economics (market failure)
5.0(11)
Card Sorting
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:30 PM on 5/11/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
market failure
failure of the market to achieve allocative efficiency
2
New cards
types of market failure
overprovision of demerit goods (negative externalities of consumption)
underprovision of merit goods (positive externalities of consumption)
underprovision of public goods
underprovision of positive externalities of production
overuse of common access resources
threat to sustainability (negative externalities of production)
asymmetric information
underprovision of merit goods (positive externalities of consumption)
underprovision of public goods
underprovision of positive externalities of production
overuse of common access resources
threat to sustainability (negative externalities of production)
asymmetric information
3
New cards
demerit goods
goods that are bad for the consumer and society as a whole
in a free market, demerit goods will be readily available and relatively inexpensive
overprovided
consumers of these goods are unhealthy, unproductive, and don't contribute to society
society has to pay for their healthcare costs
in a free market, demerit goods will be readily available and relatively inexpensive
overprovided
consumers of these goods are unhealthy, unproductive, and don't contribute to society
society has to pay for their healthcare costs
4
New cards
merit goods
goods that benefit the consumer as well as society as a whole
in a free market, merit goods will be rare, expensive, and only consumed by the wealthy
under-provided
educated people are more productive, commit less crimes, pay more taxes, and have jobs, and cost society less in health care
in a free market, merit goods will be rare, expensive, and only consumed by the wealthy
under-provided
educated people are more productive, commit less crimes, pay more taxes, and have jobs, and cost society less in health care
5
New cards
public goods
goods which benefit society and are non excludable and non rivalrous
like street lights
like street lights
6
New cards
non excludable
impossible to prevent someone from using it once its provided
7
New cards
non rivalrous
when someone consumes the good it is still there to be consumed by others
8
New cards
free rider problem
people use public goods without having to pay
9
New cards
quasi public good
goods that don't neatly fit the description of non-rivalrous and non-excludable, but might serve a public good
example would be museums
example would be museums
10
New cards
common access resources
essentially free to the user and anyone can get access to the resource
rivalrous and non excludable
rivalrous and non excludable
11
New cards
government intervention
if the free market results in market failure it is the role of the government to interfere
12
New cards
earn government revenue
reason governments may want to intervene
earn revenue from indirect taxes by placing them on goods with price inelastic demand
earn revenue from indirect taxes by placing them on goods with price inelastic demand
13
New cards
support firms
reason governments may want to intervene
aid small firms or firms in areas the government want to grow through subsidies or price floors
aid small firms or firms in areas the government want to grow through subsidies or price floors
14
New cards
support households on low incomes
reason governments may want to intervene
support poor households through subsidies or direct provision
support poor households through subsidies or direct provision
15
New cards
influence the level of production
reason governments may want to intervene
support firms that produce merit goods
through subsidies, price floors
support firms that produce merit goods
through subsidies, price floors
16
New cards
influence the level of consumption
reason governments may want to intervene
increase consumption of merit goods and decrease consumption of demerit goods through subsidies or indirect taxes and legislation and regulation
increase consumption of merit goods and decrease consumption of demerit goods through subsidies or indirect taxes and legislation and regulation
17
New cards
correct market failure
reason governments may want to intervene
governments are the only ones that can fix market failure
governments are the only ones that can fix market failure
18
New cards
promote equity
