Lecture 16 - accessory structures and functions
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
structure of hair
above epidermis = non-living, keratinized cells
below epidermis = living hair follicle + bulb
locations of hair
covered almost entirely with vellus hairs
darker, thicker hair = terminal hair
thick skin and mucosal regions lack hair
functions of hair
sensation (not the hair itself!)
thermoregulation
protection
social/cultural significance
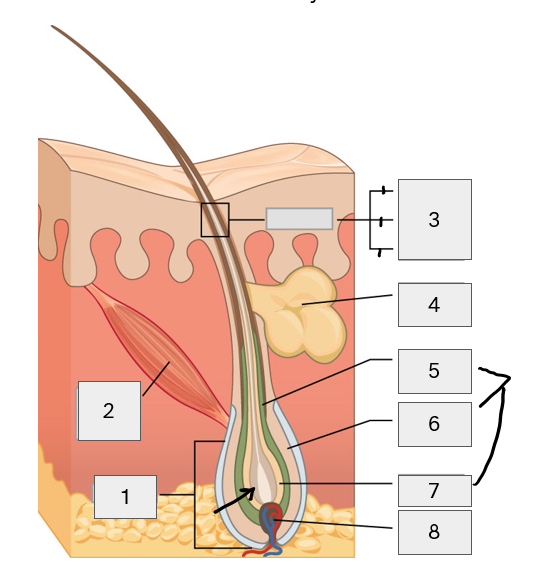
1-4
hair follicle/bulb
arrector pilli
hair shaft
sebaceous gland
hair growth cycle phases
anagen phase
catagen phase
telogen phase
description of anagen phase
2-7 years
rapid cell division in hair matrix
description of catagen phase
2-3 weeks
transition into quiescence
lose some diameter
description of telogen phase
weeks to ~ 1 year
“resting “, shedding
~10-15% in telogen at once
ends with restart of anagen
function of nails
protection
dexterity
sensation
many cutaneous and systemic diseases cause changes to the nails
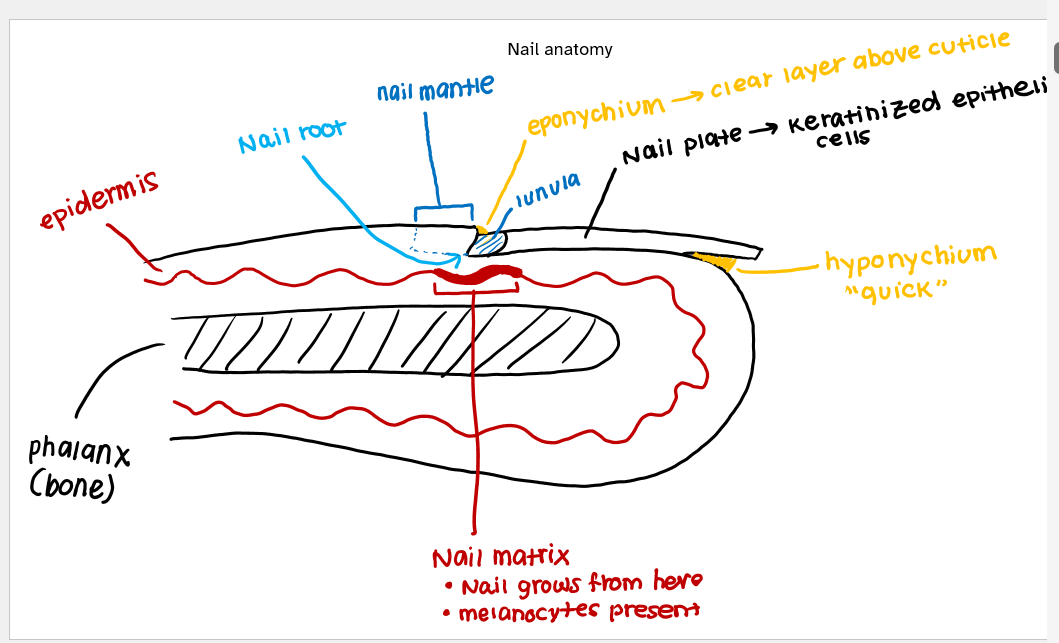
nail anatomy
what is an exocrine gland?
a gland that makes something and secretes it to a body surface
what are the exocrine glands of integumentary system?
sweat glands
sebaceous glands
ceruminous glands
mammary glands
What are sweat glands? function and types and structure
AKA sudoriferous glands
function → primarily theroregulatory
types
eccrine
apocrine
apoeccrine
structure
cuboidal or columnar epithelial cells
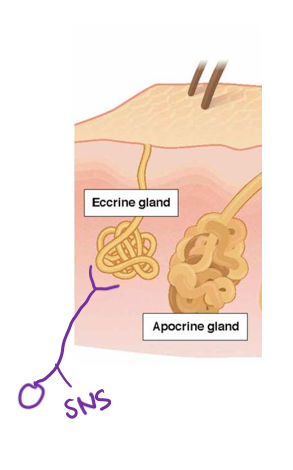
Eccrine sweat glands
2-4 million
function soon after birth
form until ~2-3 years old
fluctuates with weight and age
glabrous (palms/soles & DENSE) vs. non-glabrous (other/hairy & decreased density)
mainly H20/NaCl
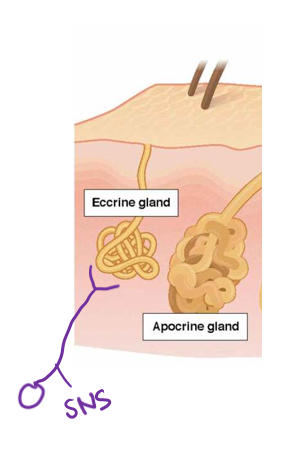
Apocrine
armpits and anogenital region
functional around puberty
larger, associated with hair follicles
ammonia, lipids, sugars, proteins
What is the mechanism for secretion for sweat glands?
merocrine secretion
nucleus
golgi complex
secretory vesicles
secretion
exocytosis