5. Personnel Monitoring 👨⚕️ - Film Badges
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are the 4 types of Personnel monitoring devices?
Film Badge
Pocket Dosimeter
TLDs
OSL
What is the most commonly used personnel monitoring device?
Film Badge
Materials used in film badge
dental film with lead foil (to absorb backscatter)
varying thicknesses (and materials) used to measure the Energy of the radiation that the worker was exposed to
Film Badge (or any personnel monitoring badge) will have ___ doses and ___ doses.
shallow (low dose)
deep (high dose)
Deep doses + shallow doses
Total Effective Dose Equivalent (TEDE)
another def for shallow dose
any internal dose
received by ingestion or inhalation
during the handling of radioactive materials
What types of radiation do Film Badges measure?
x-rays
gamma
beta
electrons
neutrons
Dose Range for film badge readings:
10mR-2000 REM
doses ↓ 10mR = M (as in minimal)
mR (miliREM)
T/F: Film Badges protect you from exposure
False
Accuracy of Film Badges
Accuracy can be affected by
± 20%
anything that affects film
heat
mechanical pressure
humidity
etc
Duration for wearing film badges:
4 weeks
Where do you wear film badges?
on the Ant surface of the body. Between the neck and waist
At the collar if there is potential for significant exposure to eyes/thyroid-best answer
When wearing a lead apron, where should you wear your film badge? Over or under the apron?
over
Where should you store a film badge?
an area unexposed to light at the facility
Film badge disadvantage
length of time between readings
ring badge
what is it made of
where do you wear it
What is it used for
radiographic film
around your finger
for brachytherapy and nuclear medicine workers
Neutron badge: who wears these?
nuclear reactor and cyclotron workers
Pocket Dosimeter
Appearance
Principle of operation
fits in your shirt pocket
It is a condenser chamber (ion)
Pocket Dosimeter
Advantages
Disadvantages
immediate readings
A. Accuracy depends on avoiding:
high humidity
mechanical shock
B. Calibration problems (FYI: has to constantly be recalibrated)
Pocket Dosimeter
Uses
Due to high upfront and calibration costs, and them being high maintenance, they are most useful for:
Personnel monitor in area of HIGH radiation concerns:
Nuclear power plants
Pantex
TLD stand for
Thermoluminescent Dosimeter
Thermoluminescent Dosimeter
Principle of Operation
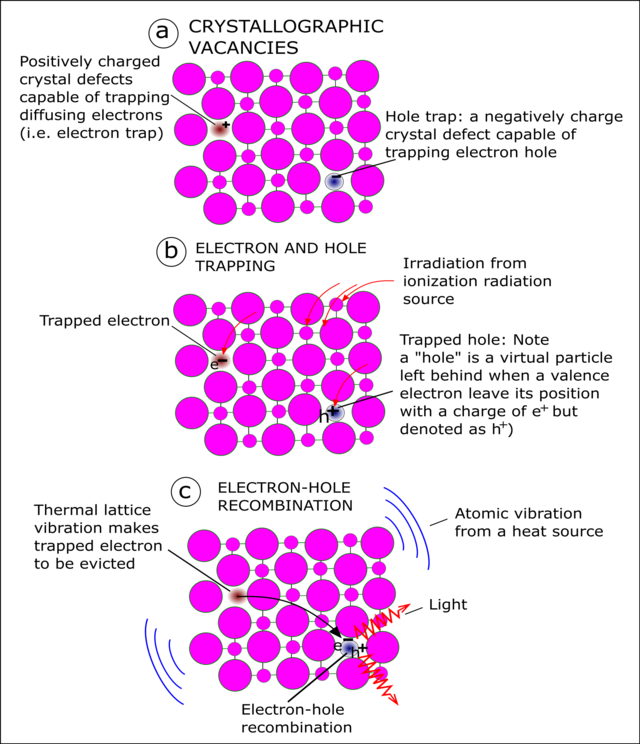
TLDR: Thermoluminescent Dosimetry is based on imperfections in the crystal lattice and their ability to capture electrons released by ionizing radiation.
Crystal lattice is exposed to ionizing radiation which releases electrons
Electrons are trapped in imperfections (Mg) in the crystal lattice
TLD is sent off to be read
Crystal is heated up which releases Energy trapped in the lattice
Energy released comes out in the form of light
TLD reader reads the amount of light released
The amount of light released is proportional to the dose
Crystals used for TLDs
Lithium Fluoride- most common
Lithium Borate
Calcium Fluoride
TLD:
advantages
disadvantages
Advantages
Reusable
Economical
Small
Accurate: ± 5%
Disadvantages:
Storage instability
Fading (less accurate after every use)
TLD readers can be unstable
TLD uses
Personnel monitoring
Machine Dosimetry (calibration of machine)- tho not as useful for this
TSI: total skin irradiation
TBI: total body irradiation
Long term area surveys (e.g. brachytherapy room)
Define
TSI
TBI
TSI: irradiate the whole skin with electron tx
TBI: irradiate the whole body with MV x-rays
OSL stand for
Optically Stimulated Luminescence
OSL
Principle of Operation
Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) is irradiated
Electrons are trapped in Aluminum Oxide
A laser light “reader” stimulates the electrons
The electrons recombine and give off light which is proportionate to the dose
Additionally, they use filters like film badges to determine radiation Energy
OSL:
Advantages
Disadvantages
Advantages
Can read doses as low as 1mR (compared to 10mR for film badges)
Accurate: ± 1mR
Disadvantages
NA
Which company produces and reads most film badges and OSLs?
The Landauer Company
