UNIT 5A.17.1: MALE GENETALIA Assessment
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
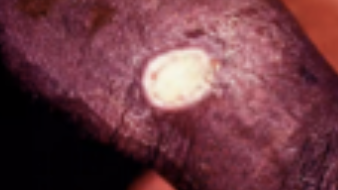
Syphilitic Chancre
Small, silvery-white papule that develops red, ovalulceration; sign of primary syphilis
Herpes Progenitalis
Clusters of pimple-like, clear vesicles that erupt and become ulcers
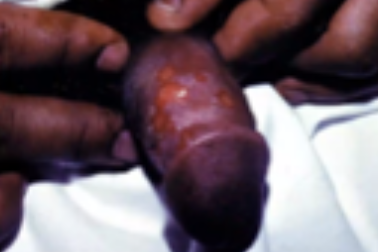
Genital Warts
Single or multiple, moist, fleshy papule; STI caused by human papillomavirus

Phimosis
Inability to retract the skin (foreskin or prepuce) covering the head (glans) of the penis.
May appear as a tight ring or “rubber band” of foreskin around the tip of the penis, preventing full retraction.

Paraphimosis
Foreskin that is left in retracted position;
Common urologic emergency that occurs in uncircumcised males when the foreskin becomes trapped behind the corona of the glans penis
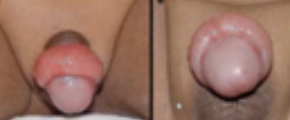
Hypospadias
Birth defect in boys in which the opening of the urethra is not located at the tip of the penis; urethral meatusis located underneath the glans (ventral side)
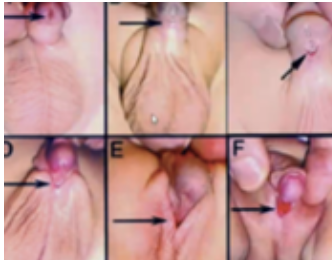
Epispadias
Rare congenital (present at birth) anomaly involving the development of the urethra;
Urethral meatus is located on top of glans (dorsal side)
Hydrocele
Type of swelling in the scrotum, the pouch of skin that holds the testicles
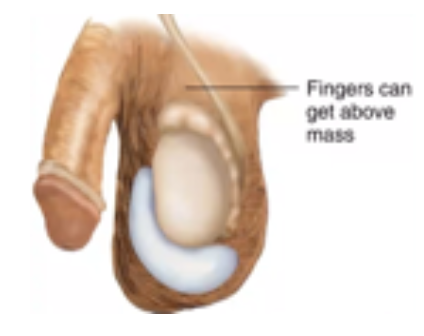
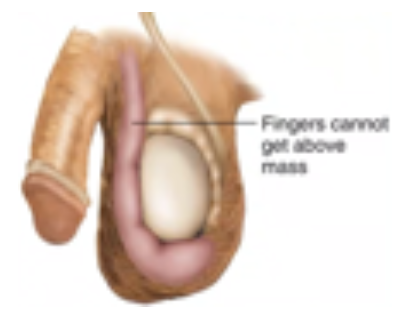
Scrotal Hernia
Large hernias can extend into the scrotum causing pain and swelling
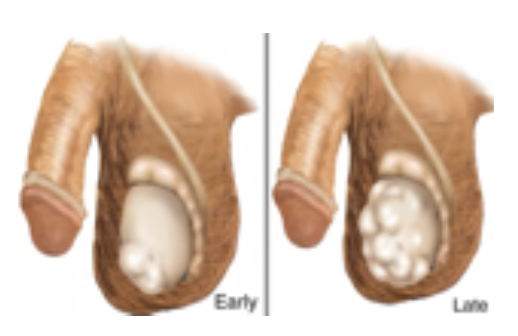
Testicular Tumor
Small, firm, non tender nodule on testis
Cryptorchidism
The absence of at least one testicle from the scrotum
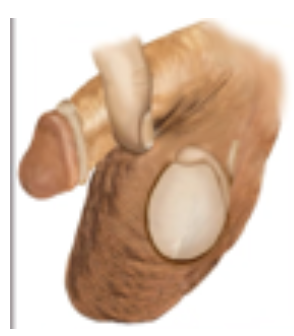
Epididymitis
Inflammation of the coiled tube, called the epididymis, at the back of the testicle
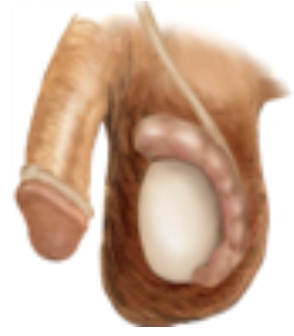
Orchitis
Inflammation of one or both testicles
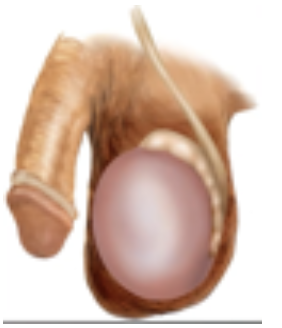
Small Testes
If less than 3.5 cm long: indicates atrophy
If less than 2 cm long: indicates Klinefelter’s syndrome
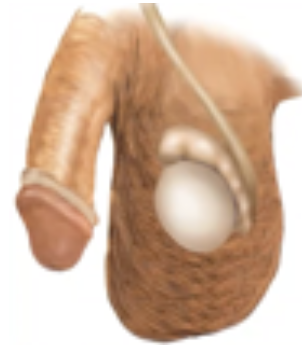
