Biology 112: Transcription and Translation in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What are the main components involved in prokaryotic translation?
Ribosomes, transfer RNA (tRNA), and messenger RNA (mRNA).
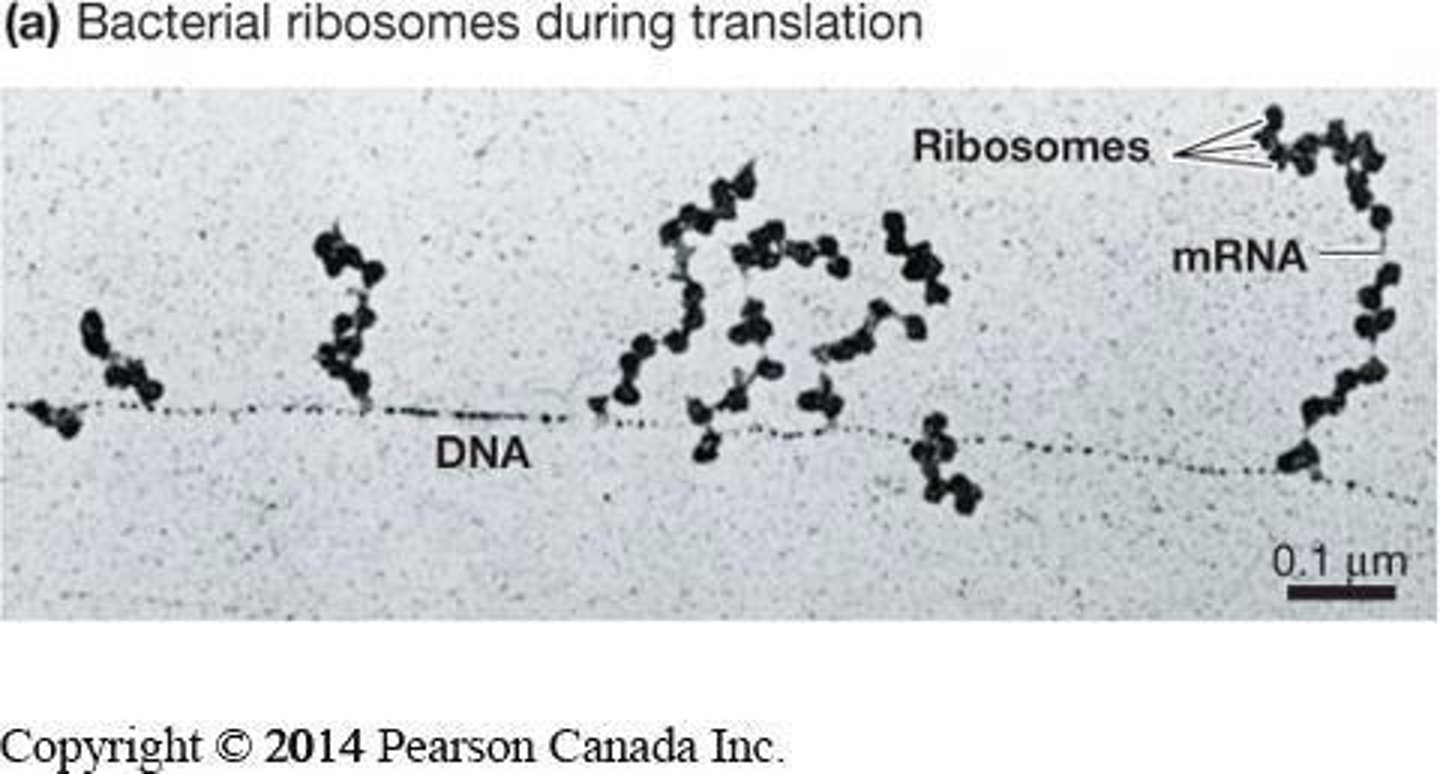
What are the three stages of the translation mechanism?
Initiation, elongation, and termination.
