Biochem 285 Exam 2
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
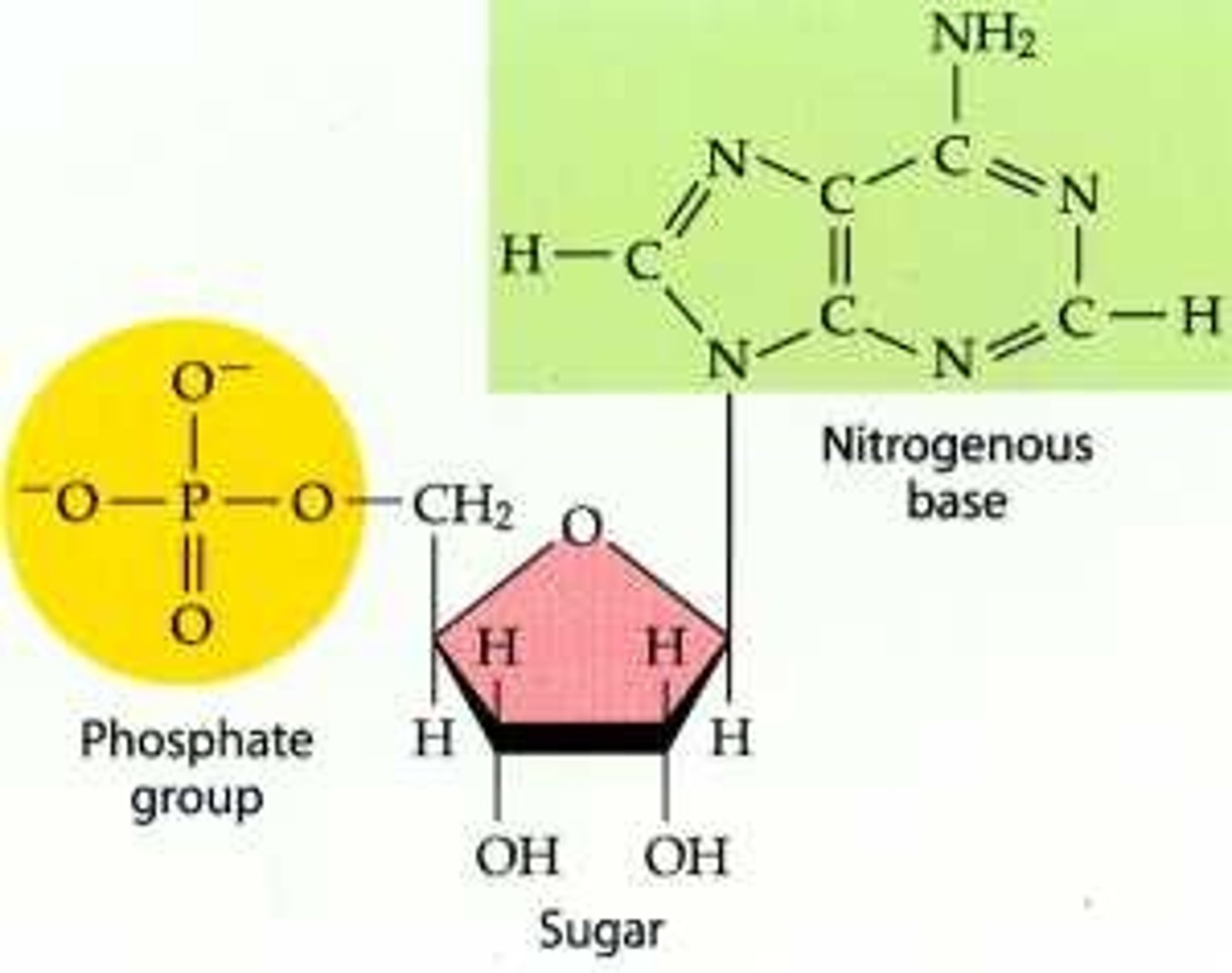
What are the three components of DNA?
sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
Purines
Adenine and Guanine. 2 structures.
Pyrimidines
Cytosine and Thymine. 1 structure.
Genome
all of an organism's genetic material
Gene
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait
Gene isoforms
mRNAs that are produced from the same locus but are different in their transcription start sites (TSSs), protein coding DNA sequences (CDSs) and/or untranslated regions (UTRs), potentially altering gene function.
Chromatin
Linear DNA wound around histones and non-histone proteins. Histones alter chromatin structure.
Euchromatin
loosely packed chromatin. histones are wound around DNA but short stretches of DNA are exposed to other proteins
Heterochromatin
condensed chromatin. Genes not expressed.
Nucleosome
Double stranded DNA wraps around histones ~1.5 times to make a nucleosome. A histone is made up of 8 protein subunits, each of which have N-terminal "Tails" that can be chemically altered by enzymes. The modifications placed on the histone tails help to determine how strong of an association the histone will have with DNA, and thus tighten or relax chromatin structure
What is the protein structure of histone
Histone is an octomer
Acetylation / histone acetyltransferase (HAT)
Adds Acetyl group to Lysine, removes amino group.
