Chemical Foundations of Life: Elements, Bonds, and Water Properties
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element?
An atom.
What are the three types of subatomic particles in an atom?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons.
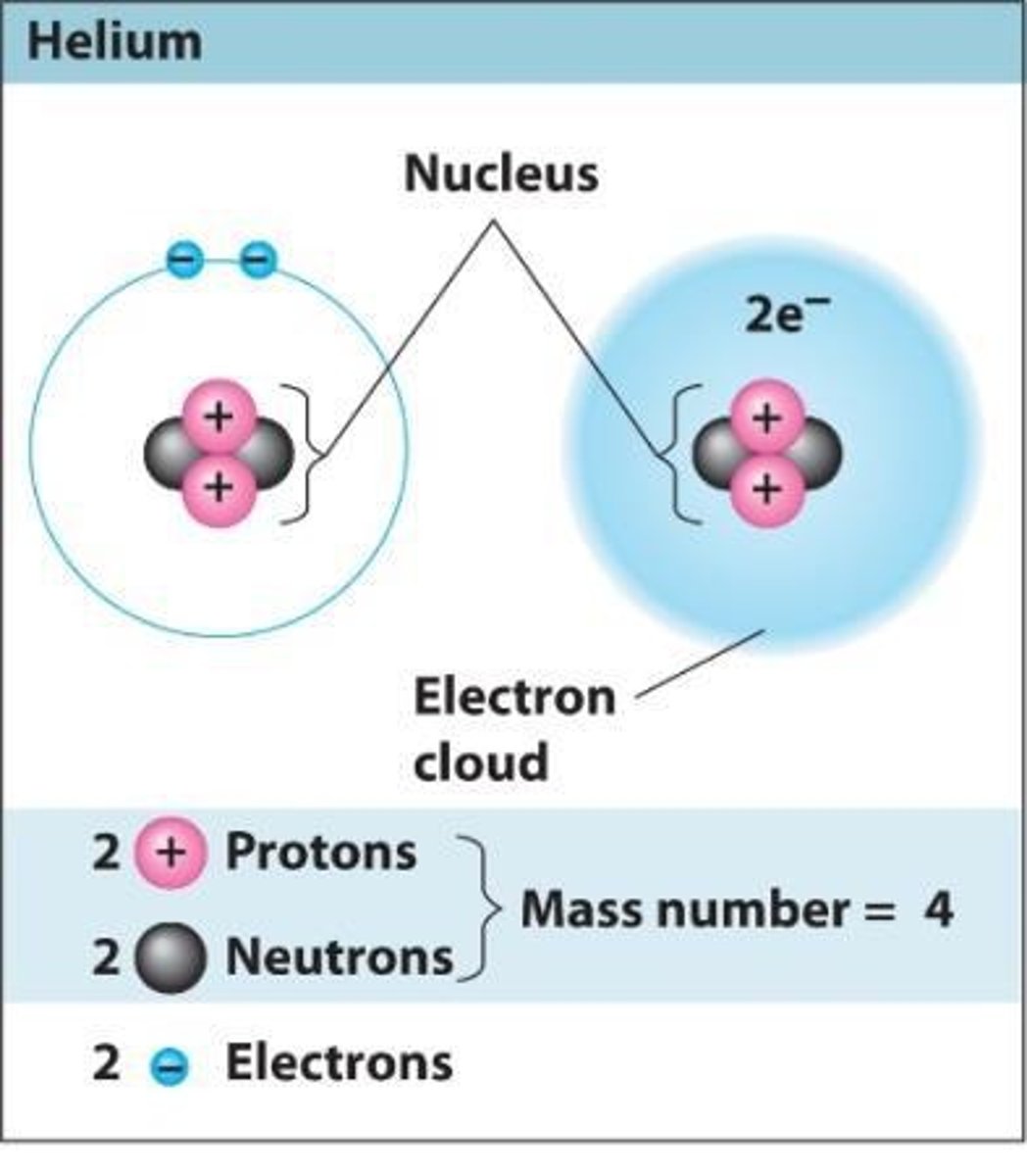
What is the atomic number of an element?
The number of protons in its nucleus.
What is the mass number of an element?
The sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
What are isotopes?
Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons.
What is the significance of trace elements in human health?
