water & carbon cycle - PG unit 1 Y12
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
What does the inputs of a system mean?
an input into the system from the outside e.g precipitation
What does the outputs of a system mean?
an output from the system to the outside e.g evaporation
What does energy mean in a system?
the power or driving force
What does the stores and components of a system mean?
the individual elements or parts of a system e.g plants
What does the flows/transfer of a system mean?
the links or relationships between components e.g photosynthesis
What is positive feedback?
a cyclical sequence of events that amplifies or increases change
What is negative feedback?
a cyclical sequence of events that damps down/neutralises the effects of a system, promoting stability and a state of dynamic equilibrium
What is dynamic equilibrium?
this represents a state of balance within a constantly changing system
What are the 3 types of system?
open , closed and isolated systems
What are open systems?
allow the exchange of mass and energy with the surroundings e.g a thermal coffee cup + house water system
What are closed systems?
where energy us transferred in and out and all matter is enclosed e.g carbon and water cycle
What are isolated systems?
where no interactions occur with anything outside of the system's boundary e.g sealed vacuum chamber
What is a cascading system?
Open systems that have interlocking relationships between different stores within the system e.g river sediment going into coastal zone
How is a dynamic equilibrium created?
When a system work on a balance of inputs and outputs and if these are even, it then creates a dynamic equilibrium
What happens if the inputs or outputs suddenly change?
the stores are forced to change and the equilibrium is disturbed (known as feedback which can be positive or negative)
What are feedback systems?
a process that uses the conditions of a component to regulate then function of the other to increase to dampen the change in the system
What is a mechanism known as when a process increases change in a system?
positive feedback
What is a mechanism known as when a process counters the change in a system and maintains equilibrium?
negative feedback
What are the 5 subsystems?
Cryosphere (ice)
Lithosphere (geology)
Biosphere (organic life)
Hydrosphere (water)
Atmosphere (air)
What is the subsection of the biosphere called?
pedosphere (rock, water and living organisms
What are the inputs and outputs of a drainage basin?
input = precipitation
Output = surface runoff
What are the stores and energy of a drainage basin?
stores = water, soil, trees
energy = latent heat associated in change in state of water , the sun
What are the flows and transfers of a drainage basin?
infiltration , evaporation , groundwater flow
What is the positive and negative feedback of a drainage basin?
positive feedback = rising sea levels, ice shelves become unstable causing them to melt and increasing sea level
negative feedback = increased surface temperature means increased evaporation from oceans , more cloud cover which block out sunlight which reduces temperature
Water on Earth percentage facts:
It is estimated that there is around 1.340 billion km^3 water in total -> 97% as oceanic water and 3% as land ice, glaciers and permafrost (cryospheric water)
What is the water table?
the upper level of saturated rock which rises and falls due to groundwater flow, water abstraction by people or by recharge (additional water flowing into the rock)
What are the 3 states of water?
solid, liquid and gas
What is the process called when a solid turns into a liquid?
melting (fusion)
What is the process called when a solid turns into a gas?
sublimation
What is the process called when a liquid turns into a solid?
freezing (fusion)
What is the process called when a liquid turns into a gas?
evaporation (needs to be 100 degrees C)
(Vaporisation)
What is the process called when a gas turns into a liquid?
condensation (vaporisation)
What is the process called when a gas turns into a solid?
deposition
What happens when water molecules get heated by the sun?
the molecules become agitated and try to break the strong bonds between them but there isn't enough heat in the sun ray to do this so the molecules absorb energy from the surroundings to give them that last bit of energy to break the bonds. This energy is known as latent heat.
What happens in evaporation?
latent heat is removed from the surroundings to cool it down e.g sweat
(evaporation could be seen as a cooling process as it removes heat)
What happens in condensation?
latent heat is released by the water molecules as they slow down and join together
(condensation could be seen as a warming process as it adds heat)
What are the 3 types of rain?
Relief, convection and frontal rain
What happens to make relief rain?
clouds rise over land and rains and then go down the land empty (rain shadow effect)
what happens to make convection rain?
high levels of solar radiation is absorbed by the trees where there is less dense air above them which rises and cools and then condenses which form clouds (usually storm clouds)
What happens to make frontal rain?
Clouds gradually rise higher over warm air and release energy once it can't hold the rain in which produces cold air
What are the cells in the atmospheric circulation?
polar cells
Ferrell cells
Hadley cells
Why does the amount of water in the Earth's stores change over space and time?
it's due to the seasons, temperature, time and where we are in the world
What is atmospheric circulation caused by?
different parts of the earth being heated up by the sun differently to other parts:
the poles are heated up less due to the curvature of the earth, meaning the radiation from the sun has an albedo affect where it reflects of the icy and snowy surface
What is the Coriolis effect?
The middle parts of the earth spin faster than the poles, making winds move in a curved and eastern direction towards the northern hemisphere
What is a drainage basin?
The area of land surrounding a river, from which the river receives water and subsequently drains this water.
What is precipitation?
rain, snow, sleet, or hail
What is infiltration?
