COA424: Aquaculture Exam 1
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Biochemical Oxygen Demand
measrument of the rate at which microbes degrade organic matter using oxygen
amount of O2 that would be consumed if all the organic material were oxided by microbes
Meausring BOD
Use oxygen meter to measure one sample
Seal the other and isolate in the dark for 5 days, and remeasure
BOD: 1st reading- 2nd readings
Chemical Oxygen Demand
Oxygen used in biological and non-biological oxidation of all organic material in water
Sample oxidized w/ acid and heat. Amunt of O2 required measured
Always higher than BOD
more oxidizable (biological treatable) material is
greater ratio BOD:COD means
Phosphates
aturally occurs in rocks and minerals, mineralized, organic P (aquaculture)
Water soluble
Plants uptake
Redfield ratio
106:16:1
C:N:P
Nitrogen Cycle
Decompostion by fungi and bacteria → NH2→ Oxdiation by Nitrosomonas Bacteria→ NO2→ oxidation by Nitrobacter bacteria→ NO3→ incopration into plant protein OR reduction by anaerobic detrinyfing bacteria (N2)
nitrosomanas
bacteria that oxidizeds NH3 to NO2
nitrobacter
bacteria that oxidizes NO2 to NO3
Total Ammonia Nitrogen (TAN)
Meausre of unionized-ammonia (NH3) and ammonium levels in water
→ ratio of ammonia and aommonium varies in equilibirum
→ determined by pH and water levels
ph and temp
TAN increases with increasing ______
Turbidity
causes light to be scattered or absorbed rather than transmitted through water in a straight line
caused by suspended materials in the water: soil partickles, plankton, and organic detritus
Total suspended solids processing
Filtered through a glass fiber filter
Dried and weighted
Settle by gravity
Determined total amount og suspended soils in mg/l of sample
Total Dissolved solids
Solids that pass through a filer with a pore size of 2.0 microm or smaller
Said to be nonfitlerable (?)
Steps of processing:
Liquid dried
Residue weighed
Calculated as mg/l
Volatile Suspended Solids
Steps of processing:
Heat to 550 degrees
Rough approx. of the amount of organic matter present in the solid fraction of waste water, activated by sludge and industrial wastes
>500 mV
redox level that is toxic to life
300mV
optimum levels of redox potential
oxio-reduction potential
measure of the ability to lose electrons or gain electrons
high reading: higher availability of oxidizing agents in the water
high oxdation levels increases bio-degradability and reduces toxicity
Tolerance range
critical thermal max and min
temp is increases progressivley to determine lealth end point
select species for outdoor production system to avoid losses
determining thermal min and max
Optimum tempetaruere
temperature determination involves comparsion to zootechnical parameters at different temperatures
ex: growth rate, food conervsion index, bioenergetics modeling
Preferendum
can be assessed based on field sampling in wild or experimentally in selection trails
isomatic
300-400 mosm or salinity of 12-15: associated with optimal growth paramters
damages GILLS and other tissues
at low concentrations, NH3
damages nervous systems and death
at high concentrations of NH3
1 ppm
toxic concentration s of NH3 in sw
Gill lesions
Edema in the skeletal muscles
Affects respiration
nitrate toxicity
Freshwater
nitire is toxic for fish living in this type of environment
2-3 ppm
oxygen levels that result in mortality events
bubble gas disease
supersaturaiton of O2 and N2 resutls in bubbles in eyes, gills, skin, and cause death
> 80%
comfort levels of O2 for most fish
Chloramine
saturation of this compound to tap water to kill microorganisms, can persist for days or weeks
removal is done through a blaster
causes Necrosis to gills
metals
this has toxic effects to inverts at levels as low as .02 ppm
supersatruation of nitrogen
occurs with rapid cahnges in temperature and saturation, entrainment of air through leaking joints or pump seals or excess nitrogen source in water
alkalinity
the buffering capacity of a liquid, resistane to pH changes
Concentration of all bases in seawater that can ACCEPT a proton
usually bicarbonate, carbonate, or borate
Hardness
carbonate alkalinity alone (Ca and Mg) moslty used in FW studies
Alkanility measurment
mesured by titration to a known end point
20mg/L
minimum alkalinity
Gravity Aeration
Water is cascaded over screens, rocks, beads to break it up and increases surface area for exchange
