PT 634 W4 Day 1 ORTHOTIC PRESCRIPTION AND DECISION MAKING FOR PHYSICAL THERAPISTS
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What are the 4 functions of orthodics?
Control motion
Compensate for weakness
Correction of deformity
Improve function and mobility
Control motion description
▪ Limit or Facilitate motion
▪ Stop plantarflexion and/or dorsiflexion
▪ Control supination or pronation
▪ Inhibit Spastic Muscles
Compensate for weakness description
• Assist dorsiflexion
• Compensate for weak plantarflexors or quadriceps
• Increase Stability
• Shock absorption
Correction of deformity description
• Assist dorsiflexion
• Compensate for weak plantarflexors or quadriceps
• Improve alignment and posture
• Improve ROM
• Prevent contracture or further deformity
• Reduce Pain
• Shock absorption
An orthotic is a __________ device applied to an individual’s lower extremity
removable, external, wearable
REVIEW OF CURRENT EVIDENCE: CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE FOR USE OF ANKLE FOOT ORTHOSES AND FUNCTIONAL ELECTRICAL STIMULATION POST STROK
purpose and consideraitons
Purpose: Provide evidence to guide decision making for the use of AFO or FES as an
intervention for individuals with hemiplegia
Rehabilitation of individuals with acute and chronic stroke
Define effects on goals based on compensation and recovery approach
Define Effects on outcomes across the ICF levels
DOES NOT recommend specific AFO types and/or FES unit/parameters