They are required in minute quantities but have a high impact on health.
Name two trace elements and their importance.
Iron: key component of hemoglobin for oxygen transport; Iodine: essential for thyroid hormone production.
What is a compound?
A substance that contains two or more elements in a fixed ratio.
What is the Octet Rule?
Atoms tend to achieve a configuration of 8 valence electrons for stability.
What are valence electrons?
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
What types of chemical bonds exist?
Covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrogen bonds.
What is electronegativity?
An atom's attraction to electrons; higher electronegativity means stronger attraction.
What is a covalent bond?
The sharing of a pair of valence electrons between two atoms.
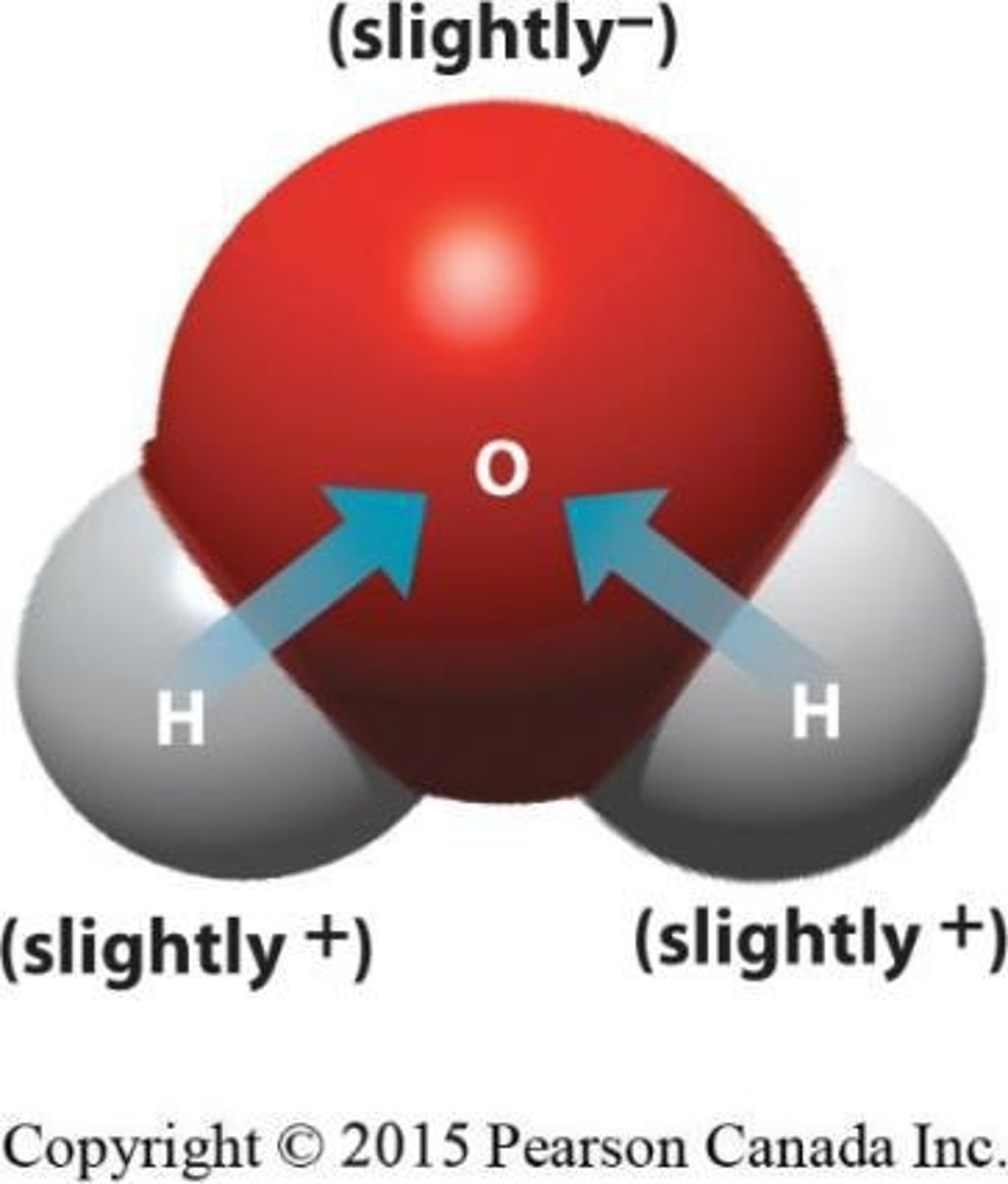
What distinguishes polar covalent bonds from non-polar covalent bonds?
