Embryonic Death and Abortion + Perinatal Mortality
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
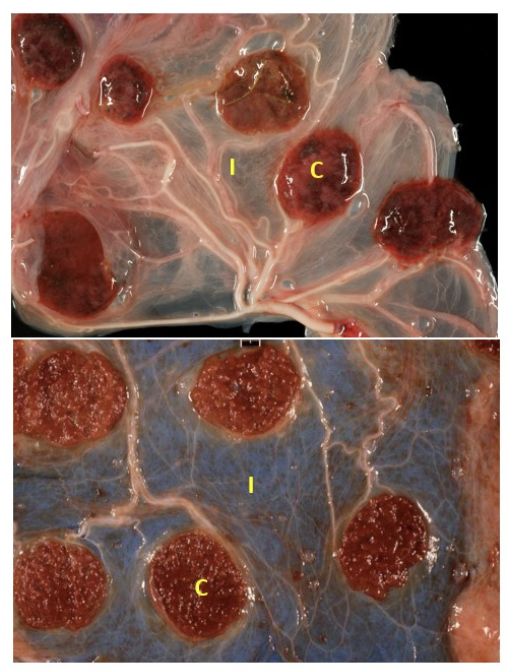
top: normal ovine placenta
bottom: normal bovine placenta
not healthy red slightly raised well-demarcated cotyledons and generally clear and thin intercotyledonary membranes
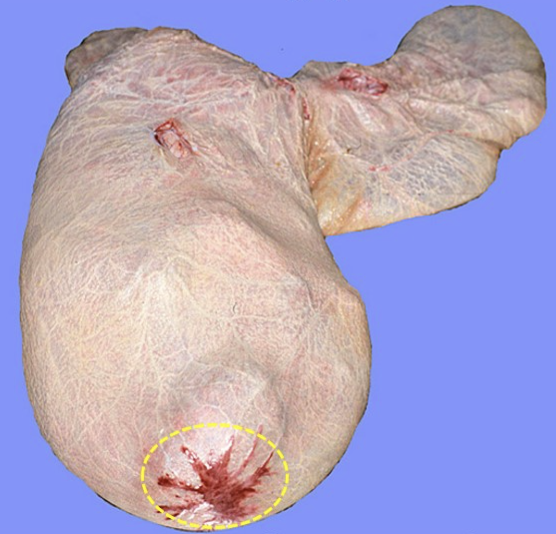
cervical star (incidental non-lesion in horses) - area of equine placenta covering the cervix where placentation doesn’t develop
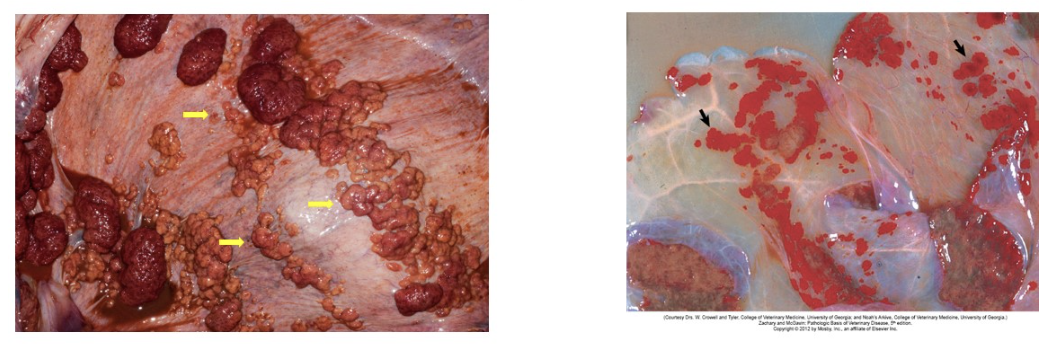
adventitial placentation (incidental placental non-lesion in cows): in the intercotyledonary chorion; these areas of extra placenta develop due to