Electronic information (ASVAB FOR DUMMIES)
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What are 3 ways in which electricity Is measured?
Volts, Amps, Ohms
What is electrical current?
The flow of electrons moving from one place to another
What does watt measure in electricity
Power ;the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or transformed into another type of energy
What is a watt-hour?
A watt-hour is an amount of electrical energy used and relates power (watts) and time (hour).
What are the smallest particles that can be broken up without losing their original properties
Atom
What 2 types of subatomic particles are in an atoms nucleus?
Protons and neutrons
What type of charge do electrons have?
Negative
What does substance atomic number tell you?
How many protons are in the substance
What do number of electrons in a valance shell determine ?
Whether an object is conductor, semiconductor, or insulator
What happens with electrons in a conductor?
flow freely between different atoms.
What happens with electrons in an insulator?
Electrons don't have much room to move in an insulator. That's because an insulator has a mostly full valence shell.
What is a circuit?
Path of electrical current
What tools can measure voltage in a circuit?
Voltmeter or multimeter
What is an electrical storage compartment in a battery called?
Cell
How is electrical current (the flow of electrons) expressed?
in amperes (amps) which represent a charge (in coulombs) over a second.
What is a circuit breaker?
- a device which stops the current flowing in a circuit when the current is too high
Rheostat
Vary the resistance against a current flow without opening a circuit
What is ohms law?
The current in a circuit is equal to the applied voltage and inversely proportional to the circuit resistance
How do you express ohms law in mathematical terms?
V=IR
I=V/R
R=V/I
Most electrons will take path of lower resistance, but some will still take a path of higher resistance.
True
What is a load in terms of electricity?
a source of resistance that converts electrical energy into another form of energy (like a lightbulb).
What happens to the electrical current if you flip a light switch from "On" to "Off"?
Circuit opens to interrupt the flow of electrical current. As a result the light turns off
What does a fuse do?
It breaks the circuit if there is a fault (you can’t replace)
When can current flow through an insulator, such as air?
if there's enough difference of potential, such as when lightning travels through the air to strike something on Earth's surface.
How many paths are there for an electrical current in single series circuit?
One
How are loads wired in a parallel circuit?
Each load is wired along its own path
What happens if there is a break in an electrical current path in a series circuit?
The electrical flow stops everywhere in the circuit
What happens if there is break in an electrical current path in a parallel circuit?
The current flow stops in the path with a break; it continues to flow to other loads
What happens to the total resistance of a current if you add a load in parallel?
decreases the total resistance of a current because it provides an additional pathway for electrons to take.
What is the most common circuit configuration for a homes electrical system?
Most homes are wired with series-parallel circuits.
What is a short circuit?
A connection that allows current to take the path of least resistance
In a wire where are the magnetic lines of force?
perpendicular to the conductor and parallel to each other
In how many directions can direct current flow?
One
alternating current constantly changes direction in a regular path?
True
What type of current enters your home from the power company?
Alternating current (AC)
What does a grounding wire do?
gives excess electricity a place to go when it's displaced from its original path.
What is the measure for the number of times an alternating current changes direction in one second?
is known as its frequency, which is measured in Hertz (Hz).
What is capacitive reactance?
The opposition of AC current flow caused by a capacitor.
What is inductive reactance?
Opposition to current flow in a circuit due to induction.
How can you express impedance in mathematical terms?
Impedance = Electromotive force / Current
What does a capacitor do?
stores or holds a charge of electrons.
What is a semiconductor diode?
A semiconductor diode is a component made of a material with conductivity somewhere between that of a conductor and an insulator.
What does a rectifier do?
Changes AC to DC
Three basic terminals on transistor?
emitter, base, collector
What function do wires perform in electrical system ?
Pass current
Transducer
converts energy from one form to another
Inductor
A coil of wire that creates a magnetic field when current passes through it
What numbers do 🔴 markings represent on nonverbal resistors?
Black= 0
Brown= 1
Red= 2
What is a pontentiometer?
Variable resistor
Diode
Allows current to flow in only one direction
What does circuit diagram show you?
How the components in a circuit are connected together
What color are positive DC wires?
Red
What color are negative DC wires?
Black
What color are DC ground wires?
White or grey
Can green wires be live?
Yes
What should you assume about electrical wires ?
They are all live
Which way does current hold?
Negative to positive
Symbol of ohms
Ω
Which object supplies the LEAST resistance to an electrical current: wood, rubber or copper?
Copper
What units are used to measure the rate of electrons moving through a conductor?
Amperes
If a diagram mentions 55 cycles per second, what is its equivalent in hertz?
55 because Cycles per second is the same thing as hertz, so 55 cycles per second equals 55 Hz.
What is electric resistance?
Opposition to the flow of current
What is electrical potential?
Voltage
What is the unit you use to measure electrical charge transported by current of one ampere in one second?
Coulomb
What measures current in a circuit?
Ammeter
What is electromotive force
voltage (same thing as electrical potential)
EMF stands for what?
electromotive force
What type of device would you use to reduce the current in an electrical circuit?
Resistor
Transistor (semiconductor)
amplify signals
A number of-12 wire, compared to a number-6 wire,
Smaller In diameter (the larger the number, the smaller the diameter of the wire)
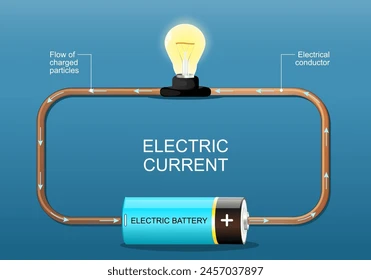
Electrical current flows with
Voltage source (such as battery)
Load (which is a source of a resistance)
Conductors (carry current)