A&P 1: Skeletal System
1/394
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
395 Terms
Parts of the axial skeleton
skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
Parts of the appendicular skeleton
upper & lower limbs, pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle
Function of the thoracic cage
protection of the heart & lungs
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12
How many pairs of ribs are there?
12
Which ribs are true ribs?
1-7
What (specifically) connects true ribs to the sternum
costal cartilage
What is another name for “true ribs”
Vertebrosternal ribs
Which ribs are false ribs?
8-10
Ribs 8 to 10 are joined by ______ to costal cartilage of rib 7 and then to the sternum
common cartilage
Ribs 8 to 10 are joined by common cartilage to ___ of rib 7 and then to the sternum
Costal cartilage
Ribs 8 to 10 are joined by common cartilage to costal cartilage of ___ and then to the sternum
rib 7
Ribs 8 to 10 are joined by common cartilage to costal cartilage of rib 7 and then to the ___
sternum
What is another name for “false ribs”
Vertebrochondral ribs
Which ribs are “floating ribs”
11-12
What is another name for “floating ribs”
Vertebral ribs

What is this?
Sternum
Functions of the vertebral column: Support ___ & ___
Trunk, head
Functions of the vertebral column: protect ___
spinal cord
Functions of the vertebral column: allow ___ to extend (off of spinal cord)
spinal nerves
Functions of the vertebral column: attachment point for ___; allow for ___
muscles, movement
How many bones make up the vertebral column in an adult?
26
How many bones make up embryo vertebral column?
33 - 34
How many bones fuse to form the sacrum
5
How many coccygeal fuse to form the coccyx
3-5
What are the regions of the vertebral column
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral bone, coccygeal bone
Cervical annotations
C1-C7
Thoracic Annotations
T1-T12
Lumbar annotations
L1-L5
Sacral bone annotation
S
Coccygeal bone annotation
CO
What are the four major curvatures in adults?
Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral/Coccygeal
