Biology A Level - Chemical Elements and Biological Compounds
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
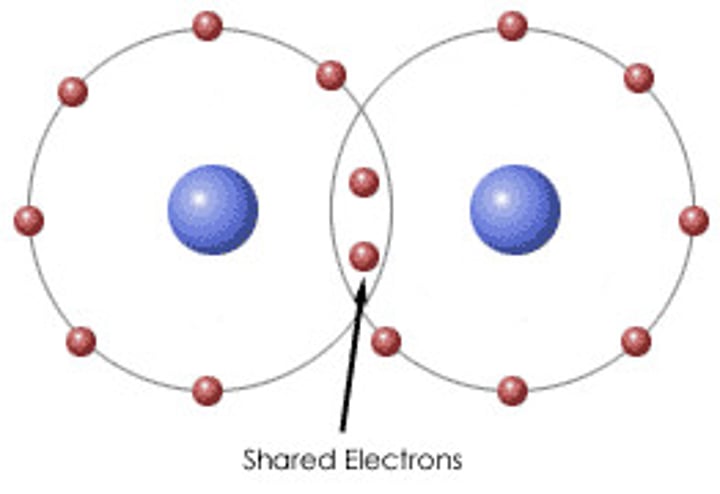
Covalent bond
Type of chemical bond in which two atoms share a pair of electrons.
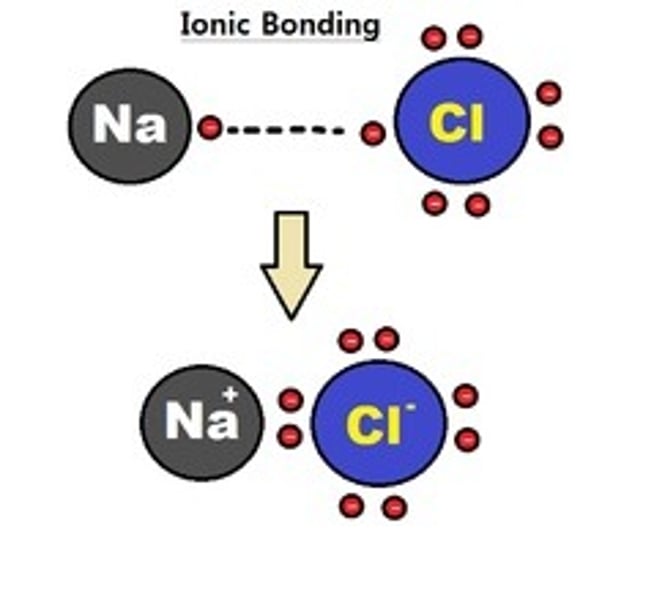
Ionic bond
A bond between a positive ion which has lost an electron(s) and a negative ion which has gained an electron(s).
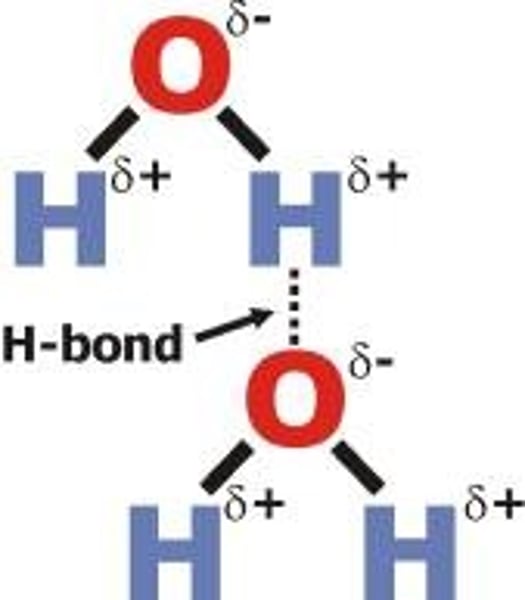
Hydrogen bond
Chemical bond formed between the positive charge on a hydrogen atom and the negative charge on another atom of an adjacent molecule e.g. between the Hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the Oxygen atom of an adjacent water molecule
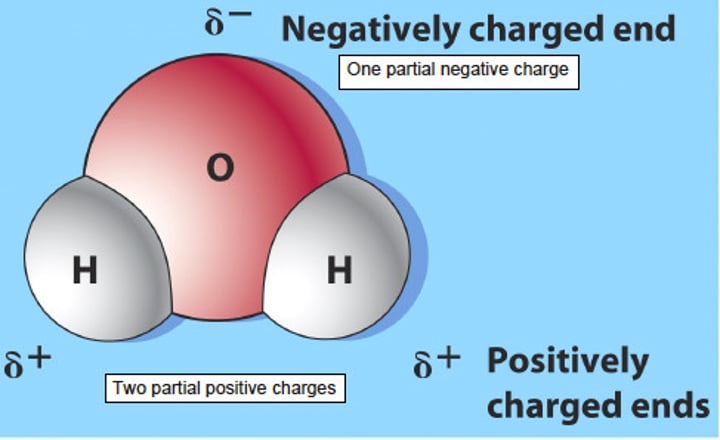
Polar molecule
A molecule which has a partially positive charge in one part of the molecule and completely negative charge in another part (a dipole).
Monomer
One of many small molecules that combine together to form a polymer
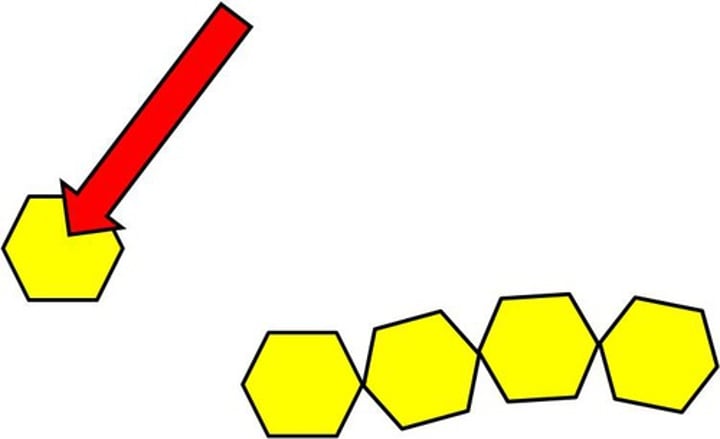
Polymer
Large molecule made up of many repeating smaller molecules (monomers).