surface active aeration
Agitate culture water up into the air
diffuser aeration (active)
Bubbles air through water which forms airstones
ex:venturi device, u-tube
u-tube
device that ibjects air on the downlfow to increase contact
Venturi device
device that restricts flow, increases speed, and decreases psrrue to get air stuck and increase exhange rates
Downflow Contactor
Device used for aeration
Water and O2 are located in the top after injection
Water velocity decreases with increasing diameter
Downward velocity then equals buoyancy of the bubbles, which increases the SA for exchange and stays suspended in the water
Results in 95-100% transfer
Biofloc system
type of intensive closed system
that mamanges waste differently than the reciriculating system
uses microbial biotechnology to increase edidcy and utlization of fish feeds
uptake nitrogen by adding carbon sources
Advantages of closed systems
Complete control over environment
Biosecure
High density: lots of animals, space efficiency
Decoupled from water source: can implement this strategy anywhere
Limited discharge rates
Disadvantages of closed systems
High maintenance, and labor costs
Complex filtration and management
Equipment
The high density of fish: no room for error and no buffer
Decoupled from water source: no room for error
4 main issues in recirculation aquaculture system
Oxygen
Solid waste
Nitrogenous waste
Dissolved organics
.5
1 kg of feed requires ____ kg of O2
Packaged Column
techqniue to degas CO2
water is cascaded over screen and air is pulled up and outgasses
pulls out O2 as well, may need to increase O2
1.38 g
____ about of Co2 produced for every g of O2 consumed
Settling Tank
technique used to mechanically filter out solids
Use gravity, and decrease flow as heavy stuff settles
Coagulation of particles does increase efficiency
Catches particles >100 microns
Take significant space
Centrifugation
technqiue to mechanically filter out solids
Spins water, more dnes particles settle faster
Continuous flow centrifuge or hydrocyclone
Increased flow is required, usually pumped
Catches particles >75 microns
Cartidge filters
Useful for small systems
Not as efficient to big systems, must be constantly replaced
Prone to fouling
Rotary drum filters
type of mechanical filtration of solids
self-cleaning
Big, mechanical, use lots of water
Choose mesh sizes up to 50 micro m
Common in raceway and pond systems
Particle filter
Mechanical method of solid filtration
Uses sand particles to trap solids
Propeller-washed bed filters
Water is forced through the bed of particles, where the solid are trapped
Cleaning occurs when flow is required
>25 microns
Foam Fractionation
Type of mechanical filtiraiton of solid particles
Air is injected into the water to form tiny bubbles
Bubbles create an air-water interface that traps contaminants
Hydrophobic molecules are attracted to air molecules
Removes dissolved susbtances and fine particles (<25 microm)
4.75g, 7.14g
1 g of waste water requires ___ of O2 and _________ of bicarbonate
Submerged
type of biofliter
made out of gravel, shells, palstic
suitable for systems with low biomass
water is puleld through it for filitration, but O2 limited
Trickle
Type of biofilter
Suspended media in air to solve O2 issue
Water is trickled by gravity
drum
type of biofitler
moves media throught he water
contact occurs on the surface for aeration
Moving bed bioreactors
type of biofilters
utilizes floating plastic carriers (media) within the aeration tank to increase the microorganism available to treat wastewater
media provides increased SA for microorganisms to gorw in aeration tanks
media is cosntnatly agitated by bubbles for aeration systmes that adds O2 at the bottom
Centrifugal ual pump
impeller that slings water out of the center, remaining vacuum slings more water in, increasing KINETIC FORCE
auger (corkscrew pumps)
type of pump that picks up water at the bottom of the system
Liquid rings
pump that ceates a ring of liquid around teh side of a pump, which creates a suction area in the middle
water flow produces a vacuum
choke it
to convert conetrigual pumps to head pressure and thus produce potnetial energy, you have to
Airlift
type of pump with no moving parts and a low head (15m lift)
air is injected into a column of water> bubbles move up and moves water out w/ increased bubbles
Continous weak sunction
L:D important
UV Light
disingection tech.
