ECG practical
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
arrhythmias
an ECG is only used clinically to find ______________
anamnesis
clinical history
physical exam
we should only do an ECG after already doing:
ECG
thorax xray
echocardiography
blood tests
serology/PCR
blood gas analysis
CT scan/MRI
what complementary tests can we perform to assess the heart better?
thoracic xray
what is the best complementary test to perform to evaluate the lungs?
ECG
which complementary test should we perform if we want to evaluate the heart rhythm?
echocardiography
which is the best complementary test to evaluate the heart chambers?
hemopericardium
dilated cardiomyopathy
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
if there is an enlarged heart, what may be the cause?
a record produced by electrocardiography, representing a heart's electric activity. it is derived by an amplification of the electric impulses produced by the heart, and is measured by skin electrodes that capture the difference of potentials
what is an ECG?
-heart rate
-heart rhythm
-electrical axis deviation
-heart chamber enlargement
-abnormalities in the conduction of the electrical impulse
what information can we obtain by performing an ECG?
bipolar- the potential differences between 2 limbs (2 electrodes)
unipolar- the potential between one electrode placed on the body and a reference point that is typically an average of all the limb electrodes
what is the difference between bipolar and unipolar leads?
specific combinations of electrodes placed on the body to record the electrical signals from different perpectives
what are leads?
red- right front limb
yellow- left front limb
green- left hind limb
black- right hind limb
where do we place the red, yellow, green, and black electrodes on the dog's body?
right lateral recumbency
how should the dog be positioned in order to perform our ECG?
yellow- left thorax
red- right shoulder
green- left hind limb
black- chest or cranial left region of the left hind limb
where do we place the red, yellow, green, and black electrodes on the horse's body?
horse has negative QRS and sometimes has a double P wave because they have a much bigger heart, and the 2 waves represent the 2 atria contracting. in dogs, since they are much closer together (because of the smaller size of the heart), it appears as just 1 peak
what is the difference between the horse and dog ECG?
bipolar II
which lead to we use to assess the ECG?
