Lec 4: Cardiorespiratory Fitness (Pt 2)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Lab Measures for Submaximal Exercise Tests:
Lab Measures for Submaximal Exercise Tests focus on what?
Lab Measures for Submaximal Exercise Tests often require multiple…
Fixed amount of work per unit of time
Multiple stages/levels
Lab Measures for Submaximal Exercise Tests:
What are the 3 modes of testing?
What is the KEY POINT for Lab Measures for Submaximal Exercise Tests?
3 Modes:
Bench Step
Cycle Ergometer
Treadmill
KEY POINT:
Limit a participant’s effort to LESS THAN Max Exertion
Lab Measures for Submaximal Exercise Tests:
HR is measured throughout the test at different outputs and this info is used to estimate what?
Which of the 3 Lab Measures for Submaximal Exercise Tests is shown to be more exact with quantifying work other than other modes of exercise testing?
Estimate CRF
Cycle Ergometer
Assumptions for Submax Exercise Test:
Linear relationship between…
HR max can be predicted by what?
Steady State Heart Rate (HRss) can be achieved how?
VO2 Max and HR btwn 110-150
Age
3-4 minutes at a constant sub max workload
Assumptions for Submax Exercise Test:
A cadence of what is comfortable and mechanically efficient?
Submax work output can predict what?
HR at 2 separate work outputs can be plotted as what?
And extrapolated to the estimated what?
Cadence of 50 rpm
Maximal aerobic capacity
HR-VO2
HR max
What are the 5 sources of error in submax exercise tests?
Prediction of HR max by age
Efficiency of the participant performing the ergometer test
Equipment calibration
Accurate measurement of HR in each stage
Having a HRss at each stage
Deciding on which Method to use:
What is the Chief Goal?
Keep participants safe
Deciding on which Method to use?
What are the 6 considerations?
Reasons for the test
Risk level
Expense
Time required
Personnel required
Equipment and facilities required
What are 4 ADVANTAGES of Submaximal Exercise Testing?
Relatively inexpensive and requires less equipment, personnel, med supervision like MAX test
Allow for testing of large groups
Shorter duration time
Multistage Tests
Can assess multiple HR and BP
What are 4 DISADVANTAGES of Submaximal Exercise Testing?
Max measurements (HR, BP, VO2) are not taken but often delivered
VO2 Max prediction error range around 10-20%
Limited diagnostic utility for certain disease (CAD)
Limited exercise prescription purpose with no measured HR max
Pretest Standardizations for CRF Assessments? (6)
Wear comfortable shoes
Avoid tobacco and caffeine 3 hrs prior to test
Avoid alcohol 12 hrs prior
Consume plenty of fluids
Avoid strenuous exercise for 24 hrs prior to test
Get adequate sleep night before test
Pretest Standardizations for CRF Assessments:
As a tester, you should do what 4 things?
Obtain consent and PAR Q
Instruct procedure
Make sure pt understands that they can terminate test at any time
Instruct used of Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) scale
What are the 2 Exercise Modes for Lab Submax Tests?
Cycle Ergometer
Treadmill
Cycle Ergometer:
T/F: MC mode of submax testing
4 ADVANTAGES:
TRUE
4:
Low impact
Safe mode of exercise
Ease of monitoring pulse and BP
Less expensive and more portable than treadmills
Cycle Ergometer:
2 DISADVANTAGES:
2
Not common mode of exercise/activity in US adults
Mechanically breaked cycle ergometers require constant pedaling cadence to keep work rate constant
NOTE: These disadvantages should be noted as they can limit activity before meaningful end point for estimating CRF
Cycle Ergometer:
T/F: Monark Cycle is the most popular brand for submax exercise testing.
What type of Ergometer is the Monark Cycle?
The Monark Cycle needs ___ for accurate work outputs
TRUE
Type
Mechanically braked cycle ergometer
Calibration
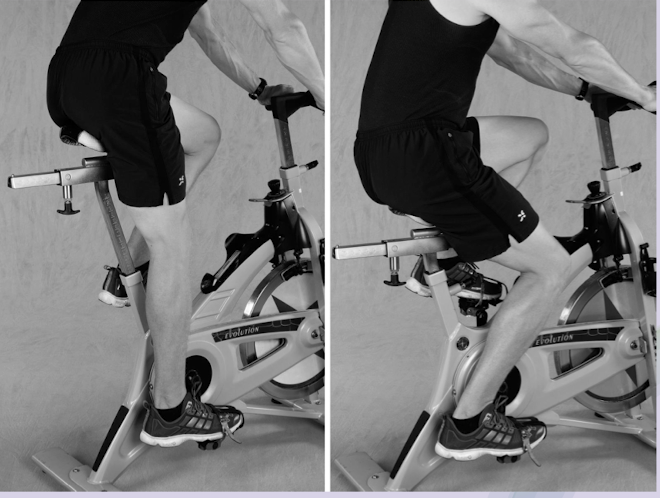
Cycle Ergometer: Calibration
Seat Height: Inappropriate seat height can result in what?
Appropriate height:
What is proper foot placement?
Adjust handle bars to allow what during test?
Seat height:
Inefficiency and early fatigue
Height:
Knee slightly bent with sole of foot centered on peddle while in bottom position
Handlebars
Upright posture

