Ch 52 - Physical Environment & Biogeography
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1. Speciation rate is higher than extinction rate in the tropics
larger geographic area (largest diameter)
Warm and stable climate
2. Tropics had more evolutionary time to diversify
No ice ages like in temperate latitudes (increases accumulation of species)
More accumulation of species over time
3. Higher productivity in tropics
More resources and less competition: lower extinction rates
____ a natural process now altered by human activity
Greenhouse effect
_____ is the factor responsible for global climate patterns
Solar radiation
albedo
% of light reflected by any surface
Climate
Long term expectation of area's weather
Coriolis effect
Air and water deflect at different latitudes due to planet rotation
Deforestation leads to
higher temperature and lower precipitation
Distribution of species is determined by ____
evolutionary history
Ecological systems are _____
hierarchical
Global biodiversity peaks at ____
tropics
Global precipitation is maximum at ____
equator
habitat fragmentation
habitats broken into smaller pieces due to human interference (deforestation, agriculture, urbanization)
Hadley cells
Atmospheric circulation and precipitation (0o-30o)
Heat islands
pockets of warm air created by cities
Hypotheses that explain high diversity toward tropics
1. Speciation rate is higher than extinction rate in tropics
2. Tropics had more evolutionary time to diversify
3. Higher productivity in the tropics
In the northern hemisphere, wind blows ______
clockwise
In the southern hemisphere, wind blows ______
counterclockwise
Incoming solar radiation disperses into
20% absorbed by atmosphere
50% absorbed by surface
30% reflected (by clouds/atmospheric gas & surface)
The atmosphere absorbs ___ of solar radiation
20%
Earth’s surface absorbs ___ of solar radiation
50%
Clouds/atmospheric gas & surface reflects ___ of solar radiation
30%
increasing # of species
small far, small near, large far, large near
Large + close to mainland =
more species
Ocean currents redistribute ____
heat in the planet
Ocean gyres and surface currents
spinning motion of ocean created by prevailing winds
Patterns of biomes where plants may be similar due to global patterns of temperature and precipitation
Terrestrial biomes
Physical environment is determined by ____, not weather
climate
Prevailing winds created by
deflected air circulation and rotation
Rain shadow phenomenon is due to ____
mountain ranges being close to oceans.
Mountain causes dry side on lee-ward side (sheltered from prevailing winds)
smaller islands have less diversity
due to higher extinction rates (less resources, more competition)
Species diversity increases with
area (island) and proximity to source of species (mainland)
Subtropical deserts are formed around
30N and 30S
The amount of solar radiation received changes during the year, resulting in _____
seasons
The amount of solar radiation received changes with ____
latitude (E/W)
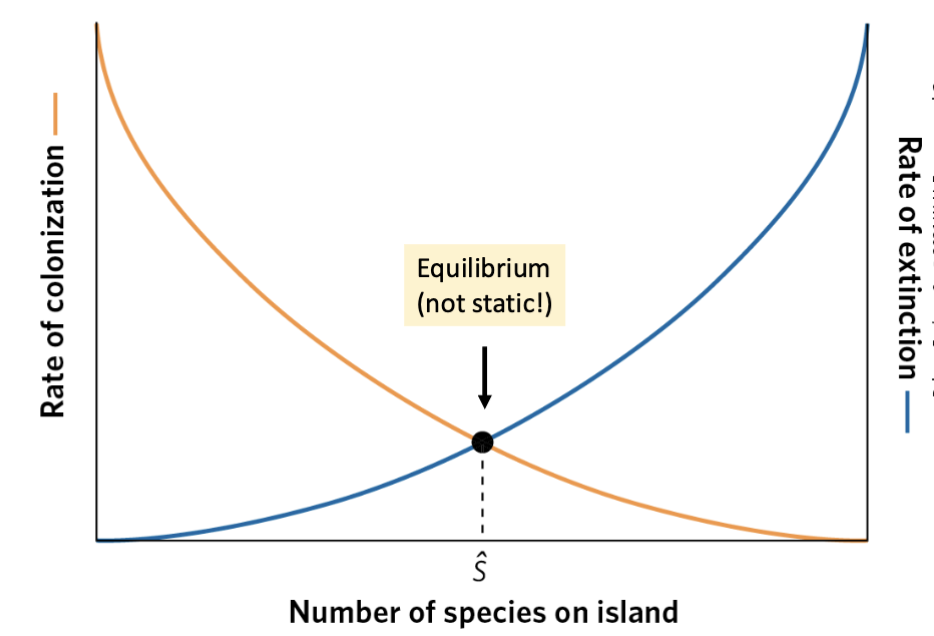
Theory of island biogeography
diversity in an island reflects balance between rates of colonization and extinction
Upwelling zones
deep, nutrient rich ocean water rises to surface
Vicariance
Separation via physical barrier
Weather
What happens in the immediate future/present
Where organisms can live is determined by ______
physical environment
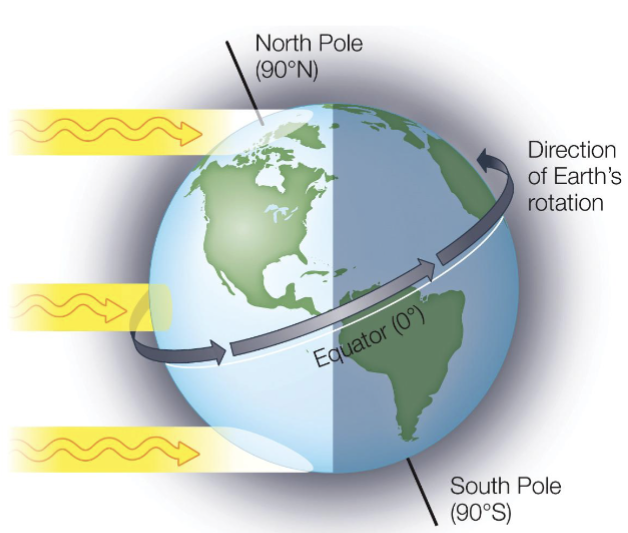
Angle closer to poles
Spread over larger area
More absorption by atmosphere
Less radiation reaches surface = colder
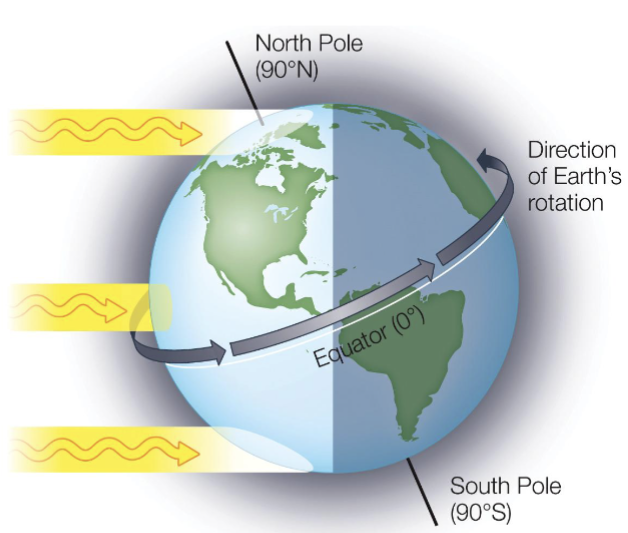
Angle closer to equator
Spread over less area
Less absorption by atmostphere
More radiation reaches surface = hotter
Laurasia
North pangaea split
Gondwana
South pangaea split
Biogeographic regions
Nearctic
Neo-tropical
Ethiopian
Palearctic
Oriental
Australasian
Antarctic