length of the waves, segments, and intervals
height and morphology of the waves
electric axis
heart rate
cardiac rhythm
what do we want to assess when we look at an ECG?
atrial depolarization
the P wave of an ECG represents what?
ventricular depolarization
what does the QRS complex represent?
ventricular repolarization
what does the T wave of the ECG represent?
because it represents the electrical impulse traveling from the SA node to the AV node. when the impulse travels towards the heart's apex, it is positive.
why does the P wave normally appear positive in the ECG?
because when the impulse reaches the AV node, it goes slightly upwards, towards the base of the heart- which appears as negative
why does the Q wave negative in the ECG?
the AV is sending the electrical impulse to the apex of the heart
what is happening during the R of the ECG?
the impulse is now traveling up the ventricular walls, towards the base.
when the impulse is directed towards the heart's base, it appears negative on the ECG
the S of the QRS complex is negative because...
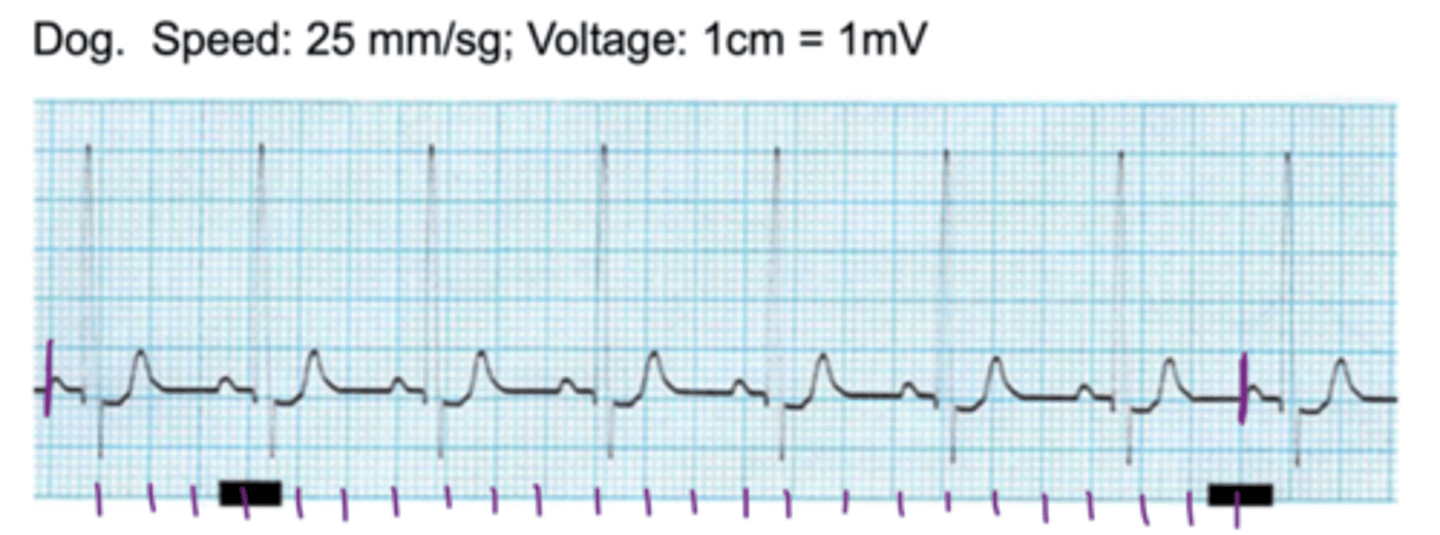
0.04; 5
if the ECG is run at 25mm/sec, each small square is _____ seconds. this means that _________ large squares= 1 second
5 large squares (each composed of 5mm)
if the ECG is running at 25mm/sec, how many squares make up 1 second?
compare them to a table of reference values
when we measure the wave lengths or interval lengths, what do we do with these values?
0.08 sec
if we are running the ECG at 25mm/sec, and the P wave is 2 small squares long, how many seconds does it take for the atria to depolarize?
0.02
if we are running the ECG at 50mm/sec, each small square (mm) is ____ seconds.
count the # of small squares and divide by 10
(in normal conditions, each cm is 1mV, but this can change according to the animal's size)
how do we calculate the voltage of a wave?
the time it takes for the atria to contract to the arrival of the impulse to the AV
(time elapsing between the beginning of the atrial and ventricular depolarizations)
the P-R interval represents what heart activity?
1.5 mV
(15 mm / 10)
what is the amplitude of this QRS complex?

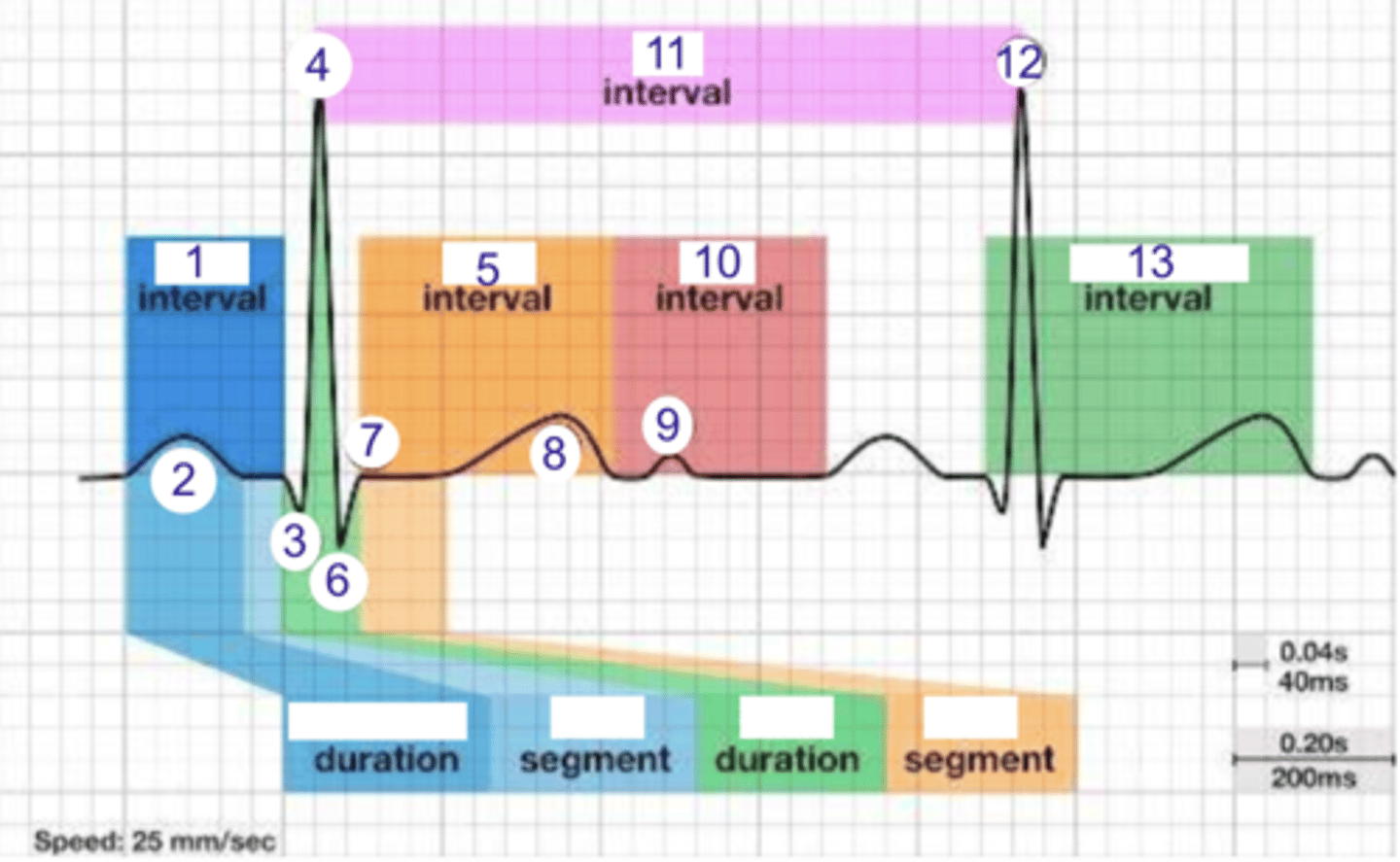
PR interval
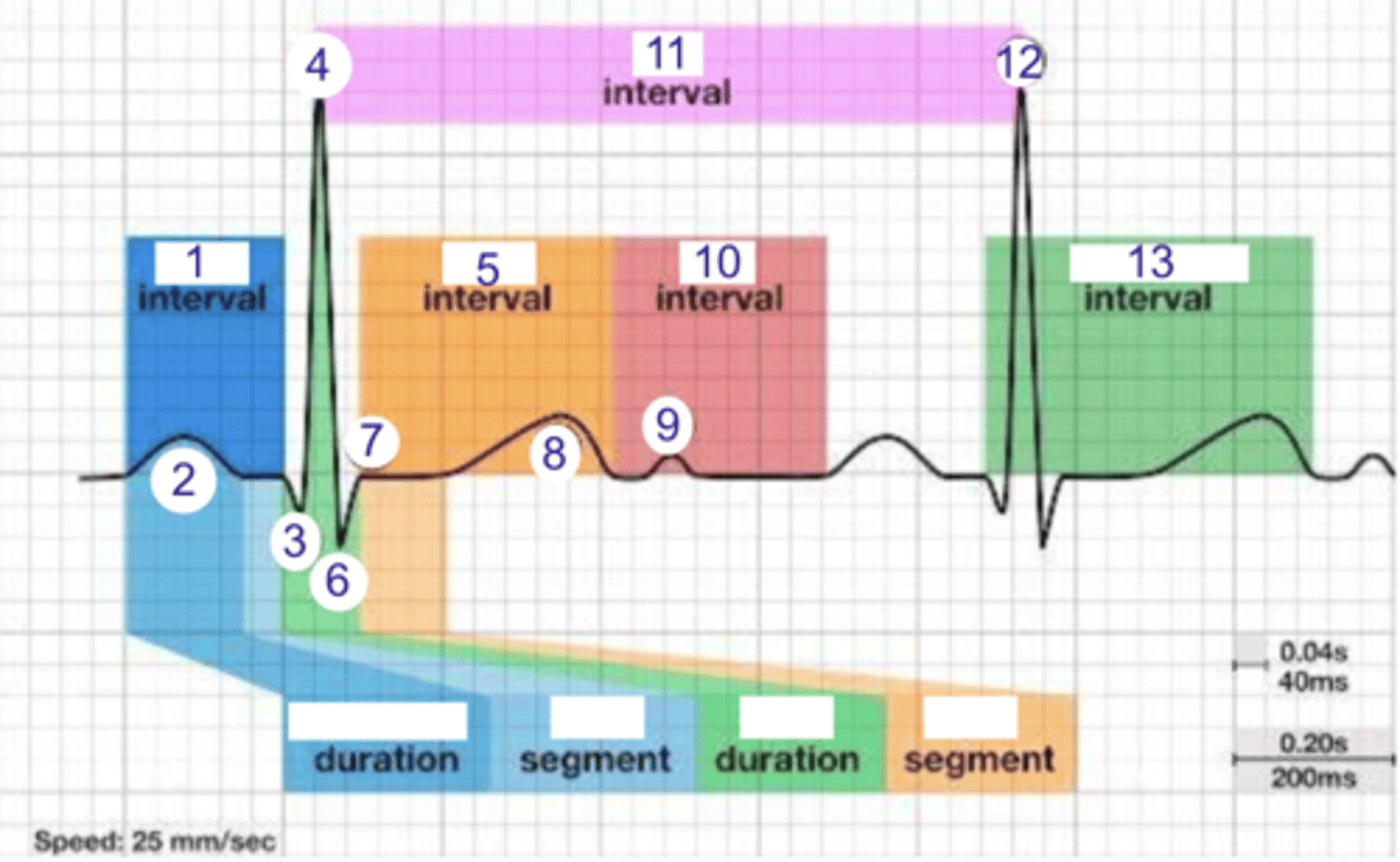
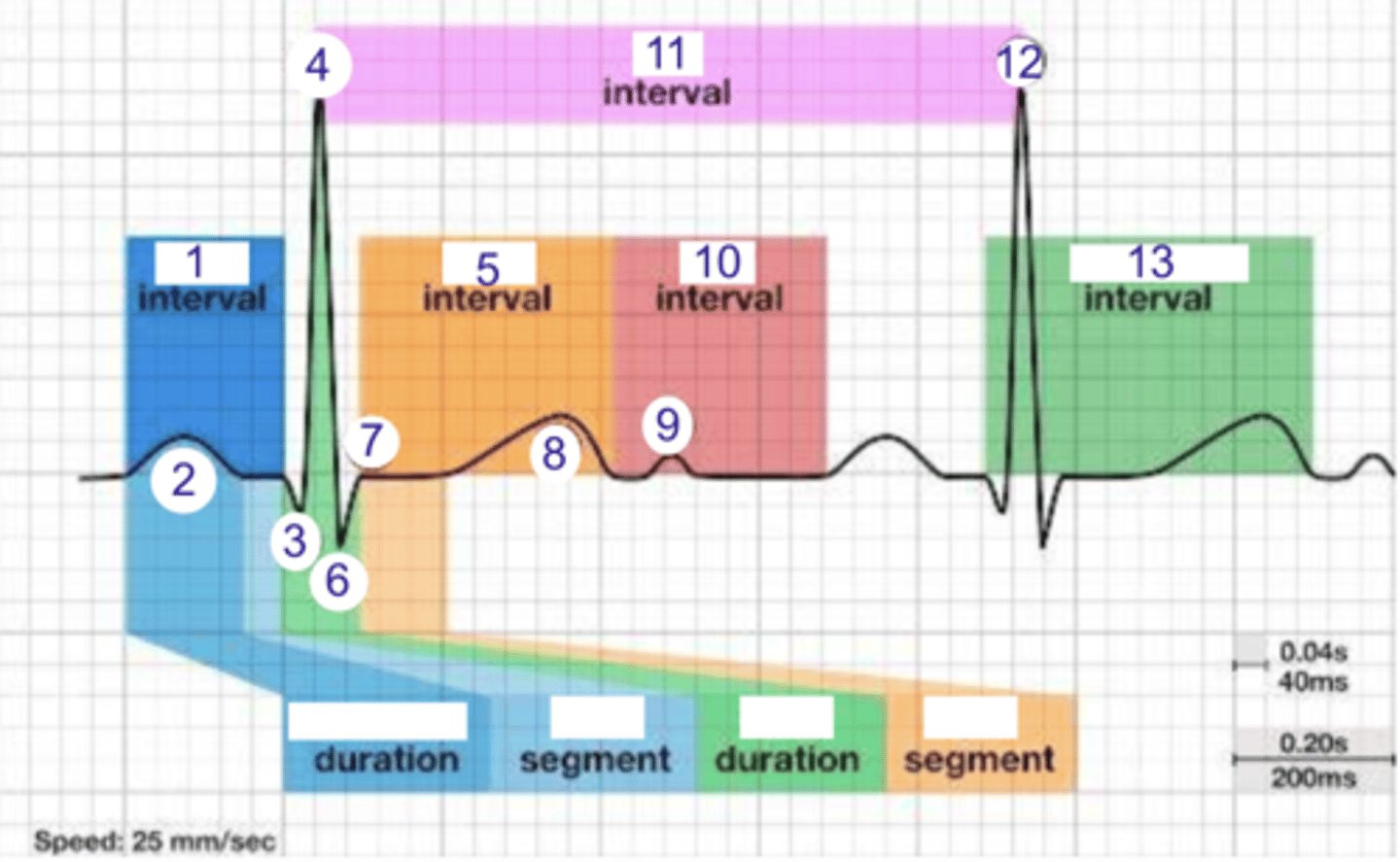
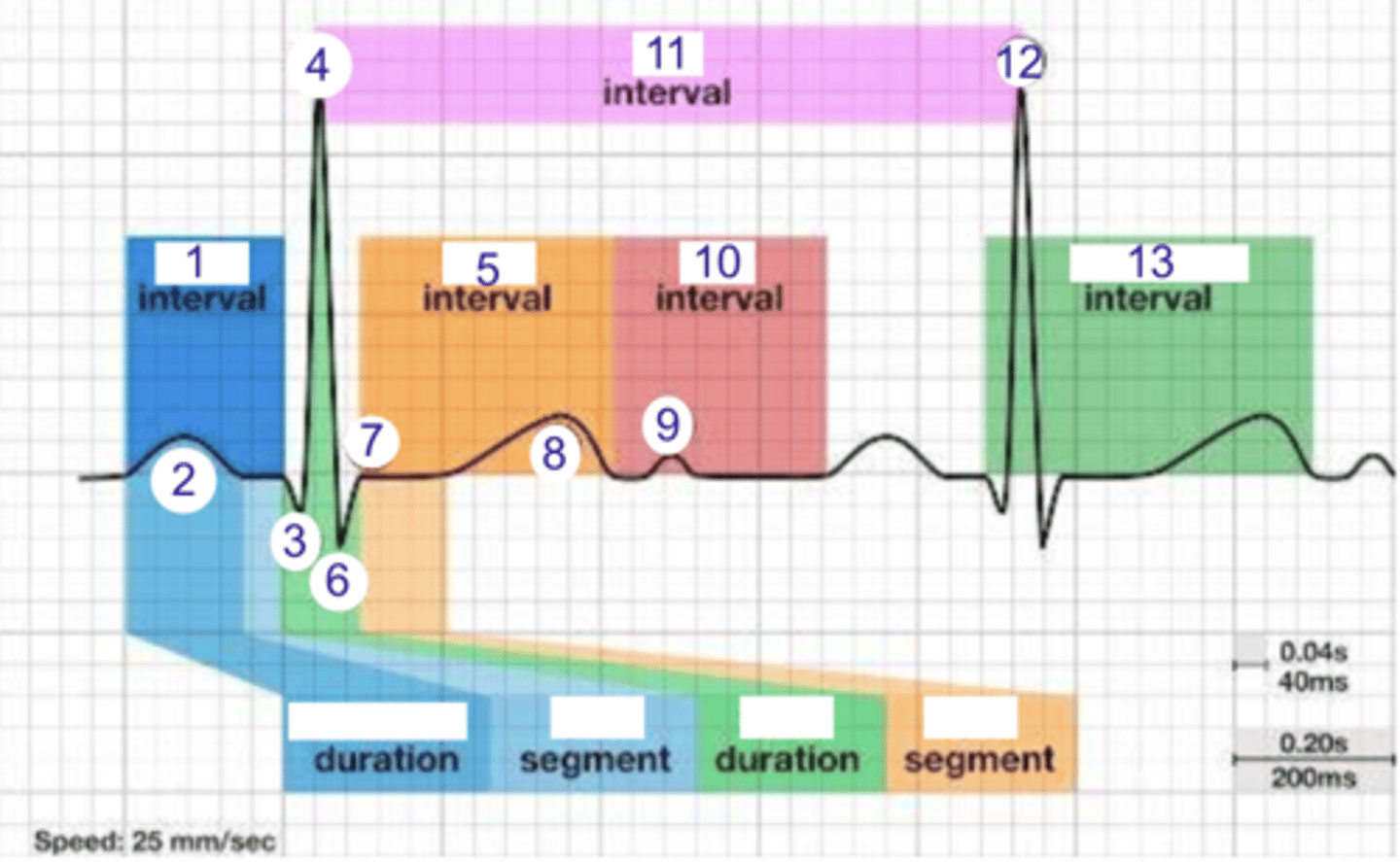
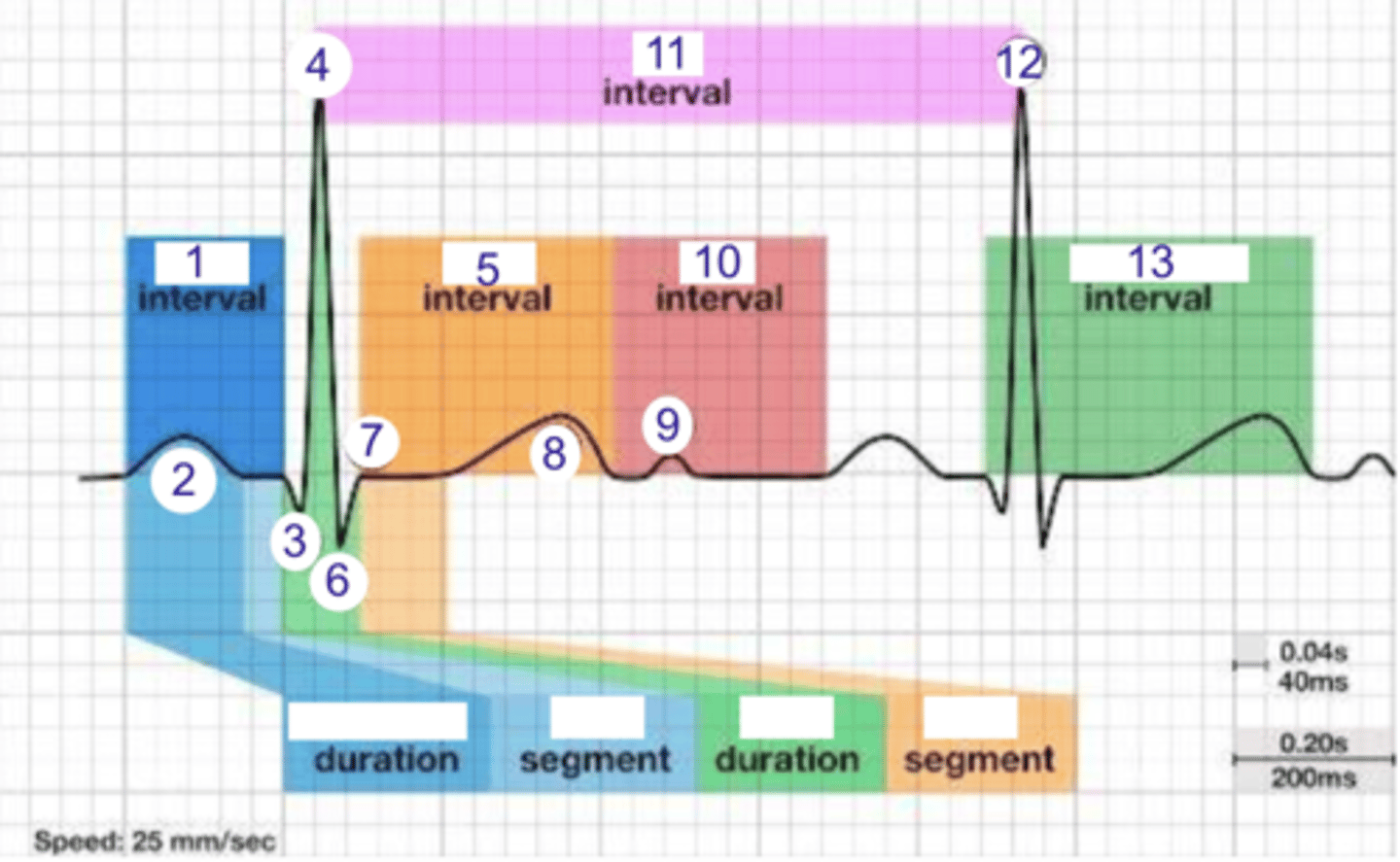
what is 1?
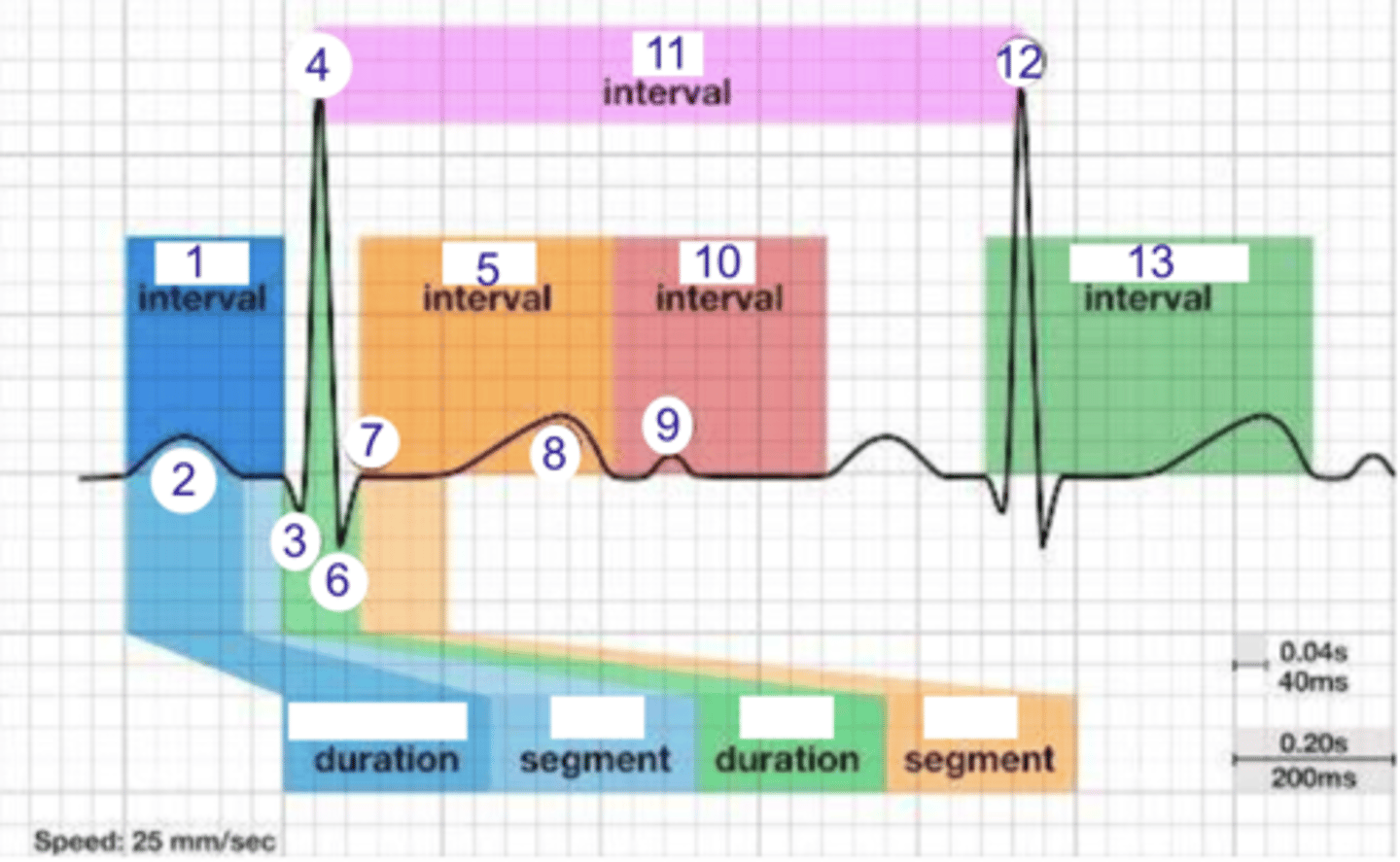
1
where is the PR interval?