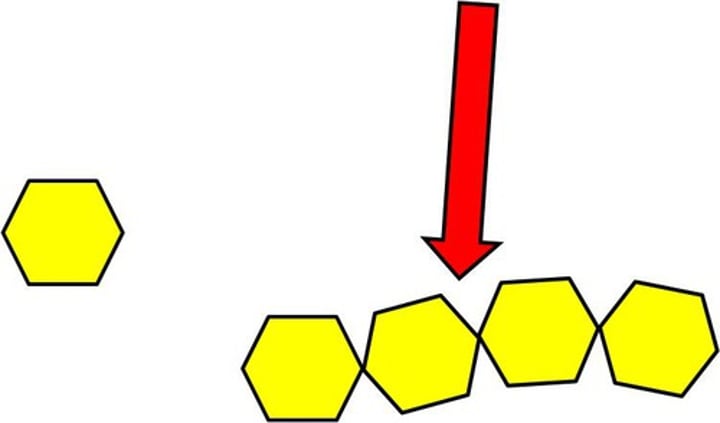
Polymerisation
The process of making a polymer
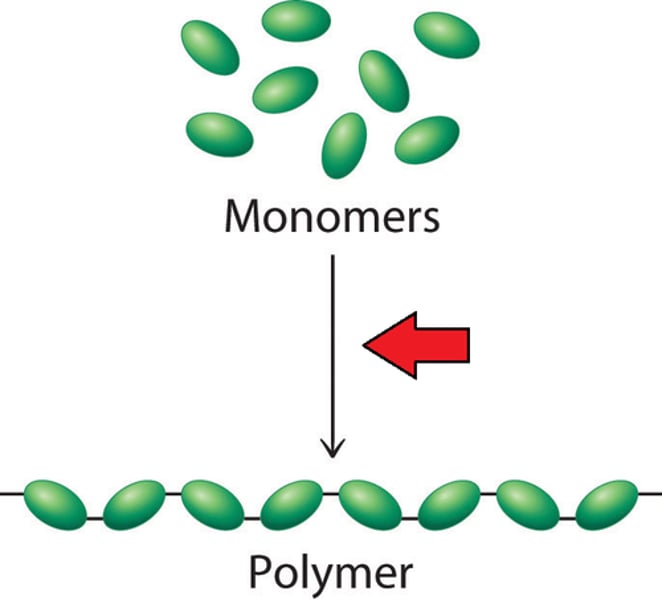
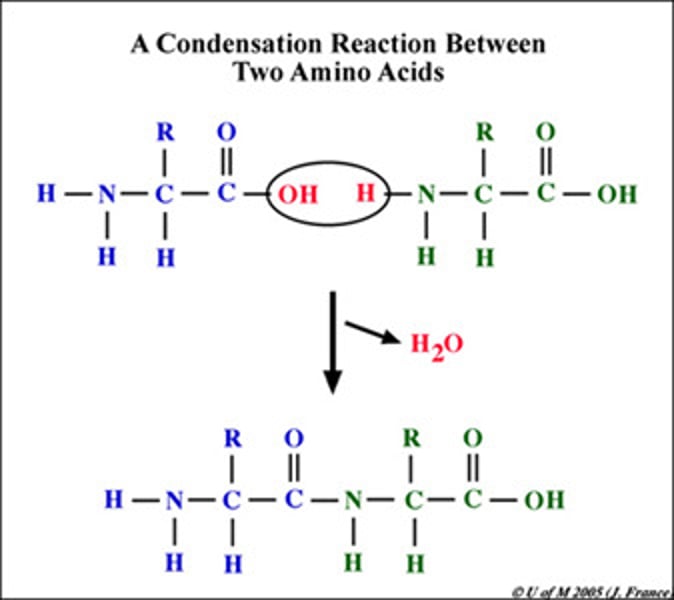
Condensation
Chemical process in which two molecules combine to form a more complex one with the elimination of a simple substance, usually water. Many biological polymers (e.g. polysaccharides, polypeptides) are formed by condensation.
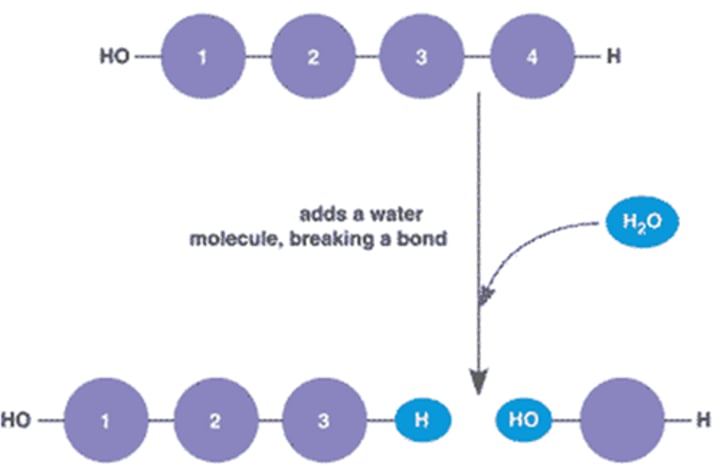
Hydrolysis
The breaking down of large molecules into smaller ones by the addition of water molecules.
Carbohydrates
Compounds made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Either monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
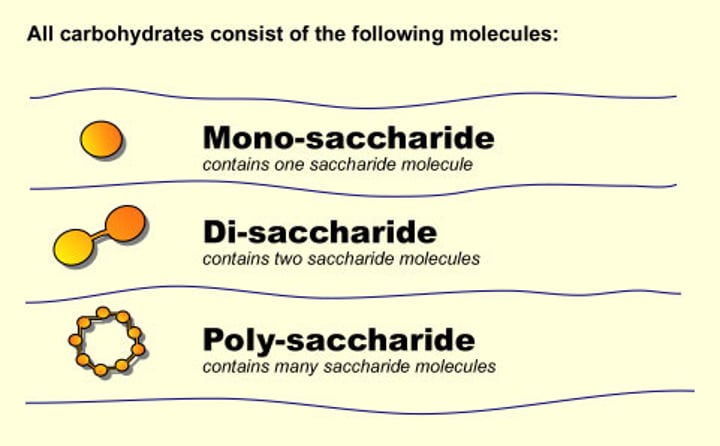