reason governments may want to intervene
fix the unequal distribution of wealth that the free market creates
fix the unequal distribution of wealth that the free market creates
19
New cards
negative externalities
external costs that are paid by a third party (society) due to a financial transaction
20
New cards
negative externalities of production
when there is a cost to the community that is greater than the cost of production paid by the firm
MSC is greater than MPC
example. production of fossil fuels
MSC is greater than MPC
example. production of fossil fuels
21
New cards
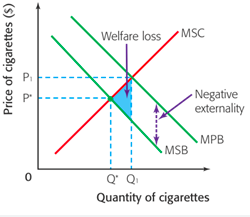
welfare loss
when the market is not able to achieve allocative efficiency and community surplus is reduced
22
New cards
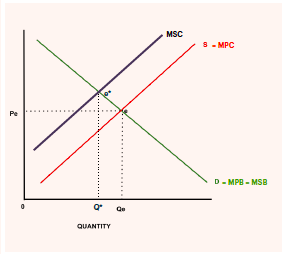
positive externalities of production
when there is a benefit to society that is greater than the private benefit of the producer
MSC is greater than MPC
example. tree farms
MSC is greater than MPC
example. tree farms
23
New cards
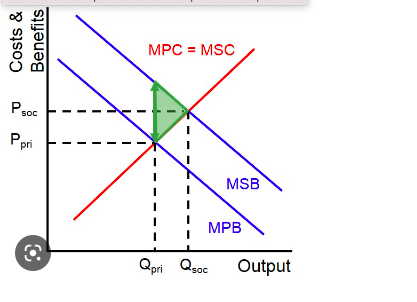
negative externalities of consumption
when society would benefit if less of a good or service was consumed
MPB is greater than MSB
example. drugs, cigarettes
MPB is greater than MSB
example. drugs, cigarettes
24
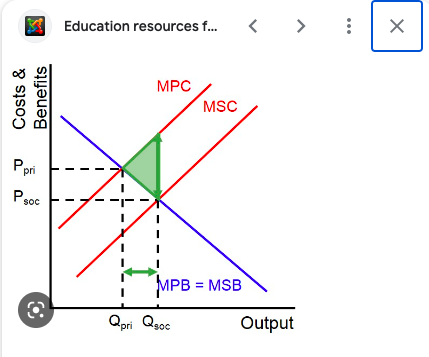
New cards
positive externalities of consumption
when there is a benefit to society that is greater than the private benefit of the consumer
MSB is greater than MPB
example. education
MSB is greater than MPB
example. education
25
New cards
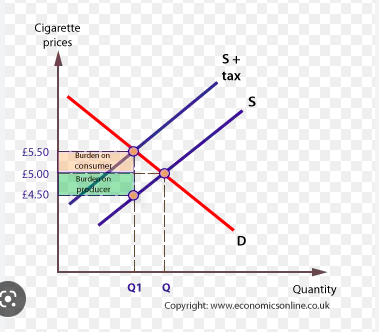
indirect tax (pigouvian)
type of government intervention
tax placed on the firm for every unit of output of a good or service
firms raise prices and the consumer pays for part of the tax indirectly
shifts supply to the left
placed on demerit goods
shifts supply vertically up or down
tax placed on the firm for every unit of output of a good or service
firms raise prices and the consumer pays for part of the tax indirectly
shifts supply to the left
placed on demerit goods
shifts supply vertically up or down
26
New cards
carbon tax
type of government intervention
indirect tax placed on producers who emit carbon into the atmosphere
the more carbon emitted the higher the tax
firms raise prices and the consumer pays for part of the tax indirectly
indirect tax placed on producers who emit carbon into the atmosphere
the more carbon emitted the higher the tax
firms raise prices and the consumer pays for part of the tax indirectly
27
New cards
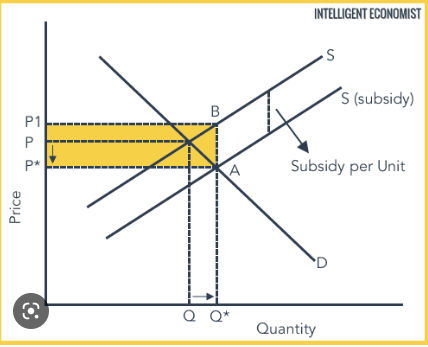
subsidies
type of government intervention
payments to a firm to encourage the production of a good or service
used for merit goods
reduce costs for firms
shift supply to the right
payments to a firm to encourage the production of a good or service
used for merit goods
reduce costs for firms
shift supply to the right
28
New cards
government responses to market failure
subsidies
indirect taxes
carbon taxes
tradable permits
direct provision
contracting private firms
price floors
price ceilings
legislation and regulation
education
self governance
international agreements
indirect taxes
carbon taxes
tradable permits
direct provision
contracting private firms
price floors
price ceilings
legislation and regulation
education
self governance
international agreements
29
New cards
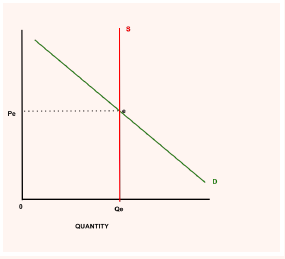
tradable permits (cap and trade)
type of government intervention
potential solution to carbon emissions and global warming
government places a CAP on how much each firm can pollute, firms are issued permits to pollute a certain amount
firms who keep their level of pollution under the cap can TRADE their remaining permits to a firm who can't keep their pollution levels under the cap
supply is fixed and demand will go down
government can reduce the cap, shifting supply to the left and reducing carbon emissions
potential solution to carbon emissions and global warming
government places a CAP on how much each firm can pollute, firms are issued permits to pollute a certain amount
firms who keep their level of pollution under the cap can TRADE their remaining permits to a firm who can't keep their pollution levels under the cap
supply is fixed and demand will go down
government can reduce the cap, shifting supply to the left and reducing carbon emissions
30
New cards
evaluation of tradable permits