insufficient placentomes; appear as red-orange regions which may be variable rounded and bulge out or more flattened red plaques
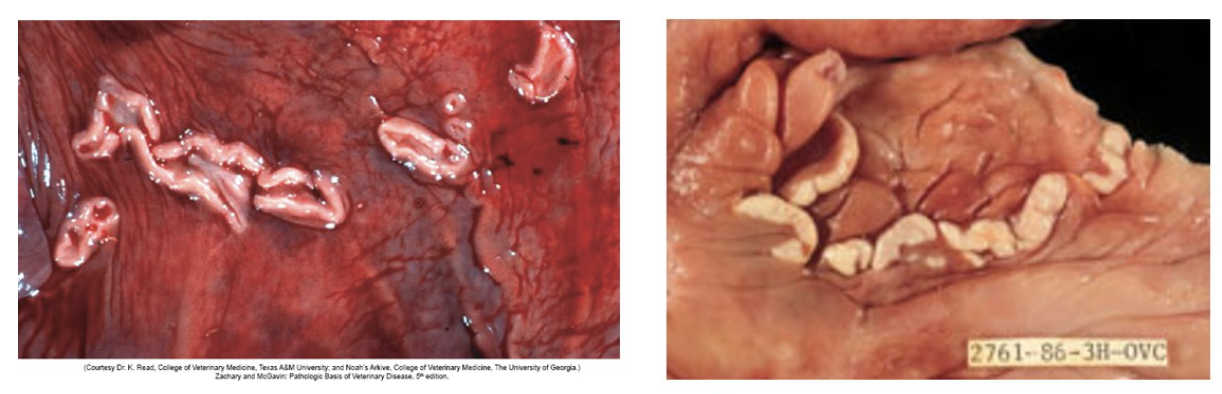
endometrial cups (incidental endometrial non-lesion in horses): plaque-like structures in the equine endometrium forming from trophoblastic invasion of the endometrium during early pregnancy; present between 40-150 days of pregnancy and secrete equine chorionic gonadotropin (eCG)
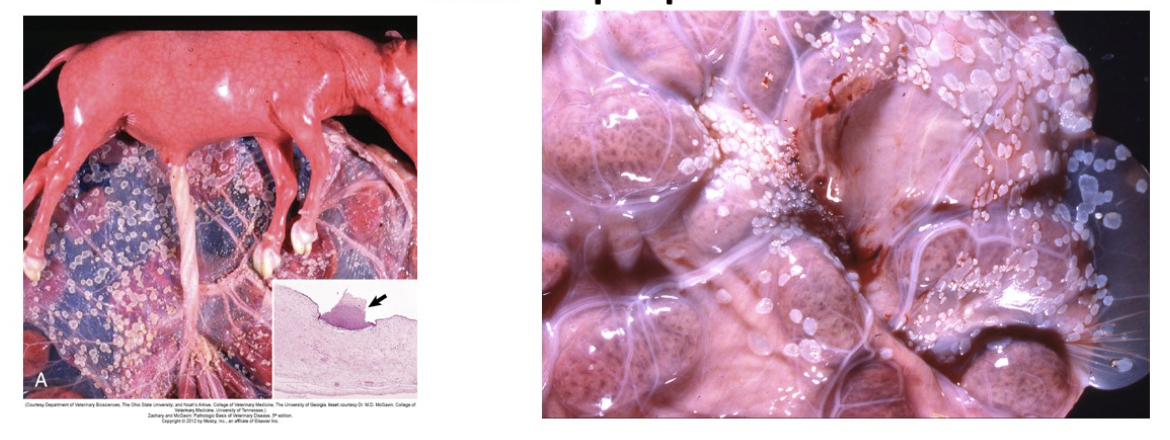
amniotic plaques (incidental placental non-lesion in bovine): multiple white, raised circular plaques are foci of squamous epithelium on the internal (fetal) side of the amnion; incidental structures with no significance