Torsion of Spermatic Cord
The spermatic cord is coiled
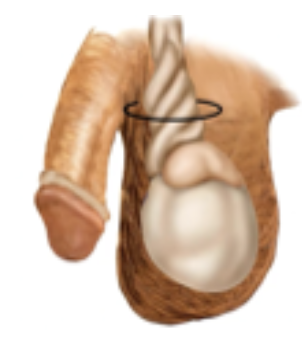
Varicocele
Enlargement of the veins that transport oxygen-depleted blood away from the testicle
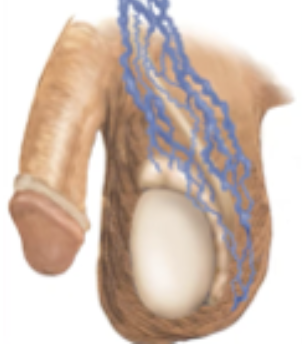
Spermatocele
Abnormal sac (cyst) that develops in the epididymis
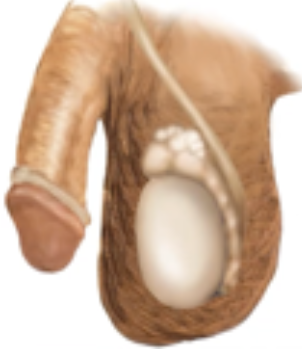
Cancer of Prostate
Hard area on prostate or hard fixed, irregular nodules on prostate
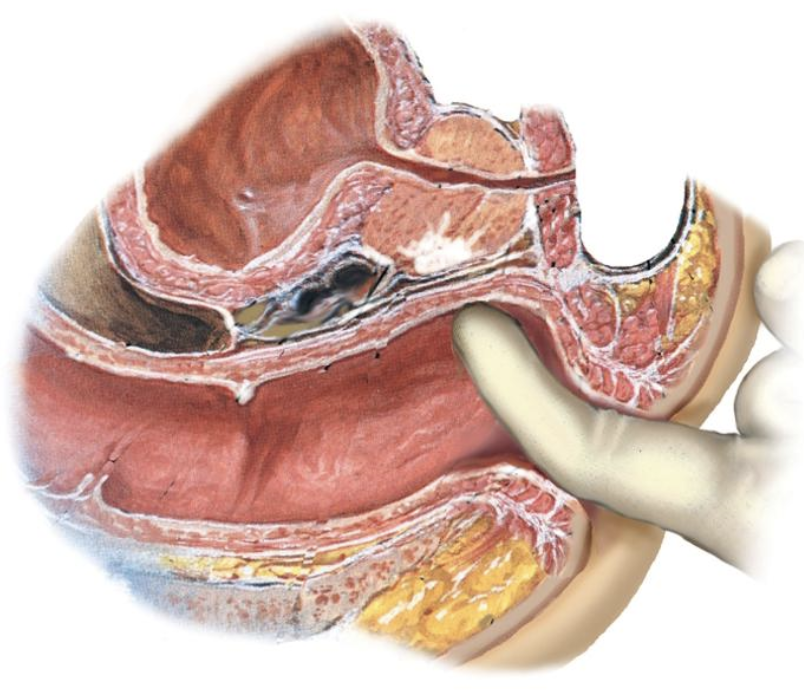
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy
Prostate is enlarged, smooth, firm, and slightly elastic
Median sulcus may not be palpable
Common in men older than 50 years
Pediculosis Pubis/Crabs
Lice or nit (eggs) infestation at the base of the penis or pubic hair
Hypospadias
Displacement of the urinary meatus to the ventral surface of the penis
Epispadias
Displacement of the urinary meatus to the dorsal surface of the penis
Gonorrhea
What does a yellow urethral discharge indicate?
Urethritis
What does a clear or white urethral discharge indicate?
Prehn’s Sign
If the client has epididymitis, passive elevation of the testes may relieve the scrotal pain
Indirect Inguinal Hernia
Bowel herniates through the internal inguinal ring and remains in the inguinal canal or travels down into the scrotum
Most common type of hernia
May occur in adults but more frequent in children
Direct Inguinal Hernia
Bowel herniates from behind and through the external inguinal ring, rarely travels down into the scrotum
Less common
Occurs mostly in adult men older than 40
Femoral Hernia
Bowel herniates through the femoral ring and canal; never travels into the scrotum and the inguinal canal is empty
Least common type of hernia
Mostly in women
Acute Prostatitis
Prostate is swollen, tender, firm, and warm to touch
Caused by bacterial infection
Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy
Prostate is enlarged, smooth, firm, and slightly elastic
Median sulcus may not be palpable
Common in men older than 50 years
Prostate Cancer
Hard area on the prostate or hard, fixed, irregular nodules on the prostate
Median sulcus may not be palpable