uses the market to solve market failure, supply and demand are set by the price of permits, firms are motivated by profits to reduce emissions
cap can be reduced over time, further reducing carbon emissions
reduce carbon not the output
firms that switch to lower pollution levels with the least expense will do so
what should the cap be? how much is enough pollution? how high do the fines need to be?
any fine or tax will increase costs of firms making them less competitive
it will take a lot of regulation and policing to enforce this
political favoritism is an issue
cap can be reduced over time, further reducing carbon emissions
reduce carbon not the output
firms that switch to lower pollution levels with the least expense will do so
what should the cap be? how much is enough pollution? how high do the fines need to be?
any fine or tax will increase costs of firms making them less competitive
it will take a lot of regulation and policing to enforce this
political favoritism is an issue
31
New cards
evaluation of subsidies
increase in consumer and producer surplus
government loses money
society benefits
government loses money
society benefits
32
New cards
evaluation of carbon taxes
reduces consumer and producer surplus
government earns money
society benefits
government earns money
society benefits
33
New cards
evaluation of indirect taxes
reduces consumer and producer surplus
government earns money
society benefits
government earns money
society benefits
34
New cards
direct provision
type of government intervention
government directly providing merit goods, public goods
government directly providing merit goods, public goods
35
New cards
evaluation of direct government provision
consumer surplus increases because they have more goods at little to no cost
governments lose because they have to spend time and resources to provide these goods
society benefits from these public and merit goods
governments are not motivated to keep costs low because there is no profit motive
governments lose because they have to spend time and resources to provide these goods
society benefits from these public and merit goods
governments are not motivated to keep costs low because there is no profit motive
36
New cards
contracting private firms
type of government intervention
governments hire private firms to provided public and merit goods
paid for with tax revenue
firms bid on contract and government selects the best bid
governments hire private firms to provided public and merit goods
paid for with tax revenue
firms bid on contract and government selects the best bid
37
New cards
evaluation of contracting private firms
consumers benefit because consumer surplus increase and live better overall
producers benefit because revenue and producer surplus increases
government doesn't benefit due to opportunity cost and spending money and resources
society benefits because there are more public and merit goods
producers benefit because revenue and producer surplus increases
government doesn't benefit due to opportunity cost and spending money and resources
society benefits because there are more public and merit goods
38
New cards
legislation and regulation
type of government intervention
legislation are laws that ban or limit the supply/consumption of a good or service
regulation are rules that limit the consumption or production of goods and services
can be laws that ban or limit demerit goods
educate people on merit goods
maintain consumption of common access resources
legislation are laws that ban or limit the supply/consumption of a good or service
regulation are rules that limit the consumption or production of goods and services
can be laws that ban or limit demerit goods
educate people on merit goods
maintain consumption of common access resources
39
New cards
evaluation of legislation and regulation
consumers and producers of demerit goods are hurt as they loose surplus and revenue
consumers and producers of merit goods are helped as they gain surplus and revenue
government doesn't benefit as they have to spend more resources to enforce these laws
society benefits as society is healthier and more productive
consumers and producers of merit goods are helped as they gain surplus and revenue
government doesn't benefit as they have to spend more resources to enforce these laws
society benefits as society is healthier and more productive
40
New cards
legislation and regulation on demerit goods