How does translation occur in prokaryotes?
Translation occurs in the cytoplasm and can be coupled with transcription due to the absence of a nuclear envelope.
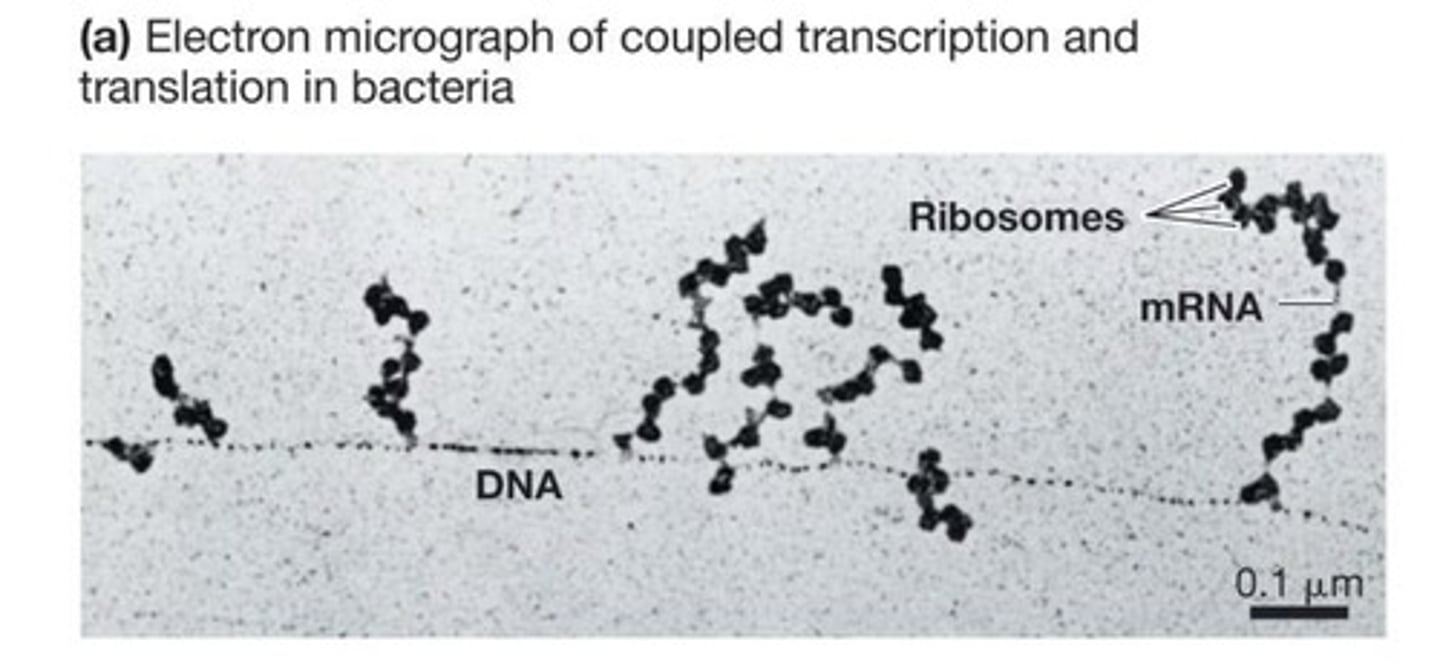
What is a codon?
A three-nucleotide sequence on mRNA that dictates which tRNA is needed.
What is an anticodon?
A complementary sequence found on tRNA that pairs with a codon on mRNA.
What is the significance of the genetic code being redundant?
All amino acids except methionine and tryptophan are coded for by more than one codon.
What does it mean for the genetic code to be unambiguous?
A given codon never codes for more than one amino acid.
Why is the genetic code described as nearly universal?
With few exceptions, all codons specify the same amino acids in all organisms.
What is the conservative nature of the genetic code?
When several codons specify the same amino acid, the first two bases in those codons are usually identical.
How are transcription and translation separated in eukaryotes?