Makes charge neutral instead of positive
This weakens the bonds and makes chromatin loose, allowing gene expression.
Histone deacetylases (HDACs)
remove acetyl groups, leading to chromatin condensation and no gene expression
Phosphorylation / Kinase
enzyme that replaces a hydroxyl group with a phosphate group: leads to loosely packed chromatin (due to phosphate having a negative charge like DNA) leading to gene expression. Occurs at the N-terminal tails of histone proteins
Phosphatase
removes a phosphate group from a molecule: leads to tightly packed chromatin
Histone Methylation / Histone methyltransferase (HMT)
methylates lysine and arginine in the histone tails, inhibits gene expression. Acetylated (Ac) chromatin is "immune" to trimethylation by HMT. Occurs at the N-terminal tails of histone proteins.
histone demethylases (HDMTs)
removes methyl groups from histones, activates gene expression.
methylation and acetylation
Methylation competes with acetylation as a methylated positively charged amino acid cannot be acetylated. D. methylation influences histone-histone interactions
DNA Methylation of CpG islands.
CpG islands is where methylation occurs. represses transcription. Protects DNA. Hypermethylation of promoter prevents tumor suppressor gene expression
origin of replication
a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated. Firing of ORIs are linked to distinct stages in the cell cycle
What way is DNA replicated and why?
5' to 3'. During DNA replication, the new (incoming) nucleotide is always added to the 3' carbon's hydroxyl group, meaning the DNA is always replicated in the 5' to 3' direction.
Helicase
Binds DNA at ORI and separates strands without ATP
Primase.
synthesizes RNA primer
DNAP alpha
grows DNA primer by adding bases. Does this on lagging strand
Sliding clamp (PCNA)
loads DNAP in replication fork
DNAP epsilon
adds bases on the leading strand
DNAP delta
adds bases on the lagging strand
DNA ligase
seals nicks in DNA
Okizaki fragments
the fragments formed by the discontinued replication on the lagging strand
Topisomerase
A protein that functions in DNA replication, helping to relieve strain in the double helix ahead of the replication fork. Keeps Helicase binded to DNA
RFC
sliding clap (PCNA) loader
Telomeres
a sequence (DNA nucleotides) at the end of chromosomes that shortens with each replication acting as a biological clock. They are protected by shelterin cap to prevent them from looking like double strand breaks.
Telomerase
An enzyme that extends the 3' end of a DNA parent strand by adding telomers so that a complementary primer can be added in the 5' to 3' direction.
Taq polymerase
A DNA synthesis enzyme that can withstand the high temperatures of PCR
Cloning
Moving DNA fragments into a plasmid to express a specific gene
1. Obtain DNA from PCR
2. Cut DNA fragment using restriction digest
3. Paste DNA in vector using ligase
restriction enzymes / nucleases
Enzyme that cuts phosphodiester bond in DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides. Isolated from bacteria
agarose gel electrophoresis
Used for size separation of PCR products (smaller molecules travel further); compared against a DNA ladder. DNA moves towards the positive electrode. Different DNA structures with the same number of base pairs move different amounts on the gel so linear DNA is used.
RT-qPCR
A combined process of reverse transcriptase and quantitative PCR in which cellular mRNA is amplified by using RT-PCR to generate cDNA, followed by measuring the relative amount of amplified DNA with qPCR. The amount of cDNA can then be compared against the original samples of mRNA.
Mis-match repair (MMR)
Fixes a point mutation right after DNA synthesis. MutS, MutL, UvrD, Exol, DNA polymerase repairs, Ligase seals nick
MutS
Scans for a mismatch in MMR
MutL
Determines old vs new strand in MMR through methylation patterns.
UvrD
helicase in MMR, unwinds DNA
Exol
exonuclease in MMR, cuts out DNA from the nick
MMR in prokaryotes
uses methylation to determine old vs new strand
Depurination
the loss of a purine (G or A) base from a nucleotide
Deamination
Removal of an Amine group from a C, A , or G base.
C to Uracil
A to hypoxanthine
G to xanthine
Base Excision Repair (BER)
Repair pathway that repairs a single base damaged by deamination or depurination. DNA Glycosylase, AP endonuclease, DNA Polymerase adds correct base, Ligase seals the bond
DNA glycosylase
In BER flips damaged base out and removes base from the phosphate backbone.
AP endonuclease
Recognizes the AP site and removes the phosphate backbone.
pyrimidine dimers
covalent bonds between pyrimidies that form from radiation and causes DNA to not function properly. Repaired by NER
Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER)
a DNA repair system in which several nucleotides in the damaged strand are removed from the DNA to fix pyrimidine dimers. 2 pathways. UvrAB or RNAP, UvrC, UvrD, DNA Polymerase, Liagse.
UvrAB (NER)
recognizes pyrimidine dimers in DNA sequence. UvrB stays as a marker form UvrB.
UvrC (NER)
interacts with UvrB and cuts the damaged strand
UvrD (NER)
a helicase that unwinds DNA after UvrC cuts out the pyrimidine dimer (bad strand).