Other considerations
Providing a device without intervention or practice may limit an individual's ability to fully achieve
potential gains
Clinicians should use outcome measures that are most responsive to the benefits of an AFO/FES
Periodic assessments are important, as needs may change over time
Limited evidence in acute stage vs. chronic
SUMMARY OF RECOMMENDATIONS: 8 ACTION STATEMENTS for orthodicts
To improve QOL: Clinicians should provide AFO/FES for individuals with foot drop in chronic hemiplegia: Level II; moderate
To improve gait speed: Clinicians should provide AFO/FES in acute or chronic hemiplegia: Level I; Strong
To improve other mobility: Clinicians should provide AFO/FES in acute or chronic hemiplegia: Level I; Strong
To improve Dynamic Balance: Clinicians should provide AFO/FES in acute or chronic hemiplegia: Level I; Strong
To improve Walking Endurance: Clinicians may provide AFO/FES in acute hemiplegia: Level II; Moderate
To improve PF spasticity: Clinicians should not provide AFO/FES in acute or chronic hemiplegia: Level II; Moderate
To impact muscle activation:
Clinicians may provide AFO with decreased stiffness to allow activation of TA/GAS/SOL in acute or chronic hemiplegia: Level II; Moderate
Clinicians should provide FES to improve activation of TA in chronic hemiplegia: Level II; Moderate
To improve Gait Kinematics: Clinicians may provide AFO/FES to improve ankle DF at initial contact, loading response and swing in acute or chronic hemiplegia:
Level III; Weak
Participation outcomes of 8 action statement
To improve QOL: Clinicians should provide AFO/FES for individuals with foot drop in chronic hemiplegia: Level II; moderate
Activity outcomes of 8 action statement
To improve gait speed: Clinicians should provide AFO/FES in acute or chronic hemiplegia: Level I; Strong
To improve other mobility: Clinicians should provide AFO/FES in acute or chronic hemiplegia: Level I; Strong
To improve Dynamic Balance: Clinicians should provide AFO/FES in acute or chronic hemiplegia: Level I; Strong
To improve Walking Endurance: Clinicians may provide AFO/FES in acute hemiplegia: Level II; Moderate
body structure & function outcomes of 8 action statement
To improve PF spasticity: Clinicians should not provide AFO/FES in acute or chronic hemiplegia: Level II; Moderate
To impact muscle activation:
Clinicians may provide AFO with decreased stiffness to allow activation of TA/GAS/SOL in acute or chronic hemiplegia: Level II; Moderate
Clinicians should provide FES to improve activation of TA in chronic hemiplegia: Level II; Moderate
To improve Gait Kinematics: Clinicians may provide AFO/FES to improve ankle DF at initial contact, loading response and swing in acute or chronic hemiplegia:
Level III; Weak
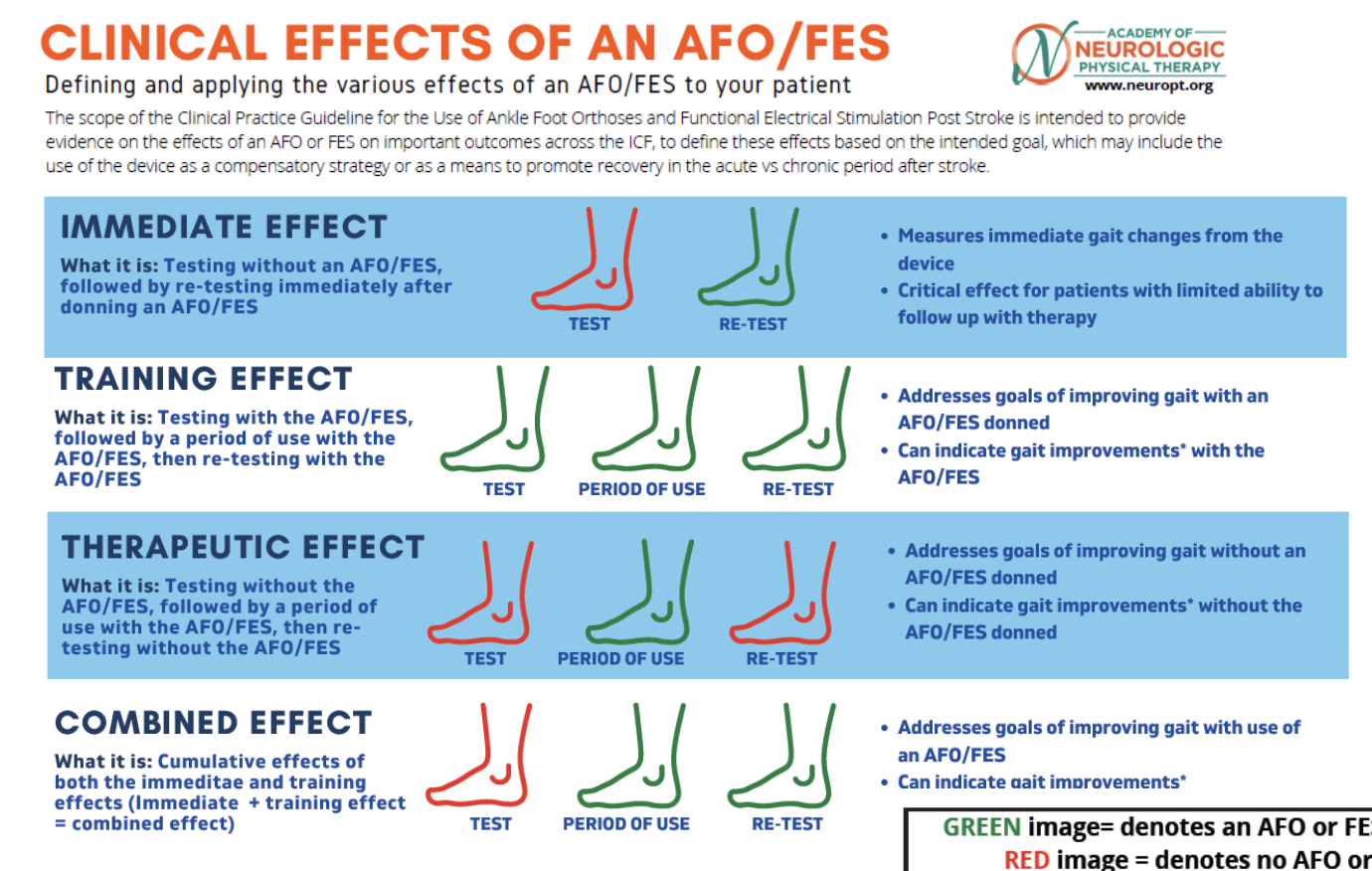
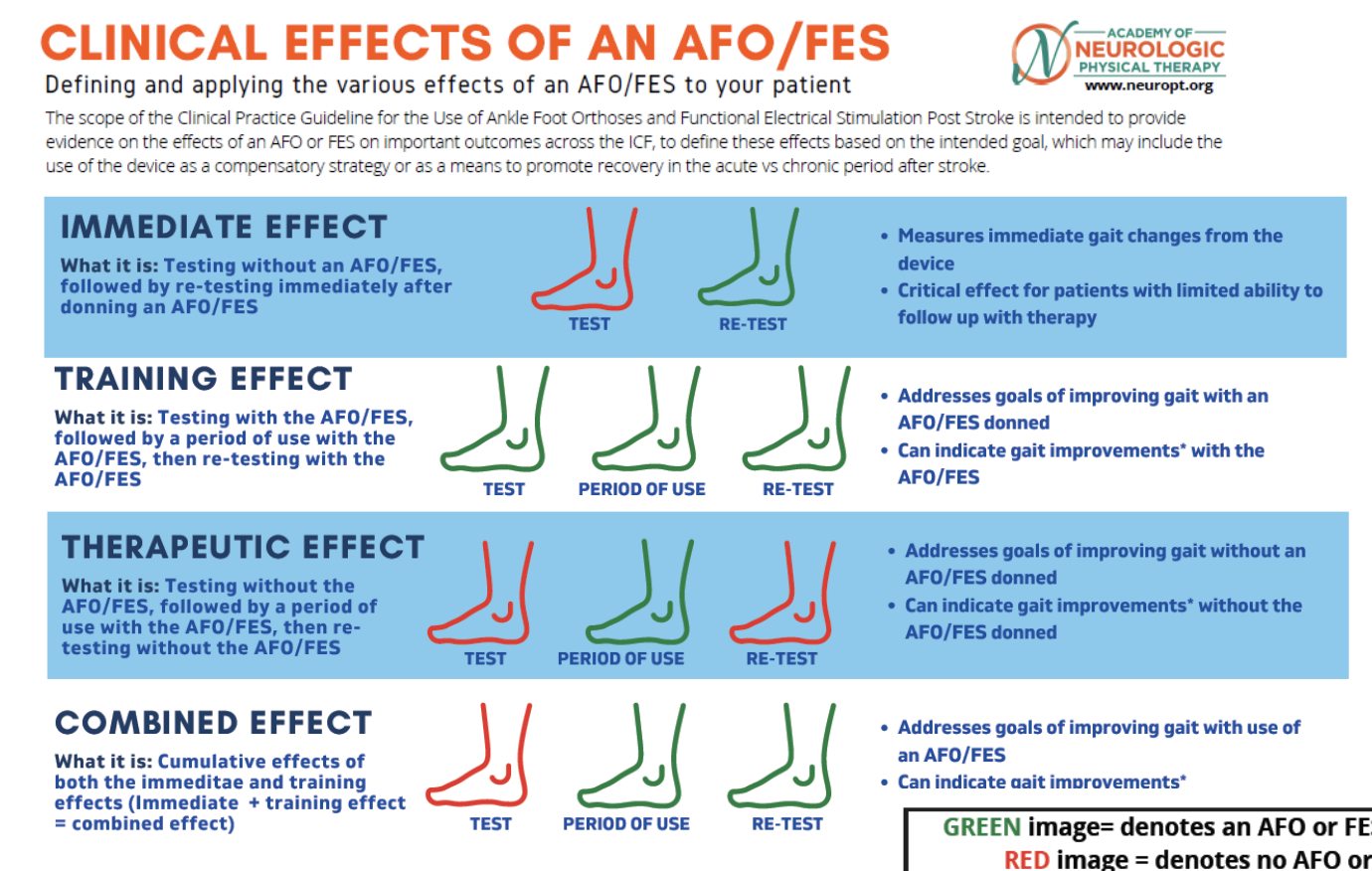


Types of LE orthoses
FO ‐ Foot Orthosis
AFO ‐ ankle‐foot orthosis
KAFO ‐ knee‐ankle‐foot orthosis