Transcription occurs in the nucleus, and the mature mRNA is exported to the cytoplasm for translation.
What is the role of tRNA in translation?
tRNA molecules translate the mRNA code by linking specific bases on the mRNA with specific amino acids.
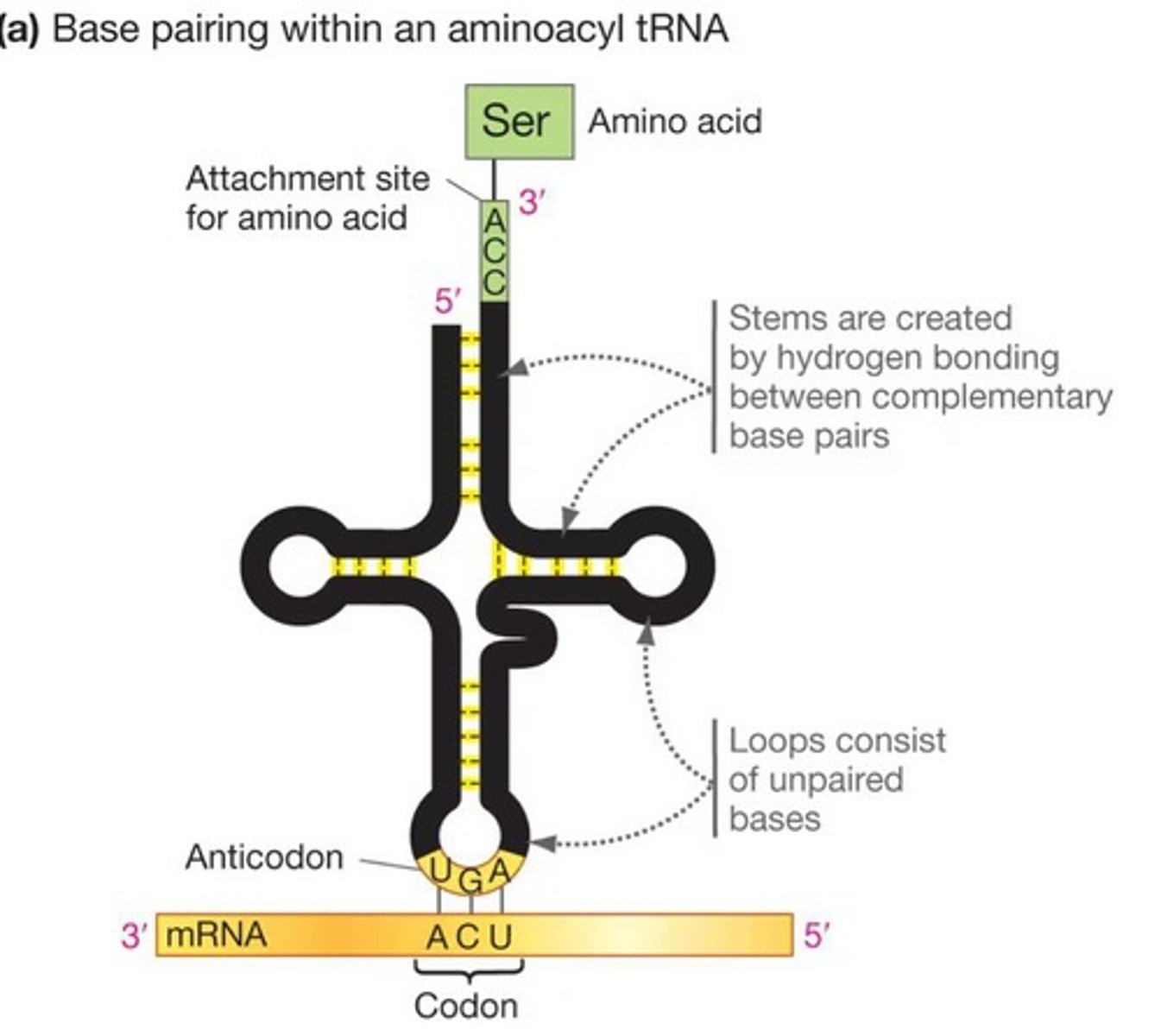
What is the structure of tRNA?
tRNA is a folded RNA strand with an attached amino acid, forming a cloverleaf shape.