When water enters the ground
What is interception?
Water being prevented from reaching the surface by trees and plants
What is stem flow?
Water running down a plant stem or tree trunk
What is overland flow?
water that flows over land
What is through flow?
movement of water through soil
What is transpiration?
evaporation of water from plant leaves
What is evapotranspiration?
Water rises as vapour from the ground or is released from leaves
What is ground water?
Water deep in the ground
What is soil water?
Water held between soil particles
What is groundwater flow?
Movement of water down through the ground
What is percolation?
The slow movement of ground water
What is surface storage?
Water stored in lakes, ponds and puddles
What is ground water storage?
Water stored underground in bed rock
What is the drainage basin system?
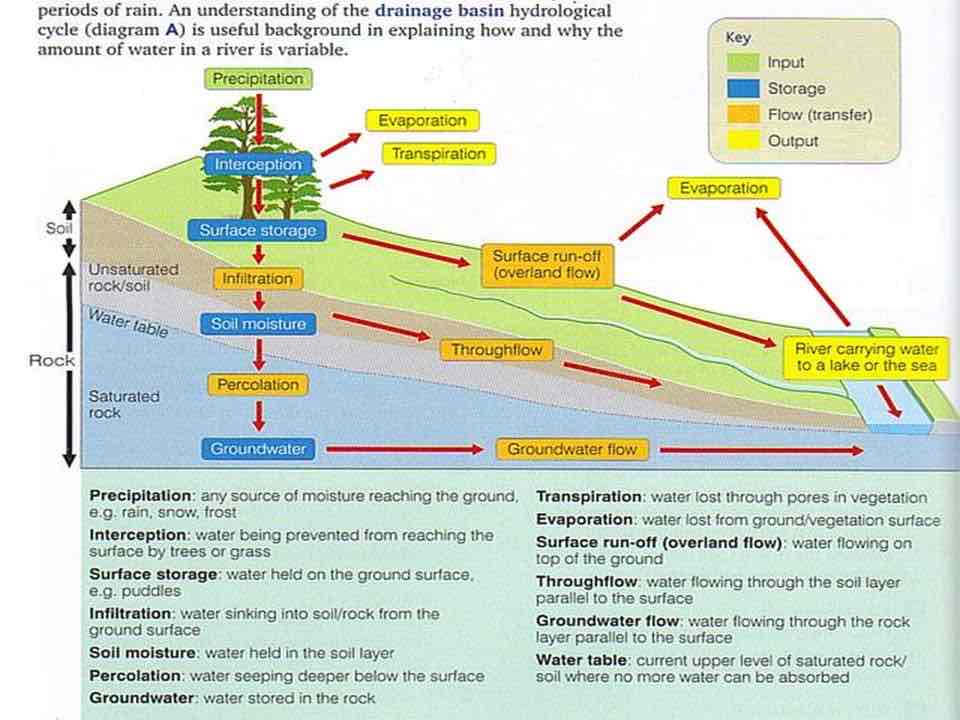
What is the formula for water balance?
Precipitation = discharge + evapotranspiration +/- changes in storage
P = Q + E +/- S
What is water balance?
when water intake equals water output
What happens to the water balance in wet seasons?
Greater precipitation that evapotranspiration created water surplus
-> ground stores fill with water = increased surface runoff , higher discharge + higher river levels = positive water balance
What happens to the water balance in drier seasons?
Evapotranspiration exceeds precipitation
-> plants absorb water leading to ground stores being depleted
-> water deficit at end of dry season
What causes variations in runoff? (Physical)
time of year/ season -> growth of vegetation = increased rated of evapotranspiration + interception
type of vegetation -> broad leaved trees will intercept greater amounts of vegetation + in summer there are more leaves on deciduous trees = higher interception and peak discharge is lower
antecedent rainfall -> heavy rain falling on already saturated soil from previous period of wet weather = rapid runoff
What causes variations in runoff? (Human)
urbanisation
• reduced infiltration through use of impermeable surfaces increases runoff
• drains and seers transport water rapidly to rivers increases surface run of
• deforestation -> reduces interception , evapotranspiration and protective canopy layer = increased rates of infiltration and result in the saturation capacity being reached quickly
What is the River Wye case study in Wales?
upper part of basin is steep slopes, acidic soils and grassland and deforestation to make more room for sheep grazing which reduces interception and increases overland flow
ditches dug to drain land to make it more productive and increase speed of water transfer
impermeable rocks in upper river basin = groundwater flow is limited and soils quickly saturated
What is river discharge?
The volume of water that flows in a river per second
How do you calculate river discharge?
Cross section area of water (m^2) x speed (m/s) = river discharge (m^3/s in cumecs)
What is river discharge affected by?
The amount or volume of water
More water means more is flowing past you which means more discharge
What is a river regime and how can it be changed?
It is the annual variation in the discharge or flow of a river at a particular point and is usually measured in cumecs
Changed by:
precipitation , temp , evapotranspiration and drainage basin characteristics
What is base flow?