In polar covalent bonds, electrons are shared unequally, leading to partial charges.
What are ionic bonds?
Attractions between ions of opposite charge formed when one atom transfers an electron to another.
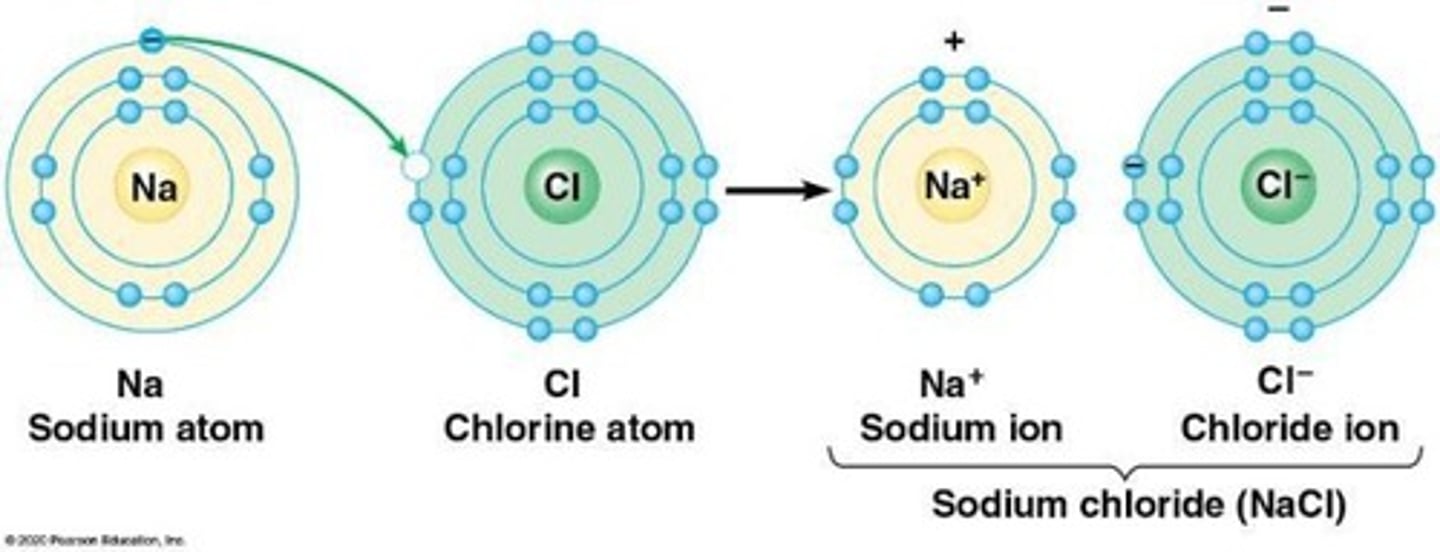
What are ionic compounds commonly known as?
Salts.
How do ionic compounds behave in water?
They dissolve easily.
What is the relationship between molecular structure and function?
The arrangement of atoms in molecules determines their properties and functions.
What happens to the nucleus of unstable isotopes?
They decay spontaneously, giving off particles and energy.
What is the role of electrons in chemical interactions?
Electrons determine how atoms interact and bond with each other.
What is the significance of the first 18 elements on the periodic table regarding electron configuration?
They typically strive to achieve 8 valence electrons for stability.
What is the difference between stable and unstable isotopes?
Stable isotopes have intact nuclei, while unstable isotopes decay over time.
What is the impact of high exposure to radioactive isotopes?
It can mutate DNA.
What is a molecule?
A group of two or more atoms bonded together by covalent bonds.
What is the difference between single and double covalent bonds?
Single bonds share one pair of electrons; double bonds share two pairs, making them stronger.
What defines a charged atom?
A charged atom is called an ion, formed when an atom gains or loses electrons.
What type of bond is formed between two hydrogen atoms in H2?
A nonpolar bond.
What type of bond is present in water (H2O)?