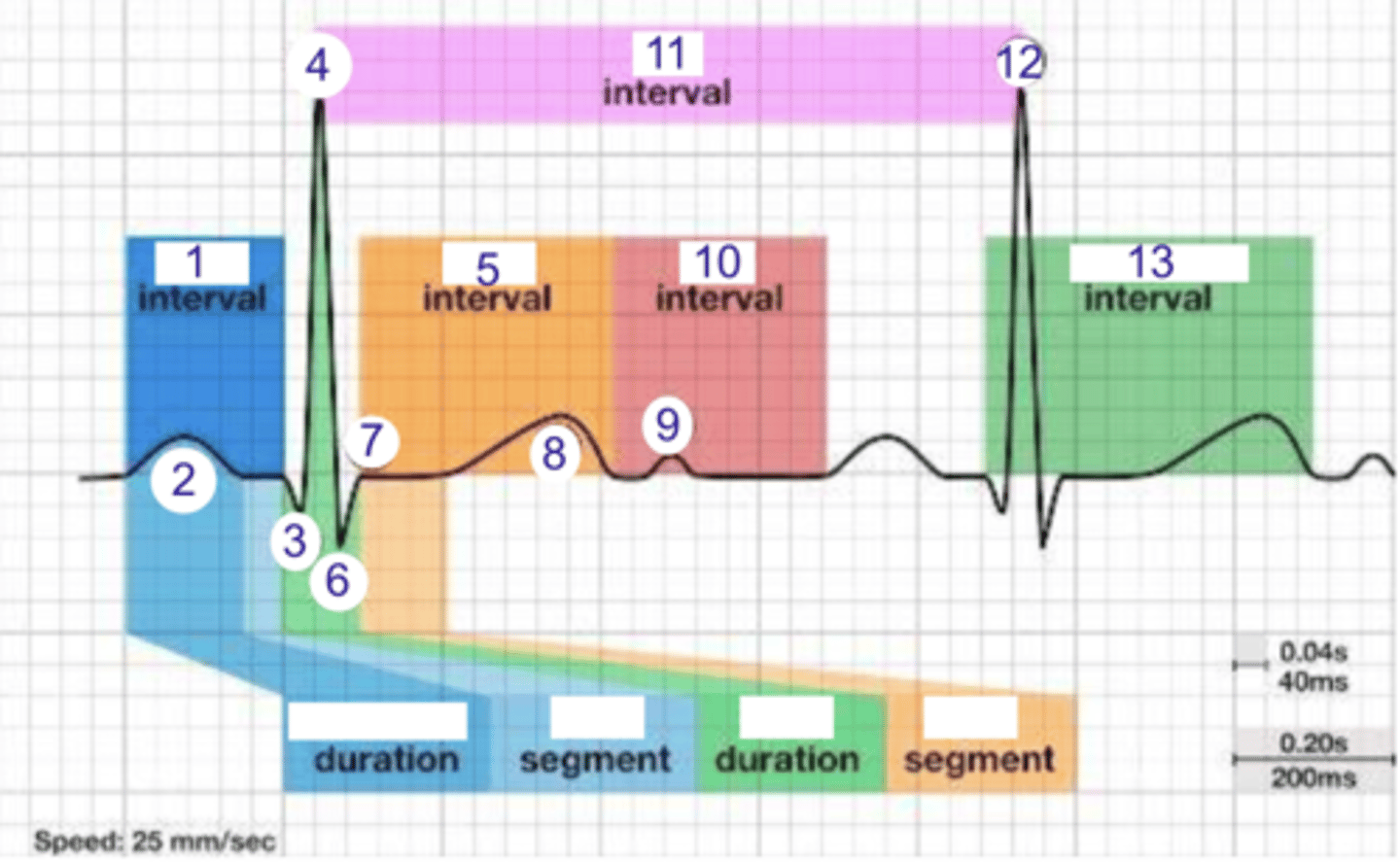
P wave (atrial depolarization)
what is 2?
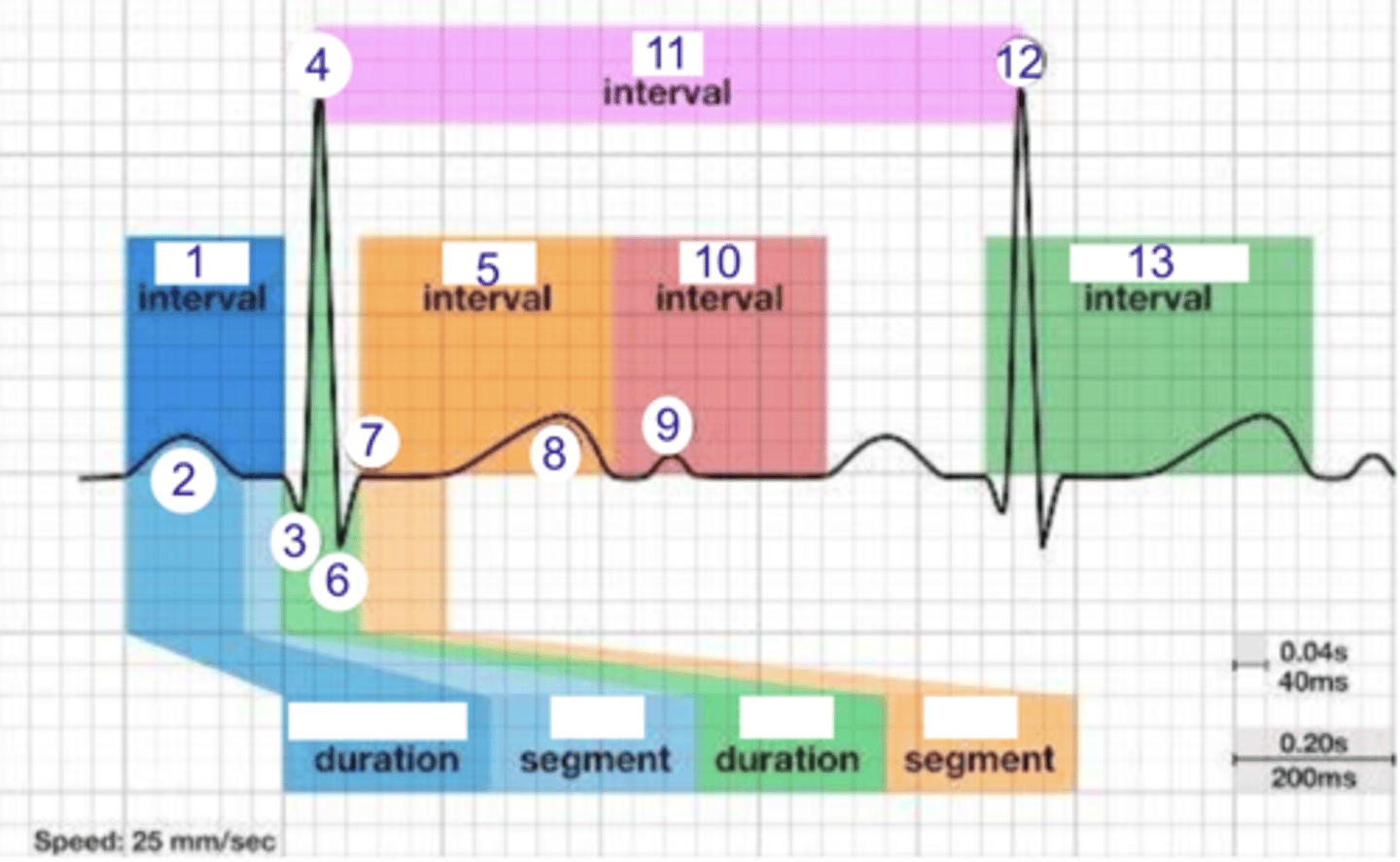
2
where is the P wave?
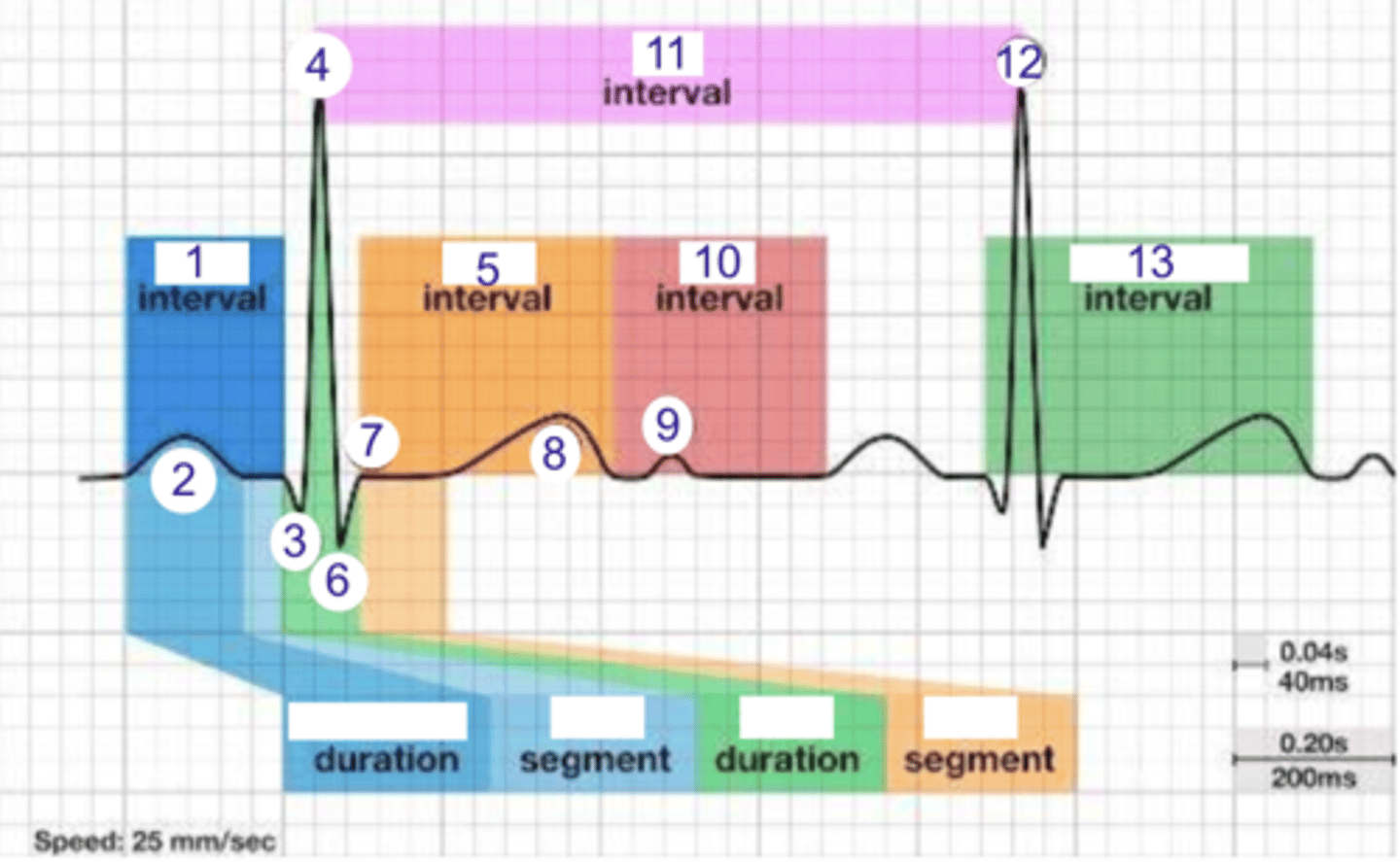
Q
what is 3?
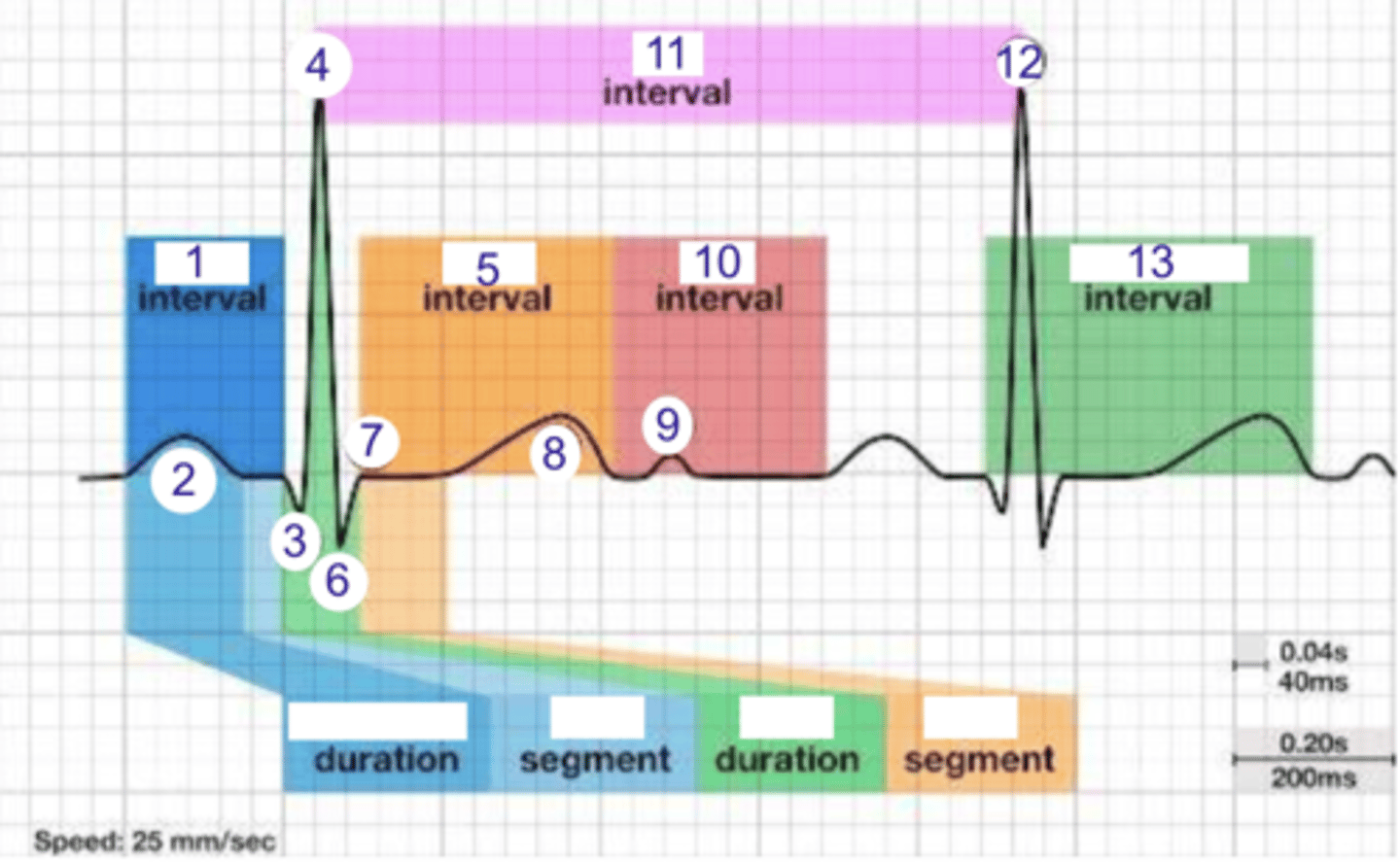
3
where is Q?