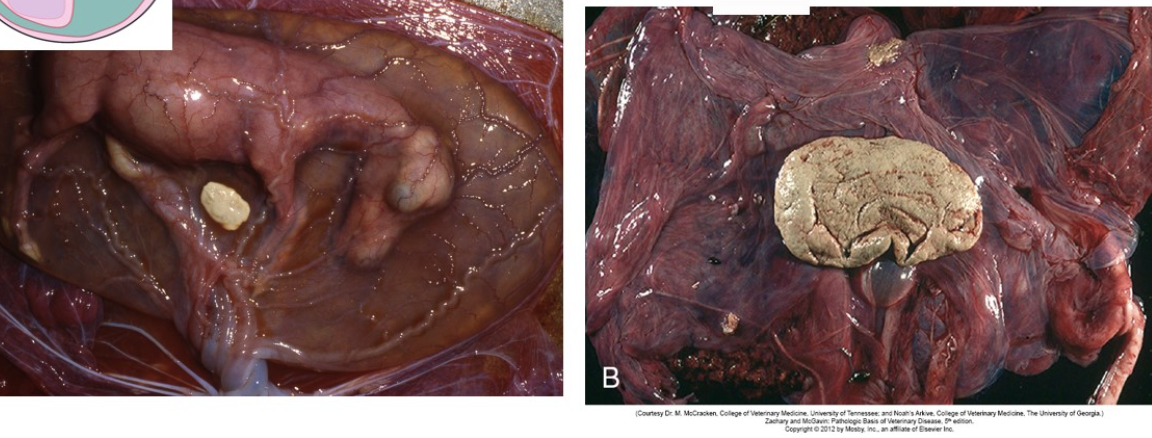
hippomanes (incidental placental non-lesion in horses): soft, putty-like flattened discs up to 10cm in diameter found within equine allantois (sometimes seen in ruminants too); results from aggregation of sediments of amniotic fluid, fetal urine and cells and are thought to bring good luck
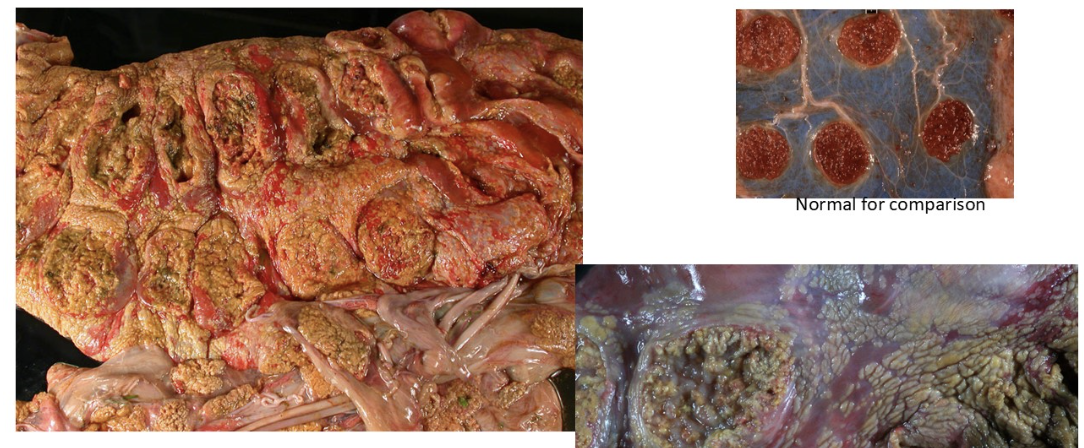
swollen, necrotic cotyledons + intercotyledonary membranes also thickened and extensively covered by necrotic plaques → indicative of fungal etiology
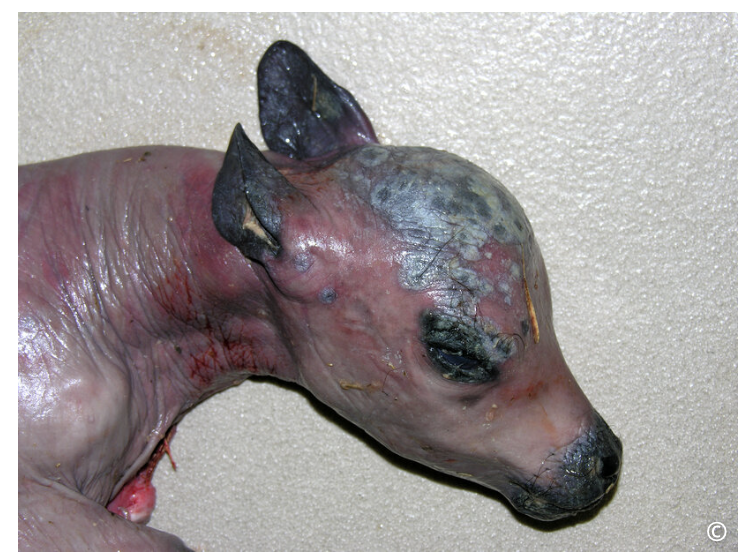
mycotic dermatitis with hyperkeratosis caused by mycotic placentitis due to Aspergillus spp.
