BIOL 112 EXAM 1
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
fixed allele
An allele that is the only variant that exists for a gene in a population.
Gene Pool
All the alleles of all the genes in a population.
Allele
Two or more alterative forms of a gene.
Genotypic Frequency
Proportion of each genotype in the population. %AA, %Aa and %aa
Allelic Frequency
% of each allele in the population %A allele and %a allele.
Germ Line Mutation
Only mutations in cells can be passed onto the offspring.
Phenotype
The product of an inherited genotype and many environemlental influences.
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an organism.
Genetic Variation
Differences among individuals in the composition of their genes.
Allopolyploidy
Resulting from viable mating between two distinct species. Source of extra chromosomes different species. Need 2 reproductive acts before the ________ is formed to make it viable and fertile.
Polyploidy
A cell or organism that has an extra set or sets of chromosomes.
Descent with Modification
A phrase Darwin used in proposing that Earths many species are descendants of ancestral species that were different from the present day species.
Natural Selection
"Survivial of the Fittest" The reproduction of individuals with favorable genetic traits that survive environmental change because of those traits leading to evolutionary change --> leads to greater adaptation of the population to its local environment.
Microevolution
A change in allele frequencies in a population over generations.
Population Genetics
The study of what changes the allele frequencies in populations.
Genetic Drift
Genetic Frequency changes due to random events. some individuals will have more offspring than others not due to an advantage. Often occurs in small populations like sampling errors in statistics.
Gene Flow
Alleles move in/out of a population.
Adaptive Evolution
evolutionary changes in an organism that make it suitable to its habitat
Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium
If a large population reproduces sexually at random, then the genetic frequencies should not change in next generation (remains in equilibrium)
Punnet Square
A square diagram that is used to predict the genotypes of a particular cross.
How does H-W let us detect microevolution?
If the actual rations do not equal the expected H-W rations, then the population is evolving.
Founder Effect
a few founders start new isolated population
founder gene pool differs from original source small population size leads to more drift better alleles may be lost.
Bottleneck Effect
An event drastically cuts population size, gene pool of survivors is random; some alleles are lost.
requirements for HWE
No mutations population should be large mating is random No natural Selection
Relative Fitness
Relative to other individuals in the population. best reproductive success. The contribution an individual makes to the gene pool of the next generation relative to the contributions of other individuals.
Directional selection
When the environment changes, selects the phenotypes at one end of the spectrum of all existing variation
Diversifying selection
Intermediates are less fit than extremes, maintains diversity, increases genetic variance
Stabilizing Selection
Intermediates types are more fit than extremes, decreases genetic variance.
Frequency-Dependent Selection
favors phenotypes that are either common (positive) or rare (negative)
Sexual Selection
A process in which same sex individuals with certain inherited characteristics are more likely to obtain mates than those who do not have those characteristics.
Sexual Dimorphism
A difference in secondary sexual characteristics between males and females of the same species. Ex: Size, color, orientation, or behavior
Intrasexual Selection
Individuals of one sex compete directly for mates of the opposite sex.
Intersexual Selection
Called mate choice, individuals of one sex (ususally the females) are choosy in selecting their mates from the other sex.
Phylogeny
The evolutionary history of a species and its relationship to other species.
Rooted Phylogenetic tree
Single Lineage (at base) represents common ancestor.
Unrooted Phylogenetic Tree
Show relationships but not a common ancestor. Illustrate the relatedness of the leaf nodes without making assumptions about ancestry.
Carl Woese, Otto Kandler, and Mark Wheelis
Who Proposed the three domain of life?
Eukarya
Cells do contain a nucleus. Include the plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Is multicellular cell wall: varies between plants and fungi, animals do not have cell wall. Has a nucleus has membrane bound organelles.
Archaea
Not multicellular Has a cell way without peptidoglycan Does not have a nucleus Does not have membrane bound organelles.
Bacteria
Not multicellular, Has a call wall with peptidoglycan, does not have a nucleus, Dose not have membrane bound organelles.
Root
Indicates that an ancestral lineage gave rise to all organisms on the tree.
Branch Point
Indicates where two lineages diverged. (nodes)
Basal Taxa
A lineage that evolved early and remains unbranched.
Sister Taxa
When two lineages stem from the same branch point
Polytomy
A branch with more than two lineages
Systematics
study of phylogenetic relationships
Taxa
The tips of the branches and represents the youngest lineages on the tree.
Clade
a grouping that includes a common ancestor and all the descendants (living and extinct) of that ancestor.
Cladistic Analysis
Grouping organisms in a way that reflects their evolutionary relationship
Monophyletic Group
Consists of an ancestral species and all of its descendants
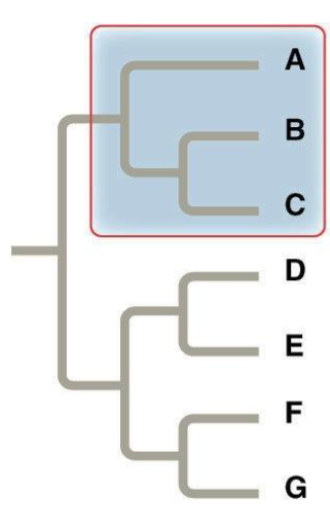
Paraphyletic Group
Consist of an ancestral species and some, but not all, of its descendants.