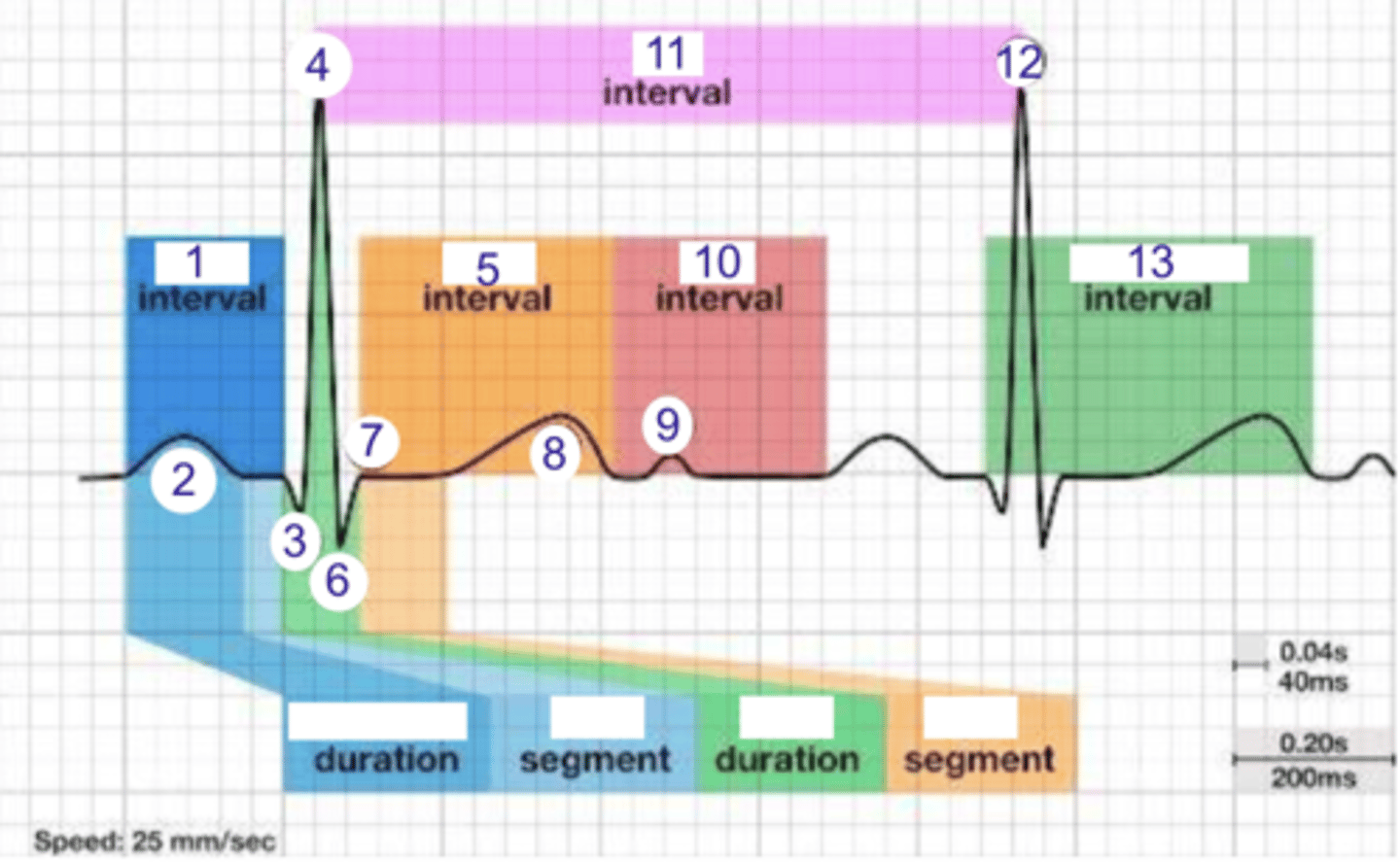
4, 12
where is R?
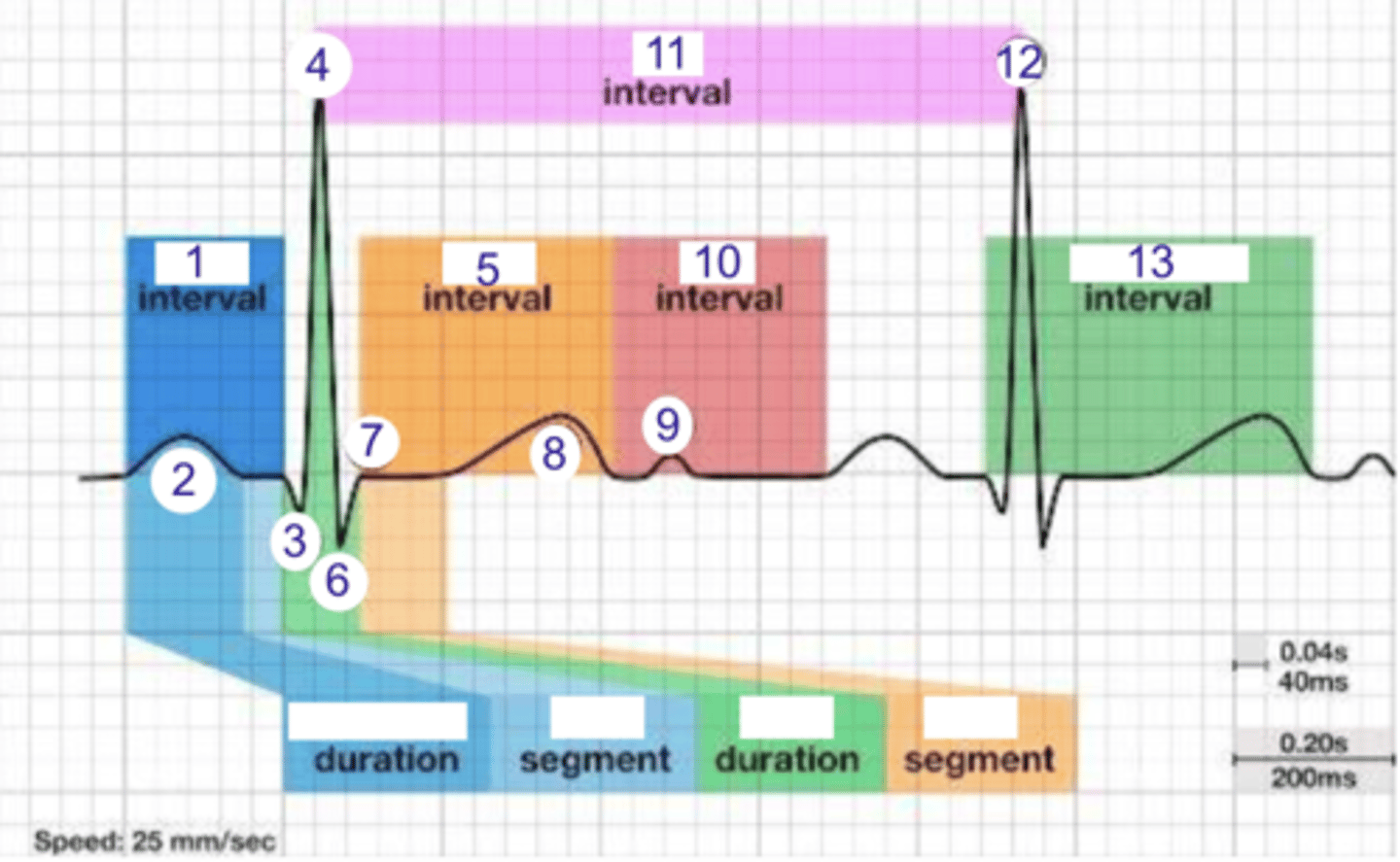
4, 12
what part of this ECG represents the impulse reaching the apex of the heart?
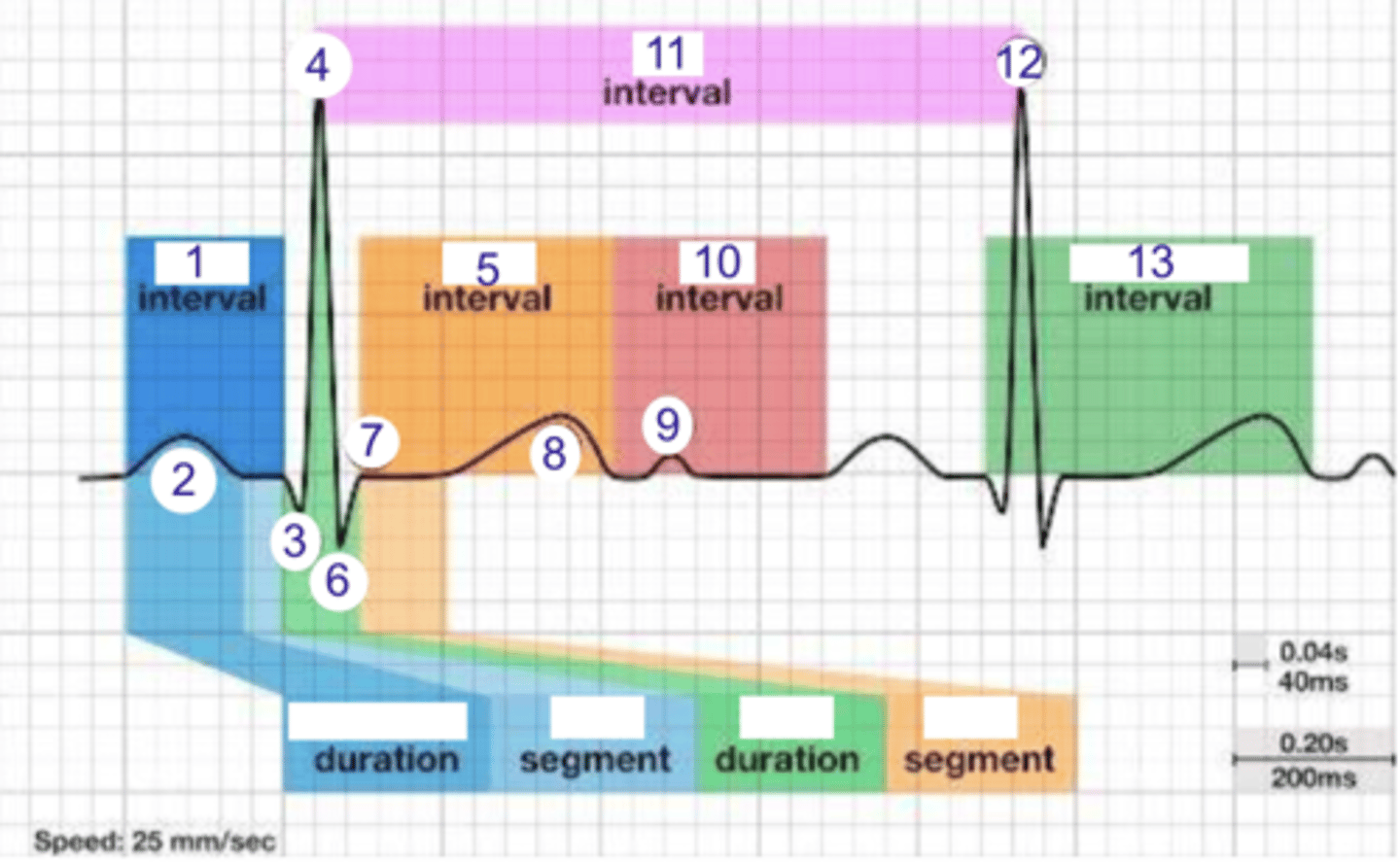
ST
what interval is 5?
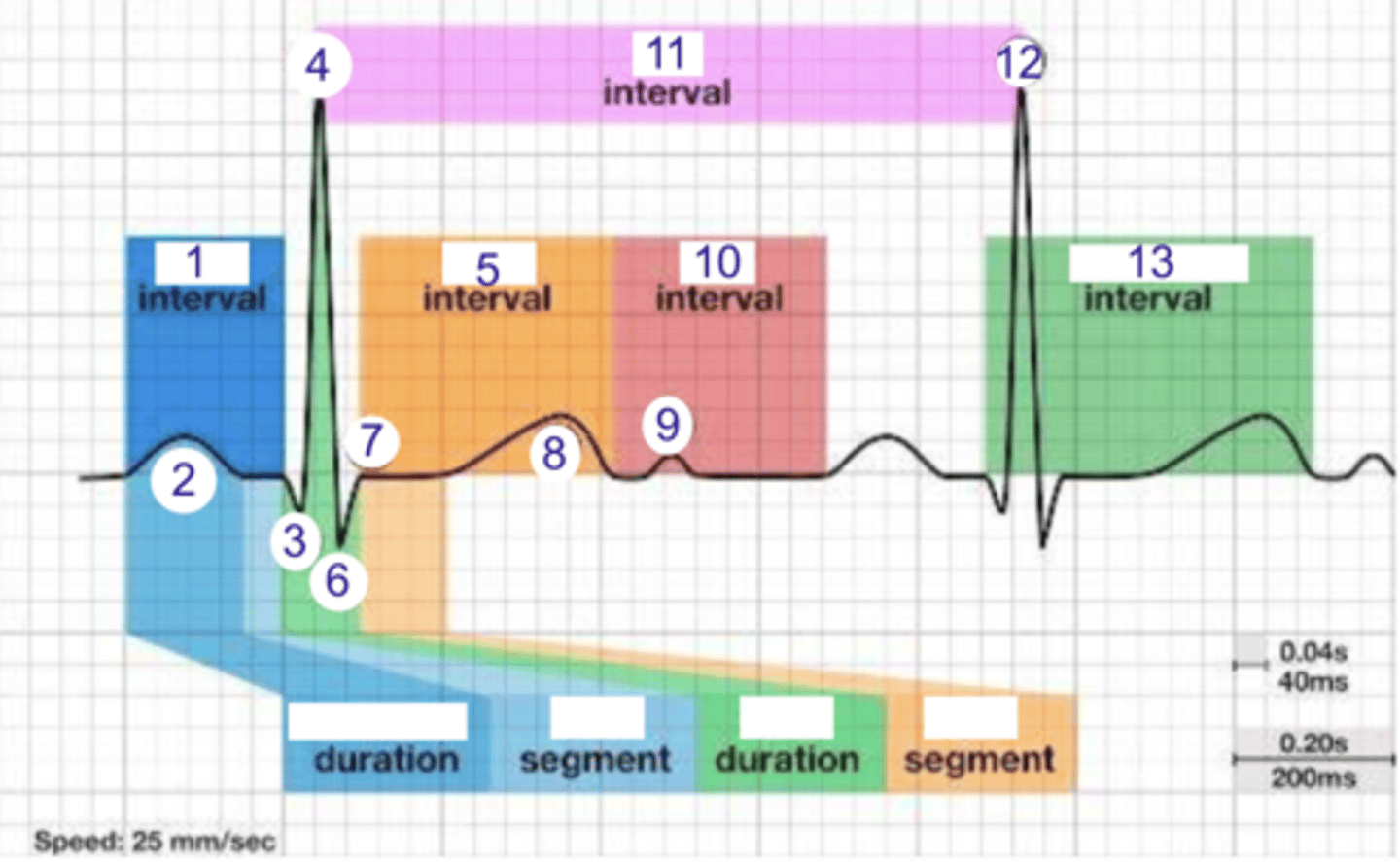
5
where is the ST interval?