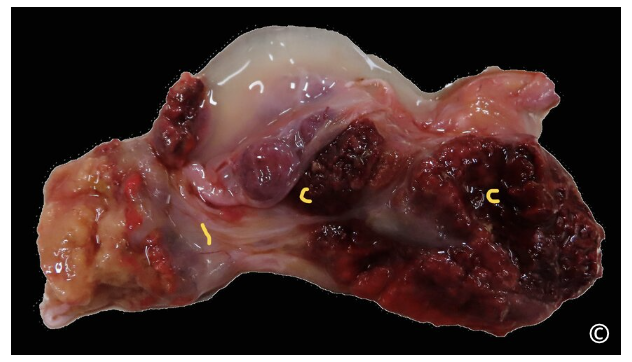
placental lesions due to Ureaplasma diversum in a cow;
thickened, hemorrhagic cotyledons with multifocal pinpoint white areas of necrosis and inflammation; intercotyledonary membrane is edematous
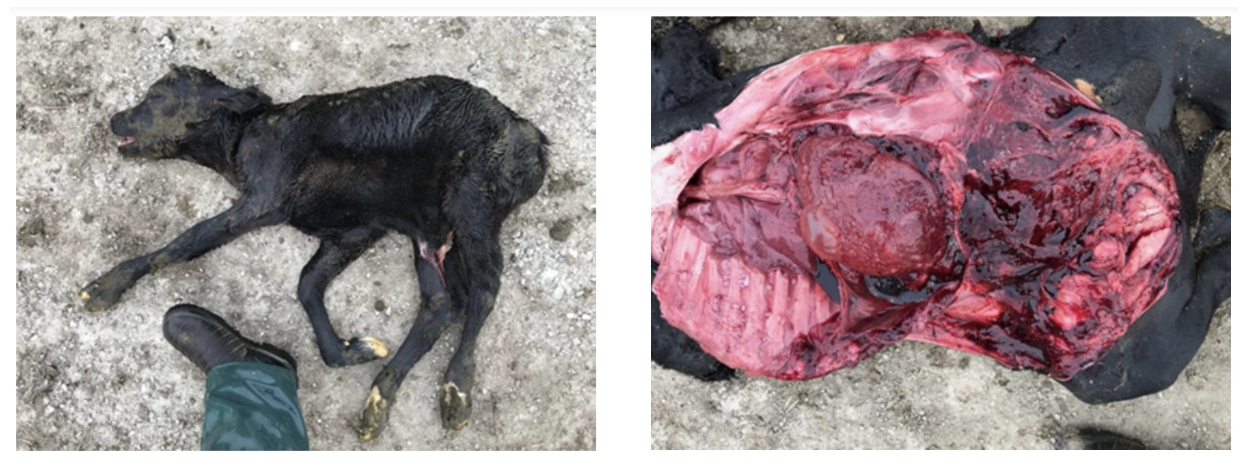

near full-tern calf aborted due to Salmonella Bovismorbificans. non-specific hemorrhages are noted grossly with emphysematous areas over the liver indicative of autolysis
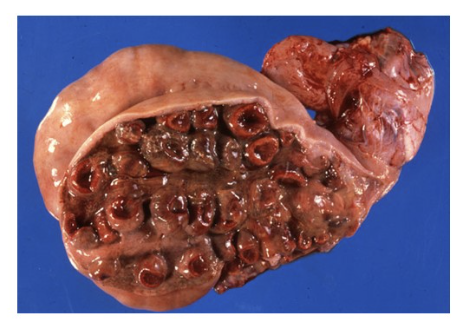
necrosuppurative metritis in a ewe that had just aborted due to Salmonella Bradenburg
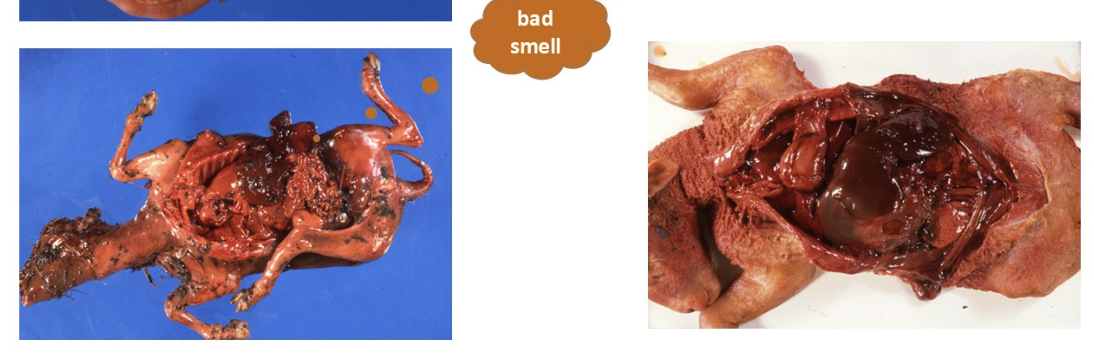
left: fetal autolysis and maceration due to Salmonella Brandenburg