A polar bond, where electrons are shared with oxygen.
What is a hydrogen bond?
A weak bond formed when positively charged hydrogen atoms bond with slightly negatively charged atoms in other molecules.
How strong are hydrogen bonds compared to covalent bonds?
Hydrogen bonds are approximately 5% as strong as covalent bonds.
What are the reactants in a chemical reaction?
The materials that undergo the reaction.
What are the products in a chemical reaction?
The resulting materials after the reaction has occurred.
Why is water considered the biological medium on Earth?
All living organisms require water more than any other substance, and most cells are 70-95% water.
What are the four emergent properties of water that support life?
Cohesive behavior, ability to moderate temperature, expansion upon freezing, and versatility as a solvent.
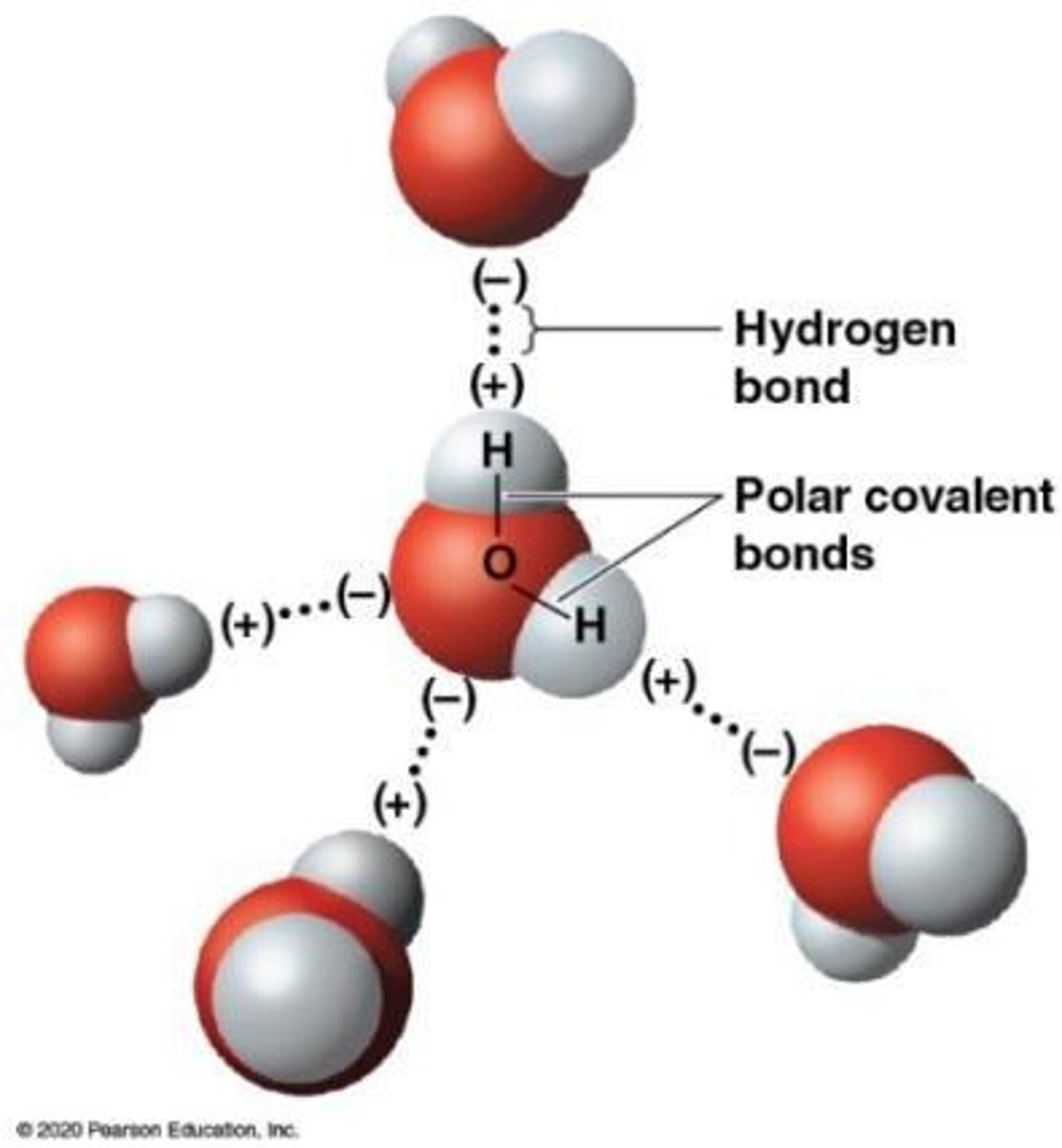
What is cohesion in relation to water?