KO – knee orthosis
HKAFO ‐ hip‐knee‐ankle‐foot orthosis
THKAFO ‐ trunk‐hip‐knee‐ankle‐foot orthosis
MOST COMMON TYPES AFOS UTILIZED IN REHABILITATION SETTING
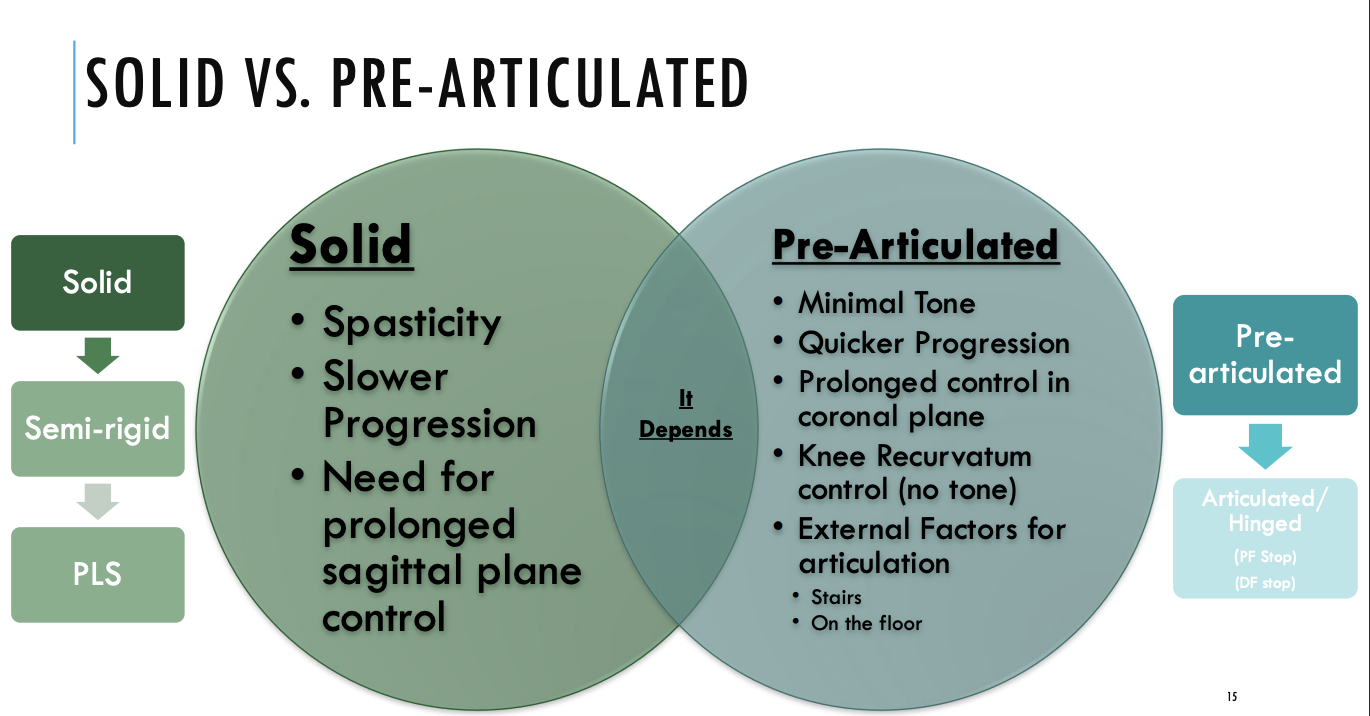
1. Solid AFO
2. Pre-articulated AFO
3. Hinged/Articulated AFO
4. Solid AFO with anterior shell/Ground
Reaction AFO
5. Carbon Fiber AFO
6. Posterior Leaf Spring (PLS) AFO
7. Conventional AFO
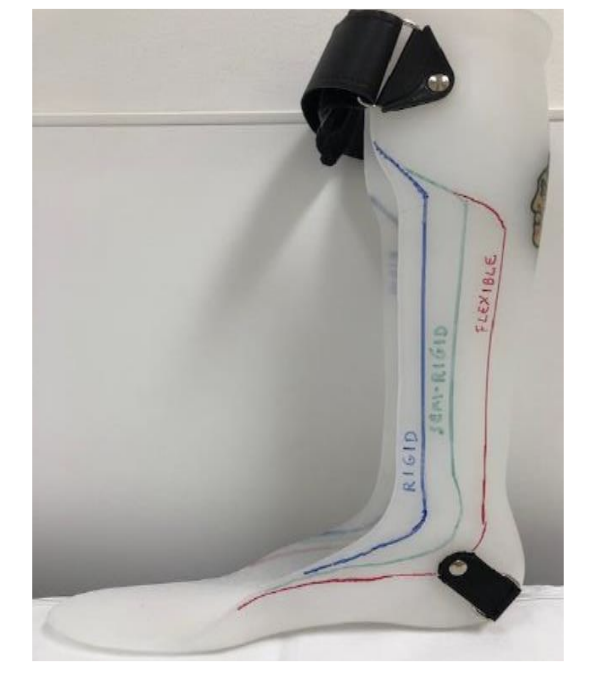
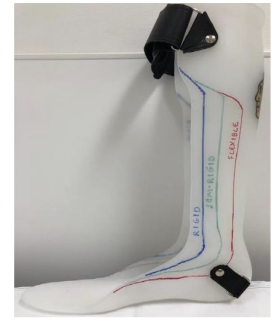
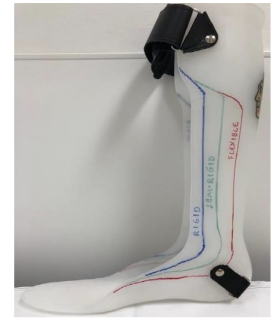
Solid AFOs restriction
trimline anterior to mallelous
DF stop, PF stop
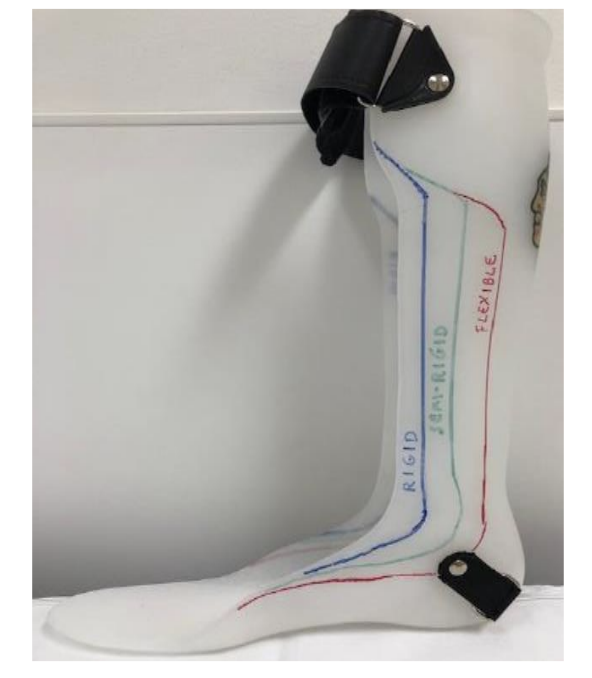
Rigid AFOs restriction
Trimline through apex of malleolus
DF resist (high), PF stop
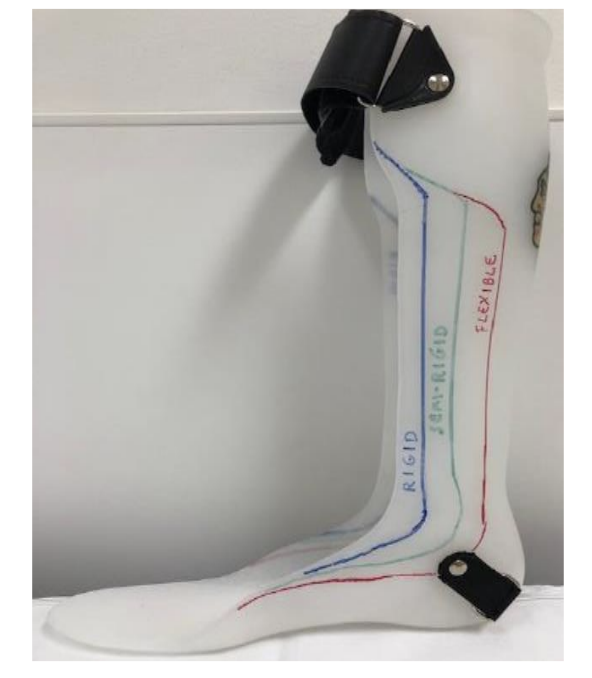
Semirigid AFO restriction
trimline just posterior to malleolus
DF resist (moderate), PF resist (moderate)
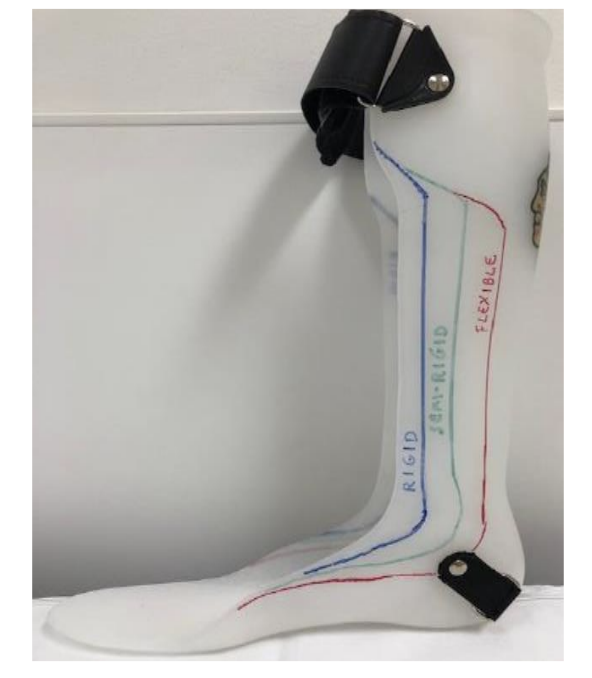
Flexible/PLS AFO restriction
trimline posterior to malleolus
DF free, PF resist (mild)
Solid AFO therapist indications
▪ Custom Fit
▪ Weakness in quad/hamstring
▪ Increase in tone/ PF Spasticity
▪ Poor knee stability in stance
▪ No active ankle DF
▪ Inability to transfer weight onto affected leg
▪ Foot abnormality- equinas, valgus/varus, combination
▪ Poor motor control/balance
Solid AFO orthotist indications
▪ Limitations in DF ROM without breaking down midfoot
▪ PF weakness/poor tibial control
▪ Likely to need continued sagittal plan control (can be
trimmed to semi-rigid/PLS)