Which way does the cervical curvature curve?
Anteriorly
Which way does the thoracic curvature curve?
posteriorly
Which way does the lumbar curvature curve?
anteriorly
Which way does the sacral/coccygeal curvature curve?
posteriorly
At birth, vertebral column is “_” shaped
C
When does the cervical curve appear?
When head is raised
When does lumbar curve develop
When sitting and walking begin
What is lordosis?
Exaggeration of lumbar
What is kyphosis?
Exaggeration of thoracic; "hunchback”
What is scoliosis?
Lateral, often accompanied by kyphosis
Where are intervertebral disks located
between adjacent vertebrae
What are the functions of intervertebral disks
prevent vertebrae from rubbing together & support of the trunk and head
What do intervertebral disks consist of
fibrocartilage
What happens to intervertebral disks with age?
become compressed & more susceptible to herniation
what is a herniated disk
breakage or ballooning of the intervertebral disk
What may a herniated disk push against (impairing function and causing pain)
spinal nerves
Cervical vertebrae have very ___ bodies
small
Cervical vertebrae tend to have ___ spinous processes
bifid
Cervical vertebrae have transverse ___
foramina
Atlas has no what?
spinous process
Which vertebrae is atlas
C1
What does the atlas (C1) allow for
nodding motion
Which vertebrae is axis
C2
What motion does axis (C2) allow for
shaking head
What is vertebral prominence
most prominent spinous process in area
Which vertebrae usually has the most prominent spinous process in area? (cervical)
C7
Superior articular facets face which way (cervical)
superiorly
inferior facets face which way (cervical)
inferiorly
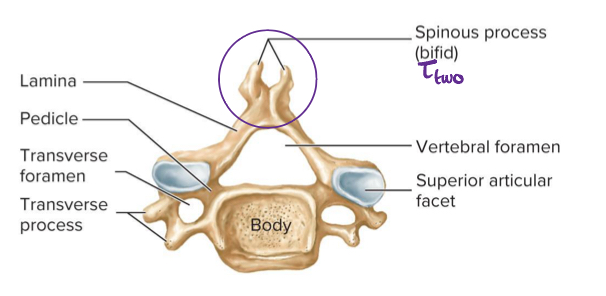
whats this
cervical vertebrae
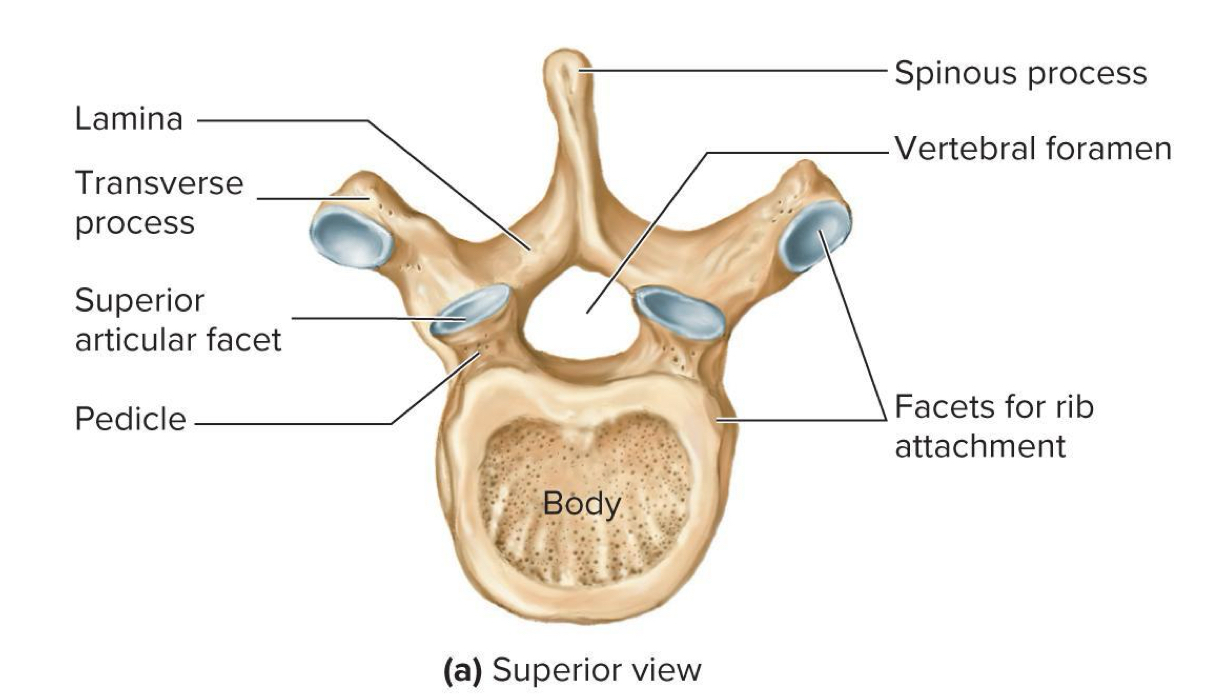
whats this
thoracic vertebrae
Thoracic vertebrae have a longer ___
transverse process
What do the articular facets of thoracic vertebrae attach to (T1-T10)
ribs
Most ribs have heads to articulate with how many vertebrae?
2
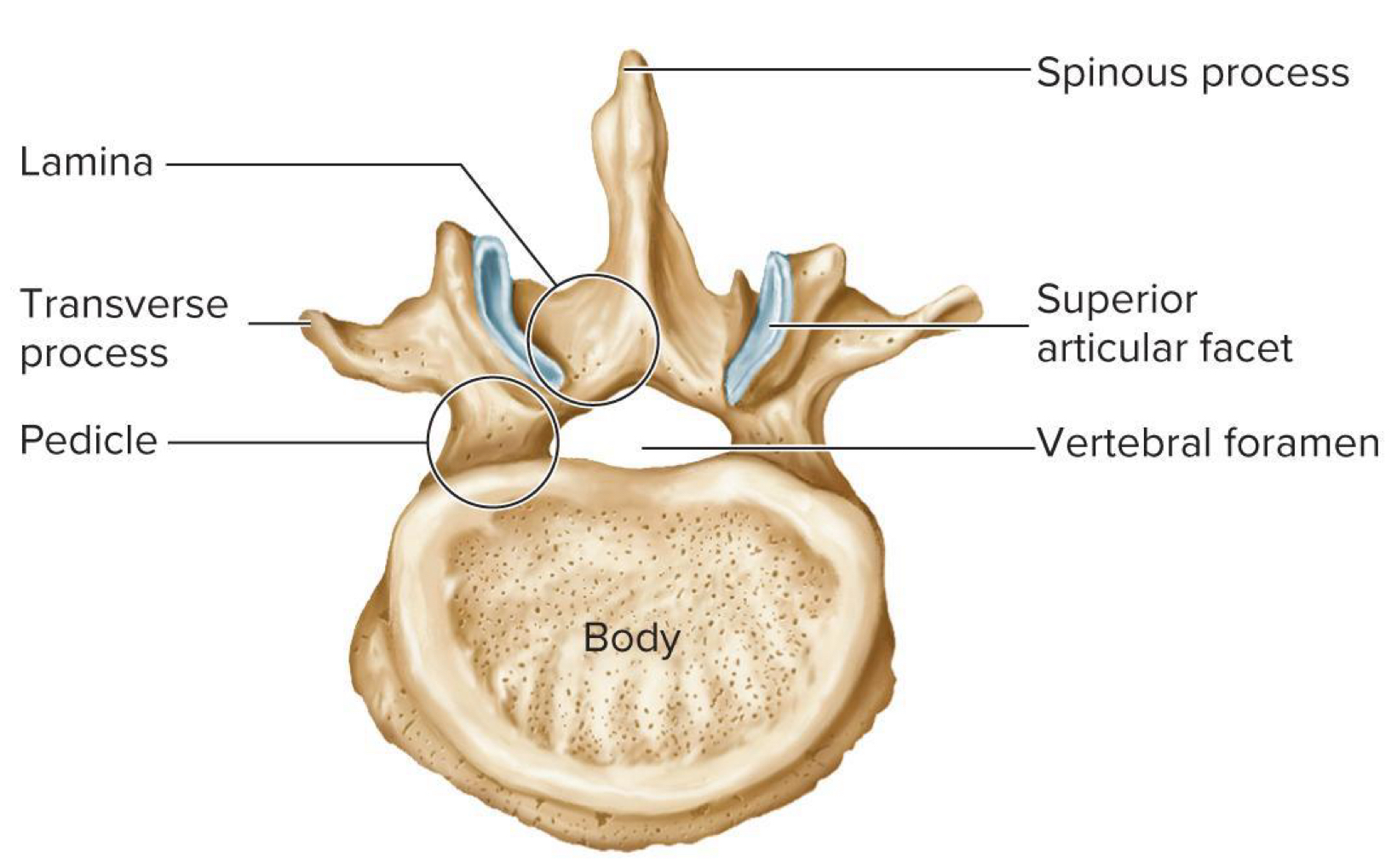
whats this