What is the significance of the CCA sequence at the 3′ end of tRNA?
It is the site for amino acid attachment.
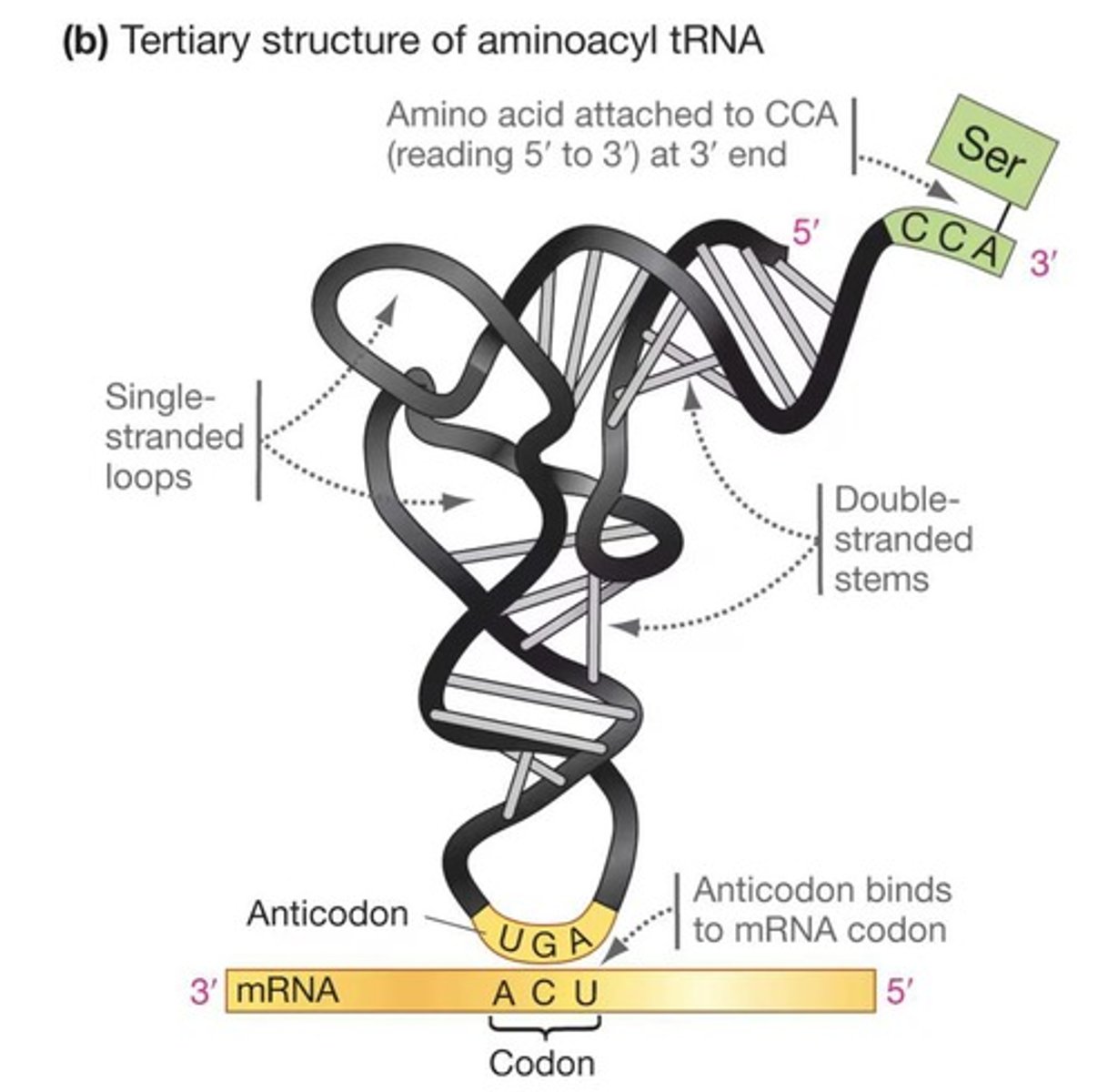
What hypothesis did Francis Crick propose regarding mRNA codons and amino acids?