PRE-ARTICULATED AFO therapist indications
▪Similar indications as solid
▪Good alignment through mid-foot
▪Minimal tone
▪Potential for recovery
PRE-ARTICULATED AFO orthotist indications
▪Likely to need continued medial-lateral
stability
▪Potential to recover PF strength and
quad strength
Solid vs Pre-articulated AFO
Hinged/Articulated AFO therapist indications
▪Good knee stability in standing and
during gait cycle
▪Anti-gravity ankle DF
▪Minimal tone
▪Functional ROM
▪Ability to achieve hip/knee extension in
terminal stance

Hinged/Articulated AFO orthotist indications
▪Need for medial-lateral stability
▪Good quad strength
▪DF stop (i.e. PF weakness)
▪ Knee instability toward buckling
▪PF stop (i.e. DF weakness)
▪ Foot drop
▪ Knee hyperextension
▪ Toe walking

Ankle control for hinged/articulated afo
• PF stop will limit PF
• Compensates for weak dorsiflexors
• Limits knee hyperextension
•DF assist
• Simulated eccentric contraction of tibia to
prevent foot slap
• Allows DF during stance
• Facilitates DF during swing

Hinged/Articulated AFO for increased dorsiflexion
Increased dorsiflexion will provide good toe
clearance but will promote a knee flexion
moment.
Increased dorsiflexion will assist patients with
increased extensor tone and increased
hyperextension of the knee.
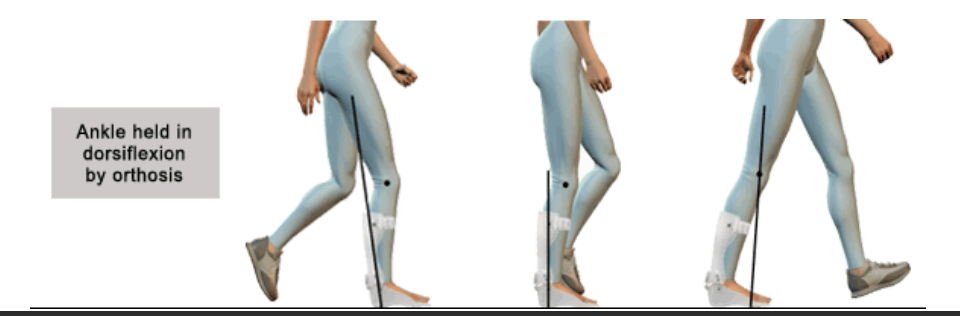
Hinged/Articulated AFO for increased plantarflexion
Increased plantarflexion will promote a knee
extension moment but may allow more toe drag.