lumbar vertebrae
Lumbar vertebrae have large thick ___
bodies
Lumbar vertebrae have heavy rectangular ___ and ____
transverse and spinous processes
Superior articular facets face ___ (lumbar)
medially
inferior articular facets face ___ (lumbar)
laterally
Lumbar vertebrae have added what
strength
Lumbar vertebrae have limited what
motion
T/F: the number of fused vertebrae that make up the sacrum per person can vary
True
Coccyx is commonly known as what
tailbone
The vertebrae that make up the sacrum are __ (fused/semi-fused/not fused)
fused
The vertebrae that make up the coccyx are __ (fused/semi-fused/not fused)
semi-fused
Hip bone is formed as a fusion of embryonic ___,___,___
ilium, ischium, pubis
Ilium, ischium and pubis contribute to what
acetabulum
The false pelvis is ___ to pelvic brim
superior
The true pelvis is ___ to pelvic brim
inferior
what is the pubic symphysis composed of
fibrocartilage
What are the two girdles in the appendicular skeleton
pectoral & pelvic
What bones make up the upper limbs
humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
What bones make up the lower limbs
femur, tibia, fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges
The femur is what bone shape
long bone
the occipital bone is what bone shape
flat bone
the vertebrae are what bone shape
irregular
the carpal bones are what bone shape
short bone
the patella is what bone shape
sesamoid bone
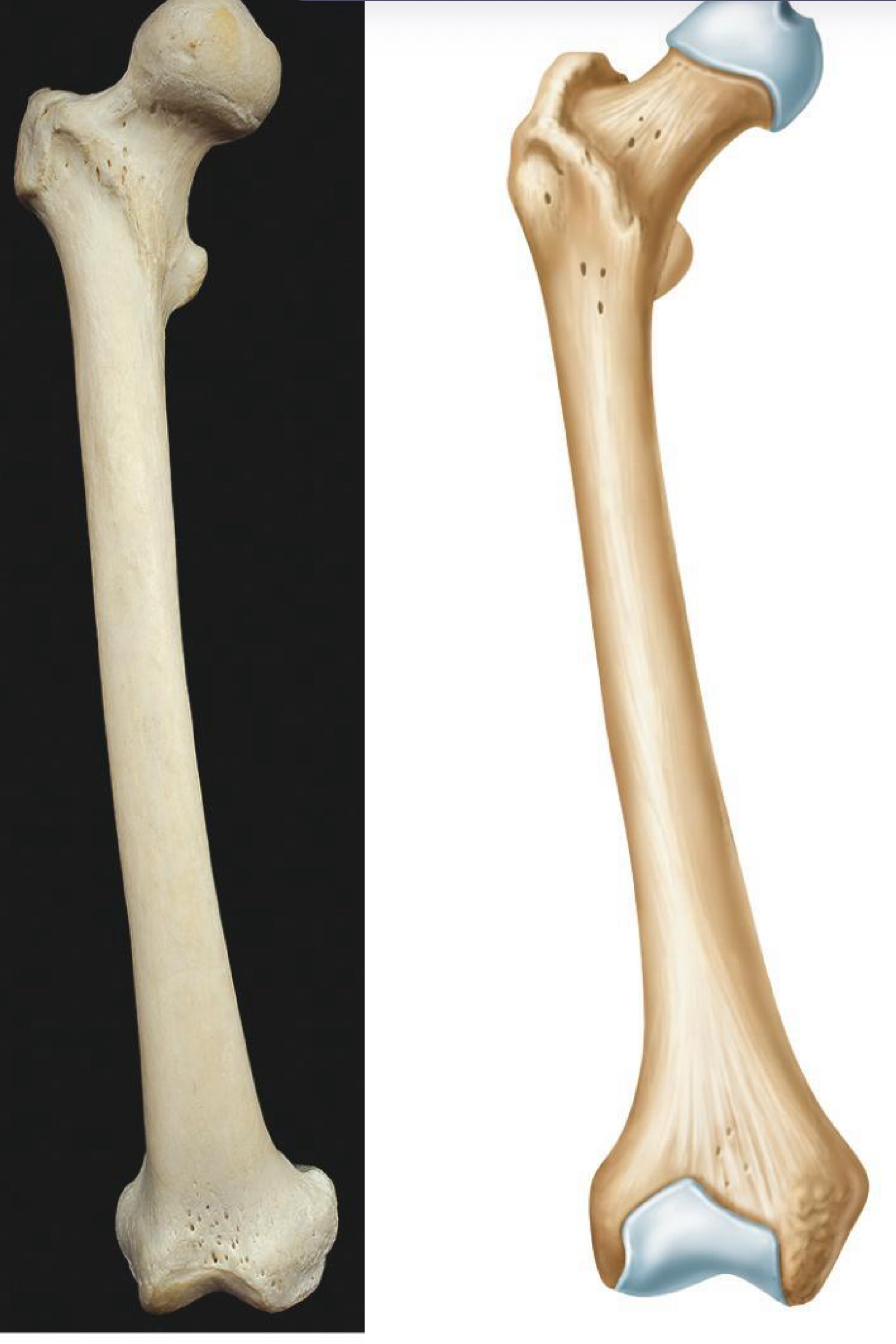
what bone shape is this
long
what bone shape is this representing
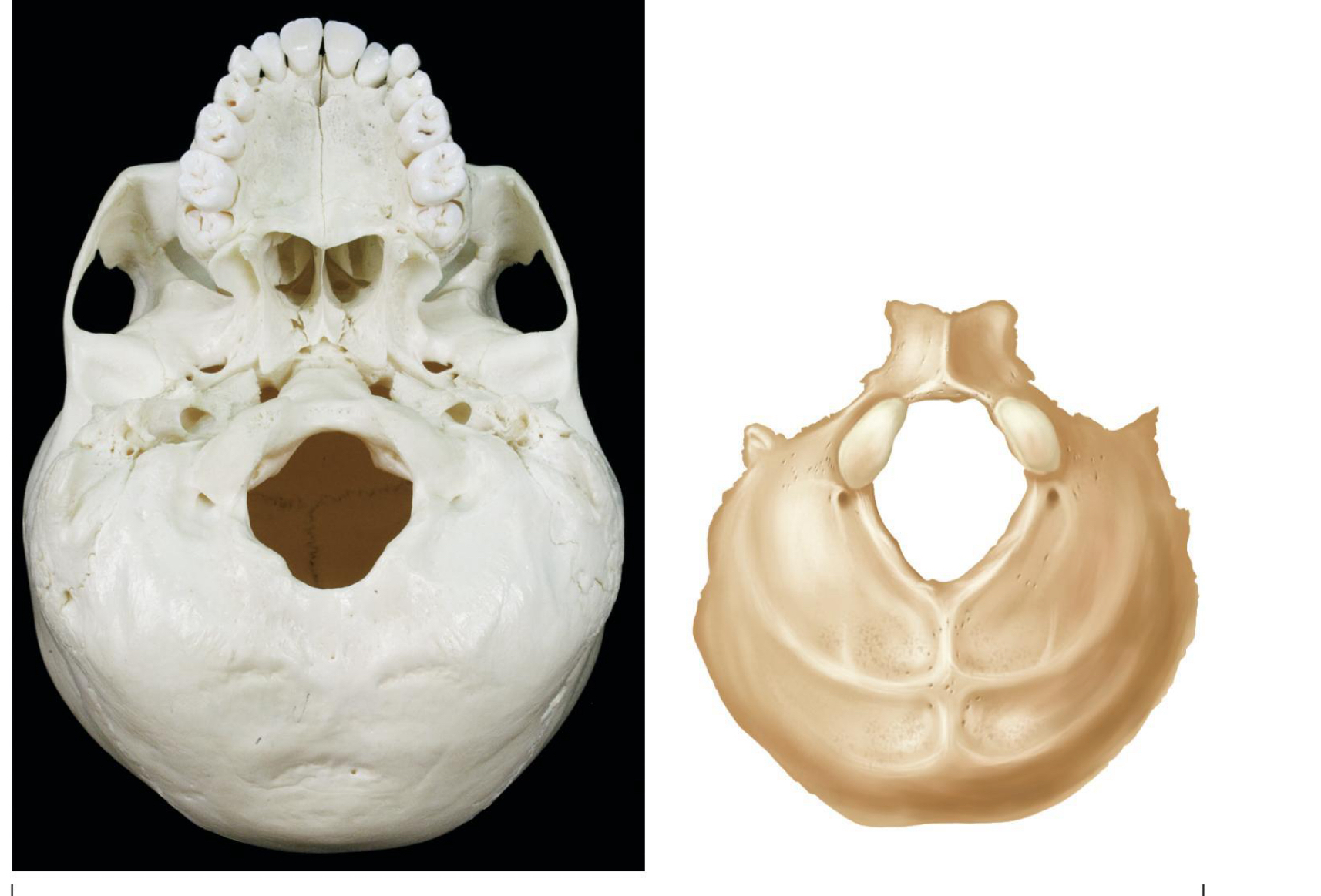
flat
what shape bone is this
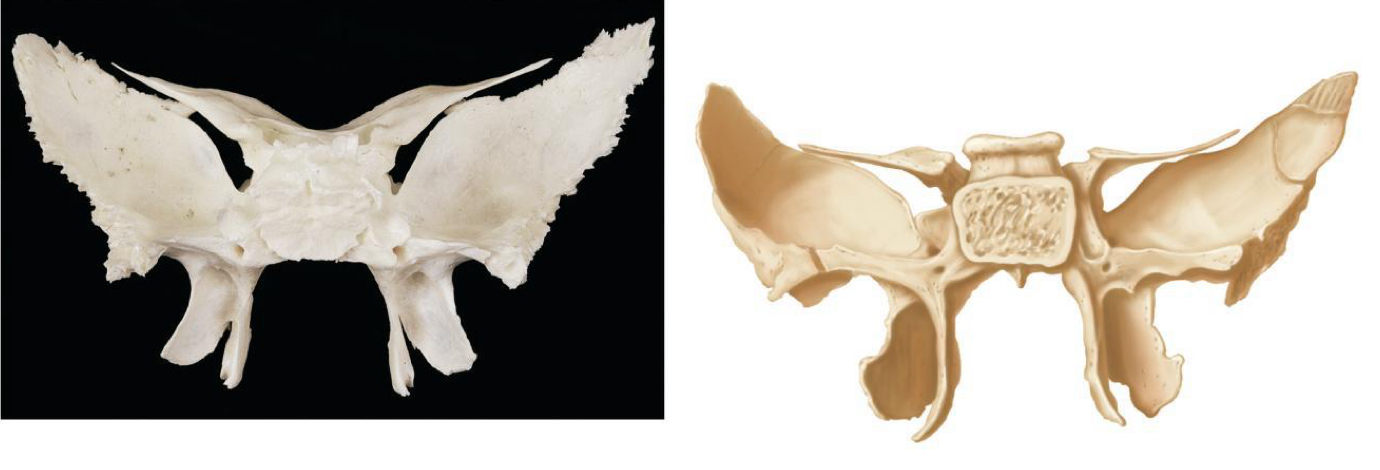
irregular
what bone shape is this representing
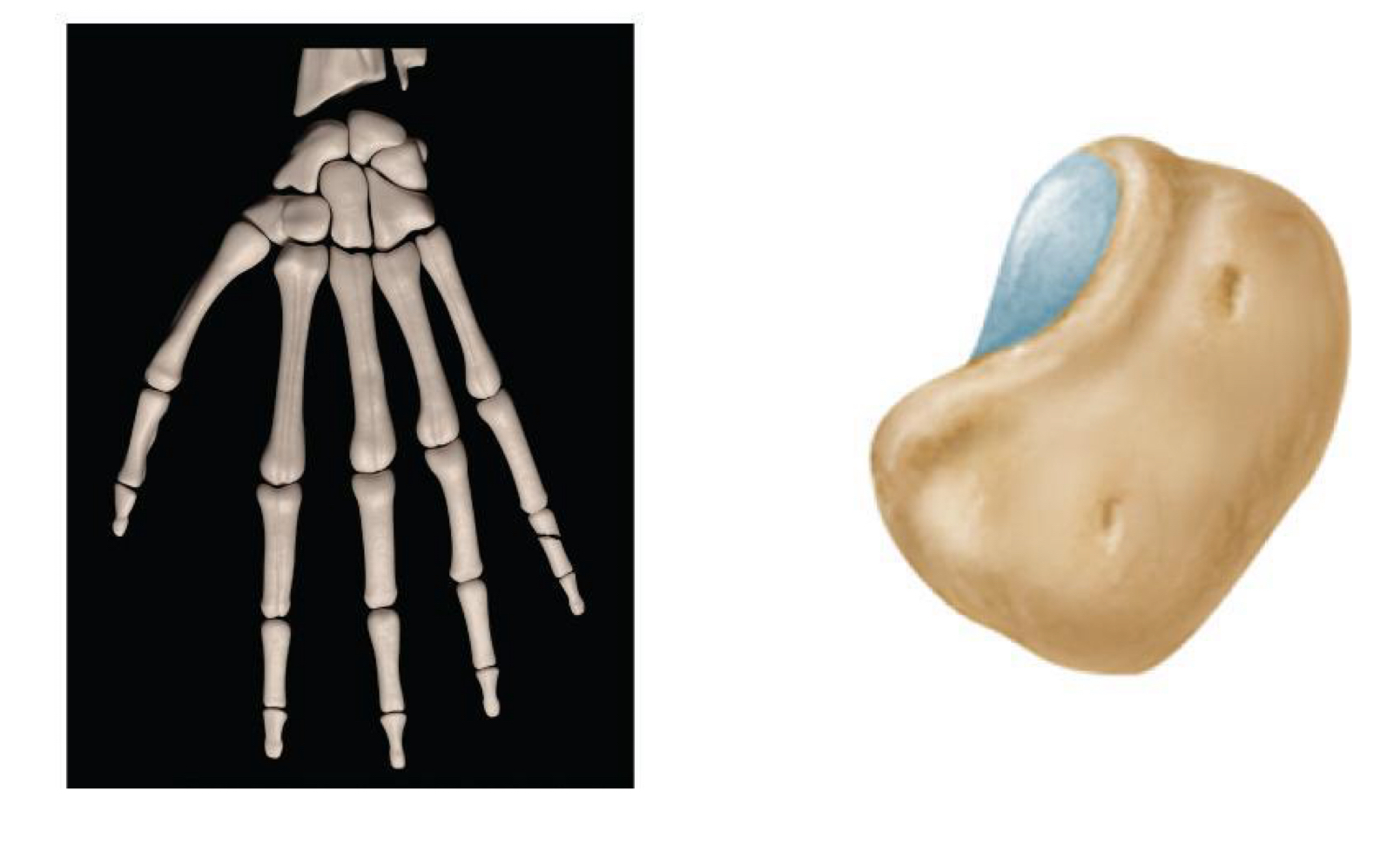
short
What does the skeletal system support
muscles
What does the skeletal system protect
organs
What connects muscle to bone
tendons
What does the skeletal system store
calcium phosphorus
what is hematopoiesis
blood cell production
What are the types of cartilage
fibrocartilage, hyaline, elastic
Chondroblasts do what
build/form cartilage; lay down extracellular matrix