Study Material on Consciousness Concepts for Undergraduate Psychology
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
activation-synthesis theory
a theory of dreaming; this theory proposes that the brain tries to make sense of random brain activity that occurs during sleep by synthesizing the activity with stored memories
somnambulism
sleepwalking
consciousness
our awareness of ourselves and our environment
dual processing theory
A theory stating that the mind is composed of both conscious and unconscious activity
circadian rhythms
The 24-hour biological cycles found in humans and many other species.
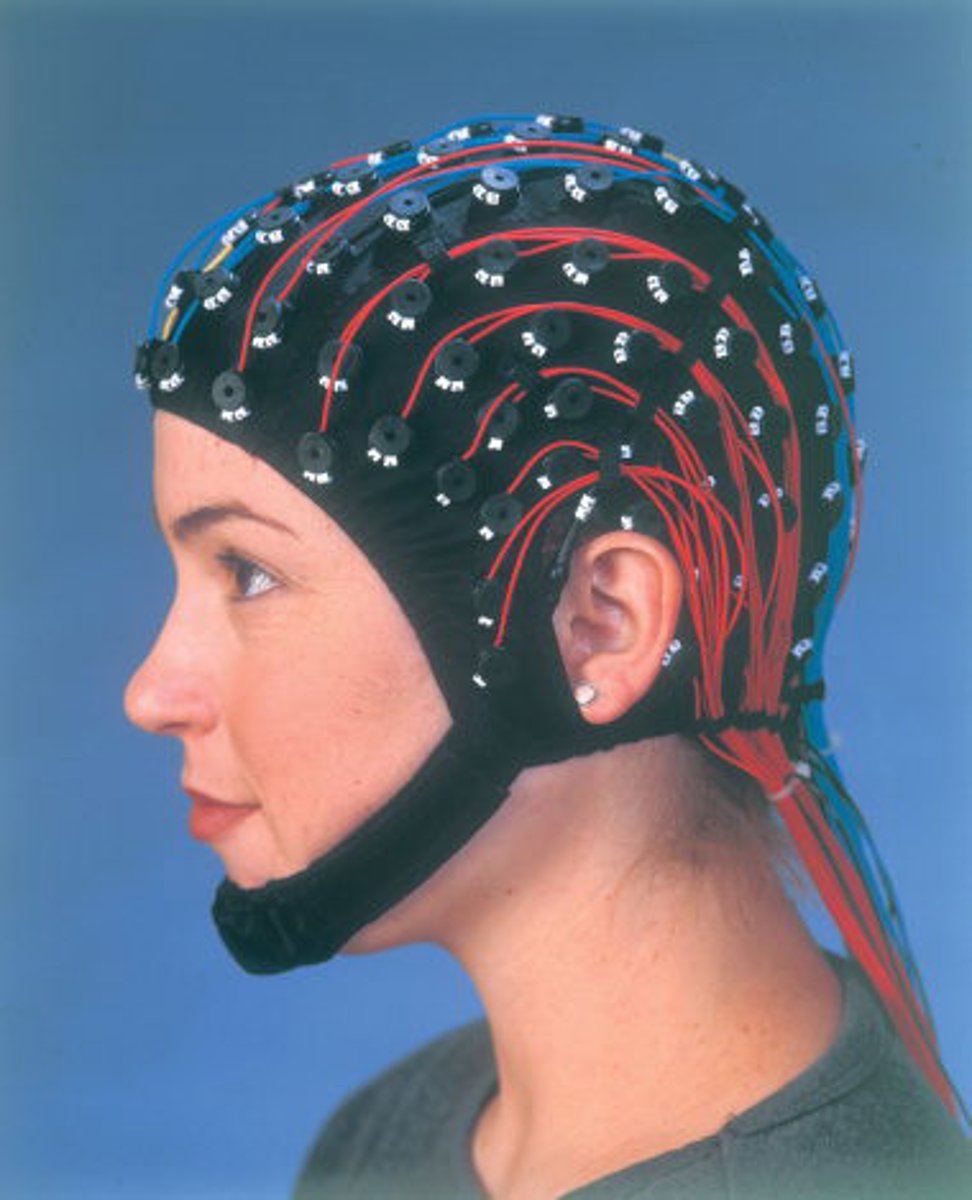
electroencephalograph (EEG)
a device that monitors the electrical activity of the brain over time by means of recording electrodes attached to the surface of the scalp
insomnia
Difficulty in falling asleep or staying asleep
Melatonin
A hormone manufactured by the pineal gland that produces sleepiness.
REM sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep, a recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur. Also known as paradoxical sleep, because the muscles are relaxed (except for minor twitches) but other body systems are active.