5' end of DNA
phosphate group
3' end of DNA
free OH on C3
TRCF
recruits UvrAB during RNA transcription when DNAP recognizes a pyrimidine dimer. Starts NER
NHEJ and HDR
repair double stranded breaks in DNA
Ku
binds to broken ends in NHEJ. Interior of has a positive charge. Is a homodimer.
DNA-PKcs
phosphorylates Artemis activating it
Artemis
is a nuclease that trims back single stranded DNA at the break in NHEJ
NHEJ (non-homologous end joining)
repairs double stranded break either removes a sequence or adds random bases at the break
HDR
repairs double stranded break but uses a sister chromatid to keep bases the same as original. Because it needs sister chromatids it is most active during and after S phase.
MRN and CtlP
nuclease complex that chews back the ends in HDR
RPA protein
protects single stranded DNA and protects it from binding to itself in HDR and lagging strand of replication
BRCA1
helps in end processing
BRCA2
recruits and stabilises Rad51
Rad51
protects single strand and replaces RPA
CRISPR
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats
CRISPR locus
region in the bacterial genome where CRISPR components are found
CRISPR array
region in the CRISPR locus where viral DNA spacers are stored
Cas genes
CRISPR associated genes that code for proteins in the CRISPR mechanism
tracerRNA
a non coding RNA that is important
Cas 1 and Cas 2
identify the viral DNA and incorporates the sequences into the CRISPR locus as spacers. Cas 1 and 2 always cut viral DNA next to the PAM sequence.
Short palindromic repeats
same forward as it is backward sections of CRISPR locus in between spacers
Cas 9
Associates with a particular crRNA and tracrRNA. Scans DNA for a PAM sequence and binds and unwinds the DNA once it finds it Once crRNA matches with DNA cas9 cuts it.
crRNA
RNA derived from spacer element that matches target DNA to cut
tracrRNA
stimulates cas9 activity
spacer
RNA that comes from viruses
gRNA
a fuse of tracrRNA and crRNA and is man made
RuvC and HNH
mutating these domains of Cas9 makes Cas9 cut 1 strand (nickase), or not cut at all if you mutate both domains.
Cas9 modifications
By tethering other proteins you can change the function of Cas9 to either alter gene expression or mark gene locations.
Nucleotide Base Pairs
A-T, 2 hydrogen bonds.
G-C, 3 hydrogen bonds.
Recognizing 5' to 3'
The first carbon will always be the carbon attached to the nitrogenous base / Guanine.
Then you count clockwise numbering the carbons
So, 5' end is the one that has the phosphorus group attached to the 5th carbon
Guanine
The non-covalent bonds that link DNA strands together occur closest to this.
Prokaryote in Genome and Genes
Genome: typically, one circular chromosome, extrachromosomal elements are also circular.
Genes: 1 gene = 1 protein, no introns, no nucleus.
Eukaryote in Genome and Genes
Genome: many linear chromosomes, mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA is circular
Gene: one gene= can be several, generally related proteins (isoform proteins)
Histone
Proteins that the DNA is wrapped around
Why is Chromatin Strucuture important?
Chromatin structure (euchromatin vs. heterochromatin) relates to how easy it is for a transcription factor to bind DNA and allow expression of the genes downstream.
Ubiquitinylation
Modifies gene expression
Readers
proteins that bind to specific modifications on the histone. Serve as binding site for other proteins, which may be involved in repair, gene expression, or gene silencing
Writers
enzymes that make histone modifications (example = Histone methyltransferase
Erasers
enzymes that remove these modifications (example = Histone demethylase)
Epigenetics
Gene silencing is the basis for this. DNA expression patterns can be inherited. They can also change based on environmental factors.
DNA methyltransferase (DNMT)
Add methyl groups to Cytosine. Occurs in promoters (regulatory regions of DNA). Blocks gene expression
Deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP)
Added to DNA, provides energy to create phosphodiester bond
DNA polymerase
makes phosphodiester bonds and grows DNA strand
leading strand
Goes towards replication fork, away from ORI
Lagging strand
Goes toward ORI
ORI and Replication Fork Steps
1) Separate strands (Helicase)
2) Add a Primer (Primase/DNA polymerase alpha)
3) Elongate DNA strand (DNA polymerase delta or epsilon)
4) Remove primers (DNA polymerase delta or epsilon)
5) Ligate nicked DNA (Ligase)
1. Helicase binds DNA at ORI and separates strands.
2. Primase make RNA primer, DNAP alpha grows primer
3. Primase not needed for leading strand, PCNA clamp adds DNA polymerase epsilon and DNA fragments made.
4. DNA polymerase grows DNA and makes phosphodiester bonds
5A. On the leading strand, DNAP epsilon adds DNA bases
5B. On the lagging strand, primase and DNAP alpha add RNA primers, DNAP delta adds DNA bases
6. Okazaki fragments form
7. DNAP delta removes RNA primer on lagging strand
8.DNA "nick" is sealed by DNA ligase.
9. Topoisomerase keeps Helicase binded to DNA