Language Change Flashcards
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What are the 5 stages of schneiders model?
Foundation, exonormaive stabilisation, nativisation, endonormative stabilisation, differentiation
What is foundation in schneiders model?
English introduced through colonialism, used by settlers, missionaries, administrators etc...
What is exonormative stabilisation in schneiders model?
English gains official status in law, education etc..., english seen as a prestige variety
What is nativisation in schneiders model?
English undergoes lexical, grammatical, phonological change due to contact with local languages, appropriation of individual purposes
What is endonormative stabilisation in schneiders model?
Codification of English begins, development of internal linguistic norms
What is differentiation in schneiders model?
Internal diversification from the established linguistic norms, social variations of the new English form emerge
What are some disadvantages of schneiders model?
- Eurocentric bias
- Doesn't account for multilinguistic nations
- Doesn't account for newer forms of globalisation in a digital age
Kachru's 3 circles

What is the Inner Circle in Kachru's 3 circles of English?
The traditional basis of English.
What is the Outer Circle in Kachru's 3 circles of English?
English has historical roots due to colonialism (norm developing).
What is the Expanding Circle in Kachru's 3 circles of English?
English is used as a foreign language for international communication (norm dependent).
What are some criticisms of Kachru's 3 circles?
- Clear cut divisions between Englishes no longer realistic
- Doesn't recognise lingua franca variations
- Suggestive of linguistic hierarchies
- Ignores intranational variations
What is McArthur's Circle of World English?
Despite the wide variations of English, all of them have a central World Standard English at their core.
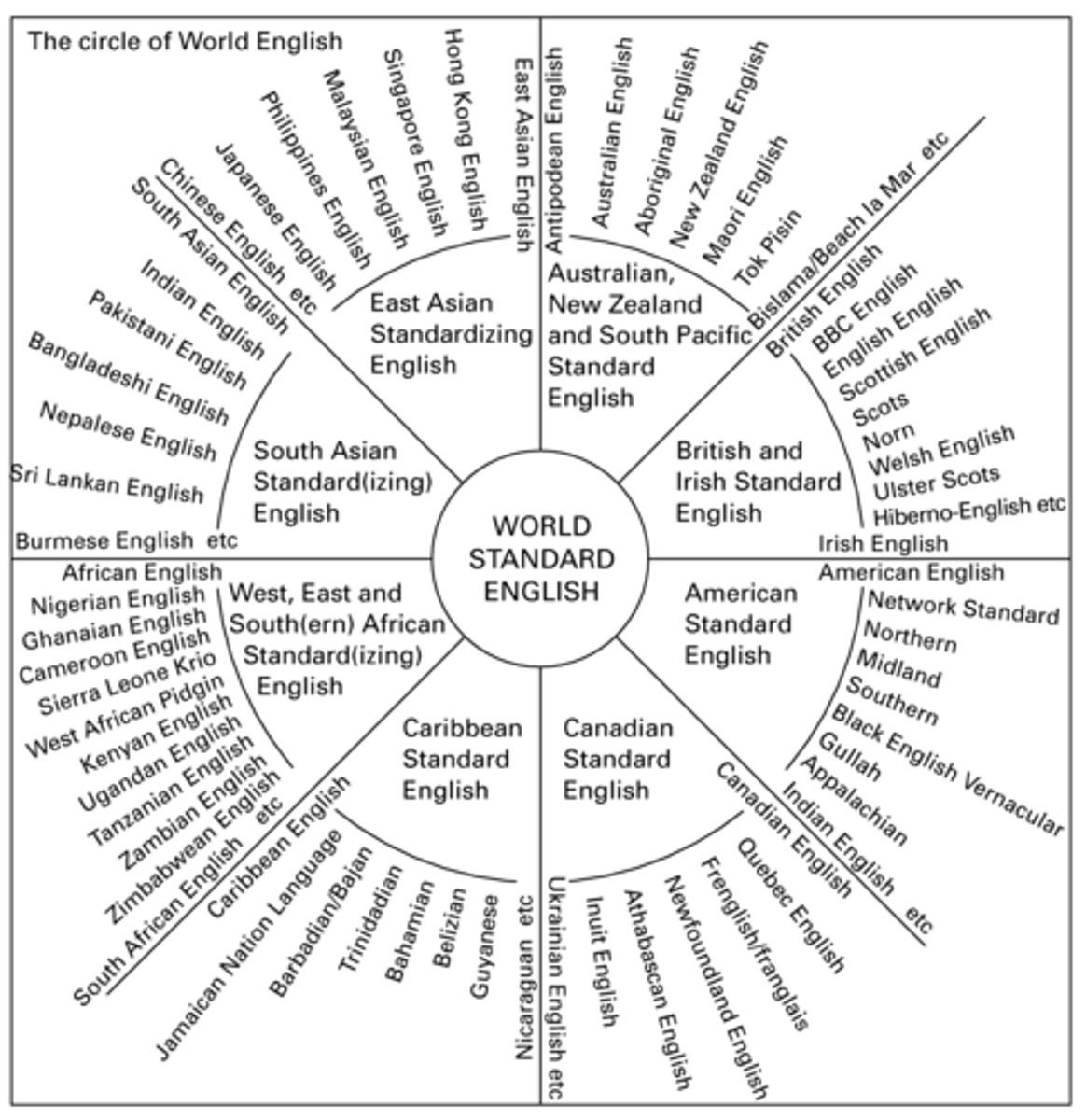
How are the norms described in Mcarthur's model different to that of Kachru?
Norms are based on linguistic codification rather than native or non-native status
What are some criticisms of Mcarthur's model?
- No single world standard english exists
- Doesn't address how they arose
- Under represents power imbalances
What is status language planning?
Changing of the social role of language and its prestige
What is corpus language planning?
Prescriptive rule changing by standardisation and codification
What is acquisition planning?
How language is taught and learnt
Why was Swahili chosen as the new national language of Tanzania after its independence in 1961?
- Was spoken as a lingua franca
- Not identified with any particular tribe