The normal day to day discharge of the river and is the consequence of groundwater seeping into the river channel
What is bank full discharge?
The maximum discharge that a particular river channel is capable of carrying without flooding
How can you tell if a hydrograph is flashy?
Short lag time
Steep rising limb
Much higher peak discharge
why does water get into the river quickly after the rainfall event?
Because of:
Deforestation
Saturated soils
Impermeable bedrock = no percolation
How can you tell if a hydrograph is subdued?
Long lag time
Gentle rising limb
Much lower peak discharge
Why does water get to the river slowly after the rainfall event?
Because of:
Afforestation
Unsaturated soils
Permeable rock allowing percolation
What are the positive impacts of soil drainage?
increases ease which the soil can be warmed = possible earlier sowing if seeds = improved germination
Improved aeration = conditions more favourable for microorganisms to thrive
Makes it easier to achieve greater root penetration, enabling roots to grow faster and further
What are the negative impacts of soil drainage?
topsoil can dry out in periods of low rainfall
Changes the amount of water reaching rivers and the speed which it gets there
The discharge in rivers become more flashy and peak discharges increase making flooding more likely
What has happened the the Aral Sea in Asia?
it uses the be the largest lake in the world, however only 10% of it is left
The 2 biggest rivers of Central Asia were used to feed the Aral Sea but were dammed to allow for irrigation
The Bugun village was found on the shore of the Aral Sea, but is now found 9 miles away from it
What is London’s aquifer problem?
industrialization from the 1800s to 1960s led to the increase in exploitation of the groundwater sources
this has caused recession in the groundwater levels in London
However in some areas of London, there has been a significant recovery in the aquifer due to water dependant industries moving
But, this has threatened some of London landmarks, e.g London Underground
Who manages the water levels in London?
But the General Aquifer Research, Development and Investigation Team
west London seen increase of 4-8 metres a year since 2000
What has happened in the Mekong Delta in Vietnam?
thousands of hectares of farmland and crops are being threatened due to salt water incursion occurring
Over abstraction of these coastal wells mean droughts are occurring, causing up to 60km of incursion inland
What is the landscape like in the upper catchment of the River Ouse?
it has lots of heather moorland
The ground is often saturated and full of sphagnam moss which holds lots of water
The landscape was drained post WW2 to grow grass for sheep grazing and wheat
Where is the river Ouse?
in the north of England
Covers most of Yorkshire dales and vale of York
The river enters the North Sea via the number estuary
There are 4 major river systems forming the Ouse
What is the geology at the River Ouse?
upper valley made of old permeable rock (limestone)
There is a lot of clays which are impermeable
What is vegetation like at the River Ouse?
low interception rates from the heathers in the upper basin
Areas of scattered coniferous trees offer better interception
How is the land used at the River Ouse?
the catchment area covers districts of Leeds, Selby, York etc
Urban land occupied 2.2% of catchment area → vital to regional economy as York and Harrogate fall in the ‘golden triangle’ as they are a commuter district for Leeds
What are the flood defences in York?
Clifton Ings → embankments surround the river, increasing capacity of river
Almery Terrace → concrete flood walls with rubber sealed gates to protect the houses
River channelisation → river been straightened so water moves through efficiently
Why does York have a high flood risk?
The landscape in York is very flat and low, meaning flood water easily spreads
What are the predicted impacts of climate change on the future related to flood risk?
more frequent and intense storm, causing more regular flooding
Increased winter rainfall, increasing likelihood of large scale flood events
What are the 3 forms of carbon?
solid form → when stored in living things, minerals of rocks, soil and ice
Liquid form → when carbon dissolved in water, in form of carbonic acid
Gaseous form → when carbon combines with oxygen to form CO2 and other elements to form gases like methane
What are the main stores of carbon?
lithosphere , hydrosphere , cryosphere , atmosphere , biosphere
What is carbon sink and carbon store?
Carbon sink ~ a store that absorbs more carbon than it releases
Carbon source ~ releases more carbon than it absorbs
What is carbon measured in?
Gigatonnes (GtC)
How does the lithosphere store carbon?
biggest store of carbon (99.9%)
Stores carbon in rocks like limestone and chalk and in fossilized organic matter (coal, oil, gas)
How does the biosphere store carbon?
stores around 3,170 GtC
Stores carbon in vegetation , plant litter and little in animals
Plants and animals release carbon when they decompose
How does the pedosphere store carbon?
is partly the biosphere and lithosphere
Stored around 950 GtC (little amount)
Stores carbon in organic matter in soils , peat which stores around 250 GtC
How does the atmosphere store carbon?
Carbon only takes up 0.04% of atmosphere
CO2 + water vapour = carbonic acid = weathering
2022 CO2 levels = 413 ppm
2013 CO2 levels = 400ppm
1958 CO2 levels = 317 ppm
start of industrial rev = 280ppm
How does the cryosphere store carbon?
carbon mostly stored here in permafrost and tundra
Permafrost is carbon sink and stores around 1600 GtC