CH 18 | The Foreign Exchange Market
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Exchange Rate
The price of one currency in terms of another.
FACT
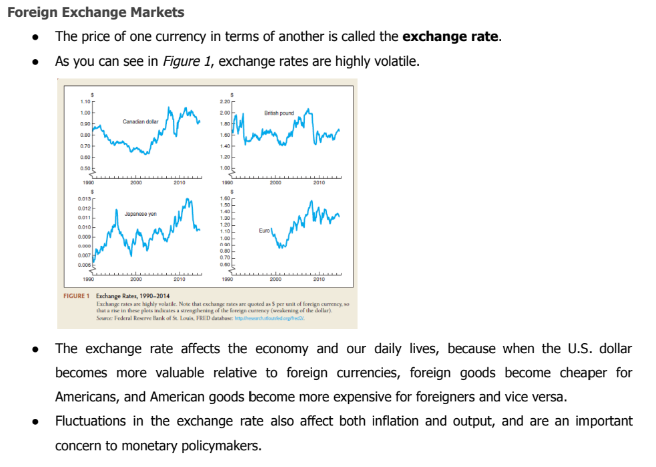
Fluctuations in the exchange rate also affect both inflation and output, and are an important concern to monetary policymakers

Foreign Exchange Market
The financial market in which exchange rates are determined.
Transactions conducted in the foreign exchange market determine the rates at which currencies are exchanged, which in turn determine the cost of purchasing foreign goods and financial assets.
2 kinds of exchange rate transactions
Spot transactions
Forward transactions
Spot Transactions
Involve the immediate (two-day) exchange of bank deposits.
Immediate exchange of bank deposits occurring within two days.
spot exchange rate
the exchange rate for the spot transaction
Forward Transactions
Exchange of bank deposits set for a specified future date.
forward exchange rate
exchange rate for the forward transaction.
Currency Appreciation
When a currency increases in value.
Currency Depreciation
When a currency decreases in value.

Why are Exchange Rates Important?
Exchange rates are important because they affect the relative prices of domestic and foreign goods.
How Is Foreign Exchange Traded?
Foreign exchange market is organized as an over-the-counter market.
Most trades involve the buying and selling of bank deposits denominated in different currencies.
Exchange Rates in the Long Run
Law of one price
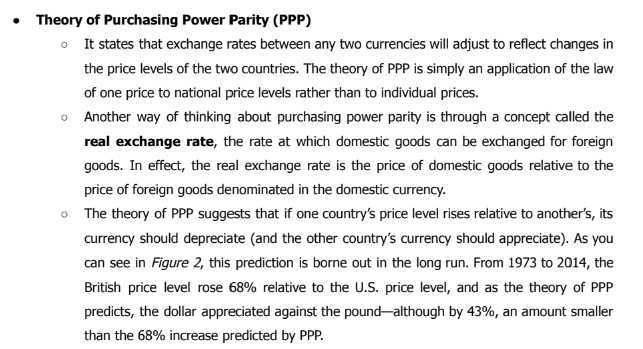
Theory of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)

Law of One Price
Identical goods prices should be the same globally…
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Theory suggesting exchange rates adjust to reflect changes in price levels between countries.
The theory simply applies the law of one price to national price levels rather than to individual prices.
Another way of thinking about purchasing power parity is through a concept called the real exchange rate, the rate at which domestic goods can be exchanged for foreign goods.
In effect, the real exchange rate is the price of domestic goods relative to the price of foreign goods denominated in the domestic currency.
Real Exchange Rate
The rate at which domestic goods can be exchanged for foreign goods.

Why the Theory of Purchasing Power Parity Cannot Fully Explain Exchange Rates
The PPP conclusion that exchange rates are determined solely by changes in relative price levels rests on the assumptions that all goods are identical in both countries and that transportation costs and trade barriers are very low.
