Week 7: Quantitative Hypothesis testing
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is a confidence interval?
A range within which a population parameter is likely to fall, based on sample statistics.
What is the sample mean?
The mean of a sample, used as an estimate of the population mean.
It is known as a point estimate of the population mean
What is the population mean?
Mean in the population
What does a 95% confidence interval indicate?
That 95% of samples will have the true population mean within this interval.
→ Greater variation in population = greater confidence interval
→ Larger samples = smaller confidence intervals
How does population variation affect confidence intervals?
Greater variation in the population leads to greater confidence intervals.
How does sample size affect confidence intervals?
Larger samples result in smaller confidence intervals.
What is standard error?
The deviation of the sampling distribution of the mean.
What is the formula for calculating the standard error?
Standard error = SD / √n, where SD is the standard deviation and n is the sample size.
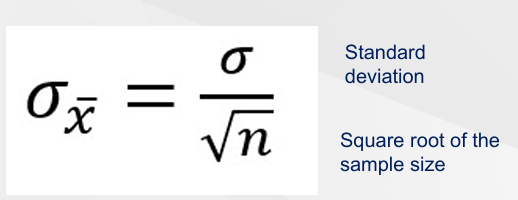
What are some issues with standard error?
• Small samples have larger confidence intervals.
• Larger samples have narrower confidence intervals.
• The larger the sample size the better the estimate of the population – better confidence interval – better approximate the mean -> Representative sample and random, probability sampling
What is the purpose of hypothesis testing?
To determine if there is enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
What is a directional hypothesis?
A hypothesis that specifies the direction of the expected effect between variables.
What is a non-directional hypothesis?
A hypothesis that predicts a difference between groups but does not specify the direction.
What is the central limit theorem?
As the sample size increases, the distribution of sample means approaches a normal distribution.
What is sampling error?
The discrepancy between the sample statistic and the actual population parameter.
What does a p-value represent?
The probability of obtaining the observed data if the null hypothesis is true.
What is the significance threshold commonly used in hypothesis testing?
A p-value of 0.05.
What does it mean if p < 0.05?
There is sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
What does it mean if p > 0.05?
There is insufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
What is a causal hypothesis?
A hypothesis that suggests a particular causal influence between variables.
What is a non-causal hypothesis?
A hypothesis that suggests a relationship between variables without implying causation.
What is the formula for calculating the 95% confidence interval?
Mean ± (1.96 * Standard Error).
What is the relationship between sample size and the accuracy of the population estimate?
Larger sample sizes provide better estimates of the population mean.
What is the effect of a one-tailed hypothesis?
It specifies the direction of the relationship or difference between variables.
What is the effect of a two-tailed hypothesis?
It predicts a relationship or difference without specifying the direction.
What is the logic behind null hypothesis significance testing?
To determine if observed data patterns are likely to have occurred by chance under the null hypothesis.