- Symbol of freedom and national identity
What is Aitchison's PIDC model of language change?
Potential - Gap for potential change
Implementation - A change occurs
Diffusion - Change slowly adopted by the population
Codification - Change is officially codified
What is the damp spoon metaphor Aitchison identified?
Bad English is a result of linguistic laziness
What is the crumbling castle metaphor Aitchison identified?
English has fallen from a once prestigious form
What is the infectious disease metaphor Aitchison identified?
Language change spreads like a disease amongst a population
What are the 7 types of innovative lexical change? Explain them.
Blending - Fusing of 2 words (smog)
Clipping - Remove part of a word (synchronise --> sync)
Compounding - Two words put together (blackbird)
Conversion - Changing word class (text)
Affixation - Adding of prefix or suffix
Backformation - Removal of morpheme to change word class (enthusiasm --> enthuse)
Reduplication - Repetition of words that sound similar (tip-top)
What are the 4 types of inventive lexical change?
Neologism - Making a new word
Borrowing (from another language)
Acronymising - Making acronyms (SCUBA)
Initialising - Word said as letters (BBC)
What are the 3 types of semantic change?
Neosemic shift - Adopts a new meaning
Bleaching - Broadening meaning
Reclamation - Removal of negative connotations
What are some extralinguistic causes of semantic change?
Psychological, sociocultural, encyclopaedic
Explain how psychological factors can cause semantic change.
Affect how people perceive a word, e.g: its use as a euphemism, its use in taboo subjects, its use in metaphors
Explain how sociocultural factors can cause semantic change.
A words meaning is positively or negatively associated with political power or social change.
Explain how encyclopaedic factors can cause semantic change.
Cultural changes lead to a change in how a word is classified or codified (often dependent on sociocultural change)
What are some linguistic causes of semantic change?
Metonymy - Name of an object is swapped for an attribute or adjective e.g: the crown (a monarchy)
Metaphors - Affect perception of a word due to association, semantic extension occurs
Ellipsis - Two words are frequently used together and gain a synonymous meaning e.g: starve and death
What grammatical features of English have stayed constant from Old English?
Auxiliary verbs, prepositions, conjugations, pronouns
What are the main grammatical between modern and old english?
Loss of distinctive dative case
Non flexible syntax (analytical nor synthetic)
Introduction of strong and weak verbs
What were the importance of inflexions on Old English?