Increased plantarflexion will assist a patient with
decreased knee extension control but may allow an
unstable knee to go into hyperextension
solid afo with anterior shell/ground reaction afo therapist indications
* Commonly seen in pediatric population at
Shirley Ryan*
Crouched gait
Hypertonicity through
hamstring/adductors/PF
Decreased ROM through hip
flexors/hamstring/PF
Significant weakness through
gluts/quad/hamstring
solid afo with anterior shell/ground reaction afo orthotist indications
Proprioceptive feedback for knee
extension
Often set in slight PF
Commonly used for →
Spina bifida
SCI with limited sensation
Poor knee control but good hip control

Carbon Fiber AFO therapist indiciations
▪Good knee stability
▪Functional strength in kinetic chain
▪DF assist to achieve heel strike
▪Assist in push-off during terminal stance
▪No significant issue with tone
▪No medial-lateral instability
▪No need for orthotic influence on hip/knee

Carbon Fiber AFO orthotist indications
▪No limitations in ankle ROM
▪Good medial-lateral stability
▪Intact sensation
▪Non-fluctuating edema
▪Lightest weight option
▪Cosmetic/patient acceptance*
▪Good alternative if patient already has AFO*
▪Ease of shoe fit

Posterior leaf spring AFO therapist indications
▪Isolated DF weakness
▪Similar requirements with carbon fiber
Posterior leaf spring AFO orthotist indications
▪Lack of sensation
▪Mild medial/lateral instability
▪Extremely tall or short people
▪Ability to provide more support into knee
extension (if needed) compared to carbon fiber
▪Need mid-foot control
- Mid-foot collapse
- Hindfoot valgus
- Etc.
Indications for conventional AFOs?
▪ Decreased Sensation
▪ Diabetes
▪ Volume Changes
▪ Obesity (Stronger materials)
▪ Severe deformities/ton
the conventional AFO consists of double metal uprights attached the patient’s shoes
and parts of a conventional AFO
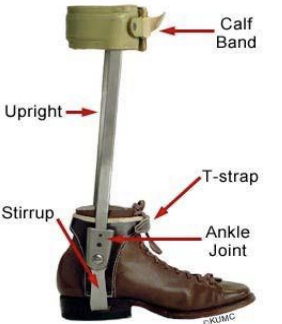
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) indications
• Activates DF muscles during swing
by stimulation of peroneal nerve
• May improve strength & motor
control
• May enhance recovery &
participation following acute
stroke
• Responsive to walking at variable
gait speeds
• May allow barefoot walking/
variety of shoe ware
• Optional thigh cuff for FES to
quadriceps & hamstrings
• ↑ gait speed
Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES) contraindications
• PF Spasticity (≥MAS 3)
• Knee buckling/ Genu Recurvatum