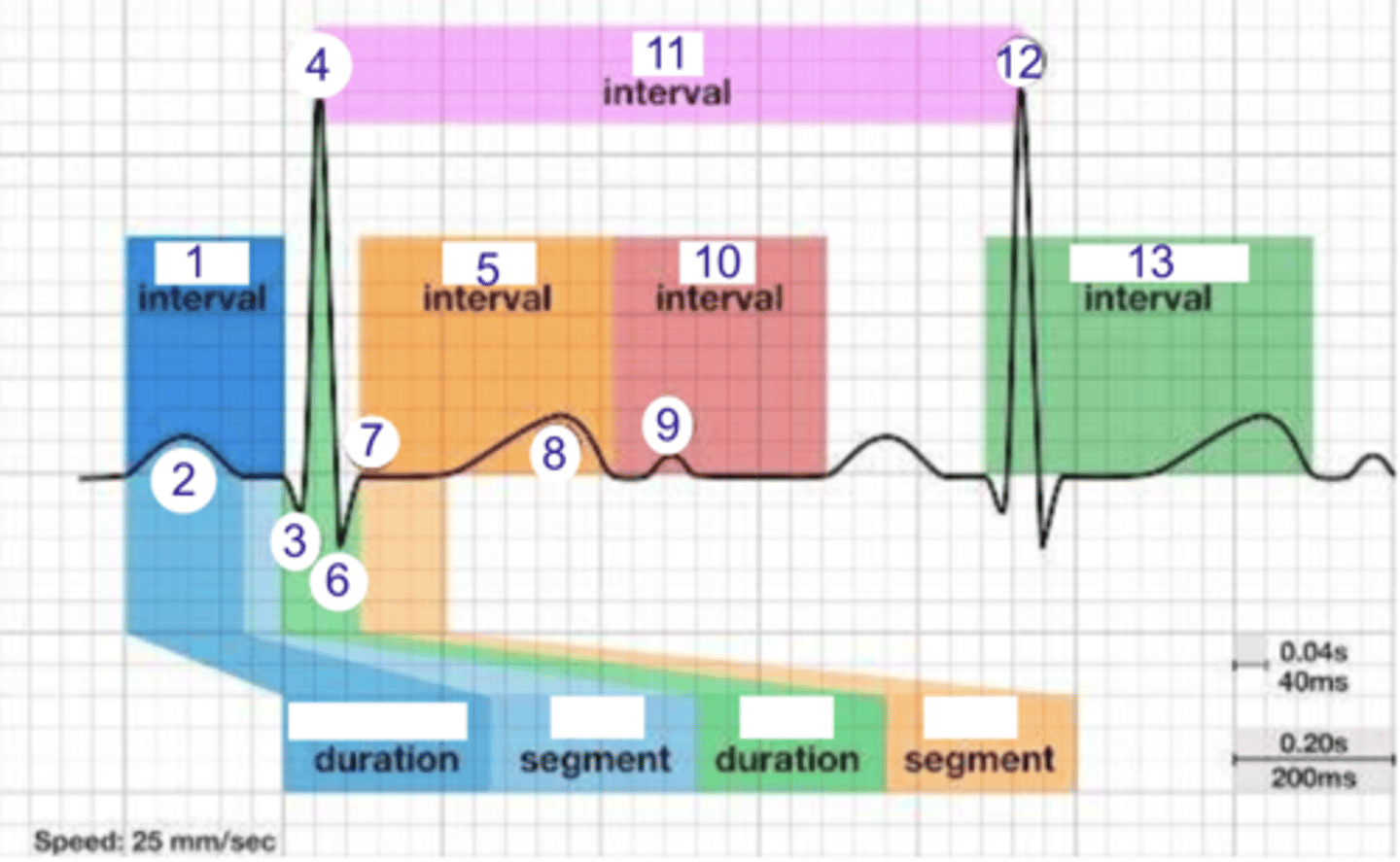
6
where is S?
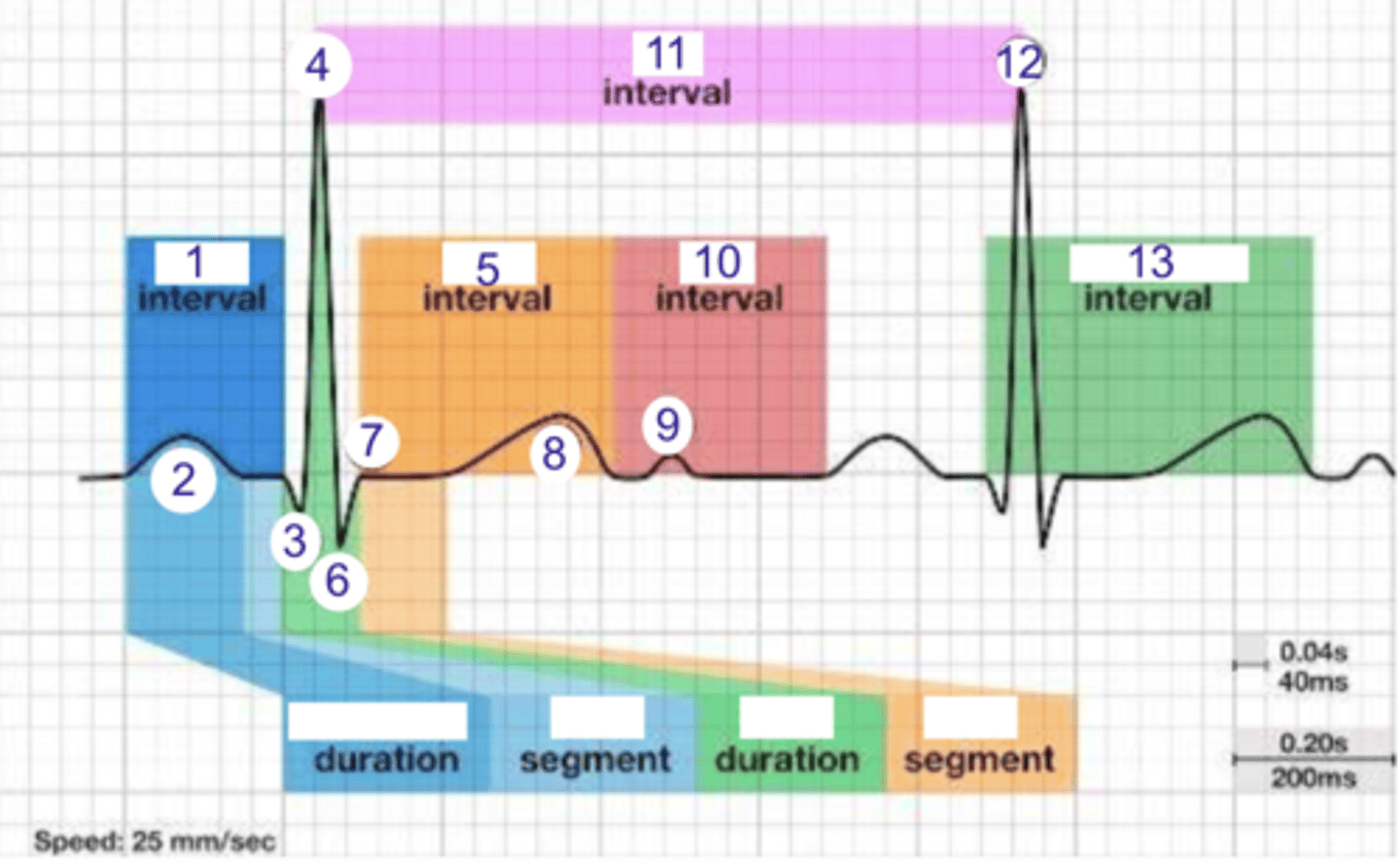
T wave
ventricular repolarization
what is 8? what is happening in the heart here?
10
where is the TP interval?
11
the duration of the cardiac cycle
where is the RR interval? what is this significance?
RR interval
what is 11?
R
what is 12?
13
where is the QT interval?
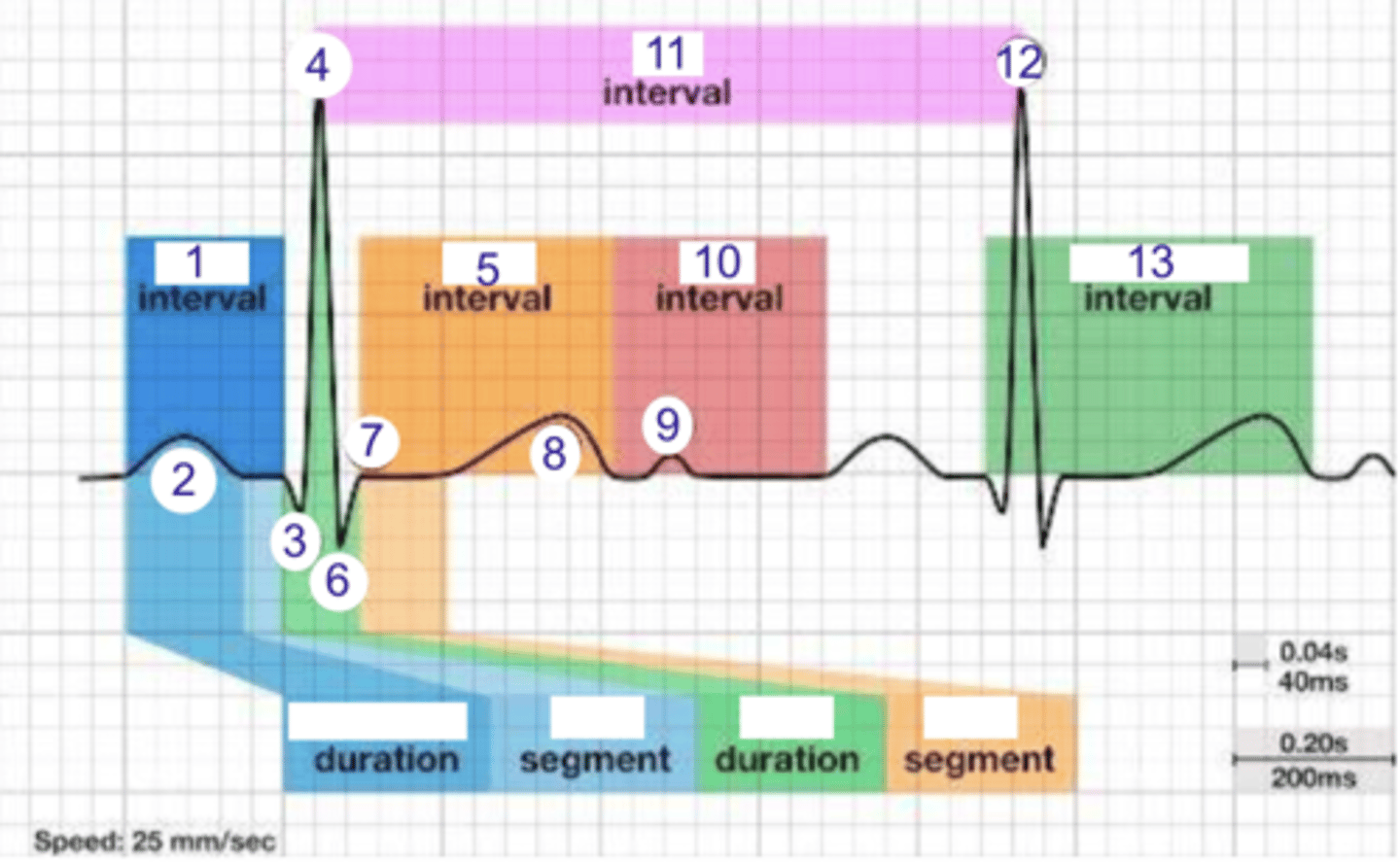
beginning of atrial and ventricular depolarizations
the PR interval represents the time elapsing between the ____________ and ___________
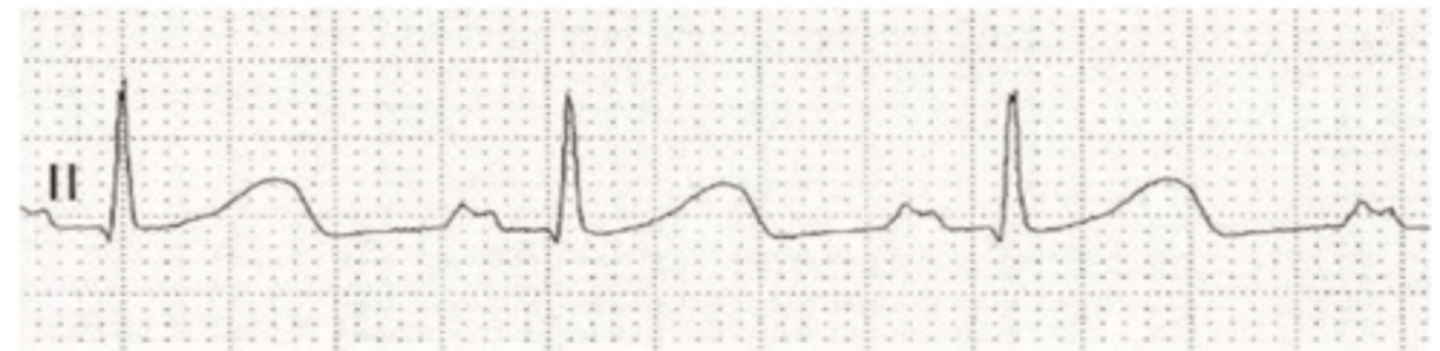
P pulmonale
the right atrium is enlarged
if the P wave has a higher voltage than normal, but a normal duration, what does this mean?
P mitrale
the left atrium is enlarged
if the P wave has a longer duration OR has 2 peaks, but a normal voltage, what does this mean?
if the P wave is taller than normal- the right atrium is enlarged (P pulmonale).
if the P wave is longer than normal (or has 2 peaks)- the left atrium is enlarged (P mitrale).
how can we tell by looking at an ECG if the atriums are enlarged?
the right atrium is enlarged (P pulmonale)
because the voltage is too high
by looking at the P wave, what do we think is wrong with this heart?
the left atrium is enlarged (P mitrale)
because it is too long and double peaked
this is a dog's ECG. by looking at the P wave, what do we think is wrong with this heart?
NO, this is normal in horses, but pathological in dogs. this means their left atrium is enlarged (P mitrale).
is it normal for a dog's ECG to have a double peaked P wave?
it is the general direction of the ventricular depolarization wavefront int he sagittal plane (the major direction of the overall electrical activity of the heart).
to find the electrical axis, we take lead I and III and count the squares between R and Q and find the matching value on the Tilly Table
what is the electrical axis? how do we measure it?
we use it to find the electrical axis of the heart.
we do this by counting the distance between the R and Q in leads I and III and then finding their union on this table.
what is the tilly table for?