He suggested that an adapter molecule holds amino acids in place while interacting with mRNA codons.
What is the length of typical tRNA sequences?
75-95 nucleotides.
What happens during the initiation stage of translation?
The ribosome assembles around the mRNA and the first tRNA is attached.
What occurs during the elongation stage of translation?
Amino acids are added one by one to the growing polypeptide chain.
What is the termination stage of translation?
The process ends when a stop codon is reached, releasing the completed polypeptide.
How does simultaneous transcription and translation benefit bacteria?
It allows for extremely rapid gene expression.
What is the role of ribosomes in translation?
Ribosomes facilitate the interaction between mRNA and tRNA, ensuring the correct amino acids are added.
What is the significance of the anti-parallel orientation of codon and anticodon pairing?
It ensures proper base pairing between mRNA and tRNA during translation.
What is the main difference between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
In prokaryotes, transcription occurs in the cytoplasm, while in eukaryotes, it occurs in the nucleus.
What is the function of the attachment site on tRNA?
It is where the specific amino acid is attached to the tRNA.
What are the two hypotheses for how mRNA codons interact with amino acids?
1) Direct interaction between codons and amino acids; 2) Interaction via an adapter molecule (tRNA).
What is the role of the loop in tRNA opposite the amino acid attachment site?
It contains the anticodon that pairs with the mRNA codon.
Why is the genetic code described as degenerate?
Because most amino acids are encoded by more than one codon.