• Peripheral nerve injury/
neuropathy
• Sensory tolerance
Other options than AFOs
ankle brace/aircast
provides medial-lateral stability
does not provide DF/PF control
steady strider
provides only DF
no medial/lateral support
foot up
provides only DF
No M/L support
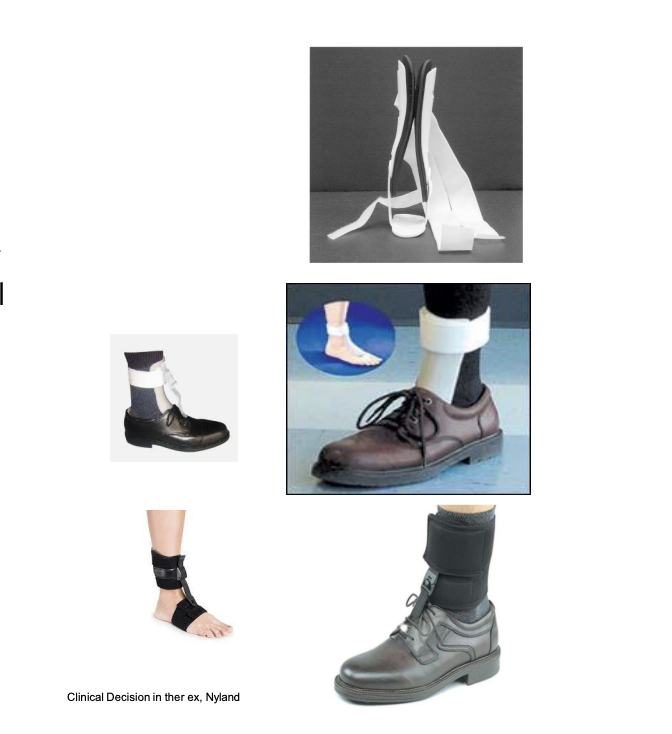
External shoe modifications
▪ Heel modifications
Heel cushion
Heel wedge
Heel elevation
▪ Sole modifications
Sole wedge
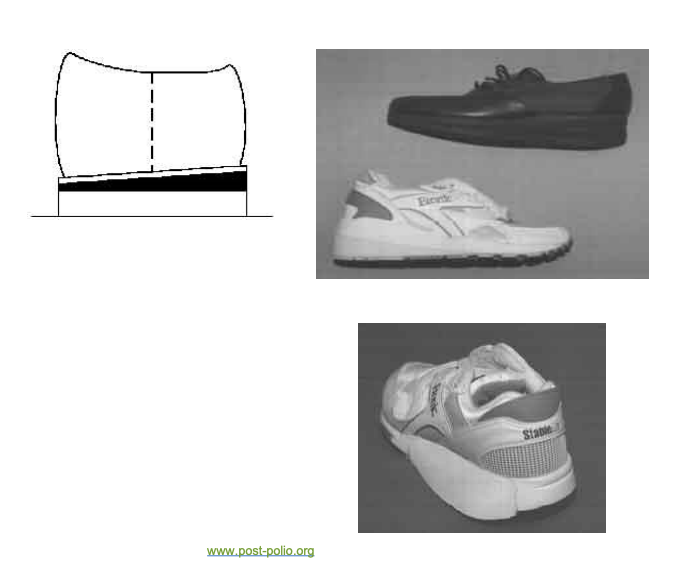
Internal shoe modifications
▪ Heel modifications
Heel cushion
Heel wedges
▪ Sole modifications
Metatarsal pad
Scaphoid pad
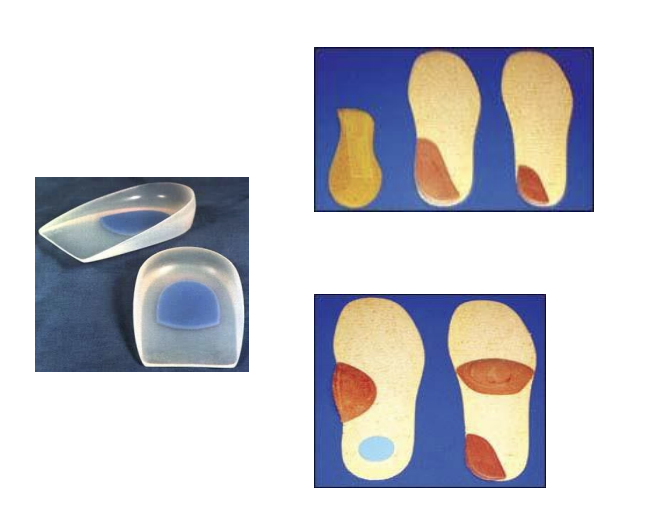
What is a KAFOS?
▪ Consists of an AFO with metal uprights,
a knee joint, and thigh bands.
▪ Used in quadriceps paralysis or
weakness to maintain knee stability.
▪ Precaution – fatigue, weakness, this is
a heavier choice
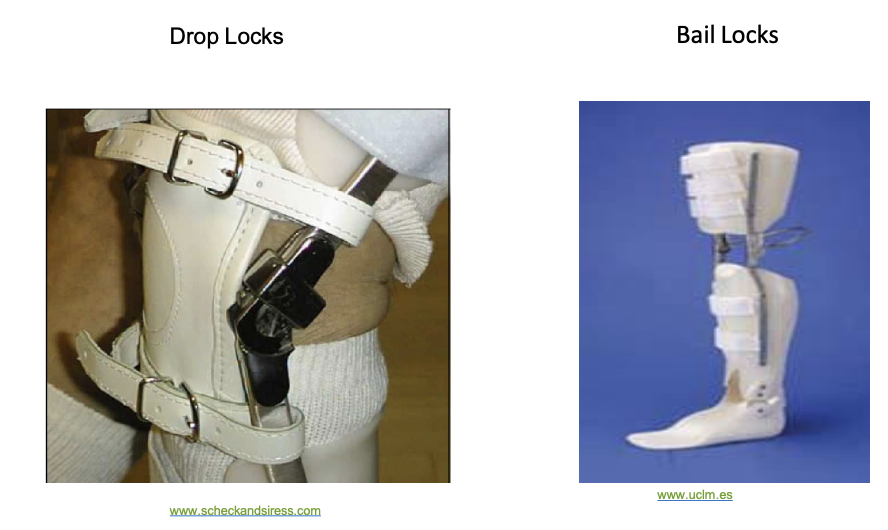
What is a conventional KAFOS
▪ Double metal upright
▪ Centered knee joint
▪ Pretibial strap
▪ Choice of locks, but usually drop
locks
▪ UCB insert or shoe or plastic
solid AFO
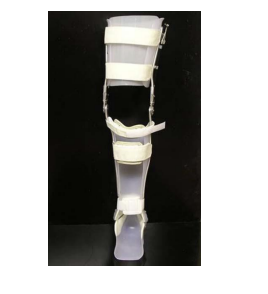
What is a craig-scott KAFOs
▪ Double metal uprights
▪ Offset knee joints
▪ Pretibial band
▪ Rocker bottom shoe
▪ Bail locks
▪ Shoe attached

What are the types of knee controls for KAFO
drop locks and bail locks
What is a knee orthosis KO?
▪ Provides support and control of the knee but not
the foot or ankle
Swedish Knee Cage
▪ The knee joint is centered over the medial femoral
condyle.
▪ Control knee hyperextension with minimal M/L stability
▪ with/without AFO
Contracture management
▪ Patients may present with decreased ROM in one or both
ankles
▪ Left unmanaged →permanent contracture, loss of function,
poor positioning, and pain
▪ Contractures causes: hypertonia/spasticity and capsular
changes from generalized immobility
▪ Evidence traditional stretching for 30 second intervals is not
effective for preventing or maintaining ROM in the
neurological population, including but not limited to CVA,
SCI, and brain injury
▪ Stretch only provided brief short term affects on the joint
mobility, but research does not support long term effects
Functional positioning for stretching has been shown to be more effective in preventing and maintaining ROM
_______ positioning for stretching has been shown to be more effective in preventing and maintaining ROM
Functional
Indiciations for contracture intervention?