disrupts unsaturated bonds in DNA
requires space
dose depends on the goal, noramly 250nm is used
O3
Disinfect tech.
pass air through high voltage to create O3, bubbles through water like a protein skimmer
powerful oxidizer
adds O3 to the system
dangerous: corrosive and degrades elastic
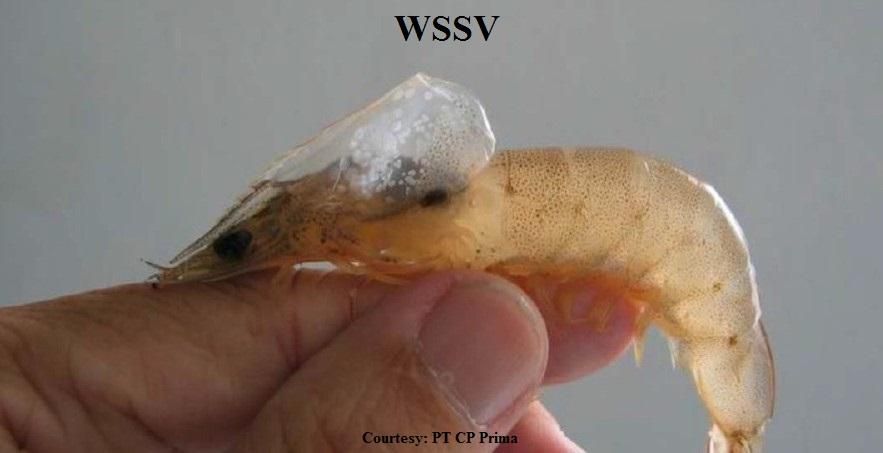
white spot syndrome
type of dsDNA 300kbo
enveloped virion
causes 80-100% morality within 10 days
impacts shrimp populations espeically in pond systems
impacts the pancreas
alwasy a revision for animals in a pond to infect
first emerged in 1992 in taiwan

Taura Syndrome Vrius
type of ssrna virsus
non eveloped viron
paneid shrimp pathogen
gross signs: melanated spots on carapace
histological signs: disrupts digestive eptihelial systems
emerged in South America in early 90s
Infectious Salmon Anemia Virus
type of ssRNA noneveloped viron
apart of family Orthomyxovirus
consists of 8 RNA sequeuces that will coe apart and resemble, generating a DIFFERENT virus
develops slowly (incubation period of 2-4 weeks)
significant problem anywhere that grows atlatnic salmon
gross signs:
systematic virus, hemoragging on skin, anemia, pale gills, enlarged liver and spleen, hemorages in visceral fat
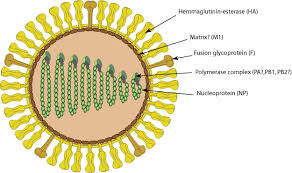
V.parahaemolytics
type of bacterial pathogen
symptoms:
Acute Heptopancreatic Necorsis syndrome
Shrimp early mortaility syndrom
disrupts pancreatic function