What is the role of aminoacyl tRNA synthetases?
They load amino acids onto the appropriate tRNA.
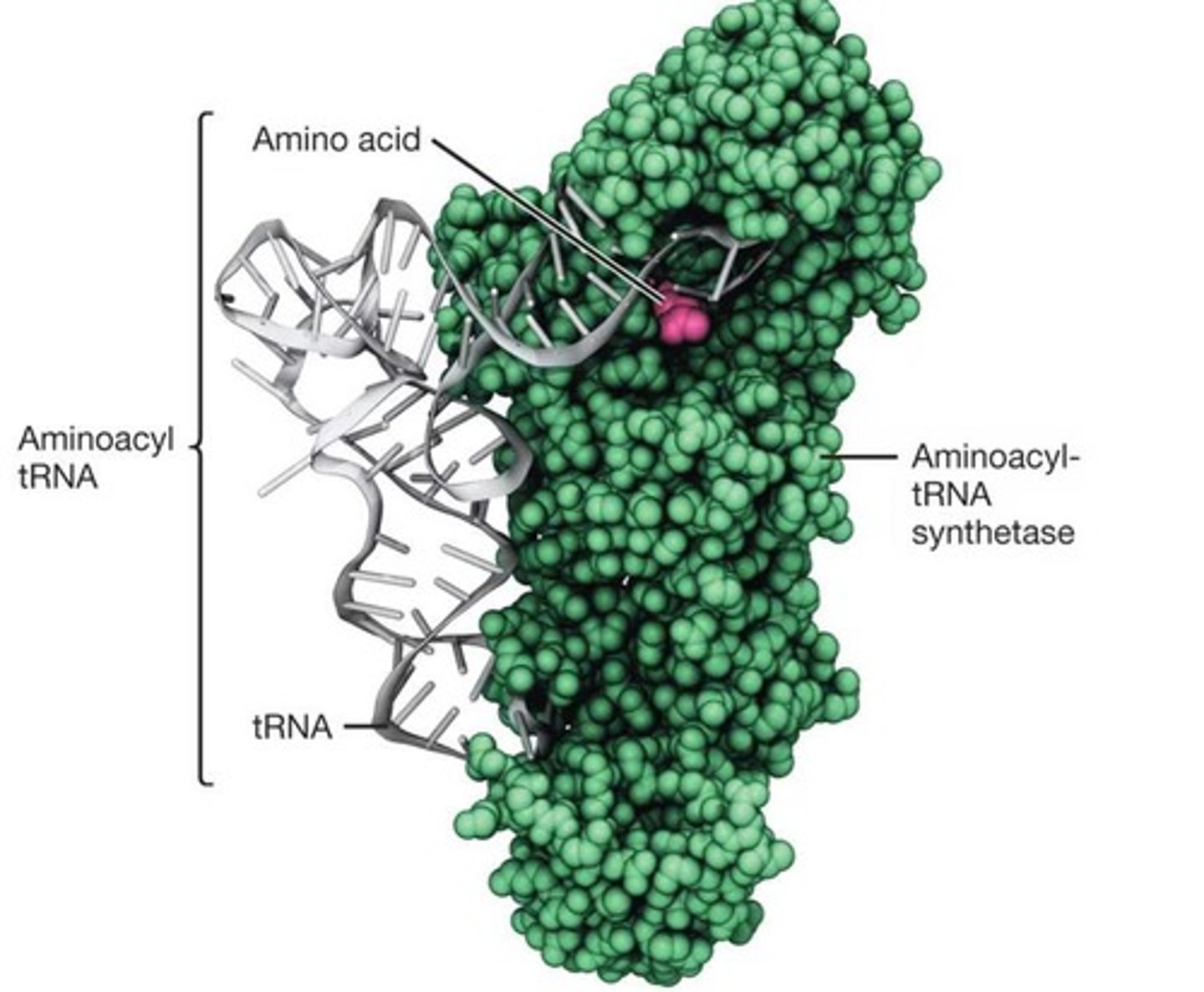
What is required to attach an amino acid to a tRNA?
ATP is required.
How many major amino acids are there, and how many tRNAs correspond to them?
There are 20 major amino acids, each with a different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and one or more tRNAs.
What does the Wobble Hypothesis explain?
It states that a nonstandard base pair in the 3rd position of a codon is acceptable as long as it does not change the amino acid coded by the codon.
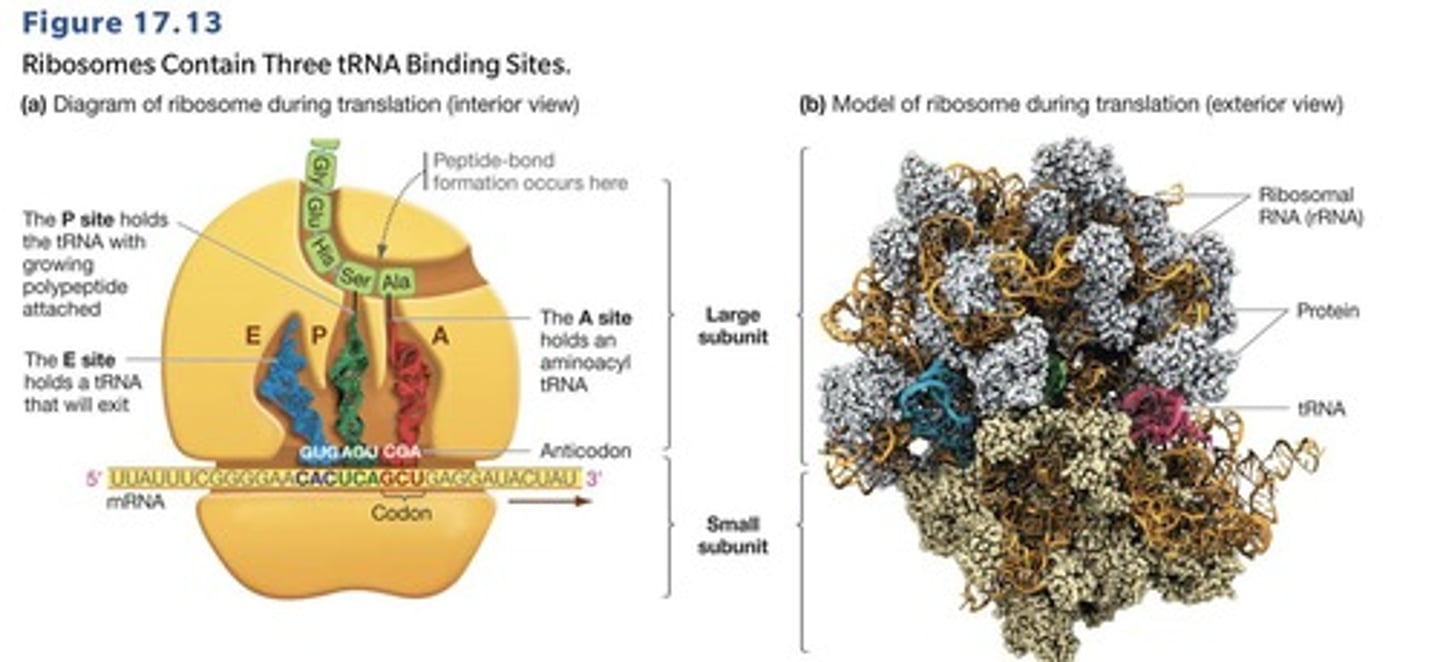
What is the structure of a ribosome?
Ribosomes consist of a large subunit and a small subunit, made of RNA molecules and proteins.
What are the three sites of a ribosome during translation?
A site (acceptor), P site (peptidyl), and E site (exit).
What initiates the translation of mRNA into a polypeptide chain?
The binding of the anticodon of an aminoacyl tRNA to the codon in mRNA.
What occurs during the elongation phase of translation?
An aminoacyl tRNA binds to the A site, a peptide bond forms between amino acids, and the ribosome translocates.
What are the three phases of protein synthesis?
Initiation, elongation, and termination.
What is the start codon in mRNA and what does it code for?
Most start codons are AUG, which codes for the amino acid methionine.
What is the role of initiation factors in translation?
They help deliver the mRNA and hold it in place during the initiation phase.
What is unique about the initiator tRNA in bacteria?
It carries a modified form of methionine called N-formylmethionine (f-Met).