REM rebound
increased amounts of REM sleep after being deprived of REM sleep on earlier nights
addiction
compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse consequences
amphetamines
drugs that stimulate neural activity, causing speeded-up body functions and associated energy and mood changes

Barbiturates
drugs that depress the activity of the central nervous system, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgment
cannabis/marijuana
the dried part of the hemp plant; a hallucinogen that is the most widely used illegal substance
depressants
drugs (such as alcohol, barbiturates, and opiates) that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
hallucinations
false sensory experiences, such as seeing something in the absence of an external visual stimulus
hallucinogens
psychedelic drugs, such as LSD, that distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
psychoactive drugs
chemicals that affect the central nervous system and alter activity in the brain
Substance use disorder/addictive

tolerance (drug)
the same dose has less of an effect, or more drug is needed to achieve the same effect
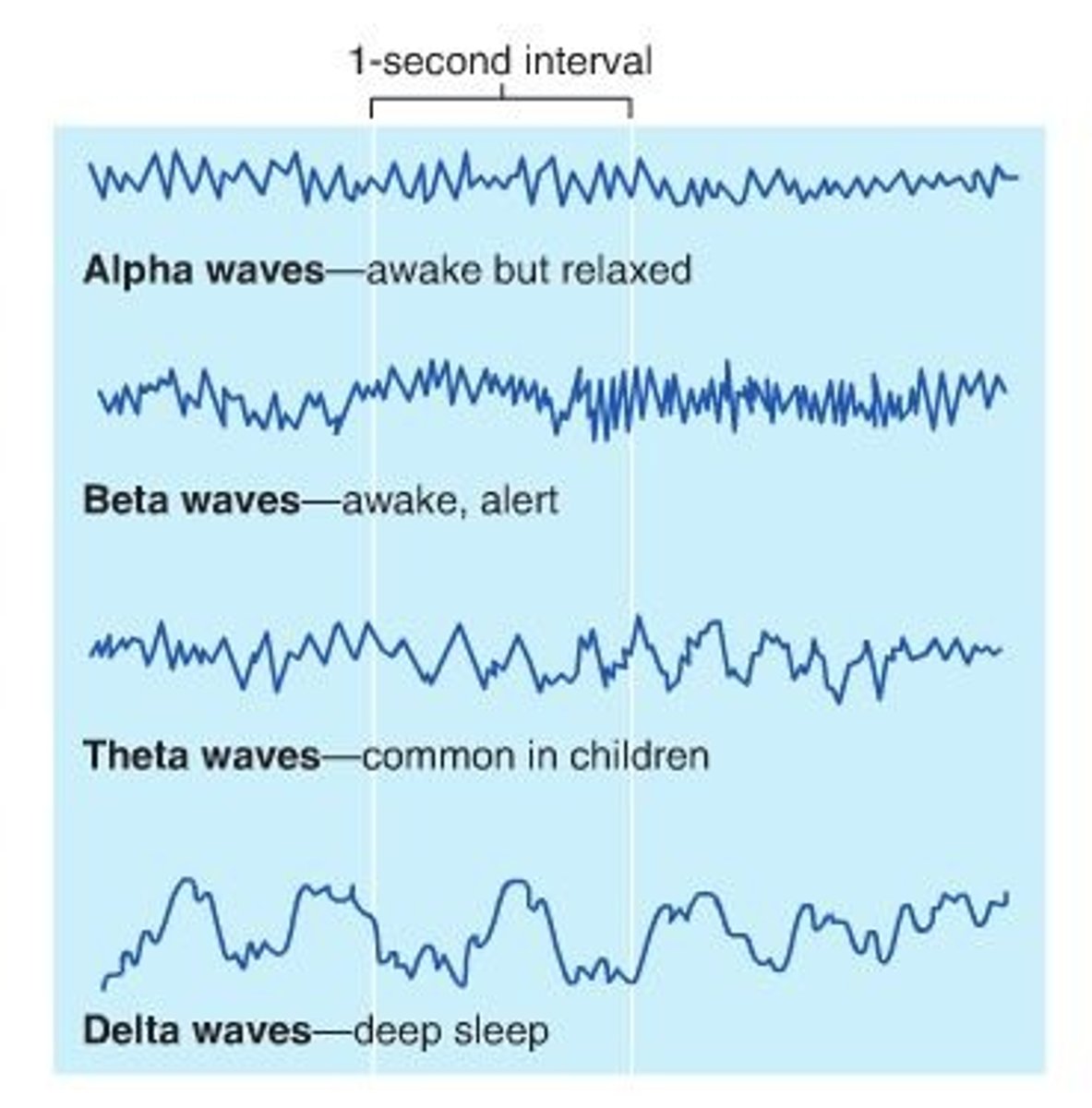
alpha, theta, delta waves
Brain waves. Alpha-light sleep. Theta-early stages of sleep. Delta- deep sleep