V. anguillarium
type of bacteria that affects close to 50 species of fresh and saltwater fish
major obstacle to salmoid marine culture
mycobacterium marinum
gram positive,
Slow growing
CHRONIC fish Diesease
Non-motile
Symptoms:
Weight loss
Open ulcers
Distended Abdomen
Anorexia
Perkinsus marinus: dermo
Host: eastern oyster, Crossotrea viriginca
Depends on: temperature, salinity
Temps >20 C and salinity >15ppt
Spread:
80% infection oyysters in GoM and along the US atlantic cost
Not as devastating effects in the gom due to increased ouster growth rate
Spreads via hemolymph through tissues: causes deterioration and organ failure
Depleted host energy resources, causing decreased growth and reproduction and increased mortality
Amyloodinium ocellatum
DINOFLAGELLATE
Parasitic
Spread:
Infects warm water marine and brackish water bony fish
Causes extensive mortailityes in aquaculture systems
Development:
Trophont (feeding stage)
Tromont (reproductive stage): can produce up to 250 dinospores for 1 tromont
Dinospores: infective stage
Hematodinium spp
DINOFLAGELLATE
Crab parasite
Symptoms:
Bitter crab disease
Survivial range: 12-61 ays
Simialr lifecycle to Amyloodinium
Aphanomyces invades
Epizootic Ulcerative Syndrome
Oomycete
More than 100 estuarine and reshwae=ter species are susceptible to EUS
Siginficaint impacts for aquaculture industries
Life cycle:
Direct (no intermediate host)
