Bio Chapter 2 Study Guide
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Element
Any substance that cannot be reduced to any simpler set of constituent substances through chemical means. Each element is defined by the number of protons in its nucleus.
Atom
The fundamental unit of matter that retains the properties of an element, consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Proton
A positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
Neutron
A neutrally charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
Electron
A negatively charged particle that orbits the nucleus of an atom.
Atomic Number
The number of protons in an atom's nucleus, which can also indicate the number of electrons in a neutral atom.
Atomic Weight
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus.
Isotope
Different forms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell that allow atoms to interact with each other to form bonds.
Valence Shell
The outermost electron shell of an atom.The number of unpaired electrons needed to complete the atom’s outermost shell is called the atom’s valence.
Ion
A charged atom that has lost or gained electrons; positively charged ions are called cations, and negatively charged ions are called anions.
Molecule
A structure formed when two or more atoms bond together.
Covalent Bond
A bond involving the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. It can be single, double, or triple based on the number of shared electron pairs.
Electronegativity
The attraction of a particular atom for the electrons of a covalent bond.
Hydrophilic
Means 'water-loving' and refers to molecules that dissolve well in water.
Hydrophobic
Means 'water-fearing' and refers to molecules that do not dissolve well in water.
Ionic Bond
A bond resulting from the attraction between ions with opposite charges.
Hydrogen Bond
A bond formed when a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom.
Compare covalent, ionic, and hydrogen bonds. Which is strongest? Weakest?
Covalent bonds are generally the strongest, followed by ionic bonds, with hydrogen bonds being the weakest.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonds
Significant in biological processes such as DNA structure and properties of water.
Properties of Water
Includes high specific heat, cohesion, adhesion, high surface tension, and ability to dissolve many substances.
What types of substances does water dissolve?
Water is known as a universal solvent because it can dissolve many substances, including ionic compounds (salts), polar covalent compounds (sugars and alcohols), and some gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide).
Cohesion vs. Adhesion
Cohesion is the attraction between molecules of the same substance, while adhesion is the attraction between molecules of different substances.
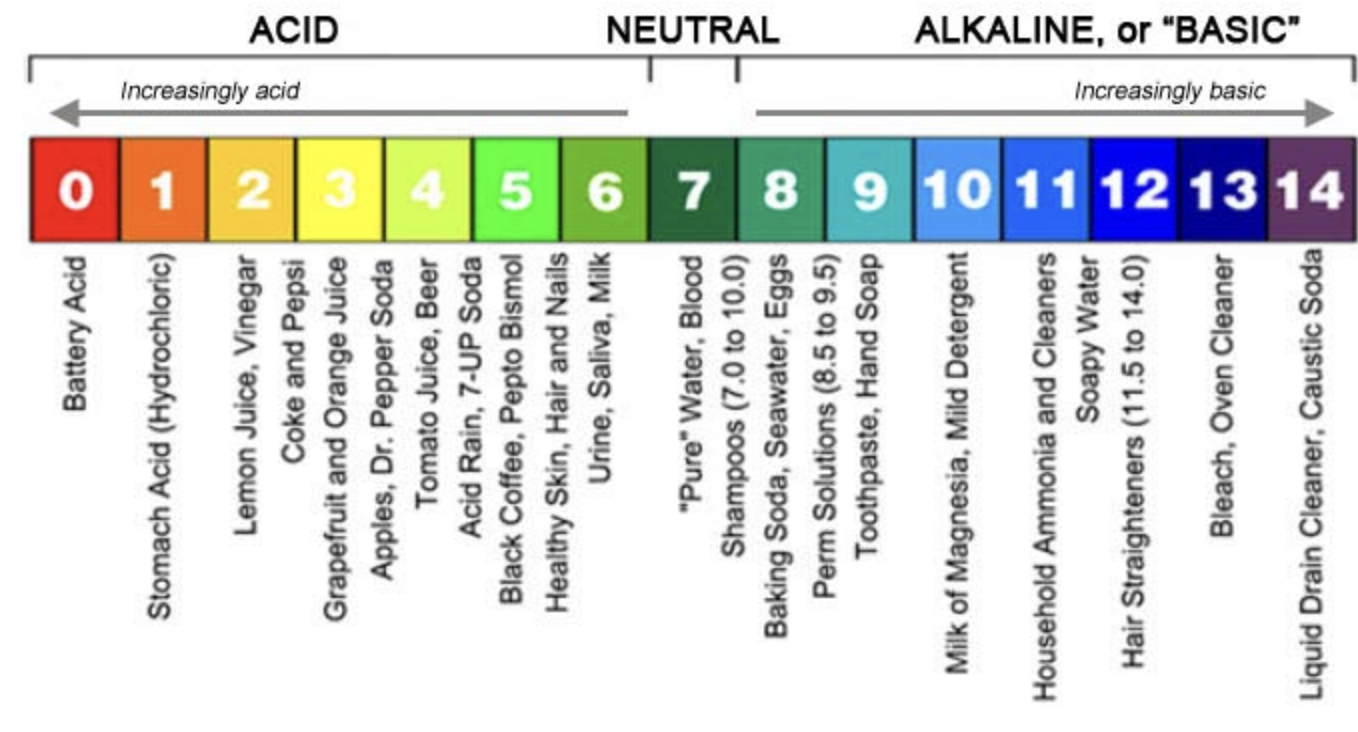
pH
A measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, calculated as pH = -log [H⁺].
Buffer
Substances that reduce changes in the concentration of H⁺ and OH⁻ in a solution.
Atom’s Electron Shells
The first shell can hold 2 electrons. The second and third shells can hold eight electrons.
Octet rule
atom’s with two or more shells are most stable when they have eight electrons in outermost shell
Unlike nearly all other liquids, water expands when it freezes. Why does this happen?
It expands when it freezes due to the formation of a crystalline structure.