Monosaccharide
A single molecule of sugar e.g. glucose
Organic molecule
Molecules containing carbon that can be found in living things; four types are carbohydrates, proteins (chain of amino acids), lipids, and nucleic acids
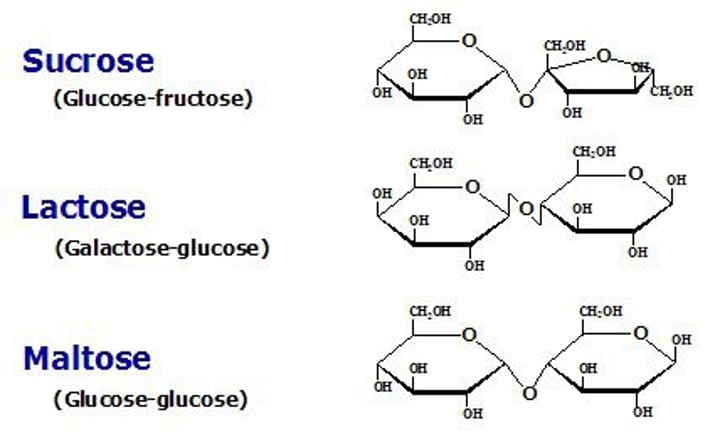
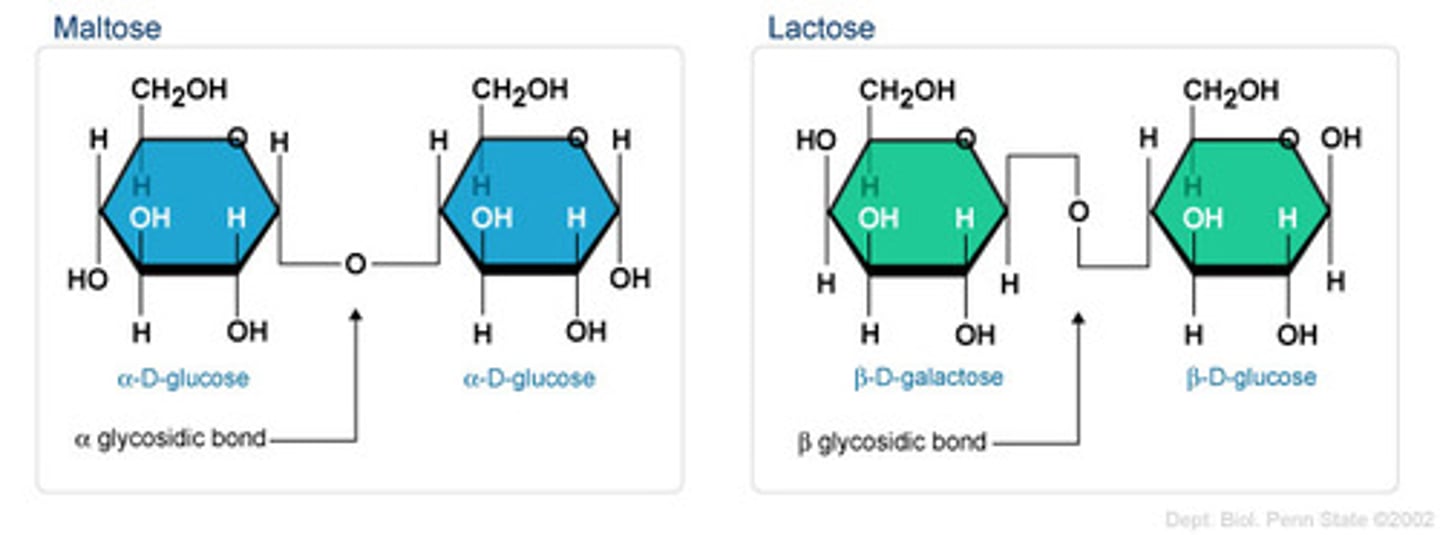
Disaccharide
Made up of two sugar units joined by a condensation reaction. Monosaccharides are joined by a glycosidic bond.
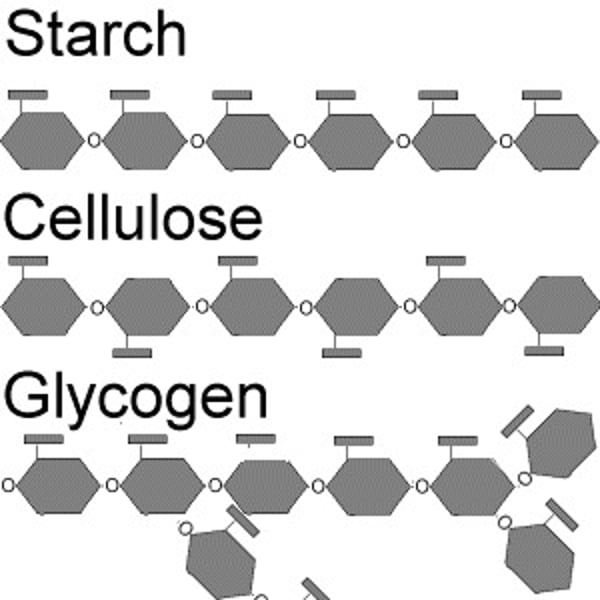
Polysaccharide
Made of many sugar units that are formed by a condensation reaction. Monosaccharides are joined by a glycosidic bonds. For example starch, glycogen, cellulose and chitin.
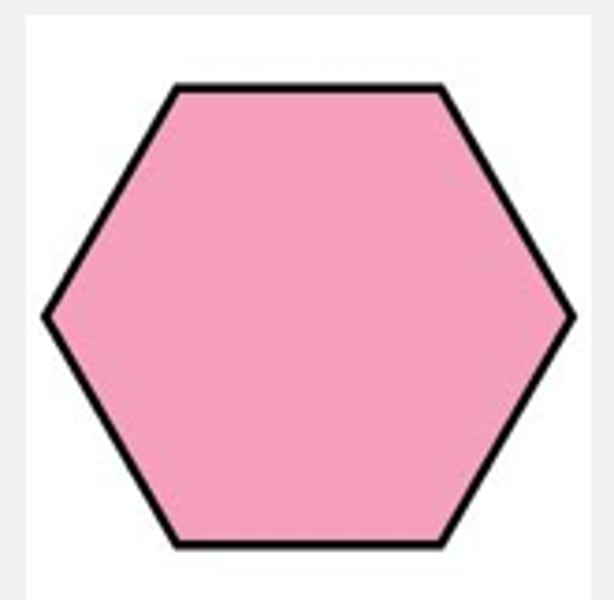
Hexose
A sugar made up of 6 carbons.