information-processing theory
dreams help us sort out the day's events and consolidate our memories
NREM Sleep stages
1. drifting off, lightest, drowsiness, few minutes, eye movements and muscles slowing
2. deeper, 10-15 minutes, movements cease, brain waves slow
3. deep sleep, slow waves, large delta waves, blood pressure heart rate and respiration drop
4. deepest, speech and movement are rare, human growth hormone released
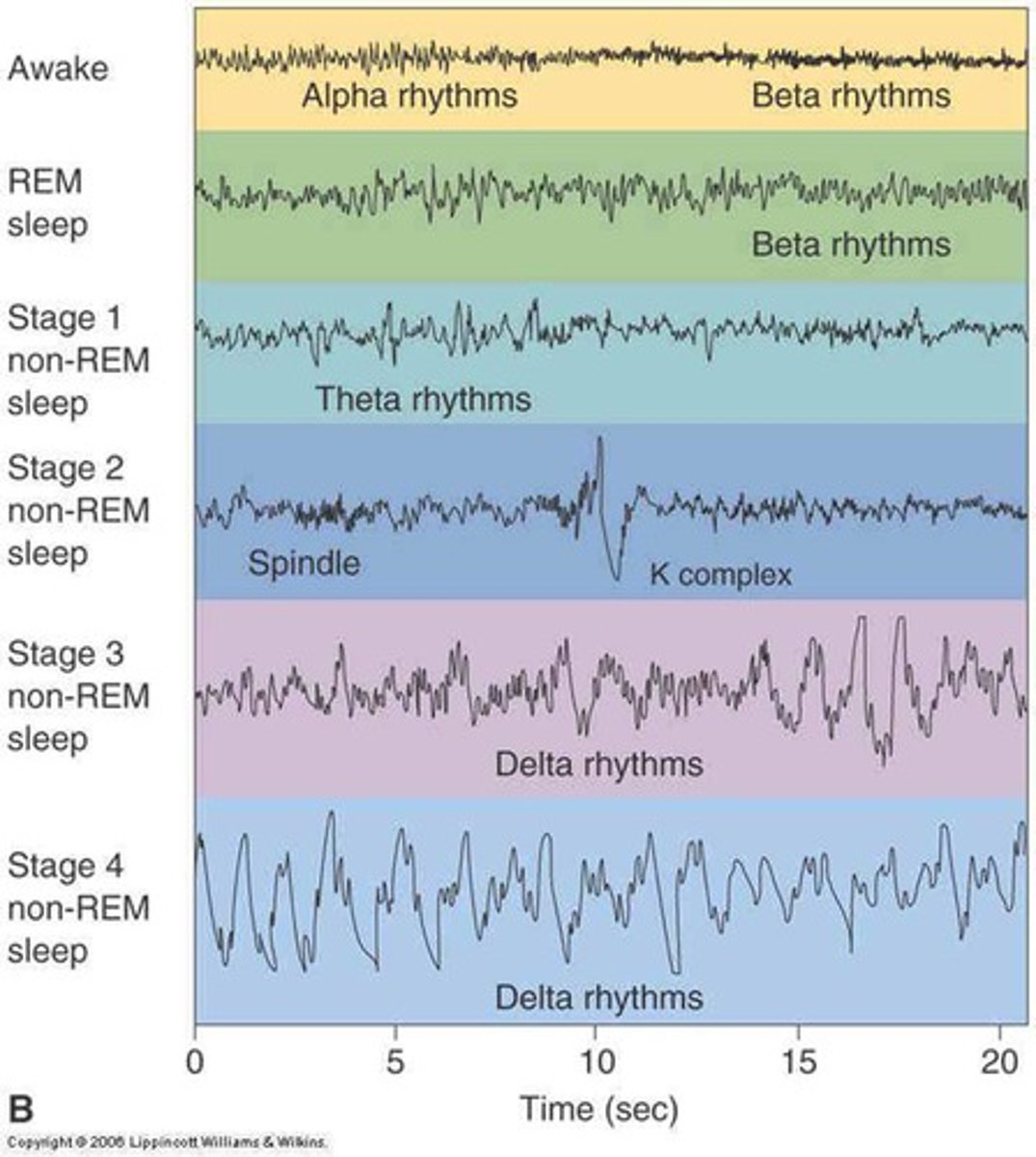
paradoxical sleep
The type of sleep encountered during REM when internally, the brain and body are active; while externally, the body appears calm and inactive
Pineal Gland
produces melatonin
night terrors
a sleep disorder characterized by high arousal and an appearance of being terrified; unlike nightmares, night terrors occur during Stage 4 sleep, within two or three hours of falling asleep, and are seldom remembered
sleep apnea
a disorder in which the person stops breathing for brief periods while asleep
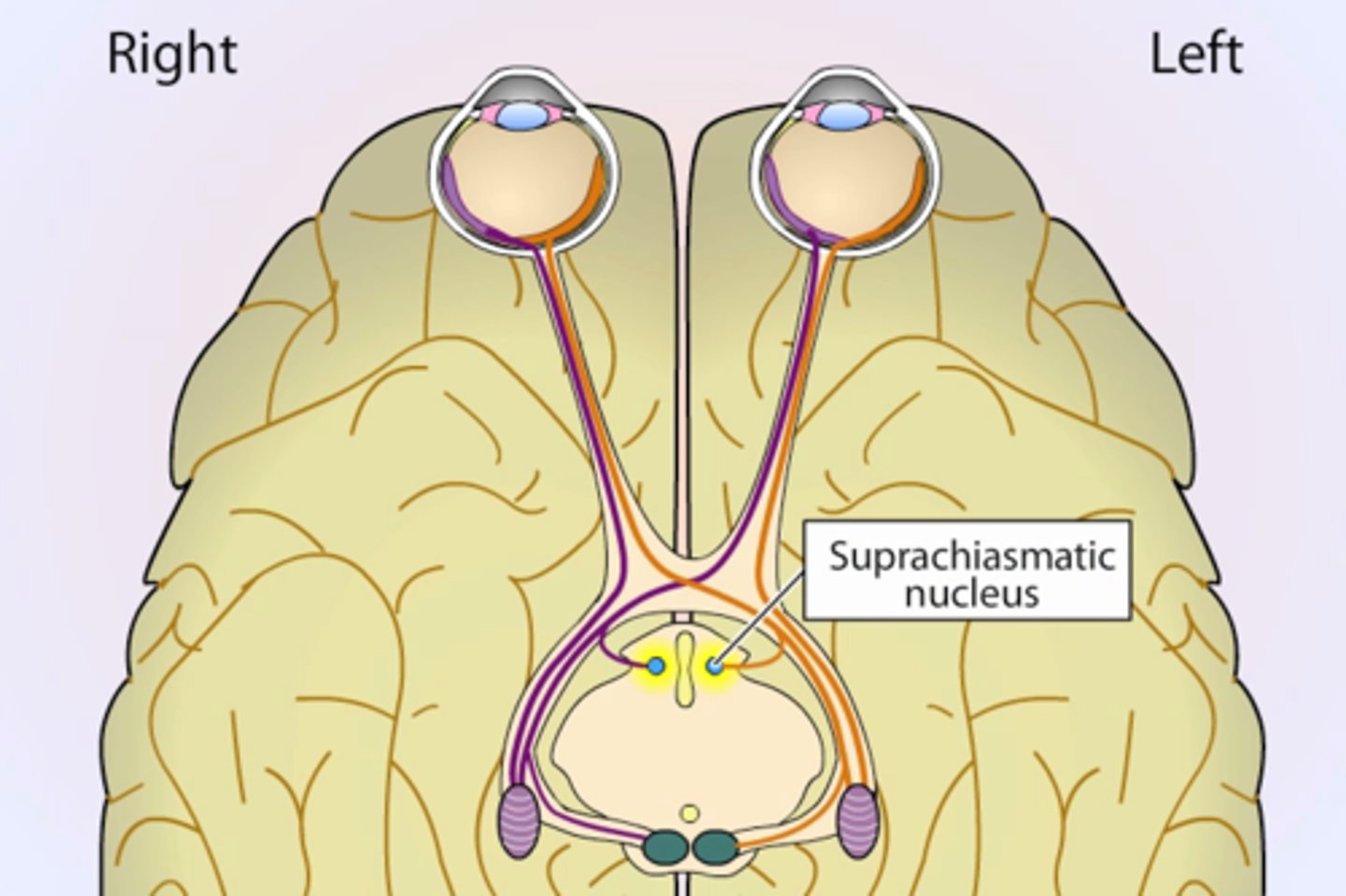
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
a pair of cell clusters in the hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythm. In response to light, the SCN causes the pineal gland to adjust melatonin production, thus modifying our feelings of sleepiness
antagonists
drugs that block the function of a neurotransmitter
drug dependence
a severe drug-related problem characterized by impaired control over the use of the drug
opiates
opium and its derivatives, such as morphine and heroin; they depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety
Stimulants
Drugs (such as caffeine, nicotine, and the more powerful amphetamines, cocaine, and Ecstasy) that excite neural activity and speed up body functions.
Synergistic effects
Drug interactions in which the effect of a combination of two or more drugs with similar actions is greater than the sum of the individual effects of the same drugs given alone
withdrawal
the discomfort and distress that follow discontinuing the use of an addictive drug
nonconscious
descriptive of bodily processes, such as the growing of hair, of which we are not aware
Preconscious
contains material just beneath the surface of awareness that can easily be retrieved
Narcolepsy
A sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks. The sufferer may lapse directly into REM sleep, often at inopportune times.
Narcotics
Specific drugs that are obtainable only by prescription and are used to relieve pain