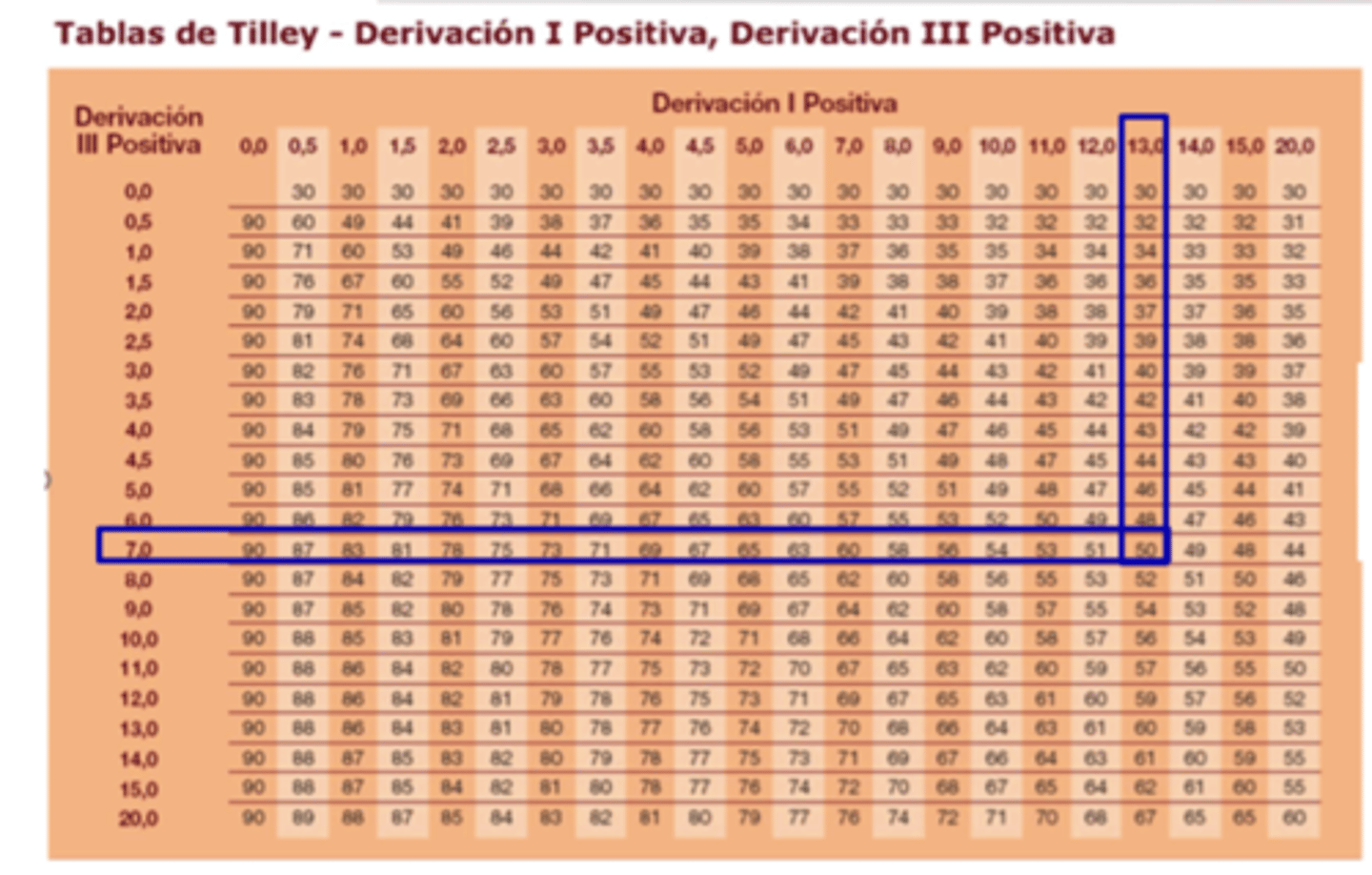
I and III
what leads do we use to find the electrical axis of the heart?
always positive
should the P wave be positive or negative?
in dogs and cats, it can be positive, negative, or biphasic
should the T wave be positive or negative?
1. are all P waves present?
2. do all P waves look normal?
3. are all of the P waves constant?
4. are all the QRS normal?
5. is there a P wave for every QRS?
6. is the PR interval constant?
to assess if there is an arrhythmia, what questions do we ask about the ECG?
1. sinusal
2. atrial
3. ventricular
4. conduction abnormality (block)
what are the 4 categories of arrhythmias?
arrhythmia due to abnormality in the SA node.
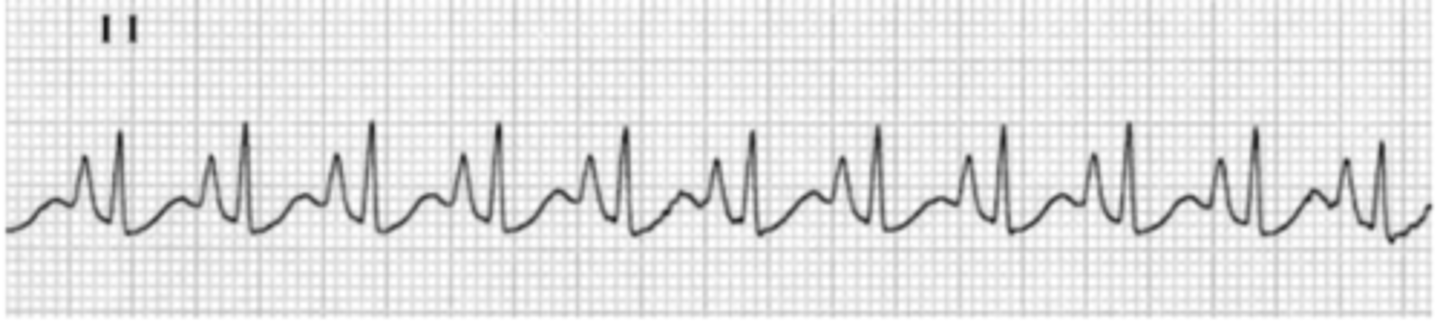
in dogs, a sinusal respiratory arrhythmia is normal, where there is a faster HR during inhalation and a slower HR during exhalation
what is a sinusal arrhythmia?
arrhythmia due to abnormality in the atrium.
there are different types- atrial fibrillation, atrial premature complex, atrial fluttering, etc.
what is an atrial arrhythmia?
a type of atrial arrhythmia, where a P complex is appearing before it normally should. this indicates that the impulse is beginning in an atrial ectopic nodule that is not the SA node.
what is an atrial premature complex/atrial extrasystole?
atrial premature complex/atrial extrasystole
a P complex is appearing before it normally should. this indicates that the impulse is beginning in an atrial ectopic nodule that is not the SA node.
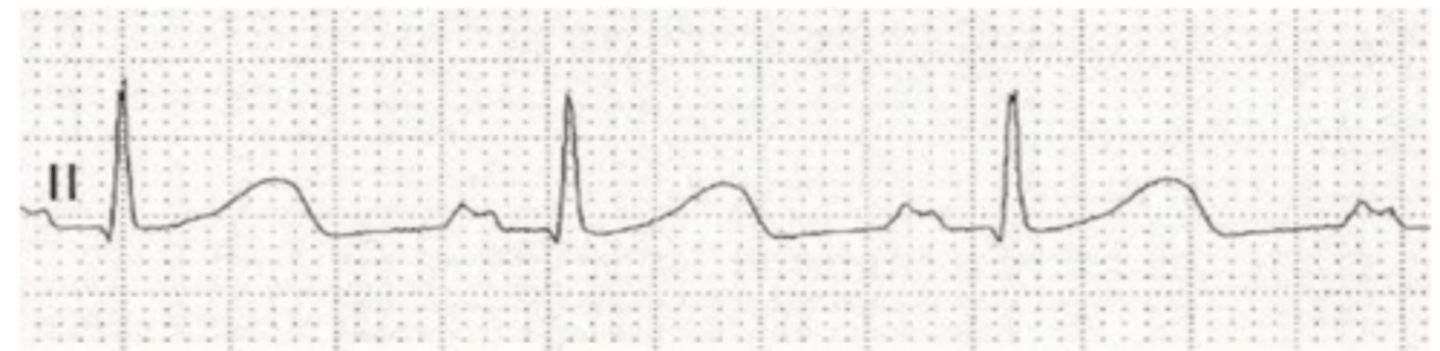
what type of arrhythmia is this? (ignore the negative QRS)
atrial premature complex/atrial extrasystole
a P complex is appearing before it normally should. this indicates that the impulse is beginning in an atrial ectopic nodule that is not the SA node.
what type of arrhythmia is this?
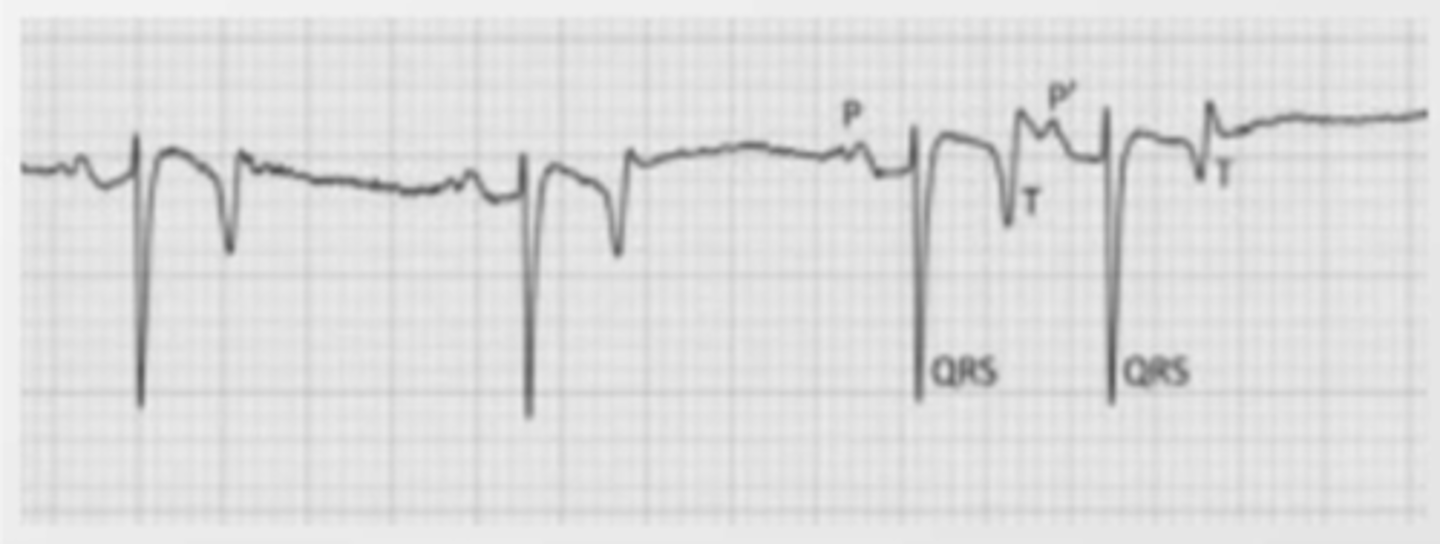
it is when 3+ atrial premature complexes appear in a row.
the QRS is normal, and the P wave usually overlaps the T wave.
what is supraventricular tachycardia?
supraventricular tachycardia/atrial tachycardia
when there are 3+ atrial premature complexes in a row, we call this...
there is an ectopic nodule in the atria that is producing electrical activity (not the SA node).
this is called an atrial premature complex/atrial extrasystole
when there is a P wave that occurs before it normally should, what is the problem?
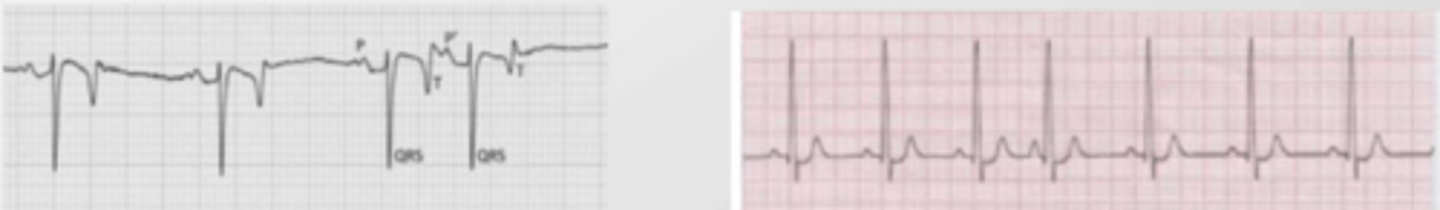
when there are several ectopic nodules in the atria that are contracting all the time.
the atrium is shaking because of all the impulses. there is irregular, chaotic atrial activity.
the QRS is not preceded by a P wave, but there are multiple small positive bumps.
this is uncommon, and can be congenital or degenerative.
what is atrial fibrillation?
atrial fibrillation
there are several ectopic nodules in the atria that are contracting all the time. there is irregular, chaotic atrial activity, presenting as many small positive points before the QRS, and the lack of a P wave.
what is the problem here?
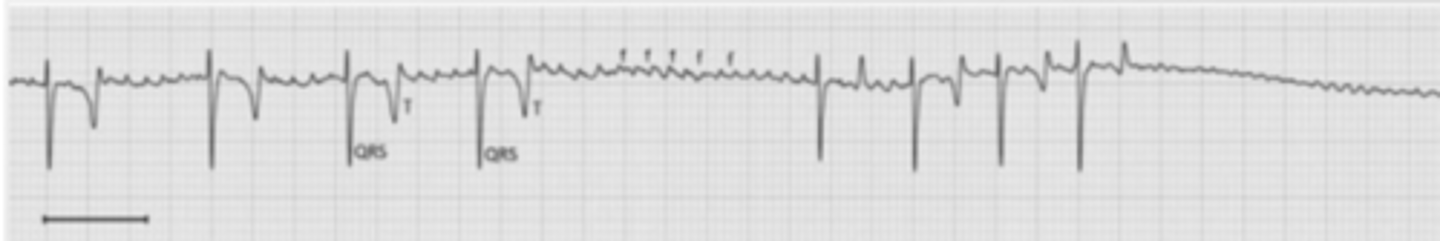
atrial fibrillation
there are several ectopic nodules in the atria that are contracting all the time. there is irregular, chaotic atrial activity, presenting as many small positive points before the QRS, and the lack of a P wave.
what type of arrhythmia is this?
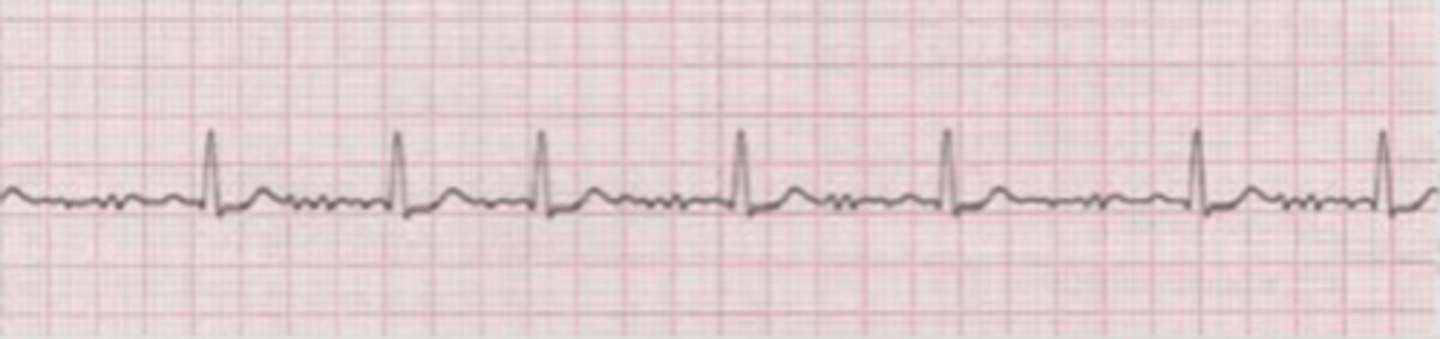
a type of ventricular arrhythmia, where there is an ectopic nodule in the ventricular walls.
this presents as an abnormal, wider QRS, not associated with a P wave (there is no P wave) because the atria have not contracted before the ventricles.
what is a ventricular premature complex (VPC)?
ventricular premature complex (VPC)
there is an ectopic nodule in the ventricular walls.
this presents as an abnormal, wider QRS, not associated with a P wave (there is no P wave) because the atria have not contracted before the ventricles.
what is the problem with this ECG? what does this mean?