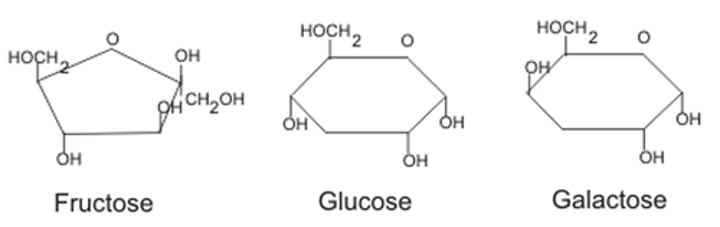
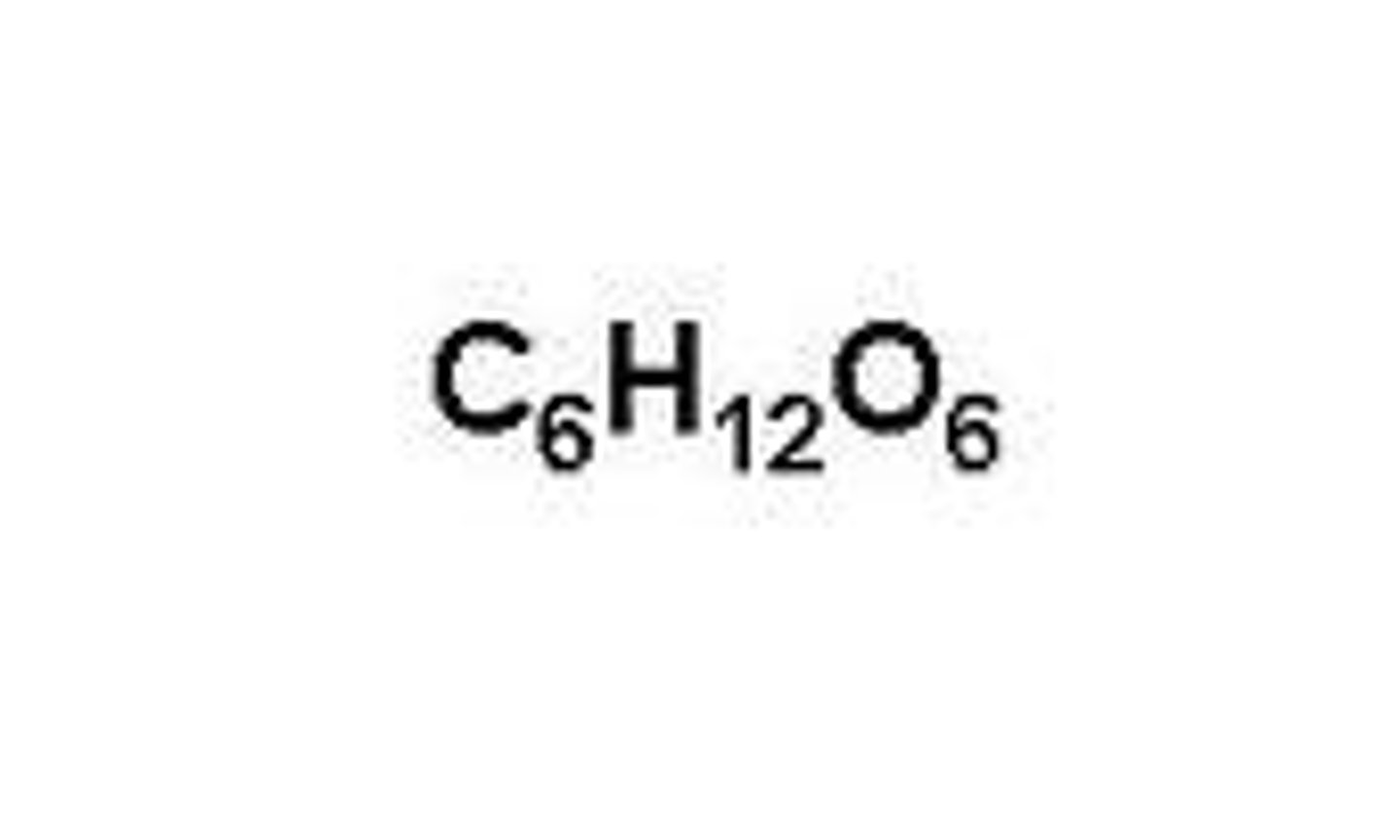
glucose
C6H12O6 - a single sugar which is used in respiration.
Reducing sugar
A sugar that serves as a reducing agent. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars along with some disaccharides e.g lactose and maltose
Reducing sugars test
Heat solution with Benedict's reagent to test for reducing sugars. If it goes brick red then a reducing sugar is present.
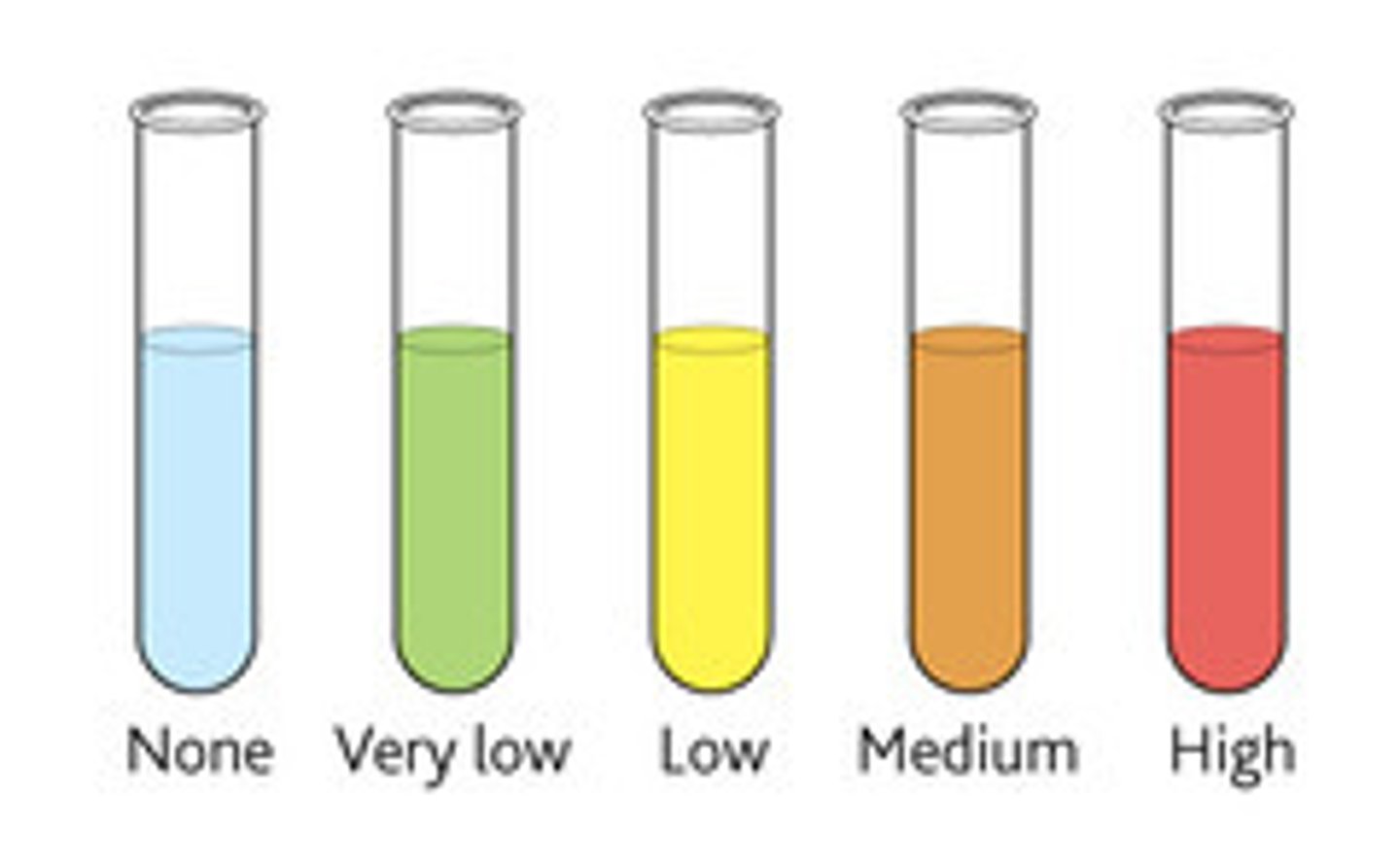

Benedict's reagent
Blue solution which is used to test for reducing and non-reducing sugars.
Glycosidic bond
Bond between sugar molecules in disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Non-reducing sugar
A sugar which cannot serve as a reducing agent. An example is sucrose.
Non-reducing sugars test
Following a negative reducing sugars test. Heat the solution with HCl to hydrolyse the non-reducing sugar into it's monosaccharides. Then perform the Benedict's test again. If you get a positive result after hydrolysis then a non-reducing sugar is present.