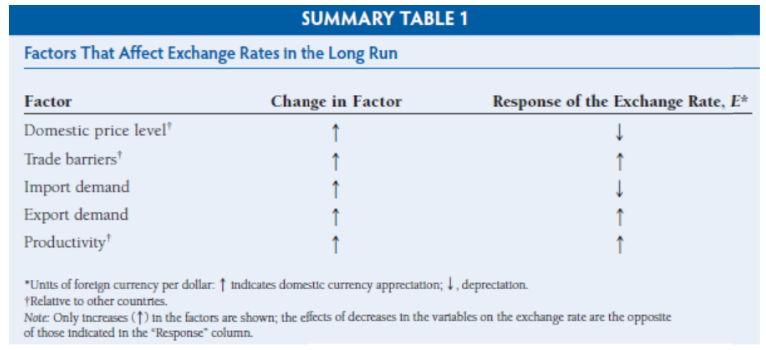
Factors Affecting Exchange Rates in the long Run
If a factor increases the demand for domestic goods relative to foreign goods, the domestic currency will appreciate;
if a factor decreases the relative demand for domestic goods, the domestic currency will depreciate.
Factors:
Relative Price Levels:
Trade Barriers:
Preferences for Domestic Versus Foreign Goods:
Productivity
1 Relative Price Levels:
In the long run, a rise in a country’s price level (relative to the foreign price level) causes its currency to depreciate, and a fall in the country’s relative price level causes its currency to appreciate.
2 Trade Barriers:
tariffs (taxes on imported goods) and
quotas (restrictions on the quantity of foreign goods that can be imported) can affect the exchange rate.
Increasing trade barriers causes a country’s currency to appreciate in the long run.
3 Preferences for Domestic Versus Foreign Goods:
Increased demand for a country’s exports causes its currency to appreciate in the long run; conversely,
increased demand for imports causes the domestic currency to depreciate.
4 Productivity
In the long run, as a country becomes more productive relative to other countries, its currency appreciates.
EXCHANGE RATES IN THE SHORT RUN
In the short run, exchange rates are determined by supply and demand dynamics, specifically through an asset market approach that views the exchange rate as the price of domestic assets relative to foreign assets.
Asset Market Approach
approach to exchange rate determination concludes that currencies are viewed as assets, similar to stocks or bonds. Investors assess the expected returns on these assets.
This approach explains how investors allocate their wealth among various assets to maximize returns while managing risk.
modern approach emphasizes asset stocks (like bank deposits, bonds, and equities) since these are far larger than trade flows and have a greater impact on short-term exchange rate fluctuations.
Thus, while long-term factors gradually influence exchange rates, short-term rates are more sensitive to immediate shifts in asset demand.
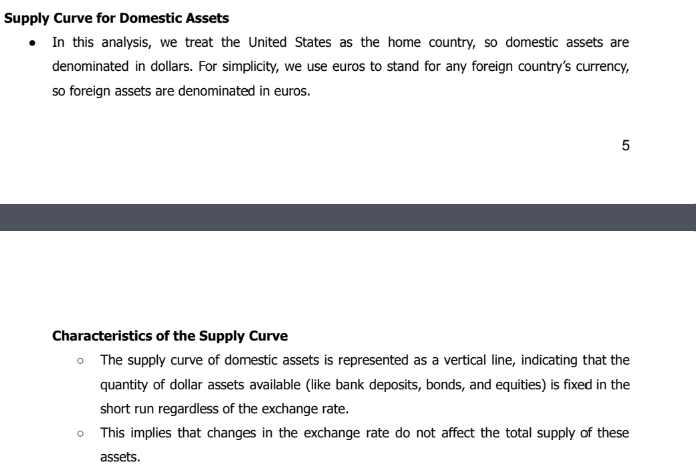
Supply Curve for Domestic Assets
Characteristics:
Represents a fixed supply of dollar assets (like bank deposits, bonds, and equities) in the short run regardless of exchange rate.
This implies that changes in the exchange rate do not affect the total supply of these assets.
Demand Curve for Domestic Assets
Shows quantity of dollar assets demanded at various exchange rates by holding everything else constant (ceteris paribus), particularly the expected future exchange rate.
Expected Returns
Theory of Portfolio of Choice: The most important determinant of the quantity of domestic (dollar) assets demanded is the relative expected return on domestic assets.
