4.1 - Organisational Structure
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is an organisational structure?
What is an organisational chart?
A plan showing the roles of, and relationships between, all the employees in a business
What would happen without an internal organisational structure?
Without this internal structure, a business would be very chaotic and not very productive - an organisational structure sets everything out so that everyone in the business knows this info
Which businesses have an internal organisational structure?
All businesses
The organisational _______ shows the _____ played by each employee in the business and ___ reports to ____ within the business.
The organisational structure shows the roles played by each employee in the business and who reports to whom within the business.
The _____ and working _________ in a business are shown in an organisational ____.
The roles and working relationship in a business are shown in an organisational chart.
What are the 5 main job roles?
CEO, Directors, Managers, Team Leaders, Shop Floor Workers
What are the responsibilities of the CEO?
In a PLC, this person will be voted into position by the shareholders at the AGM (annual general meeting).
They establish the long-term vision of the organisation + set overall aims (CEO/MD)
What are the responsibilities of the directors?
Set long-term plans and targets for the business to be aligned with the overall vision
What are the responsibilities of managers?
May be responsible for a function within the business, for example, marketing or finance
Use employees and other resources in the best possible ways (allocating resources and workload in their specific team)
What are the responsibilities of team leaders?
Take simple decisions, such as allocating jobs among different employees or deciding which area to replenish stock in
What are the responsibilities of shop floor workers?
Carry out the business’s basic duties or activities. (Eg. working on a production line, serving customers in a shop or basic office duties)
What does MD stand for?
Managing Director
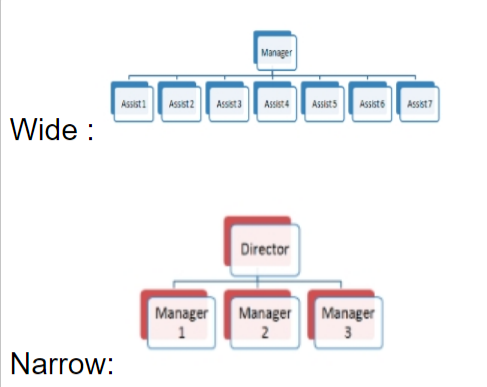
What is the span of control?
It is shown on an organisational chart
What are the 2 different spans of control?
What do experts say an ideal span of control should be?
No more than 6 people
What can the exact span of control in an organisation depend on?
- Type of business (if being a line manager requires lots of close supervision, a narrow span may be appropriate)
- Skills + attitudes of employees (if employees are highly motivated, skilled and qualified, adopting wider spans of control could be more suitable)
What are the benefits of a narrow span of control?
- More promotional opportunities can exist within the organisation
What are the limitations of a narrow span of control?
What are the benefits of a wide span of control?
- No. of managers can be reduced, lowering labour costs
What are the limitations of a wider span of control?
What does the chain of command in an organisational chart show?
The lines of authority within the business upon which communication passes
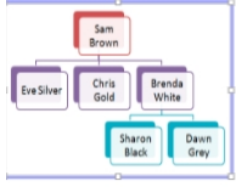
"What does this chain of command show?
"
Any issues that Sharon and Dawn may have should be directly communicated to Brenda, rather than these two members of staff communicating with Eve and Chris, or even missing a layer and going directly to Sam. If Sharon or Dawn, had a particular concern regarding Brenda however, they could directly communicate with Sam, as he is ultimately in charge of everybody.
What is a tall organisational structure?
"It has narrow spans of control and a larger number of levels of heirarchy
"
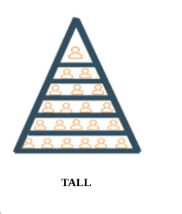
What is a flat organisational structure?
"Has a wide span of control and few levels of heirarchy
"
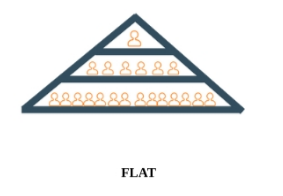
What is a subordinate?
A member of staff below a manager/senior staff member in the chain of command (under the authority of others)
In what organisational structure is passing authority to others easier?
Flat
In what organisational structure do wide spans of control exist?
Flat
In what organisational structure is there a short chain of command?
Flat
In what organisational structure do junior managers have very little involvement in decision making?
Tall
Which organisational structure do democratic (democracy - group members participate in decision making) managers prefer?
Flat
In what organisational structure do workers have a lower chance of making the wrong decisions?