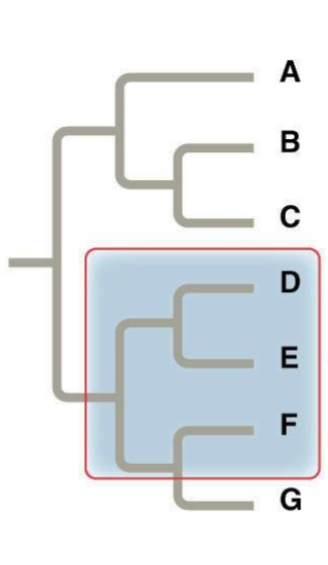
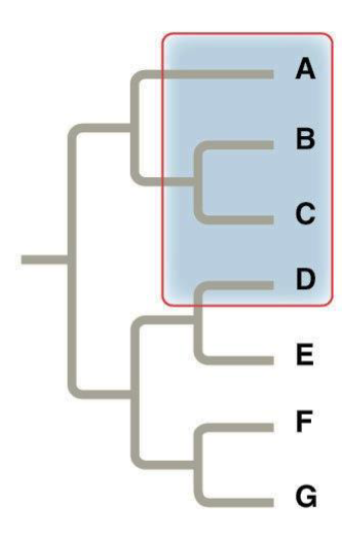
Polyphyletic group
Includes distantly related species but does not include their most recent common ancestor.
Allopatric Speciation
geographic separation of populations from a parent species and subsequent evolution
convergent evolution
where similar traits evolve independently but the species do not share a common ancestry
vestigial structures
unused structures without function
endemic species
species that can only be found in one place
speciation
the formation of 2 species from 1 species
sympatric speciation
involves speciation occurring within a parent species remaining in one location
two categories of allopatric process
dispersal - when a few members of a species move to a new geographical area
vicariance - when a natural situation arises to physically divide organisms
adaptive radiation
when many adaptations evolve from a single point of origin causing species to radiate into several new ones
aneuploidy
when chromosomes pair separate and the end cell product has too many or too few individual chromosomes
Autopolyploidy
occurs when organisms have more than two sets of chromosomes from the same species.
two groups of reproductive isolation
prezygotic barrier - a mechanism that blocks reproduction from taking place (Temporal, habitat, behavior, and gametic isolation)
postzygotic barrier - occurs after zygote formation (hybrid unviability, hybrid sterility, hybrid breakdown)
temporal isolation
difference in breeding schedules
habitat isolation
populations of a species move or are moved to a habitat and take up residence in a place that no longer overlaps with the same species’ other population
behavioral isolation
occurs when the presence or absence of a specific behavior prevents reproduction
gametic behavior
differences in gamete cells prevent fertilization from taking place
hybrid inviability
hybrid individuals cannot form normally in the womb and do not survive past the embryonic stages
hybrid zone
an area when 2 closely related species continue to interact and reproduce
reinforcement hybrid zone
species continue to diverge until hybridization no longer can continue
fusion hybrid zone
the reproductive barrier weakens until the 2 species become one

stability hybrid zone
fit hybrid continue to be produced

gradual speciation model
species diverge gradually over time in small steps
punctuated equilibrium
a species undergoes change quickly from the parent species and remain unchanged for a large period of time afterwards
hybrid sterility
different species can produce a viable offspring but that offspring cannot reproduce
Hybrid breakdown
second generation hybrids are feeble or sterile
analogous structures
features of different species that are similar in function but not necessarily in structure and which do not derive from a common ancestral feature
homologous structures
structures derived from a common ancestor, the same overall layout even if the bones’ shapes and size differs
divergent evolution
two groups of the same species evolve different traits within those groups in order to accommodate for differing environmental social pressures
Taxonomy Hierarchy
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
Aristotle
Placed traits on the scale nature, believing species were unchanging (ladder of nature)
Carl Linnaeus
Orderly nested classification system (taxonomy) was created through binomial naming. Grouped species in closely related species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain.
James Hutton
Father of Geology, Earth's geological features are a result of gradual mechanisms and that is a slow continuous process. Ex: canyon being carved by a river.
Charles Lyell
Uniformitarianism expanded Hutton's Ideas. Same geologic processes in past as today.
Erasmus Darwin
first person to propose the theory of evolution but did not come up with natural selection, taught that life evolved from one common ancestor and gradual complex character sare introduces as life evolves. Wrote ideas that form minute slowly acquired complexity over time.
Jean Baptiste Lamarck
Linked evolution to adaptation, extinct species have been replaced by descendants with new features. These adaptations helped them survive in the environment. Theory of inheritance of acquired characteristics through use and disuse. Acquired characteristics cannot be inherited.
Lamarckism
all the physical changes occurring in an individual during its lifetime are inherited by its offspring
Charles Darwin
Drew a Phylogenetic tree
Theory of natural selection, and evidence of evolution through fossils.
Alfred Wallace
independent of Darwin, realized evolution from his findings at the Malay Archipelago, both presented scientific papers on natural selection together before the Linnean Society in 1858
Gene Pool
Sum of all alleles in a population.