The greater the expected rise (appreciation) of the dollar, the higher is the relative expected return on dollar (domestic) assets. If investors believe that the dollar will appreciate in the future, they are more likely to demand dollar assets.
Expectations of Future Exchange Rates:
the current exchange rate falls, investors may expect the dollar to appreciate in the future, making dollar assets more attractive to investors.

Downward-Sloping Demand Curve
As the current exchange rate falls, the expected appreciation of the dollar rises, leading to increased demand for dollar assets.
Equilibrium in the Foreign Exchange Rate
Rate at which quantity of dollar assets demanded = the quantity supplied.
Excess Supply
When the exchange rate is above equilibrium leading to a surplus of dollar assets.
This excess supply will cause the value of the dollar to decrease as more investors want to sell dollar assets than buy dollar assets. The dollar's value will continue to decrease until it reaches the equilibrium rate
Excess Demand
When the exchange rate is below equilibrium leading to a shortage of dollar assets.
This excess demand leads to increased pressure on the dollar's value, and more investors want to buy dollar assets than there are available for sale. This excess demand causes the dollar's value to rise until it reaches equilibrium
EXPLAINING CHANGES IN EXCHANGE RATES
The supply and demand analysis of the foreign exchange market explains the fluctuations in exchange rates. In the simplified model, the supply of dollar assets is assumed to be fixed, resulting in a vertical supply curve that does not shift.
Consequently, to understand how exchange rates change over time, we focus on the factors that affect the demand curve for dollar assets. Changes in these demand factors lead to shifts in the demand curve, thereby influencing the exchange rate.
Shifts in the Demand for Domestic Assets
if the relative expected return on dollar assets ⬆, investors are more inclined to buy dollar assets, demand for these assets ⬆, causing the demand curve to shift to the right.
the relative expected return ⬇, demand ⬇, resulting in a leftward shift of the demand curve.
Thus, changes in expected returns, while holding the current exchange rate constant, dictate the direction of the demand curve shift for dollar assets.