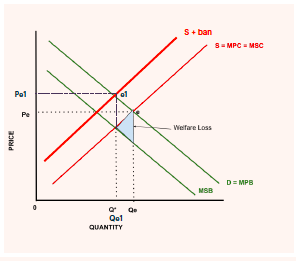
41
New cards
legislation and regulation on merit goods
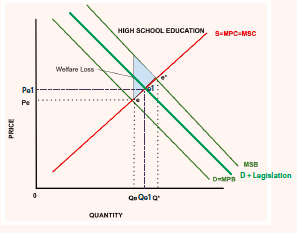
42
New cards
education
type of government intervention
using education inititatives
using education inititatives
43
New cards
evaluation of education
consumers and producers of demerit goods are hurt as they loose surplus and revenue
consumers and producers of merit goods are helped as they gain surplus and revenue
government doesn't benefit as they have to spend more resources to enforce these laws
society benefits as society is healthier and more productive
consumers and producers of merit goods are helped as they gain surplus and revenue
government doesn't benefit as they have to spend more resources to enforce these laws
society benefits as society is healthier and more productive
44
New cards
international agreements
type of government intervention
sustainability and global warming require cooperation of all nations to address
some governments place global competition above environmentalism
who is gonna monitor and control international agreements
sustainability and global warming require cooperation of all nations to address
some governments place global competition above environmentalism
who is gonna monitor and control international agreements
45
New cards
evaluation of international agreements
consumers and producers of demerit goods are hurt as they loose surplus and revenue
consumers and producers of merit goods are helped as they gain surplus and revenue
government doesn't benefit as they have to spend more resources to enforce these laws
society benefits as society is healthier and more productive
consumers and producers of merit goods are helped as they gain surplus and revenue
government doesn't benefit as they have to spend more resources to enforce these laws
society benefits as society is healthier and more productive
46
New cards
collective self governance
type of government intervention
everyone works together without government intervention
to work: everyone must have a way of communicating with each other and there must be clearly defined boundaries
everyone works together without government intervention
to work: everyone must have a way of communicating with each other and there must be clearly defined boundaries
47
New cards
evaluation of collective self governance
consumers and producers of demerit goods are hurt as they loose surplus and revenue
consumers and producers of merit goods are helped as they gain surplus and revenue
society benefits as society is healthier and more productive
consumers and producers of merit goods are helped as they gain surplus and revenue
society benefits as society is healthier and more productive
48
New cards
asymmetric information
when one party in an economic transaction possesses more information than the other party
49
New cards
adverse selection
type of asymmetric information
when one party has more information than the other party about the quality of the product
when one party has more information than the other party about the quality of the product
50
New cards
moral hazard
type of asymmetric information
when one party takes risks that another party might have to pay for like insurance of financial advisors
when one party takes risks that another party might have to pay for like insurance of financial advisors
51
New cards
government responses to asymmetric information
legislation, warning ads, regulation, provision of information, licensure, screening, signalling
52
New cards
licensure
government response to asymmetric information
rules and regulations which require professionals to have a license or certificate to practice
rules and regulations which require professionals to have a license or certificate to practice
53
New cards
signaling
government response to asymmetric information
used by the party with more information (usually the seller)
technique in which seller convinces buyers that the product is good quality
examples. warranties
used by the party with more information (usually the seller)
technique in which seller convinces buyers that the product is good quality
examples. warranties
54
New cards
screening
government response to asymmetric information
method used by the party with less information (usually the buyer)
when consumers seek to obtain more information about the product
method used by the party with less information (usually the buyer)