Meaning was not derived from word order, inflexions used instead to derive grammatical meaning
What are some grammatical differences between Early Modern English and Modern English?
Lack of dummy auxiliary verb "do" in interrogatives
Use of modal auxiliary verb "shall" rather than "will" or "going to" in declaratives
More frequent use of passive voice
Use of of-genitive phrases in possessive constructions e.g: "the hood of the coat"
According to Beal in her chapter on syntactical change from "English in the modern times", what are the 4 uses of the dummy auxiliary "do"?
Negative constructions, "did not"
Inversion of auxiliary and subject (auxiliary comes before subject), "I have never met" --> "never have I met"
Avoidance of repetition, "and so did he"
Emphatic usage in exclamatory structures
What was the great vowel shift (14th - 17th centaury)?
Longer vowel sounds pronounced higher in the mouth e.g: /e:/ to /i:/, any vowel sounds that were already high in the mouth became diphthongs e.g: /i:/ to /aɪ/
What could have been some causes of the great vowel shift?
Influx of french loanwords
Middle-class hypercorrection to align with french prestige
Anti-french sentiment
Rapid migration after the black death
What were come consonant changes during the great vowel shift?
Loss of velar fricative /x/
Less trilling of /r/
Loss of /k/ sound
What are the 7 types of phonological changes?
Omission, insertion, assimilation, dissimilation, lenition, fortition, metathesis
What is phonological omission and insertion? Give an example of each.
Omission - Sounds removed from a word e.g: /t/ in castle
Insertion
Insertion - Sounds added to a word e.g: /p/ to hamster
What is phonological assimilation and dissimilation? Give an example of each.
Assimilation - Sound changes to sound more similar to surrounding sounds e.g: hand bag to hambag
Dissimilation - Sound changes to sound more distinct from surrounding sounds e.g: the second /f/ in fifth pronounced as /θ/ (th)
What is phonological lenition and fortition? Give examples of each.
Lenition - Weakening of a sound e.g: /t/ in water in American English, becomes more of a /d/
Fortition - Strengthening of a sound e.g: addition of an extra vowel sound, "bEEautiful"
What is Labov's substratum theory?
Language change primarily occurs due to contact with other languages, in the past due to trade and colonialism, now due to social networking and immigration
What are acquisition imperfections according to Labov?
Errors occur in pronunciation and syntax (rarely vocabulary) that are passed on to subsequent generations.
What example of acquisition imperfections does Labov explore?
Yiddish hypercorrection in America and its influence on the New York accent
What is Halliday's Functional Theory (Systemic Functional Linguistics)?
Language changes to fit the needs of its users to fulfil lexical gaps or meet functional shifts
What are the 7 micro functions of linguistics that Halliday outlines?
Instrumental, regulatory, interactive, personal, heuristic, representational, imaginative.
What is Halliday's instrumental micro function?
Language is used to fulfil desires, practically expressed through simple verb phrases e.g: "I want", "Can I have..."
What is Halliday's regulatory micro function?
Language is used to control the behaviour of others through commands, persuasion or requests
What is Halliday's interactive micro function?
Language is used to form relationships e.g: "I love you"
What is Halliday's personal micro function?
Language is used to express personal opinions, feelings or identity
What is Halliday's heuristic micro function?
Language is used to discover or enquire
What is Halliday's representational micro function?
Language is used to convey facts and observations of the world
What is Halliday's imaginative micro function?
Language is used to create imaginary constructions
Why did Chaucer decide to write The Canterbury Tales in English and not Latin or French?
English was the language of the working classes, whereas french and latin were the languages of higher education, law and government. The use of English democratised literature, making his works more accessible.
Which English dialect did Chaucer use? Why?
London dialect due to the rising economic and political power of the city, being the seat of royal government and many London-based merchants.
What was significant about the time in which Chaucer was writing?
Was at a transitional stage in English, where there was a shift to a more syntactical system of language rather than inflectional.
A Short Introduction to English Grammar (Lowth 1762)
Attempted to standardise English on Latin-based rules and prescriptions.
What were some rules that Lowth outlined?
Prohibition of double negatives, discouraging split infinitives (no adverb between "to" and the verb), preference of "whom", prohibition of double superlatives