Expected Returns
Anticipated gains from an investment that influence asset demand.
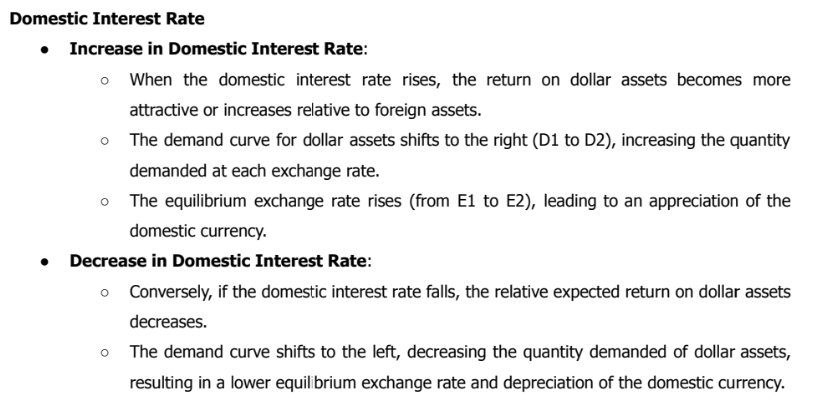
Domestic Interest Rate
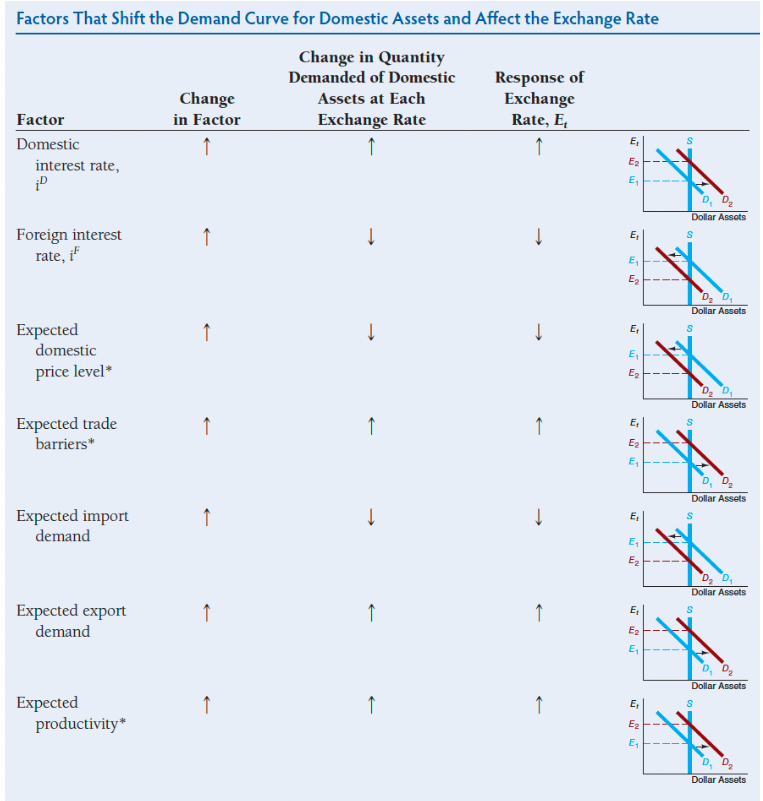
An ⬆domestic interest rate shifts the demand curve for domestic assets to the right and causes the domestic currency to appreciate
A ⬇domestic interest rate shifts the demand curve for domestic assets to the left and causes the domestic currency to depreciate

Foreign Interest Rates
An increase in the foreign interest rate shifts the demand curve to the left and causes the domestic currency to depreciate
A fall in the foreign interest rate shifts the demand curve D to the right and causes the domestic currency to appreciate.
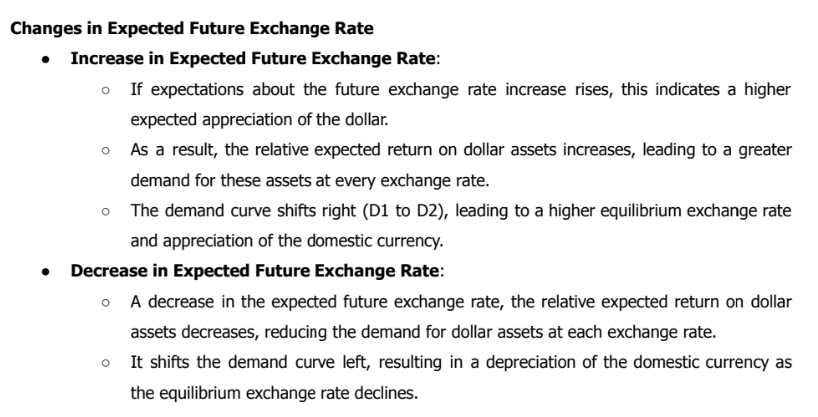
Changes in the Expected Future Exchange Rate
demand for domestic assets, like that for any physical or financial asset, depends on the future resale price
A rise in the expected future exchange rate shifts the demand curve to the right and causes an appreciation of the domestic currency.
A fall in the expected future exchange rate shifts the demand curve to the left and causes a depreciation of the currency
Explaining Changes in Exchange Rates
Shifts in the Demand for Domestic Assets
Domestic Interest Rate
Foreign Interest Rate
Changes in the Expected Future Exchange Rate
Other long-run determinants of the exchange rate that can influence the relative expected return on dollar assets and the current exchange rate:
expectations of a fall in the American price level relative to the foreign price level
expectations of higher American trade barriers relative to foreign trade barriers
expectations of lower American import demand
expectations of higher foreign demand for American exports
expectations of higher American productivity relative to foreign productivity
All of these changes increase the relative expected return on dollar assets, shift the demand curve to the right, and cause an appreciation of the domestic currency, the dollar.
Theory of portfolio choice:
asserts that changes in the relative expected return on dollar assets are the source of shifts in the demand curve
Summary: Factors That Shift the Demand Curve for Domestic Assets and Affect the Exchange Rate (!)
CONCLUSION
