Chapter 3: Periodic Properties of the Elements
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Hund’s Rule
When filling orbitals that have the same energy (degenerate), place one electron in each orbital before completing pairs
Aufbau Principle
Energy levels and sublevels fill from lowest energy to highest: s → p → d → f; orbitals that are in the same sublevel (l value) have the same energy
Pauli Exclusion Principle
There can be no more than two electrons per orbital
Core electrons
Electrons in lower energy shells
Valence electrons
The electrons in all the sublevels with the highest principal energy shell
Halogens
Nonmetals with one fewer electron than the next noble gas
Noble gases
Have 8 valence electrons except for He
Paramagnetism
Electron configurations that result in unpaired electrons mean that the atom or ion will have a net magnetic field

Dimagnetism
Electron configurations that result in all paired electrons mean that the atom or ion will have no magnetic field
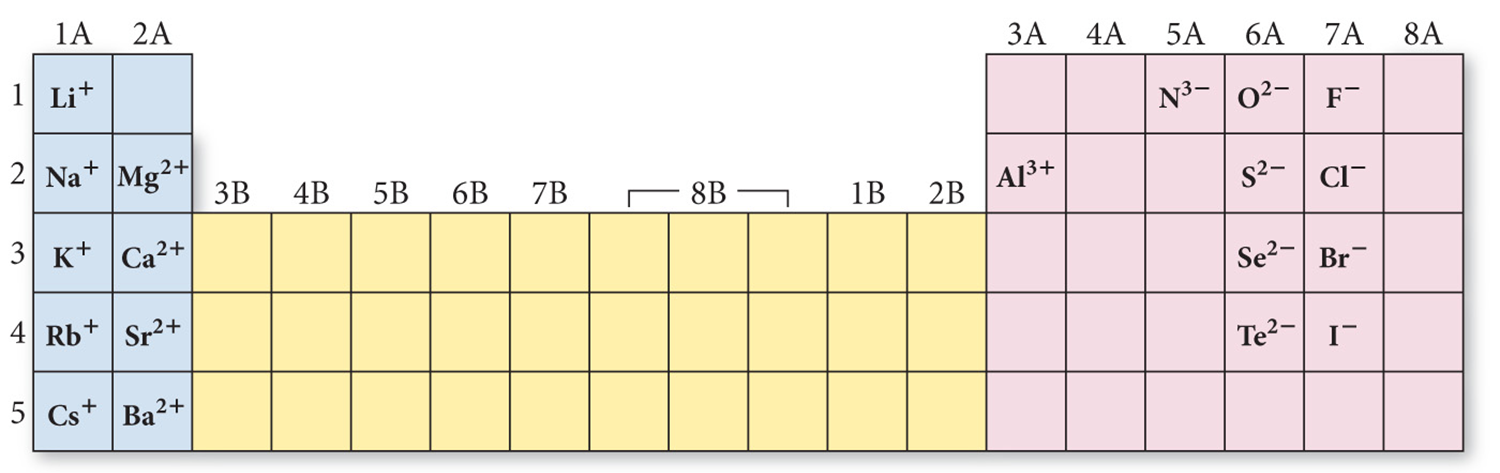
Ionic Radii Rules
More electrons = larger
Ions in the same group have the same charge
Ion size increases down the column.
Higher valence shell, larger
Cations are smaller than neutral atoms; anions are larger than neutral atoms.
All cations are smaller than anions (Except Rb+ and Cs+, which are bigger than or the same size as F− and O2−).
Isoelectric Species Rules
Larger positive charge = smaller cation
Larger negative charge = larger anion
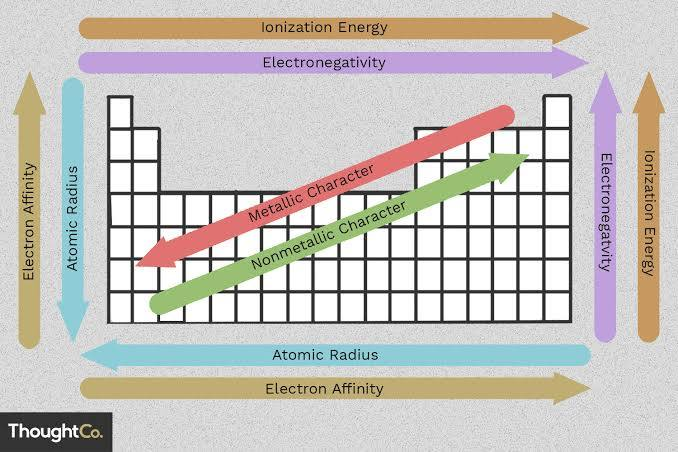
Ionization Energy (IE)
The minimum energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or ion in the gas phase; an endothermic process (requires the input of energy to remove the electron; lower IE, farther electron distance from nucleus = easier to remove
Ionization Energy Trend (IE Trend)
Decreases down the group; valence electron is farther from the positively charged nucleus with the same effective nuclear charge; increases across the period
Electron Affinity (EA)
The energy associated with adding an electron to the valence shell of an atom that is in the gas phase; an exothermic, but sometimes endothermic process; more energy released (more negative) = larger EA
Metal texture
Malleable (deform under compressive stress) and ductile (stretch under tensile stress)
Metal reflectiveness
Shiny, lustrous, reflect light
Metal conductivity
Conduct heat and electricity quickly
Metal oxides
Most oxides basic and ionic
Metal electron behavior
Lose electrons in reactions to form cations—oxidized
Nonmetal texture
Brittle in solid state
Nonmetal reflectiveness
Dull, nonreflective, solid surface
Nonmetal conductivity
Electrical and thermal insulators
Nonmetal oxides
Most oxides acidic and molecular
Nonmetal electron behavior
Gain electrons in reactions to form anions and polyatomic anions—reduced
Metallic character
How closely an element’s properties match the ideal properties of a metal
Ionic charges
Periodic Trends