1.09 Ray tracing and step along calculations
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
How to calculate vergence
Vergence (D) = Refractive index / distance from focal point (metres)
Diverging rays have positive/negative vergence
Negative
Converging rays have positive/negative vergence
Positive
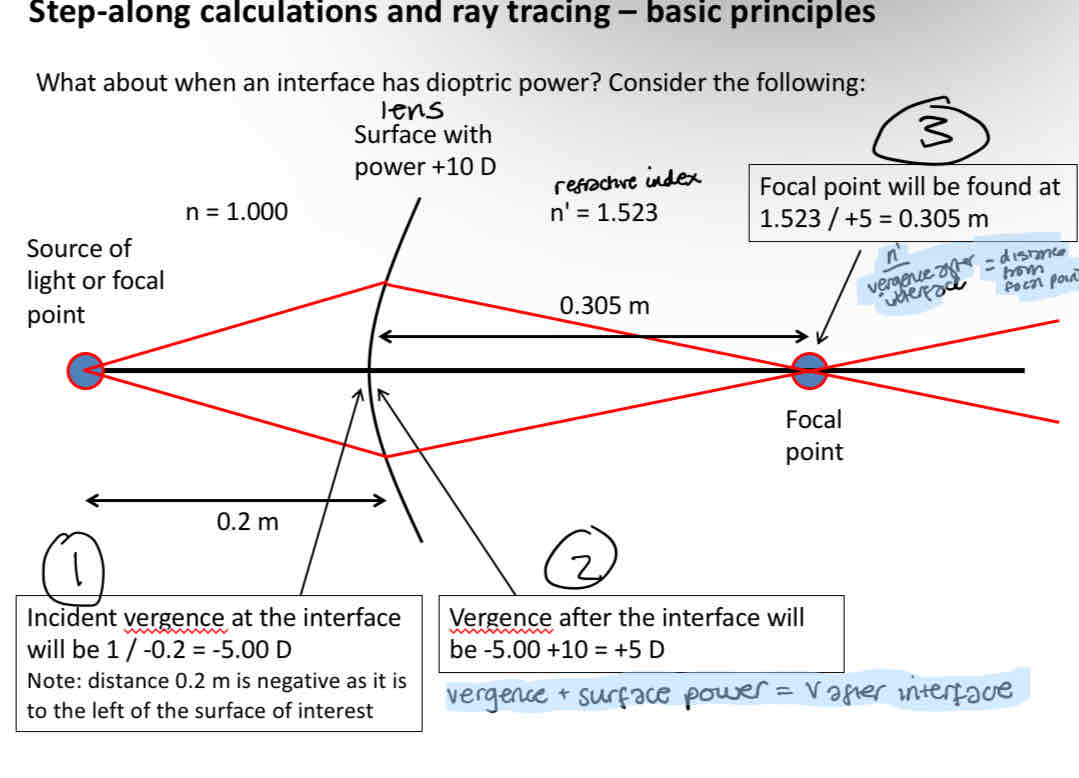
Ray tracing through a lens
Calculate incident vergence
1 / distance to surface
Calculate vergence after the interface
V after interface = Vergence + surface power
Calculate distance between surface and focal point
Distance = refractive index / vergence after interface
To calculate vergence at any point
Vergence = Refractive index / distance
Ray tracing a thick lens - calculating the back vertex focal length
Calculate incident vergence at F1
Vergence = refractive index / distance (if infinity then vergence is 0)
Determine the effect of lens surface F1 on the vergence of light
Vergence leaving F1 = incident vergence + power of lens
Positive vergence - rays will converge
Negative vergence - rays will diverge
Determine the effect of lens thickness on vergence of light
Back focal length = Refractive index / vergence of F1
Calculate vergence at F2
Vergence at F2 = back focal length of F1 - lens thickness
Calculate incident vergence at F2
Incident vergence at F2 = refractive index / vergence at F2
Calculate vergence of rays leaving F2 (back vertex power)
Vergence of rays leaving F2 = incident vergence of F2 + power of F2
Back vertex focal length of F2 (where light will form a focus)
Back vertex focal length = Refractive index / vergence of rays leaving F2
Back vertex power formula