Has an sexual and sexual life stage
Spread:
Emerged in east asia in the 70s
Symptoms:
Ulceratie lesions
Granulomatus response
Crypotocaryon irritinus
Cilitate
Pariaist of wild and cultured MARINE fish
Prevalent in ornamental fish culture
Symptoms:
Internal parasite, encapsulated in the epsidermis
Neobendeia
Helminth Ectoparasite that lives on fishes skin
Particular problem in net pen aquaculture
Life cycle:
Oviparous: consists on eggs and hatching eggs
Viviparous variety: free swimming larvae that attach themselves to fish
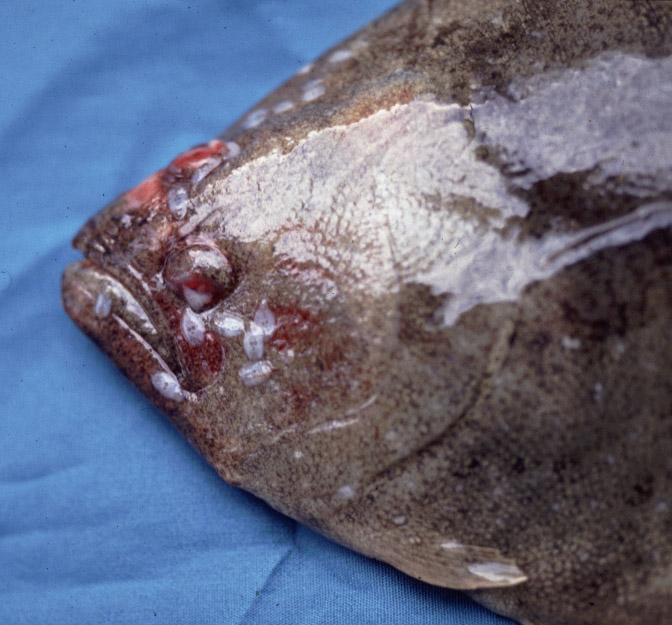
Caligus
type of copeopod parasite
“sea lice”
symptoms:
Consumption of fish skin
Life cycle: coepodid becomes chalmus→ chalmius stages molt into pre-adult stage→ motile adult stages→ mate on fish skin→ eggs hatch as free swimming nauplius
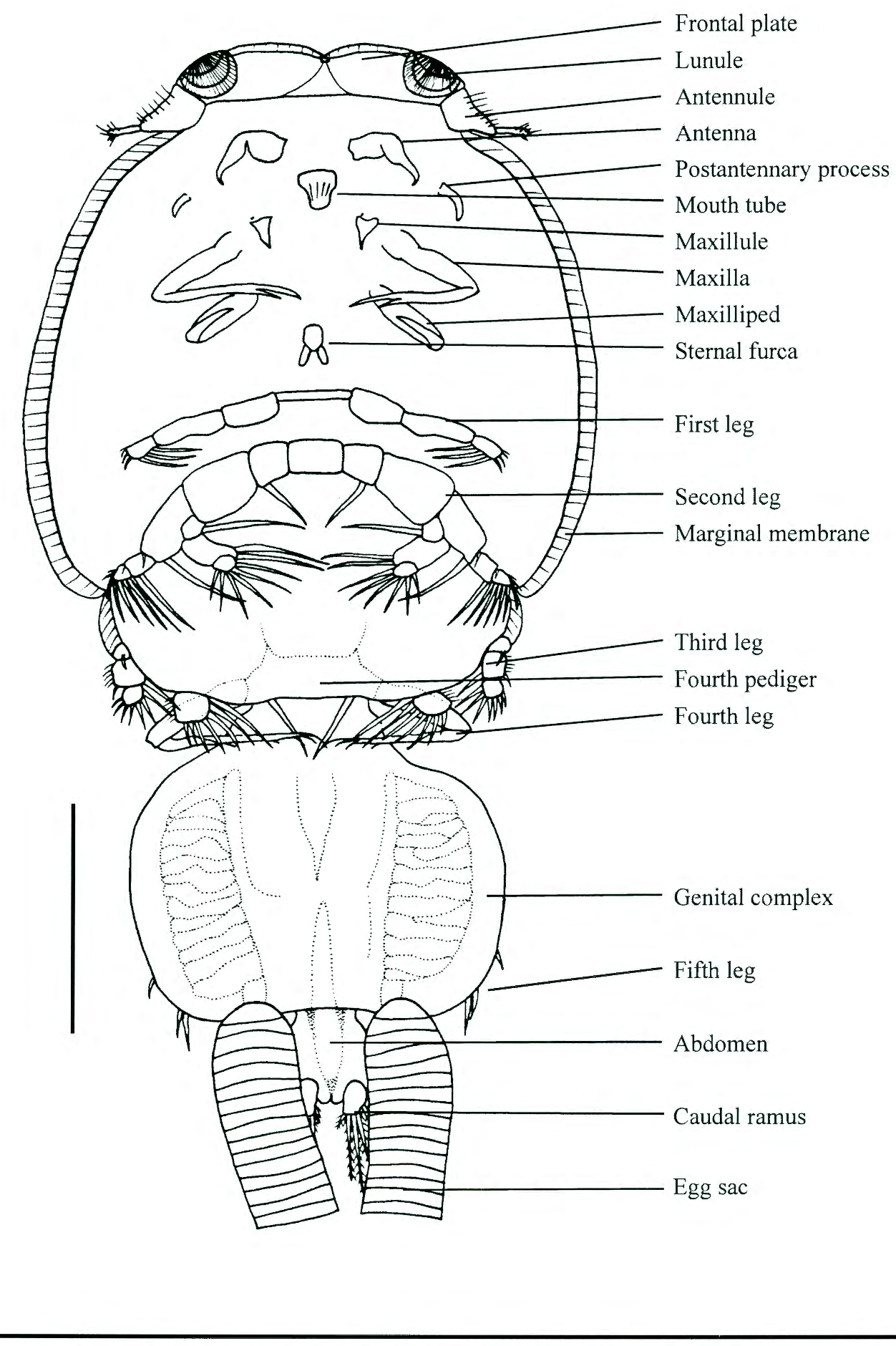
lepeoptherius
type of copepod parasite (sea lice) that is prolific in the atlatnic ocean, more pathogentic to atlantic fish than pacific s
Morbidity
illness in the system over a period of time
incidence
frequency of disease in a population over time in relation to the population in which it occurs (new cases/time)
prevelance
frequence of a disase at a particular point in time in relation to the population ( % infected)
V. vunlificus
type of vibrio bacteria that causes foos posinioning and systhamtic infecions in humans, found in shellfish