Flat
In what organisational structure is more responsibility given to workers, causing higher training costs?
Flat
In what organisational structure is there quicker communication throughout the organisation?
Flat
In what organisational structure are managers responsible for fewer workers?
Tall
In what organisational structure are managers more easily able to manage the work of subordinates?
Tall
What is delayering?
The process of removing 1 or more levels of heirarchy from a business' organisational structure
What are the advantages of delayering?
- Decision making quicker
- Business should be more flexible
- Reduced wage costs (less staff employed)
What are the disadvantages of delayering?
- Employee motivation levels may fall - staff expected to take on more responsibility (possible no extra pay)
- Business may incur additional costs to train staff in new role(s)
What is delegation?
When a manager/senior employee chooses to give some of their workload to another less senior employee
Where does delegation take place?
Down the chain of command
Does the subordinate employee take responsibility for delegated work?
The subordinate employee is given permission/authority to do the job that has been delegated, but does not take responsibility for the work.
Who takes responsibility for delegated work?
The senior employee/manager who delegated the job
What is it important that everyone in the organisation knows?
"List 3 reasons why businesses have an ""Organisational structure""?"
The _____ the chain of command (the ____ levels of authority), the _____ the span of control
The longer the chain of command (the more levels of authority), the narrower the span of control
This card is blank
What is the problem with a long chain of command?
It's often difficult for the managers to communicate with the workers because messages are often misunderstood, become distorted or even lost altogether
What is a line manager?
What is communication?
Levels of hierarchy definition
The layers of authority within an organisation
What are the 2 main forms of management of a business?
Centralised and decentralised
What is a centralised structure?
What are the advantages of a centralised management structure?
- Easier to implement common policies + practices for the business as a whole
- Decisions made for the benefit of the whole business (not just 1 division/department)
What are the disadvantages of the centralised management structure?
- More layers in the organisation - increasing costs
- Local or junior managers are likely to be much closer to customer needs, therefore the best decisions for the local area may not be taken by the business.
What is a decentralised structure?
What are the advantages of a decentralised management structure?
- Good for training + developing junior managers
What are the disadvantages of a decentralised management structure?
- Harder to control costs - possible overspending
- Decision-making isn't necessarily looking to the long term future direction of the business
- Training may be needed
What are the most common methods of communication in a business?
Which 2 categories can ineffective communication fall into?
Insufficient and excessive
Name 3 barriers to communication
What can ineffective communication result in?
What are the advantages of flat organisational structures?
- Giving employees greater authority can encourage upwards communication as they're more likely to exchange info with line managers
What are the disadvantages of flat organisational structures?
- Horizontal communication more difficult - more people on each level of heirarchy
What are the advantages + disadvantages of tall organisational structures?
- Smaller spans of control = good communication
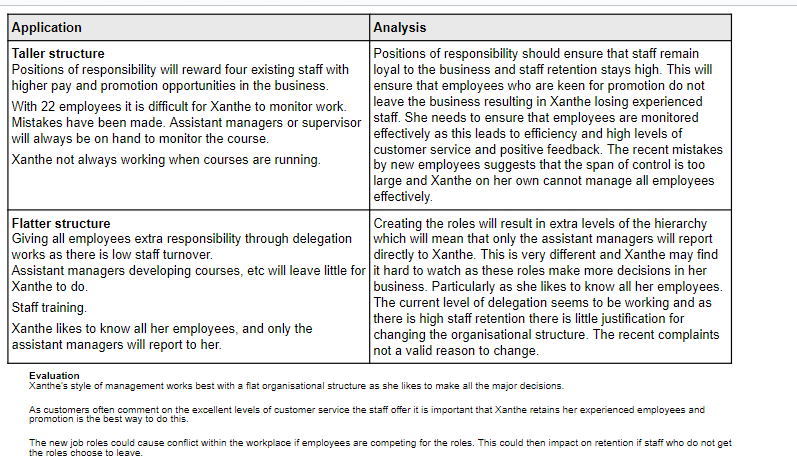
![<p>Xanthe involves her employees in some decision making but she makes all major decisions herself</p><p>Recomend whetehr Xanthe should create a taller organisational structure [9 marks']</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/df96c51f-50f3-4d25-b5b9-6f273b67f44f.png)
Xanthe involves her employees in some decision making but she makes all major decisions herself
Recomend whetehr Xanthe should create a taller organisational structure [9 marks']
““