
The helmsman’s commands for tacking the boat (also called “coming about”) are “______ ______” and “______ ______”.
“Ready about” “Helm’s a-lee”
The helmsman’s commands for jibing a boat are “______ to ______” and “______-_____”.
“Prepare to jibe” “Jibe-ho”
To jibe safely, its very important to _____ the _____ in towards the centerline as the boat bears away onto a run.
Trim, mainsail
Sailing on a run with the mainsail and jib on opposite sides of the boat is called sailing ______-on-_______.
Wing-on-wing
If the wind is on the same side of the boat as the mainsail while sailing downwind, the boat is said to be ______ by the _____.
Sailing by the lee
The danger of sailing by the lee is the increased risk of an ______ ______.
Accidental jibe
The fastest way to change the sail’s power is to change its ______ to the ______.
Angle to the wind
The shape of the mainsail may be changed by adjusting tension in the edges of the sail. The sail control with the edge of the sail it affects is ______, ______, and ______.
Foot, luff, and leech
The overhaul changes the depth of the _____ of the mainsail.
Draft
Tightening the downhaul or Cunningham moves the draft of the mainsail _____.
Forward
Tightening the ______ ______ holds the boom down on a downwind point of sail.
Boom vang
To get full power and optimum use out of the mainsail, ______ it until it just starts to luff, then trim the mainsail in so it just stops ______.
Ease, luffing
Two ways to change the sail’s angle to the wind are:
Ease or trim the sail. Head up or bear away.
The tendency for the boat to head up toward the wind on its own is called _____ helm.
Weather
The tendency for the boat to bear away from the wind on its own is called ______ helm.
Lee
While sailing close-hauled, four ways to decrease the heel of the boat are:
Move the crew to the windward side of the boat. Head up slightly, into the edge of the no-sail zone. Ease the main sheet. Move the traveler to leeward.
Reducing the size of a sail so that less area is exposed to the wind is called _____.
Reefing
Bowline
Form a non-slipping loop, tie jibsheets to clew of jib
Square knot
Tie to ends of a line together
Cleat hitch
Secure a dock line to a horn cleat
Clove hitch
Temporary tie-up to dock piling, attach fenders to stanchion
Round turn and 2 half hitches
More secure tie-up to dock piling
When you want a break while sailing, you can make the boat lie _____-____.
Hove-to
You have to heave-to by backing the ______, easing the ______, and putting the ______ to leeward.
Backing the jib, easing the mainsail, and putting the helm (tiller) to leeward.
Stern line
Secures the stern of the boat to the dock
Forward spring
Keeps the boat from moving aft.
Aft spring
Keeps the boat form moving forward
______ are used to protect the hull from contact with the dock or other boats.
Fenders
The ideal point of sail on which to approach a mooring ball is on a ______ ______.
Close reach

Which of these illustrations shows the best conditions under which to approach a dock under sail?
A - upwind approach