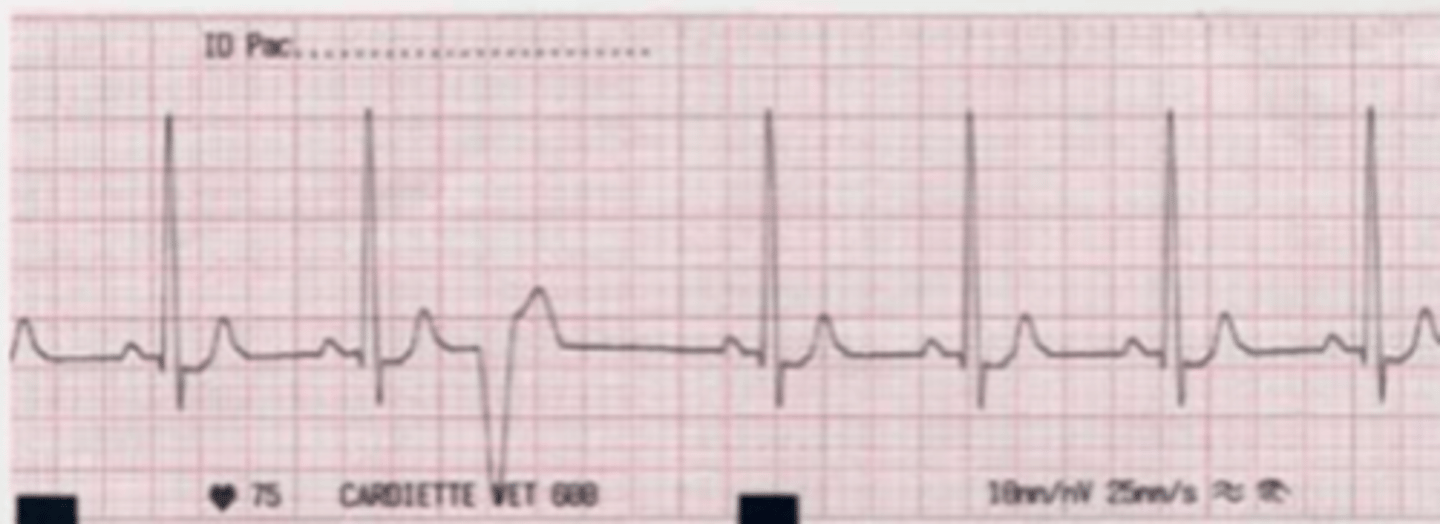
ventricular premature complex (VPC)
there is an ectopic nodule in the ventricular walls.
this presents as an abnormal, wider QRS, not associated with a P wave (there is no P wave) because the atria have not contracted before the ventricles.
what is the problem with this ECG? what does this mean?
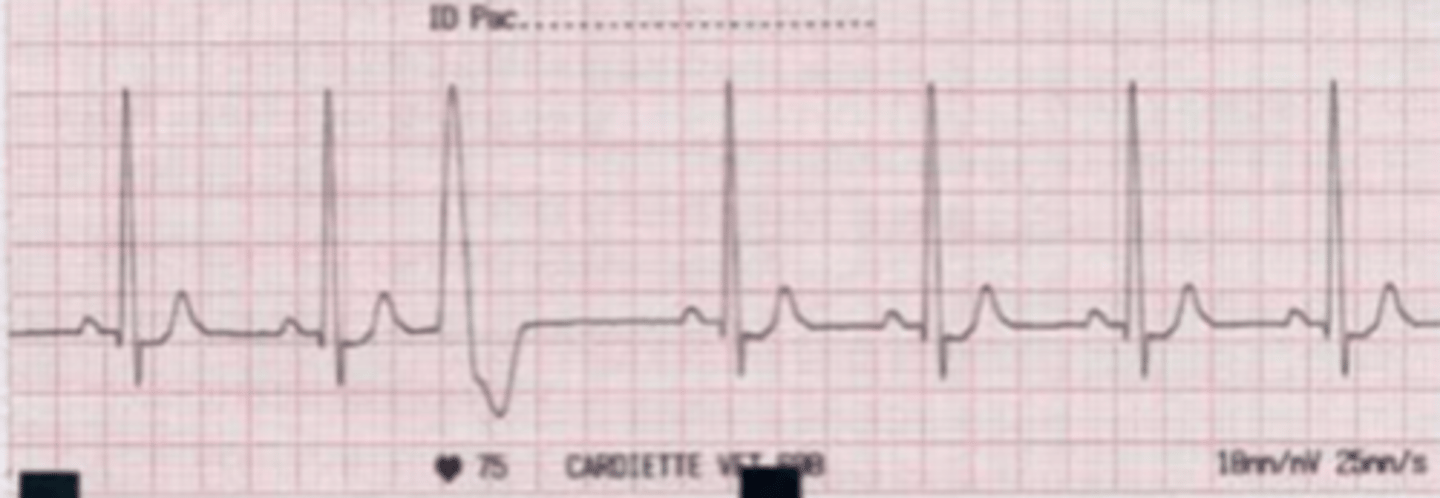
there is a vibration of the ventricles because they quiver instead of contracting effectively.
this is a life-threatening medical emergency.
in the ECG, this presents as a rapid, irregular, and chaotic waveform with no discernible P-waves, QRS complexes, or T-waves.
what is a ventricular fibrillation?
ventricular fibrillation
there is a vibration of the ventricles because they quiver instead of contracting effectively.
this is a life-threatening medical emergency.
in the ECG, this presents as a rapid, irregular, and chaotic waveform with no discernible P-waves, QRS complexes, or T-waves.
what is the problem here?
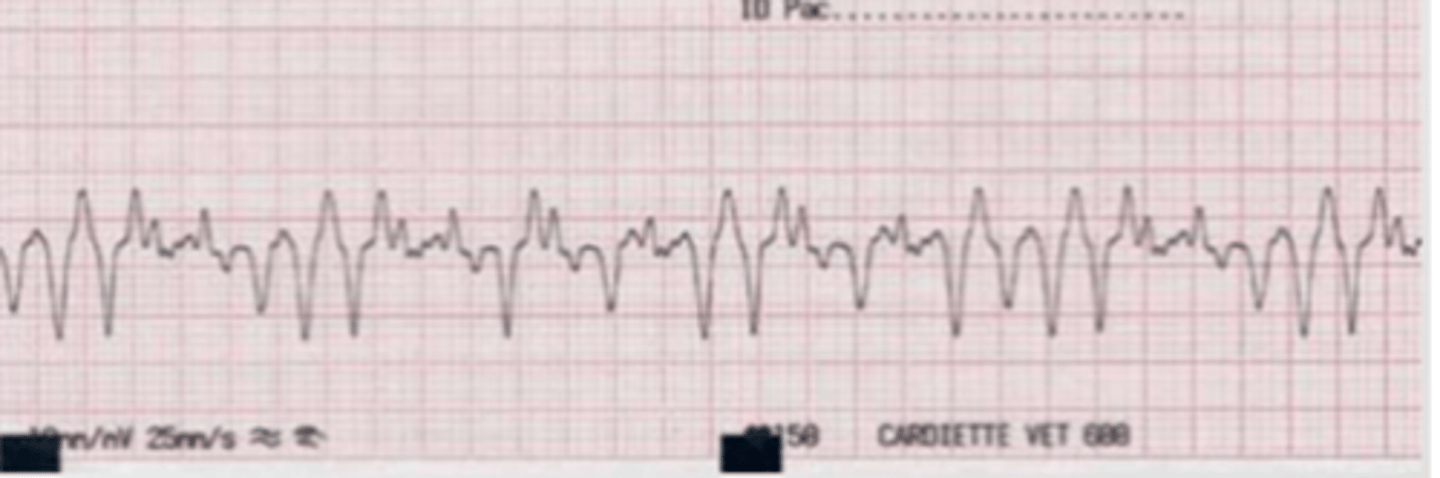
ventricular fibrillation
there is a vibration of the ventricles because they quiver instead of contracting effectively.
this is a life-threatening medical emergency.
in the ECG, this presents as a rapid, irregular, and chaotic waveform with no discernible P-waves, QRS complexes, or T-waves.
what is the problem here?
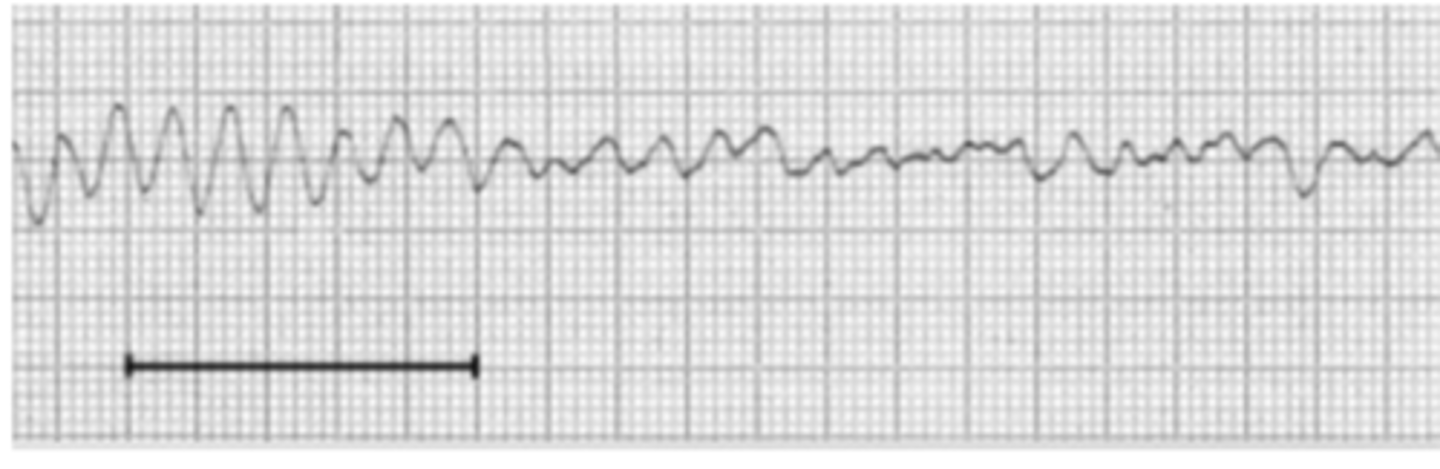
ventricular fibrillation
there is a vibration of the ventricles because they quiver instead of contracting effectively.
this is a life-threatening medical emergency.
in the ECG, this presents as a rapid, irregular, and chaotic waveform with no discernible P-waves, QRS complexes, or T-waves.
why is there a problem with this patient?
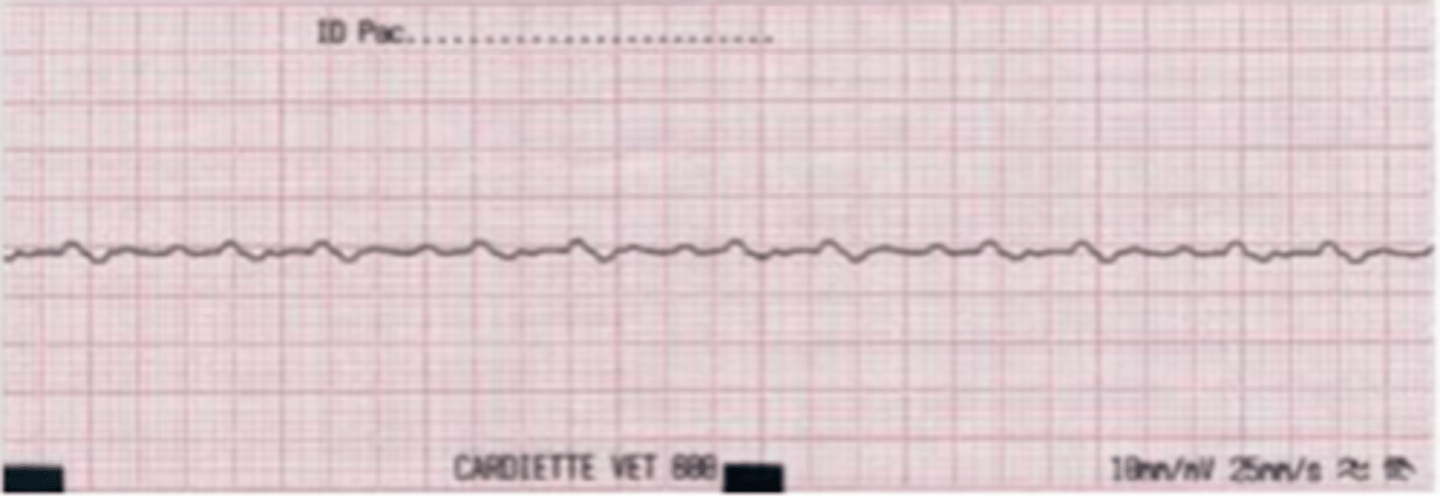
ventricular tachycardia
absent P waves, abnormal QRS
what is the problem?
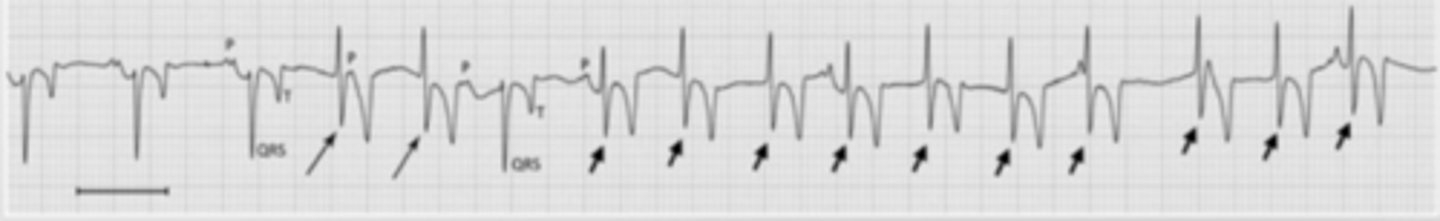
the electrical impulse is blocked in the SA node.
in the ECG, there are normal waves, but some RR intervals are very long (2x the normal length).
what is a sinus block?
sinus block
the impulse is blocked in the SA node.
in the ECG, there are normal waves, but some RR intervals are very long (2x the normal length).
what is this type of arrhythmia?