right: fetal autolysis with dark red, swollen and friable liver
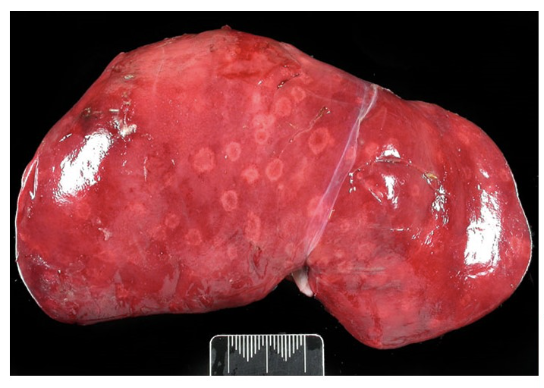
pale foci of inflammation and necrosis up to 1cm diameter with a red center (“target lesions”) in the liver of an aborted lamb; strongly supports diagnosis of Campylobacter spp. abortion
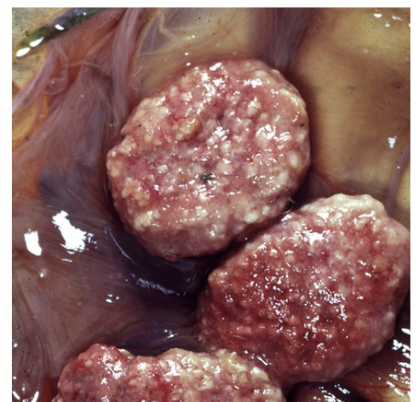
case of Toxoplasma gondii abortion → necrotic foci on cotyledons contrast with normal, red tissue of the cotyledons (aka “strawberry cotyledons”)
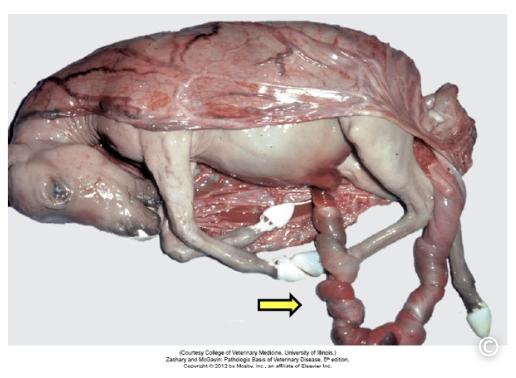
umbilical cord torsion - aborted fetus (wrapped in amnion) has a long and twisted umbilical cord
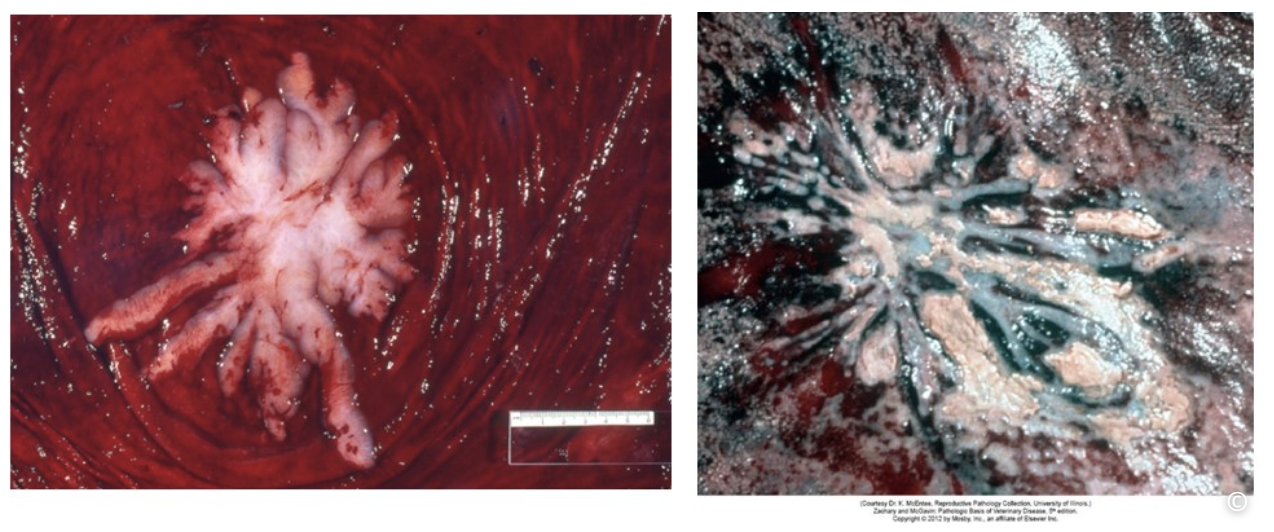
left - normal appearance of cervical star
