Ear Disorders 382 Exam 2
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Microtia
pinna abnormally small
Anotia
pinna entirely absent
basal cell carcinoma
cancer of the skin, on skin tissue on pinna
atresia
lack of canalization; may be due to congenital effect such as trencher Collins syndrome or trauma
cannot be treated with hearing aids
CHL directly related to the area and amount of occlusion
suspect that TM and Middle ear are also effected
Stenosis
narrowing of the EAC; can cause easy clogging from ear wax but wont typically cause CHL by itself
Collapsing Auditory Canal
can see a CHL in hearing test if using supra aural headphones, need to use inserts
4% of caseload
more common in elderly population
foreign bodies in EAC
if pushed too far will cause swelling and surgical removal might be required
may or may not cause CHL
External Otitis (Swimmer’s ear)
infection in the skin of the EAC
bacterial infection or otomycosis
depending on swelling and infectious debris may have mild CHL
if pain too much might not be able to do hearing test
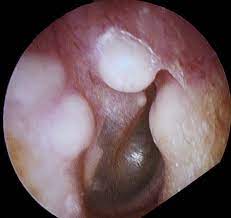
Osteoma
growth in the outer ear that is a bony tumor
Extoses (surfers ear)
outward projections; happens if spend a lot of time in cold water
Cerumen Build Up
too much ear wax occludes EAC may cause CHL - can be indicated by type B tympanogram with a small volume
Perforation of TM
causes: rapid pressure change, direct trauma, excessive pressure build up
showed by type B tympanogram with large volume
Tympanosclerosis
TM thickened or scarred in response to infection
Calcium Plaques on TM
calcium plaques may form on it, affects vibration of the TM
HL may or may not happen
eustachian tube dysfunction
negative middle ear pressure
can result from swelling from infection or blockage at the opening
slight conductive CHL and type C tympanogram
Otitis media
infection of the mucus lining of middle ear chamber
70% children get it by age 2 in US
seen by flat bilateral CHL, great WRS, type B tympanogram, reduced static compliance; absent OAEs (acoustic reflexes)
types of Otitis media (can progress into each other)
serous OM: accumulation of fluids that can usualy be drained
Superlative OM: pus that fills middle ear cavity
Mucoid OM: thick mucous secretions
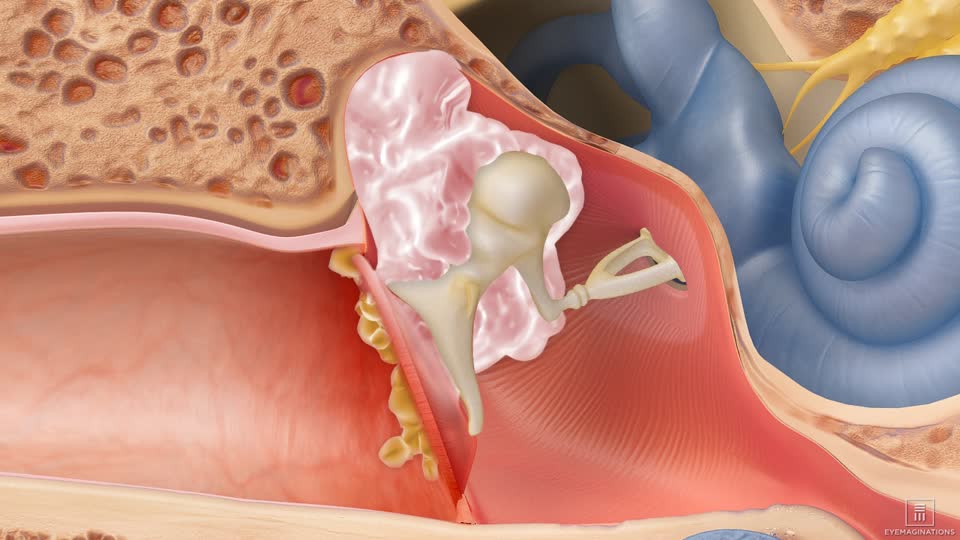
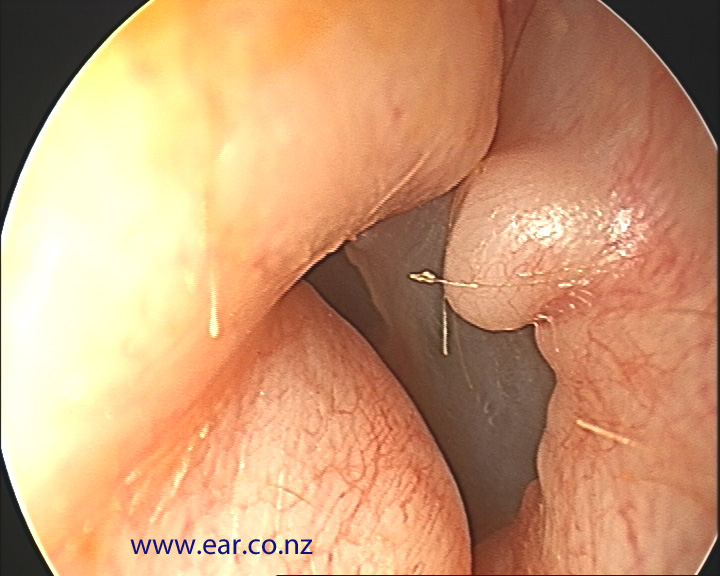
Cholesteatoma
a growth in the middle ear that occurs when skin is introduced to middle ear cavity
most likely to cause a max CHL
if gets into inner ear can cause SNHL
Facial Palsy
damage to facial nerve causing paralysis to one side of the face
can occur after chronic otitis media
often resolves spontaneously
typically no CHL
patulous eustachian tube
ET is chronically open
autophony
no CHL
otosclerosis
ossicles change and become spongy
not seen until invades middle ear cavity and causes CHL
can be identified in audiometry by Carhart’s notch
BC thresholds reduced at 2000 Hz
otospongiosis
spongy bone growth over the footplate of the stapes
if moves to cochlea, will 1st see a HL in low frequencies
Sudden Idiopathic SNHL
unilateral (usualy) HL that develops instantly or over a few days
decrease of at least 30 dB over at least 3 octaves within 72 hrs
medical emergency
manières disease
over secretion or not enough absorption of endolymph
sudden attacks of vertigo, “roaring” tinnitus, vomiting, unilateral HL, aural fullness
Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease
chronic inflammatory condition that results in bilateral, fluctuating, and progressive sensory hearing loss
Presbycusis
normal hearing loss due to age
phonemic regression, difficulty in speech recognition
Noise-Induced HL
hearing loss due to noise exposure
Temporary Threshold shift: after a loud event, normal hearing comes back
Permanent threshold shift: irreversible HL
outer hair cells die
Ototoxic HL
HL due to exposure to drugs or chemicals that are toxic to the inner ear
some antibiotics
antimalarial
chemotherapeutic drugs
repeated long-term use of diuretics, nicotine, alcohol, and asprin