How does the initiation phase differ in eukaryotes compared to bacteria?
Eukaryotes use a scanning process to find the start codon and attach a regular methionine tRNA.
What happens during translocation in the elongation phase?
The ribosome moves one codon down the mRNA, shifting tRNAs between the E, P, and A sites.
What are the stop codons in the genetic code?
UAA, UAG, and UGA.
What is the role of release factors in translation termination?
They recognize stop codons and fill the A site, leading to the release of the polypeptide and tRNAs.
What components are required for translation of proteins?
Ribosomes (rRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and messenger RNA (mRNA).
What is the significance of the ribosome binding site?
It is where the small ribosomal subunit binds to the mRNA at the start codon.
What is peptide bond formation?
It is the process where the amino acid chain from the tRNA in the P site is transferred to the amino acid in the A site.
What is the function of the A site in the ribosome?
It is the acceptor site for aminoacyl tRNA.
What happens to the tRNA in the E site after translocation?
The empty tRNA is ejected from the ribosome.
What is the role of the large ribosomal subunit during translation?
It is where peptide bonds are formed.
What is the process called when the ribosome moves down the mRNA?
Translocation.
What is the significance of the 5' cap in eukaryotic mRNA?
It is where the initiation factor proteins bind during the initiation phase.
What occurs at the termination phase of translation?
The ribosome reaches a stop codon, and the newly synthesized polypeptide is released.