right - bacterial placentitis at the region of the cervical star; chorion at the cervical star is thickened with surface fibrin, necrosis and pus
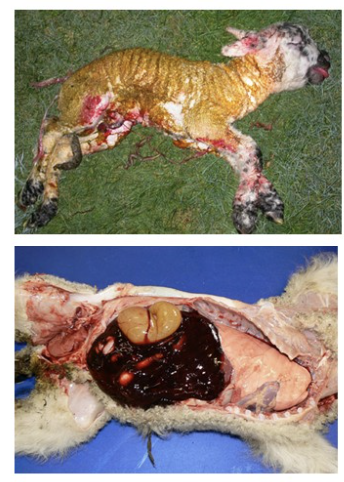
dystocia lambs - top: meconium staining of fleece; bottom: abdominal hemorrhage following liver rupture
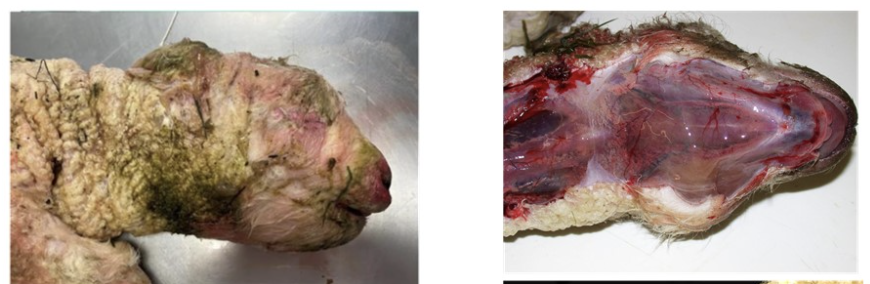
dystocia lambs - evidence of subcutaneous hemorrhage and edema (swollen, gelatinous, and wet-looking soft tissues); important sites to check for this include the ventral jaw, back of the head and dorsal neck, and over the joints of the limbs
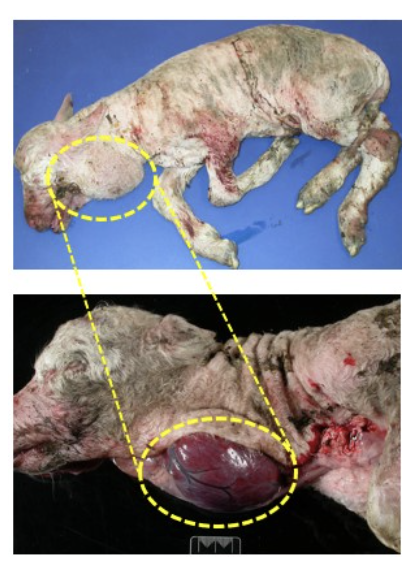
enlarged thyroid gland in dead lamb, indicative of goitre