High tone (MAS 2 or higher)
Time since onset of injury
Family compliance with any previous
orthotics
Current ROM and ROM goals
Potential functional gains or
limitations
End feel with ROM/tone assessment
Previous intervention for lower
extremity contractures
Has there been any?
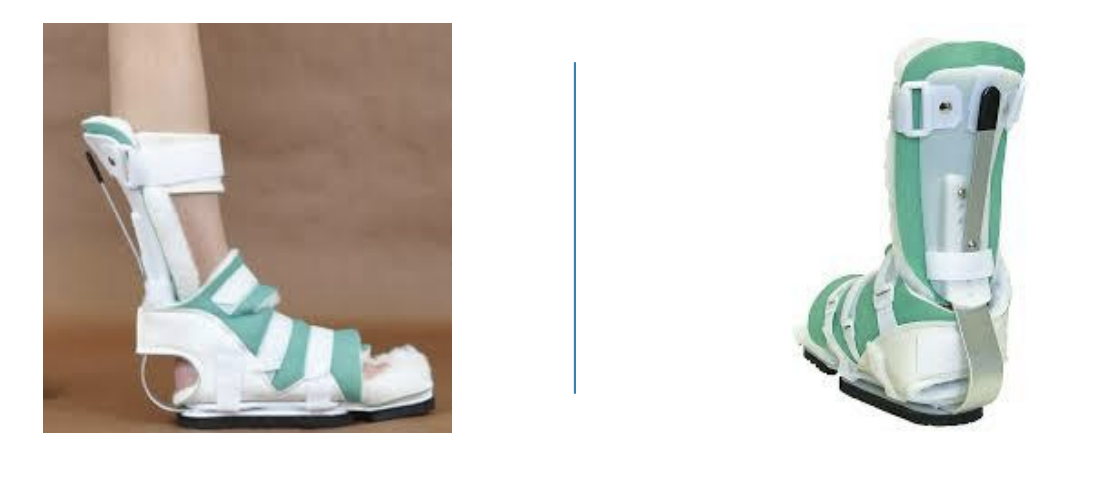
PRAFO’s are
effective in prevention of ankle contracture

What is serial casting?
Slow progressive low load stretch over an extended period of
time
Changed weekly increasing stretch each cast Indicated in patient with higher risk for permanent contracture
who currently lack ROM
Indicated for patients with potential for consistent standing
program, ambulation, functional transfers, improvement with
positioning in wheelchair
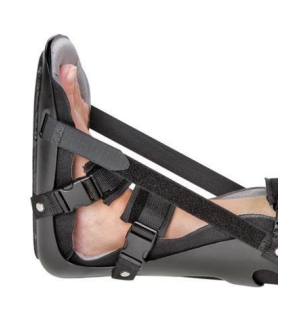
What is static progressive night splint?
Designed to maintain current ROM only
Higher risk for skin breakdown with poor fit or issues with
donning
Not designed for weight bearing
Beneficial post serial casting to maintain weight bearing
Education, education, education!
Other intervention options for contracture management
botox
ultraflex
dynasplit
What are some orthotic evaluation clinical decision depends on
• Diagnosis
• Prognosis
• What are the gait deviations?
• What Control is needed? What Assist?
• What function should remain?
• Used orthosis in the past?
• Cognition, Attitude, Compliance, Outside
support
• Patient Goals and Therapist’s Goals for the
Patient
What are things to look at when prescribing an orthotic?
▪ Isolated muscle strength/Functional muscle strength
▪ Tone
▪ ROM
▪ Postural control
▪ Sensation
▪ Prognosis
▪ Gait
▪ Kinematics: the branch of mechanics concerned with the
motion of the body
▪ Kinetics: the branch of mechanics concerned with the
forces applied to the body (Gage 1995).
▪ Coronal and Sagittal Planes
Other Considerations
▪ Functional mobility
▪ Skin integrity
▪ Cognitive function
▪ Compliance
What are some education points for PT considerations?
▪ AFO Does Not inhibit Muscle Activation
▪ Always indicate purpose
▪ Highlight independence
▪ Long term benefits for joint protection & appropriate
muscle activation
▪ Risk factors without bracing
▪ Wear schedule NOT just in therapy
▪ Skin checks
▪ Don/Doff- OT
▪ Socks and shoes
▪ May need to provide family training
What are some transition of care for PT considerations?
▪ Determine if progression of bracing can wait until the
next level of care
▪ Don’t rush into progression if instability still remains
▪ Hard to go backwards & may require new bracing
▪ Insurance/ Costs
Wearing schedule for orthodics?
▪ First day 1 hour on, check skin, if OK wait 1 hour then wear for
another hour
▪ Second day 2 hours on, check skin
▪ Increase 1 hour daily
▪ If skin is red, it should clear in 20‐30 minutes
▪ If it does not clear, or if there is ANY blistering or skin break down,
call the orthotist and do not have the patient wear the brace
LE orthosis PT interventions
• Sit <‐> stand
• Car Transfers
• Balance
• Gait
• Curbs
• Ramps
• Stairs
with and without the brace