The tendency of water molecules to stick together due to hydrogen bonds.
What is adhesion?
The tendency of different kinds of molecules to stick together.
How does water moderate temperature?
Water absorbs heat from warmer air and releases stored heat to cooler air, resisting temperature changes.
What happens to water at 4˚C?
Water reaches peak density at this temperature, causing ice to float.
What is a solvent?
The dissolving agent in a solution.
What is a solute?
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
What is the pH scale used for?
To describe the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 (most acidic) to 14 (most basic).
What defines an acid?
A chemical compound that donates H+ ions to solutions.
What defines a base?
A compound that removes H+ ions from solutions.
What is the role of buffers in biological systems?
Buffers minimize changes in H+ and OH- concentrations, maintaining pH stability.
What is ocean acidification?
The decrease in pH of ocean water due to increased CO2 levels from fossil fuel combustion.
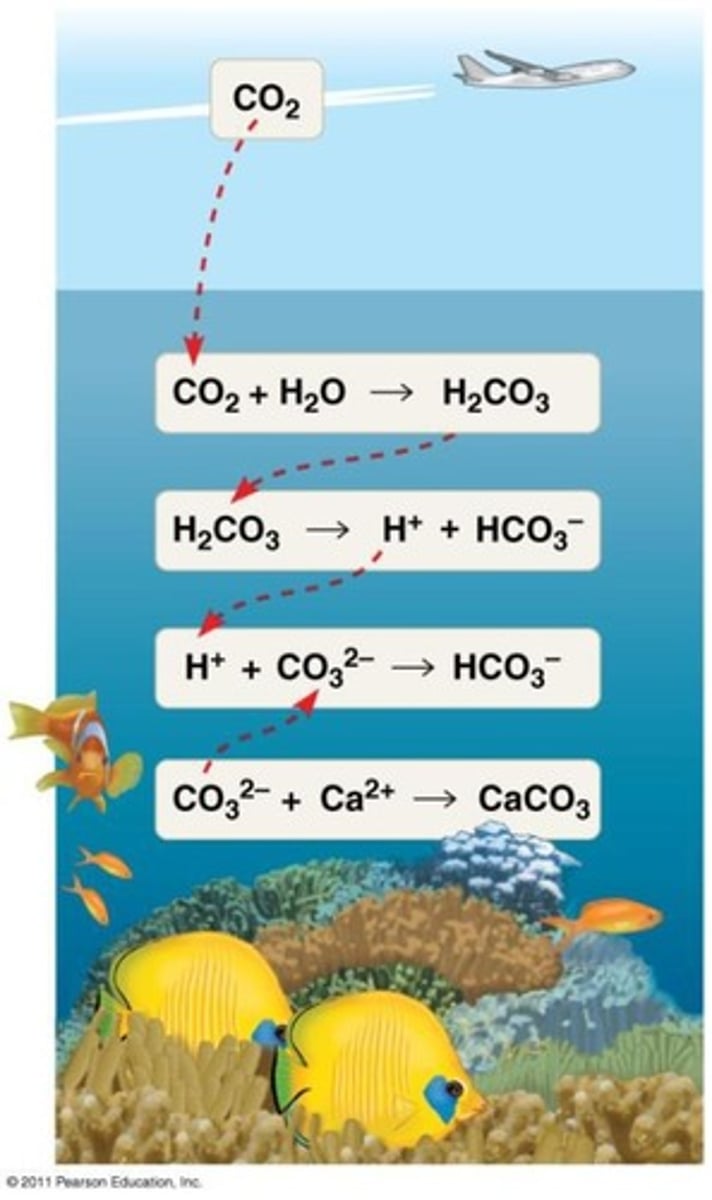
Why is ocean acidification a problem for marine life?
It reduces the availability of carbonate needed for organisms to create calcium carbonate exoskeletons.