when consumers seek to obtain more information about the product
55
New cards
price ceilings
type of government intervention
when the government places a maximum amount that a producer can charge for a good or service
designed to protect consumers
most common for food and housing needs
must be below equilibrium to have an effect
requires government subsidies on top of it to work and shifts supply to the right and removes excess demand so that producers and consumers both win
when the government places a maximum amount that a producer can charge for a good or service
designed to protect consumers
most common for food and housing needs
must be below equilibrium to have an effect
requires government subsidies on top of it to work and shifts supply to the right and removes excess demand so that producers and consumers both win
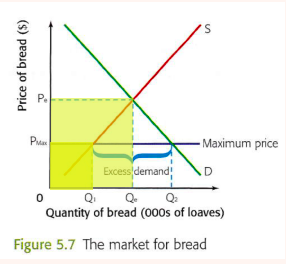
56
New cards
evaluation of price ceilings
shortages and excess demand
some consumers get the good at a lower price and some consumers get nothing because of excess demand
producers have a reduction in producer surplus and revenue decreases
society loses becuse welfare loss is created and too few resources are allocated for production however it might be worth the loss, market failure remains
government are losers: either the government doesnt apply subsidies and increases unemployment or government pays for subsidies to eliminate excess demand
eliminates price rationing so the development of underground markets may occur
some consumers get the good at a lower price and some consumers get nothing because of excess demand
producers have a reduction in producer surplus and revenue decreases
society loses becuse welfare loss is created and too few resources are allocated for production however it might be worth the loss, market failure remains
government are losers: either the government doesnt apply subsidies and increases unemployment or government pays for subsidies to eliminate excess demand
eliminates price rationing so the development of underground markets may occur
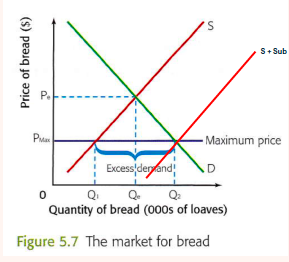
57
New cards
non price rationing
first come first serve
distribution of coupons
sell to favorite consumers
underground markets
distribution of coupons
sell to favorite consumers
underground markets
58
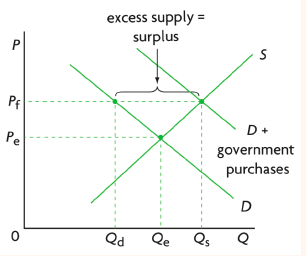
New cards
price floors
type of government intervention
when the government places a minimum amount that a producer can charge for a good or service
designed to protect producers
most common for essential firms
must be above equilibrium to have an effect
requires government purchases on top of it to work and shifts supply to the right and removes excess surplus so that producers and consumers both win
when the government places a minimum amount that a producer can charge for a good or service
designed to protect producers
most common for essential firms
must be above equilibrium to have an effect
requires government purchases on top of it to work and shifts supply to the right and removes excess surplus so that producers and consumers both win
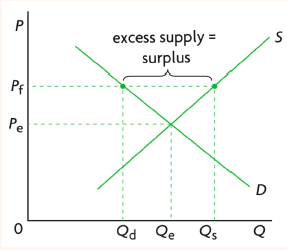
59
New cards
evaluation of price floors
surpluses and excess supply
consumers are losers: reduction in consumer surplus as price goes up and demand goes down, some consumers will not be able to afford the good
producers charge a higher price for their good as price goes up and demand goes down, will not sell much og their goods
revenue goes down
society loses because welfare loss is created and too many resources are allocated for production however it might be worth the loss, market failure remains
government are losers: must buy products from producers to eliminate excess supply, can give excess supply to poor communities, and opportunity cost of the money for surplus
consumers are losers: reduction in consumer surplus as price goes up and demand goes down, some consumers will not be able to afford the good
producers charge a higher price for their good as price goes up and demand goes down, will not sell much og their goods
revenue goes down
society loses because welfare loss is created and too many resources are allocated for production however it might be worth the loss, market failure remains
government are losers: must buy products from producers to eliminate excess supply, can give excess supply to poor communities, and opportunity cost of the money for surplus