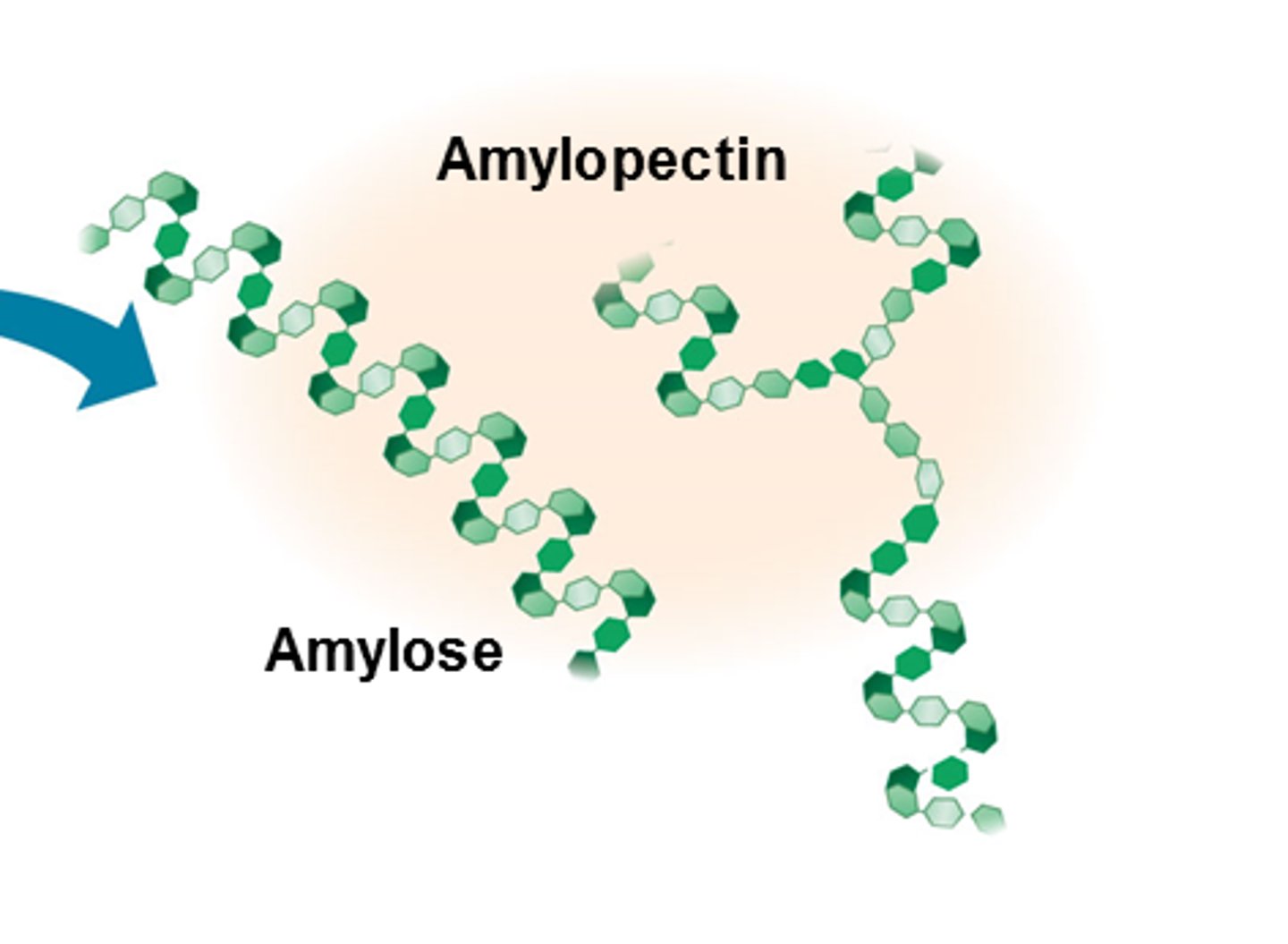
Starch
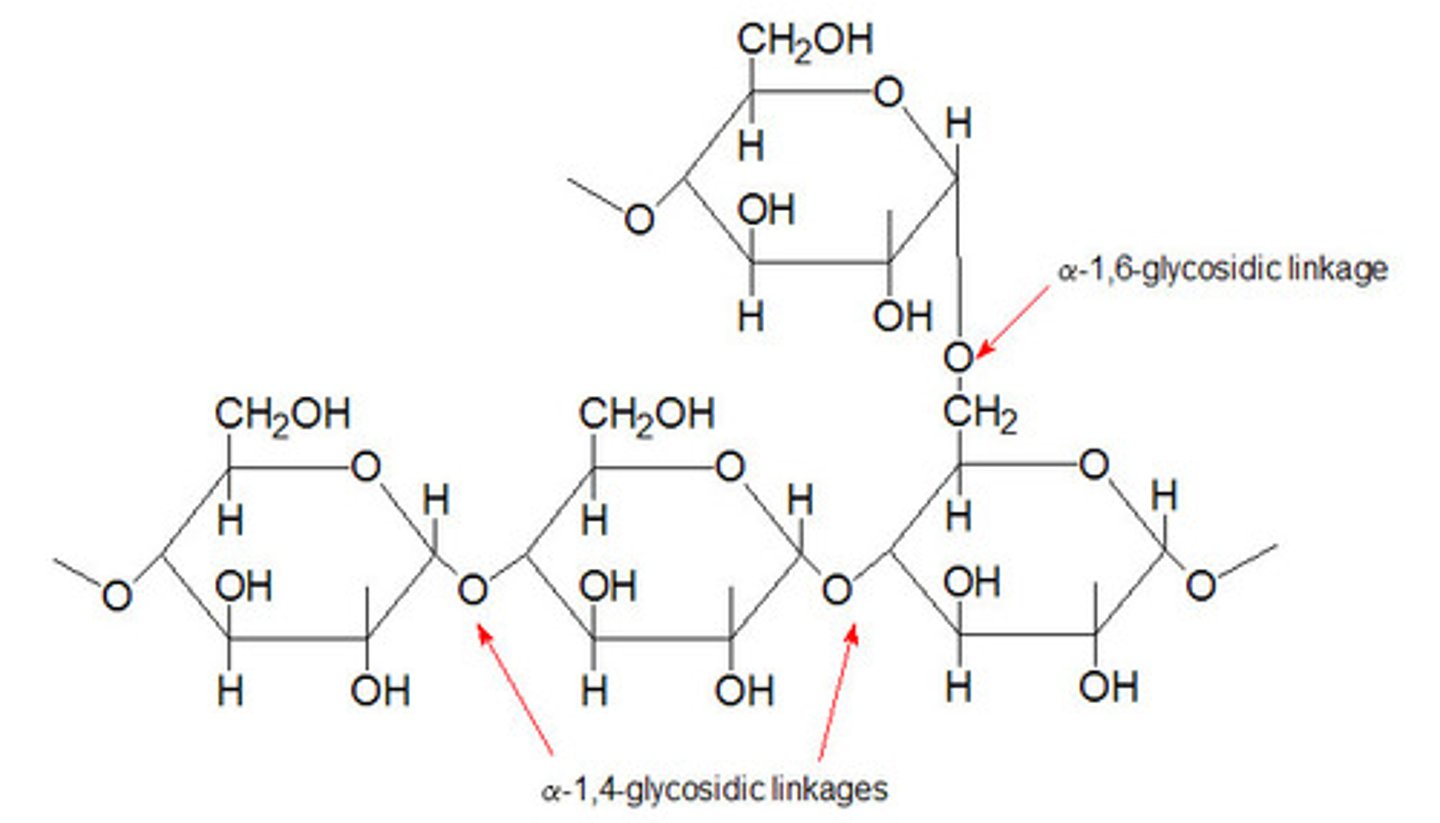
A polysaccharide found in plant cells made up of alpha-glucose - comprised of amylose (alpha-1,4 glyosidic bonds) and amylopectin (alpha-1,4- and alpha-1,6-glyosidic bonds).