Cycle Ergometer:
Cycle Ergometer is measured by what?
What 3 factors are included in equation?
Work performed per unit of time
3
Resistance (kilogram force (kg))
Cadence
Pedal rpm
Usually set at 50 rpm
Distance
Flywheel travel distance each revolution

Cycle Ergometer:
What are the 2 common protocols?
Astrand Rhyming Cycle Ergometer Test
YMCA Cycle Ergometer Test
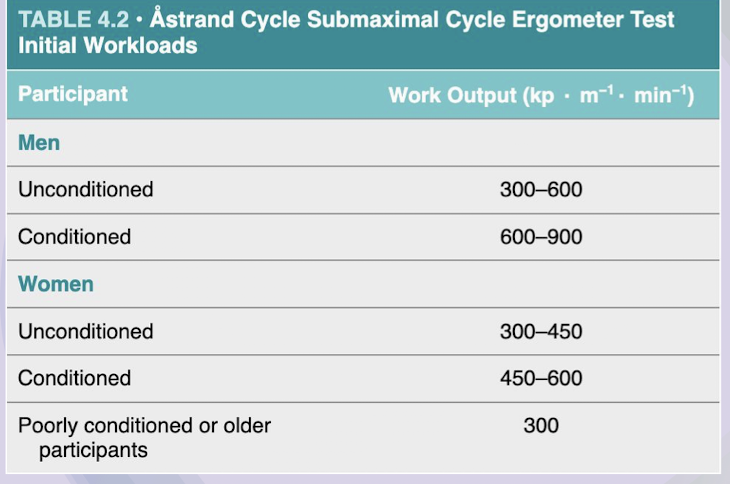
Astrand Rhyming Cycle Ergometer Test:
Participants start with:
When is HR measured?
Expected HR:
If < 125 bpm, what happens?
Start:
6 min bout of standardized work
HR
Measured: END of 6 min bout
125-170 bpm
< 125 bpm
Workload increased
Additional 6 min bout completed
YMCA Cycle Ergometer:
Describe Test:
Maintain __ rpm throughout, BUT what increased with each stage?
When does test stop?
Four, 3 minute stages at incremental workloads
50 rpm, Resistance increases
STOP
two separate 3 minute stages that result in HR balues btwn 110-150 bpm and 85% HR max
Treadmill:
What is the purpose of Treadmill test?
What is the MC protocol for Treadmill test?
Purpose:
Prediction of CRF derived from linear relationship btwn HR and VO2 Max
MC:
Bruce Protocol
Treadmill: Bruce Protocol
Similar procedure to what test?
Each stage is how long?
What 2 values are needed to STOP the test?
YMCA Submaximal Cycle Protcol
3 min
TWO HR values btwn:
110 bpm and 150 bpm
What are 6 considerations for accuracy of submaximal testing?

MET:
1 MET = what?
Equation:
METs are calculated how?
MET can also be used to calculate what?
1 MET =
Relative oxygen consumption at rest
1 MET = 3.5mL x kg^-1 x min^-1
Calculated
Dividing oxygen consumption of an activity by 3.5
Caloric expenditure
MET:
Light Intensity =
Mod Intensity =
Vigorous Intensity =
Light: 1.6-2.9 METs
Mod: 3.0-5.9 METs
Vig: ≥ 6.o METs
Summary