Bio 337 Neurbio of taste and feeding
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
The classic tastes
Sweet, salty, bitter, sour, umami
What do taste buds contain
Taste receptor cells which express specific taste receptor.
What type of channels mediate Salty and Sour
Specific ion channels
Amiloride sensitive NA+ channel and a cation channel. (PKD and TRP Family)
What type of channels mediate sweet and umami
Hetero-dimers formed by T1R3 and another subunit.
For sweet its T1R3/T1R2
For Umami is T1R3/T1R1
G PROTEIN COUPLED!!!!
What type of channels mediate bitter
Receptors are T2R (multiple subtypes) that are G Coupled proteins
Pathway for mouth to brain
Taste receptor Cells
Cranial Nerve ganglia
Brainstem NST
Thalamus VPMpc
Insular Cortex (gustatory cortex)
Chorda tympani branch of facial
ANT tongue and palate
Lingual Branch of Glossopharyngeal
Post tongue and palate
Laryngeal branch of vargus
Larynx
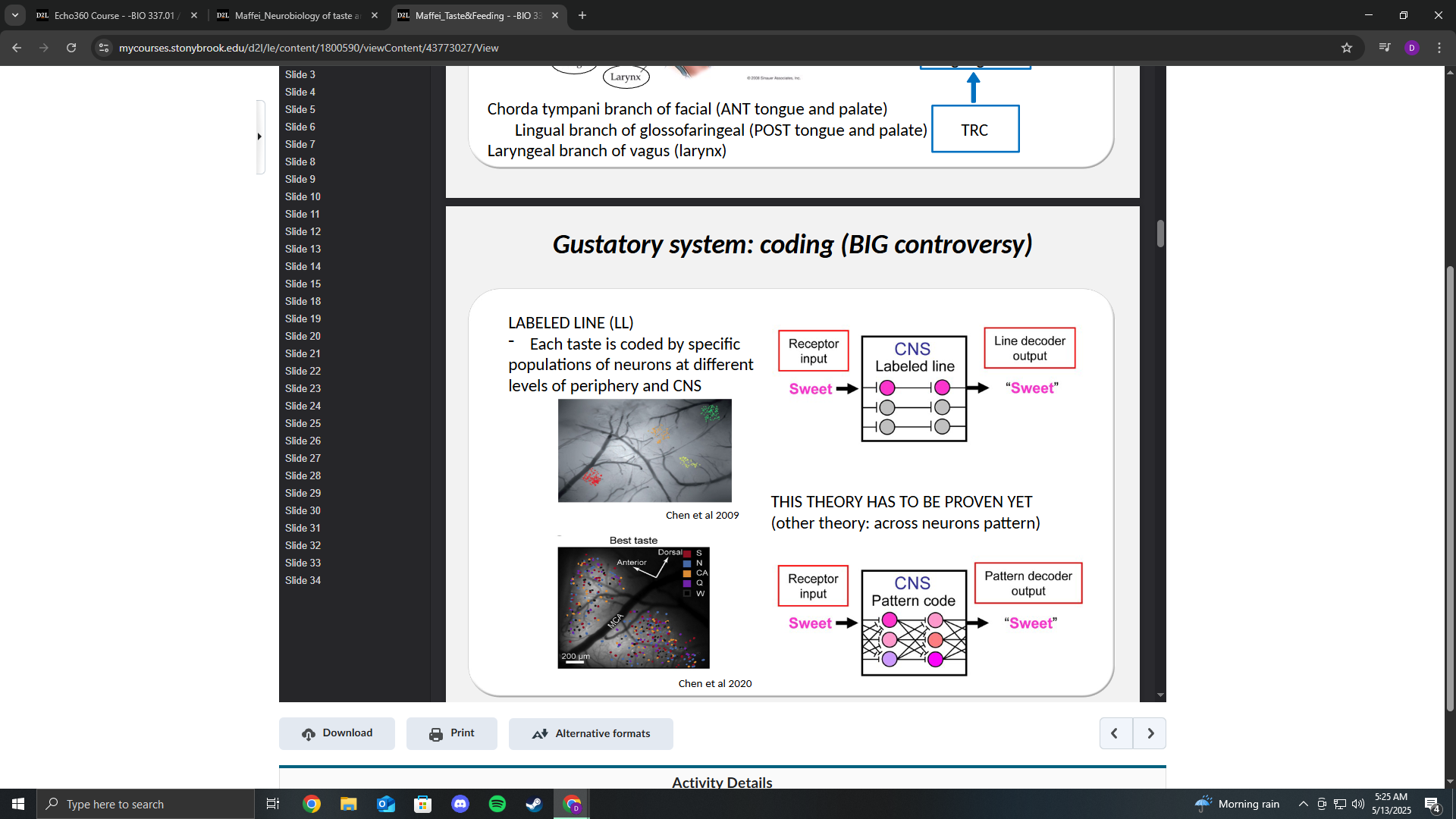
Two theories of gustatory system coding
Labeled line
There are specific sweet neurons that get activated and transfer the signal to other sweet neurons in the CNS.
Pattern Code
Nonspecific neurons send signals to other neurons in a specific pattern to code sweet versus other flavors.
Beyond the classic 5 tastes
Carbonation, Texture, Astringency, Cold (menthol), Temperature, and Spiciness (hot)
How is palatability encoded in the brain
The amygdala processes information from a stimulus and sends the signal about the reward value, expectation, motivated behaviors and learning.
Amygdala communicates with the gustatory cortex to mediate palatability.
What does the hypothalamus do for taste/feeding?
It sends signals to the Gustatory Cortex to regulate feeding behaviors (hunger/satiety)
How does the setpoint in control of feeding get set? How is it altered?
Many factors from genetic, behavioral, and environmental. If the hypothalamus is lesioned it will alter the setpoint.
What does lesions of the ventromedial hypothalamus produce?
Hyperphagia and obesity
What does lesions of the lateral hypothalamus produce?
Aphagia and weight lost
Short term control satiety signals
PYY: High lvl (after meal) promotes satiety
CCK: High lvl (after meal) promotes satiety
Gastric distention promotes satiety
Glucose
Ghrelin: High lvls (before meal) promote hunger
Adiposity signals (Longer term control of satiety)
Leptin: High levels promote satiety. Low lvls=hunger
Insulin: Levels promote satiety. Low lvls=hunger
What do satiety signals act on and where do adiposity signals act on?
Satiety signals act on the Gustatory cortex while Adiposity signals act on the hypothalamus.
How does the Lateral Hypothalamus promote food intake
Through orexin A and melanin concentrating hormone (MCH)
How does the Paraventricular nucleus decrease food intake and increase food expenditure
Through oxytocin and CRH
What does NPY/AgRP do
Inhibit the PVN and excite the Lateral hypothalamus
What does alpha-MSH/CART do?
Excite the PVN and inhibit LHA
Besides endocrine/hormonal signals, how else is food intake and hunger/satiety regulated? How?
Through cognitive and sensory signals
Reward and taste related areas receive inputs from the hypothalamus to control reward behavior. (acts on VTA and Insular cortex)
What kind of alterations do obese people show?
Both metabolic and gustatory/reward systems.
EX:
Lower sensitivity to Leptin/inability to produce leptin/alteraion of orexin
Anorexia
Alterations to AgRP and BDNF genes (hunger genes)
Alterations to serotoninergic system and dopaminergic in limbic areas.
What is associated with Bulimia
Decreased release of CCK, Increased release of ghrelin and alterations of several other hormones.