Glycogen
A highly branched polysaccharide made up of alpha-glucose found in animal cells (alpha-1,4- and alpha-1,6-glyosidic bonds).
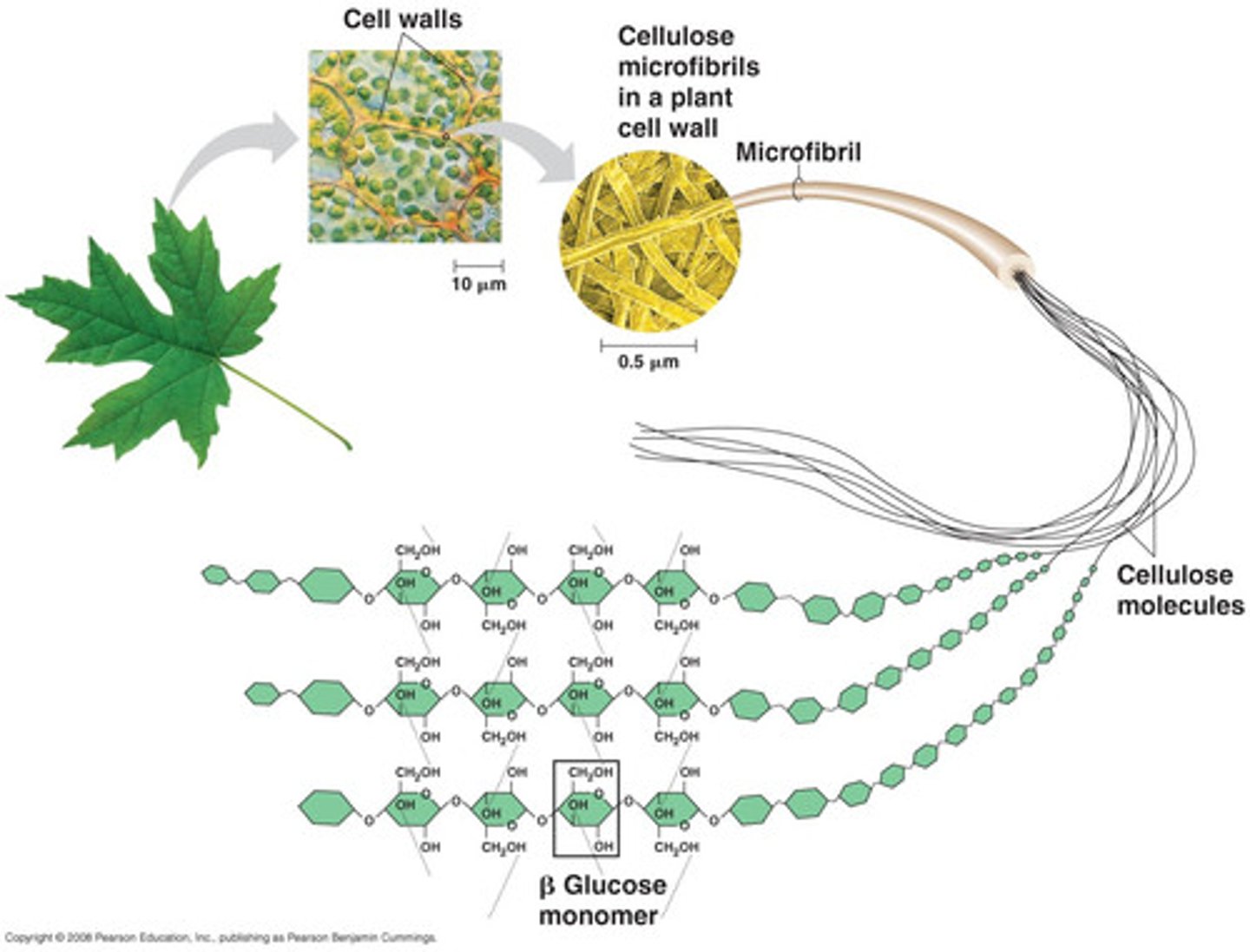
Cellulose
A polysaccharide made up of beta-glucose found in plant cells (beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds).
Alpha glucose
An isomer of glucose that can bond together to form starch or glycogen.