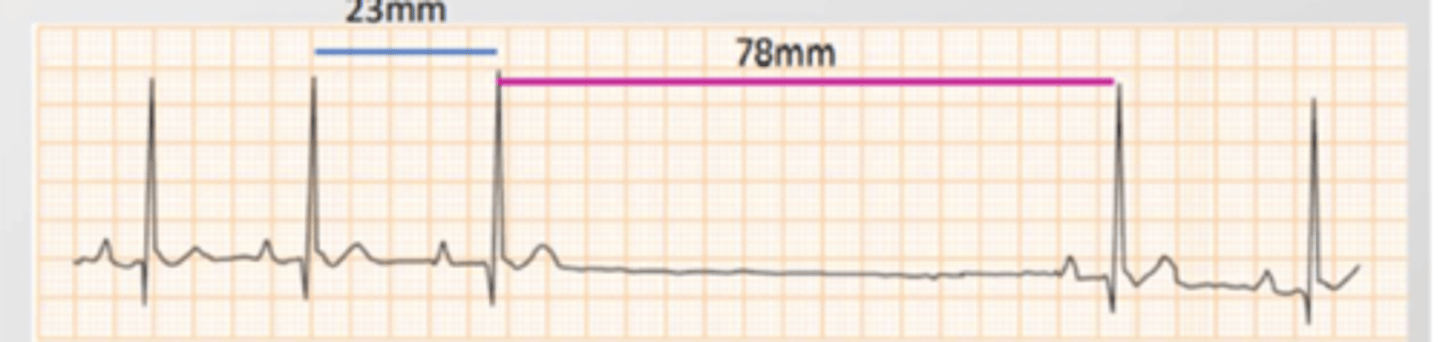
a type of arrhythmia where the impulse is blocked in the AV node
there are 3 types:
1. first degree: PR interval is longer, but always the same length
2. second degree: some stimuli do not pass through the AV. Type I: PR increases in size until there is no QRS. Type II: PRs are constant, with a sudden lack of QRS.
3. third degree: complete AV block. Normal P waves, no QRS.
what is an atrioventricular block (AVB)?
first degree- delay in the conduction of the electrical impulse to the AV. PR interval is longer, but always the same length.
second degree- some stimuli do not pass through the AV.
Type I: PR interval increases in size until there is no QRS.
Type II: PR intervals are constant, with a sudden lack of QRS.
third degree- complete AV block. Normal P waves, no QRS.
what are the 3 different types of atrioventricular block?
second degree type I AV block
PR interval increases in size until there is no QRS.
what type of arrhythmia do we see here?
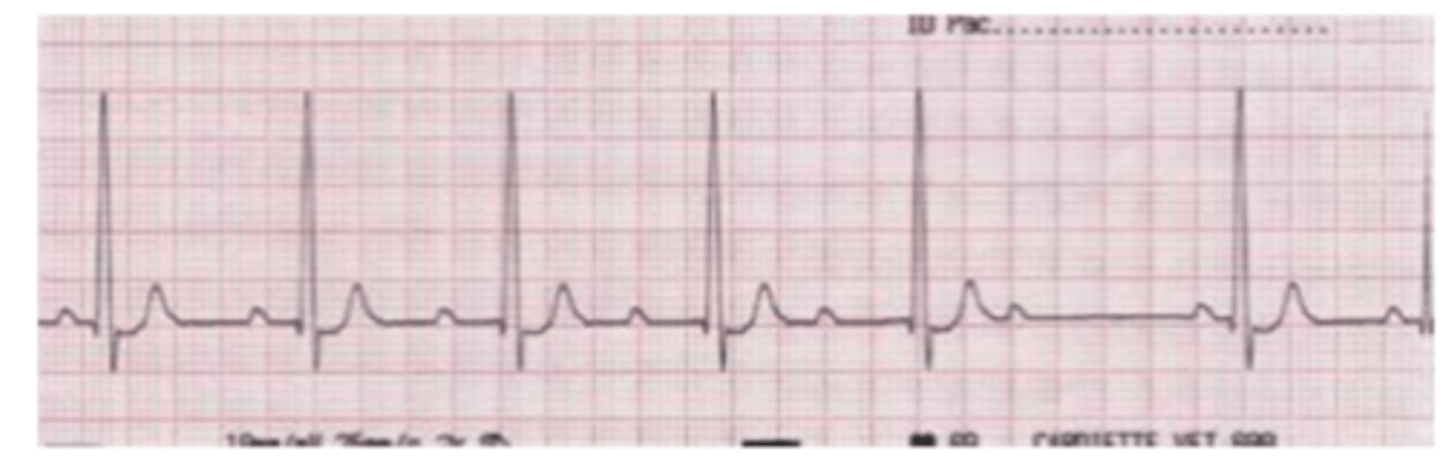
second degree type II AV block
PR intervals are constant, with a sudden lack of QRS.
what type of arrhythmia do we see here?

third degree AV block
complete block of the AV node. there are regular P waves without QRS.
what type of arrhythmia do we see here?
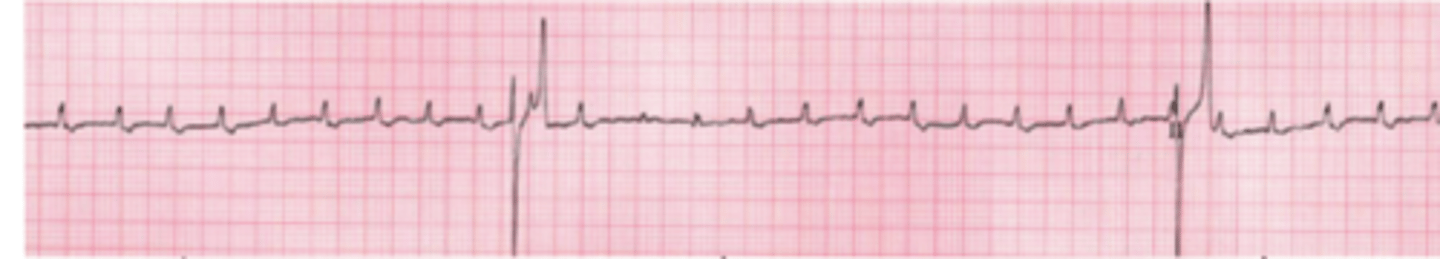
third degree AV block
complete block of the AV node. there are regular P waves without QRS.
what type of arrhythmia do we see here?
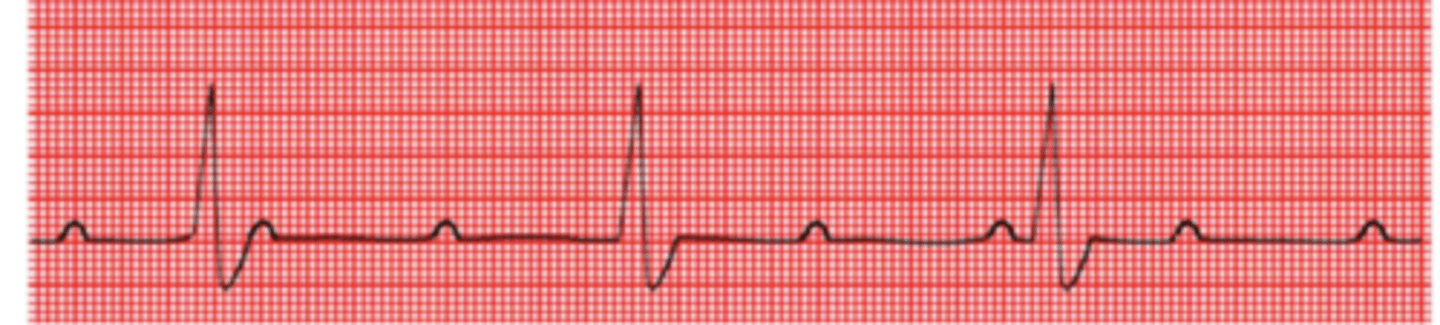
sinusal= all P waves are positive, regular, equal, and there is 1 before every QRS
how can we tell if an ECG is sinusal or not sinusal?
measuring the distance of the RR intervals. if they are all the same, this is regular. if not, this is irregular (arrhythmia)
by looking at an ECG, how can we tell if the HR is regular?
if the paper is run at 25mm/sec:
(# of full cycles x 60)/seconds
how do we calculate the HR by looking at an ECG?
adults- 70-160
toy breeds- up to 180
puppies- up to 220
what is the normal heart rate of a dog?
160-240
what is the normal heart rate of a cat?
AV block
if it is always the same, long length- 1st degree
if it increases in length each time- 2nd degree type I
if the PR interval is not constant, what is the problem?
AV block
what does it mean if there is not a QRS complex for each P wave?
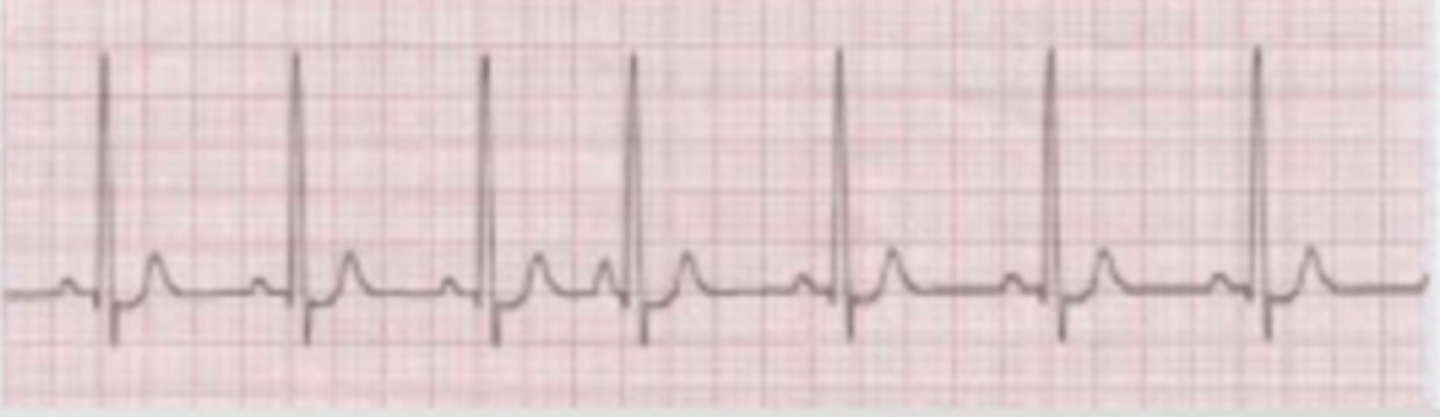
yes
(all P waves are constant, equal, positive, and precede a QRS)
is this sinusal?
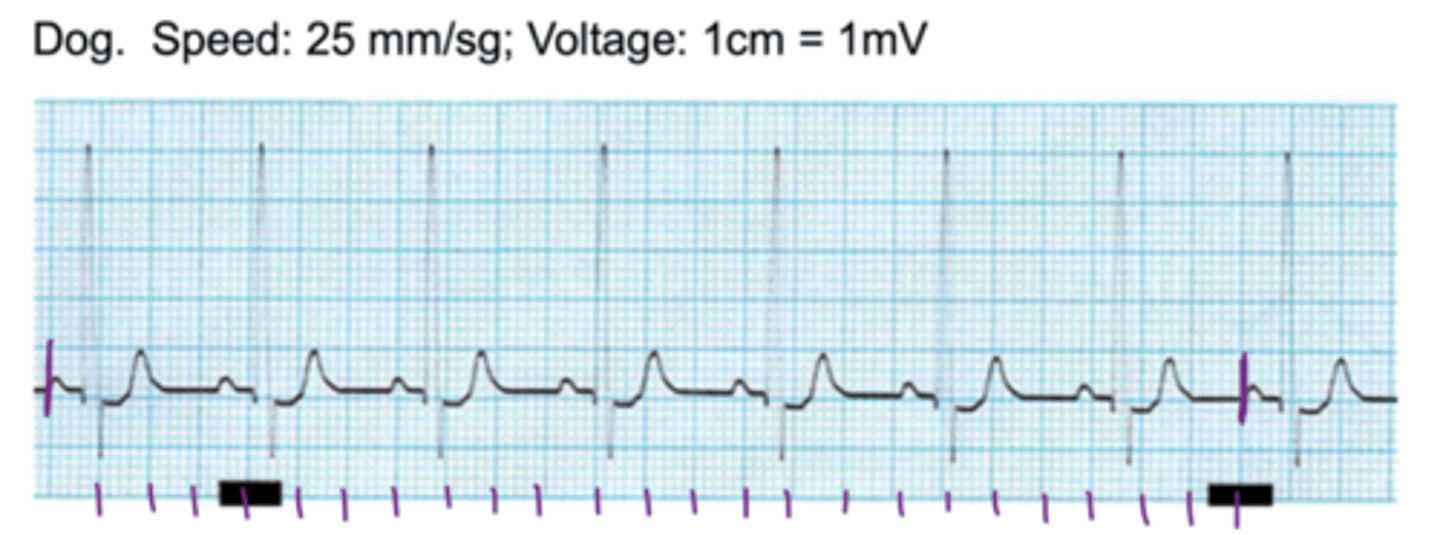
regular
(all RR intervals are the same length)
is this HR regular or irregular?
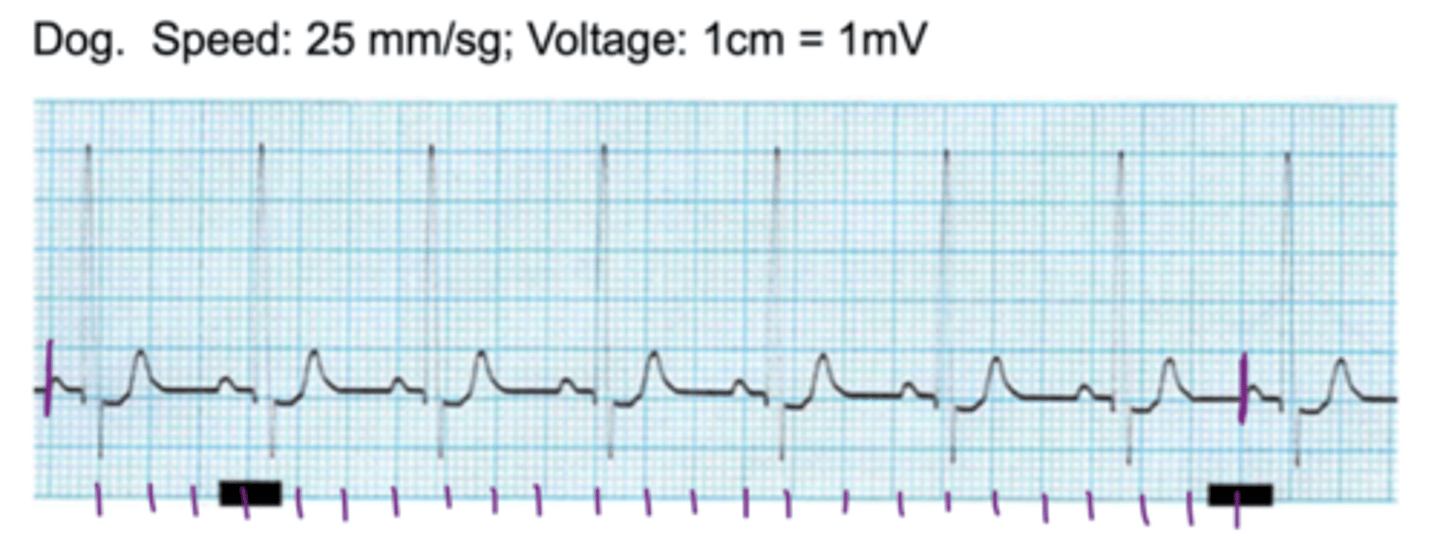
around 87.5
(normal)
what is the heart rate?