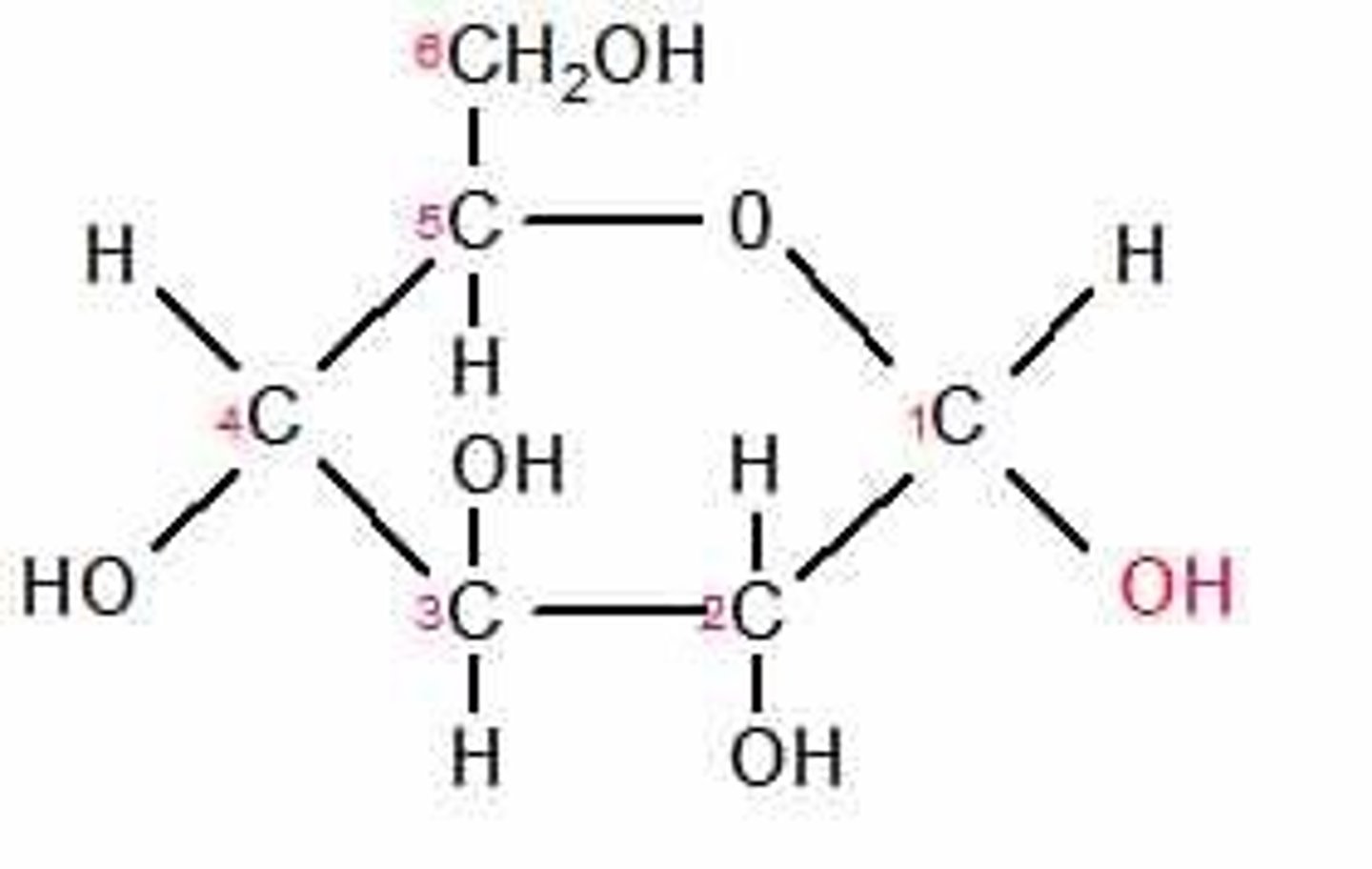
Beta glucose
An isomer of glucose that can bond together to form cellulose.
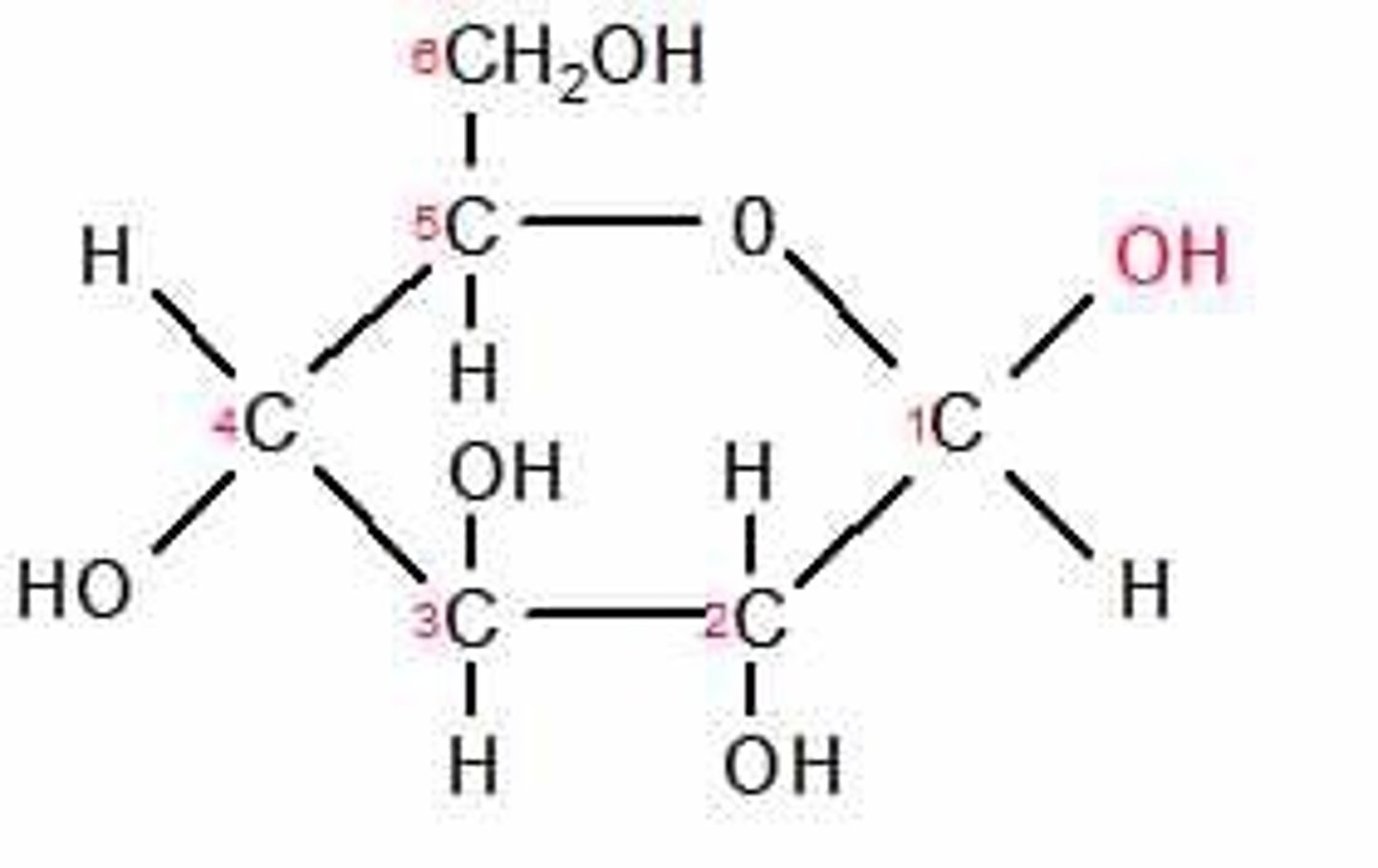
Lipid
A class of organic compounds that are fatty acids are their derivatives and are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They include triglycerides, phospholipids, waxes and steroids.
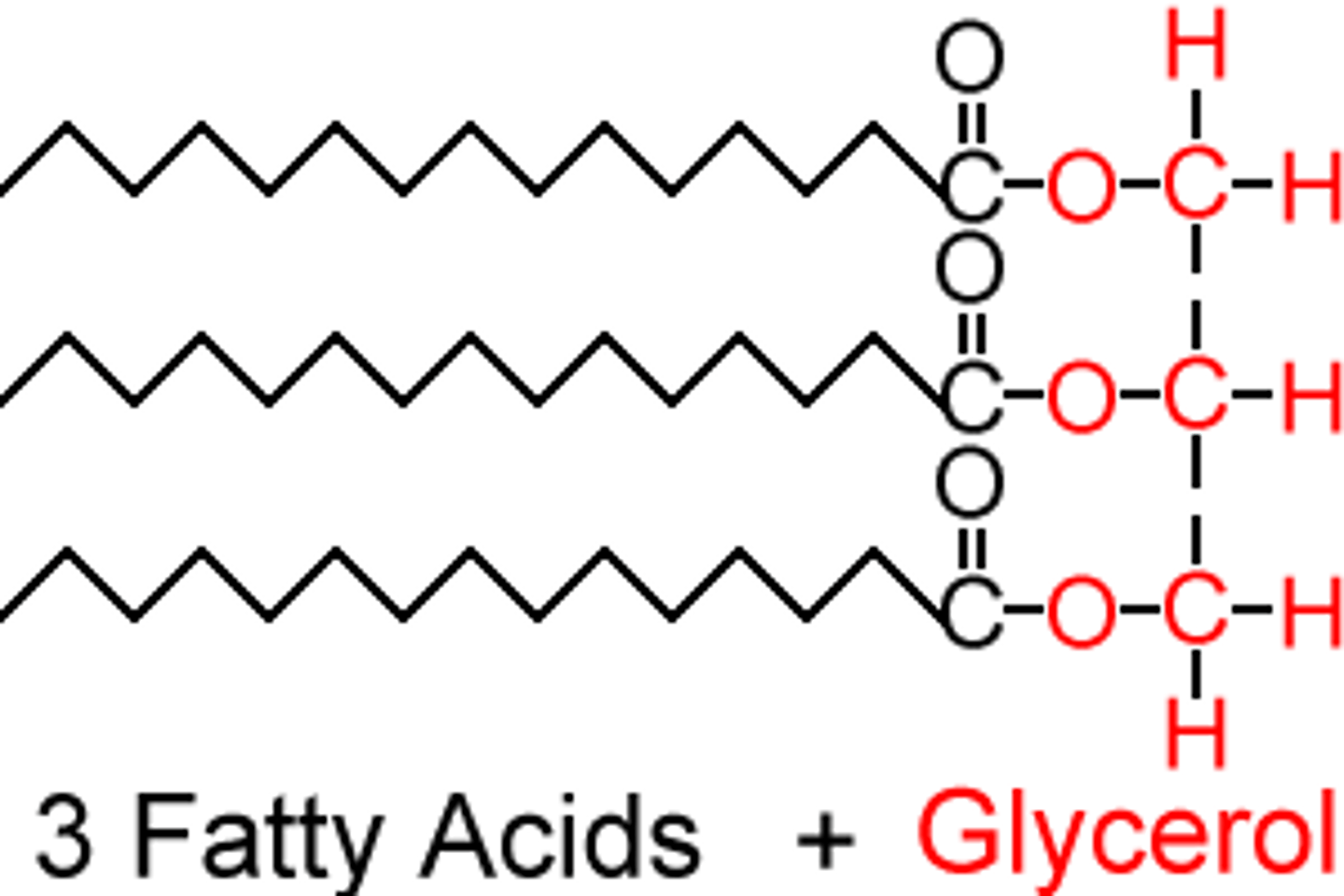
Triglyceride
An individual lipid molecule made up of a glycerol molecule and three fatty acids. Contains ester bonds.
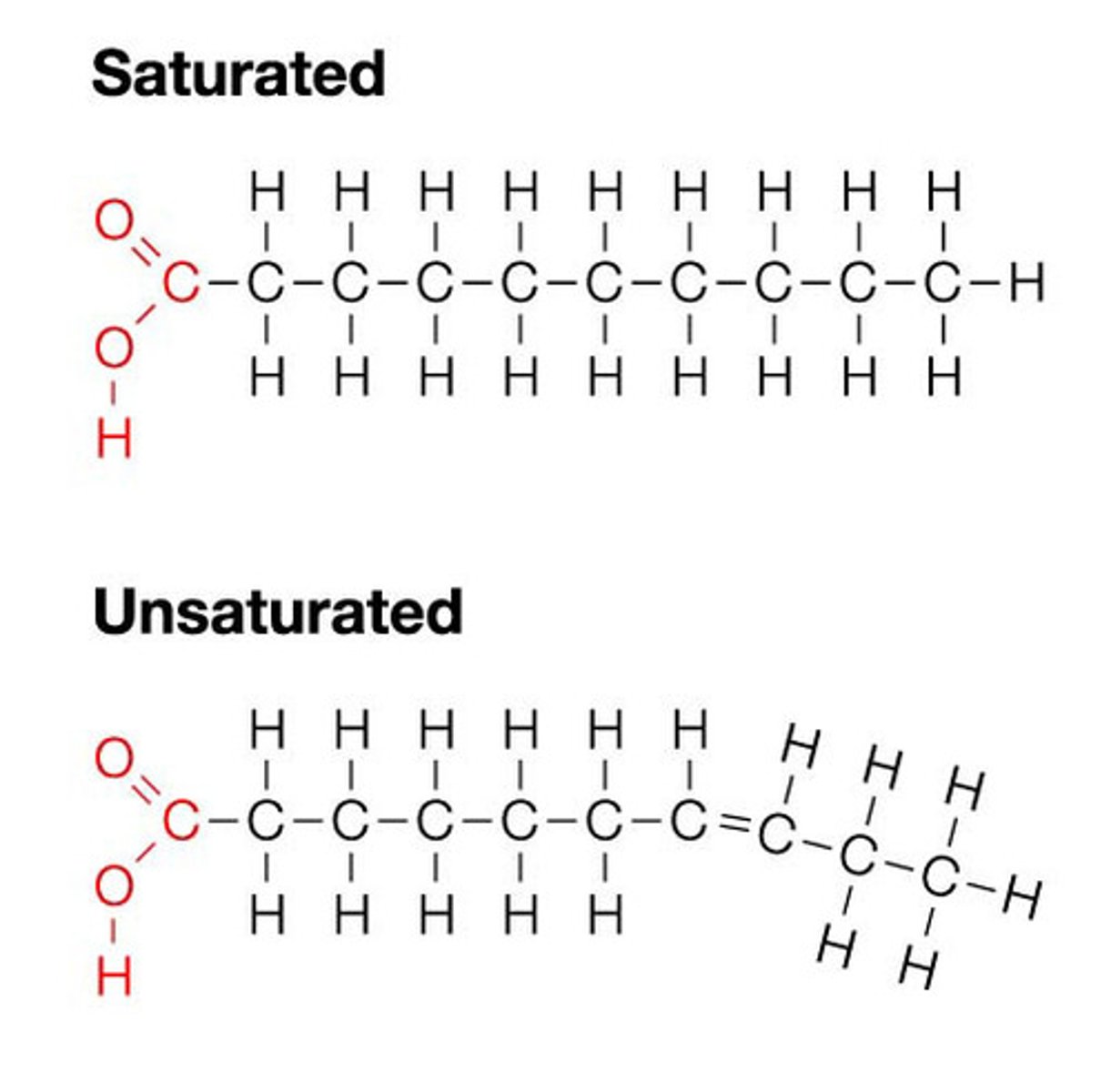
Fatty acid
A carboxylic acid with a hydrocarbon tail. Can be saturated or unsaturated.
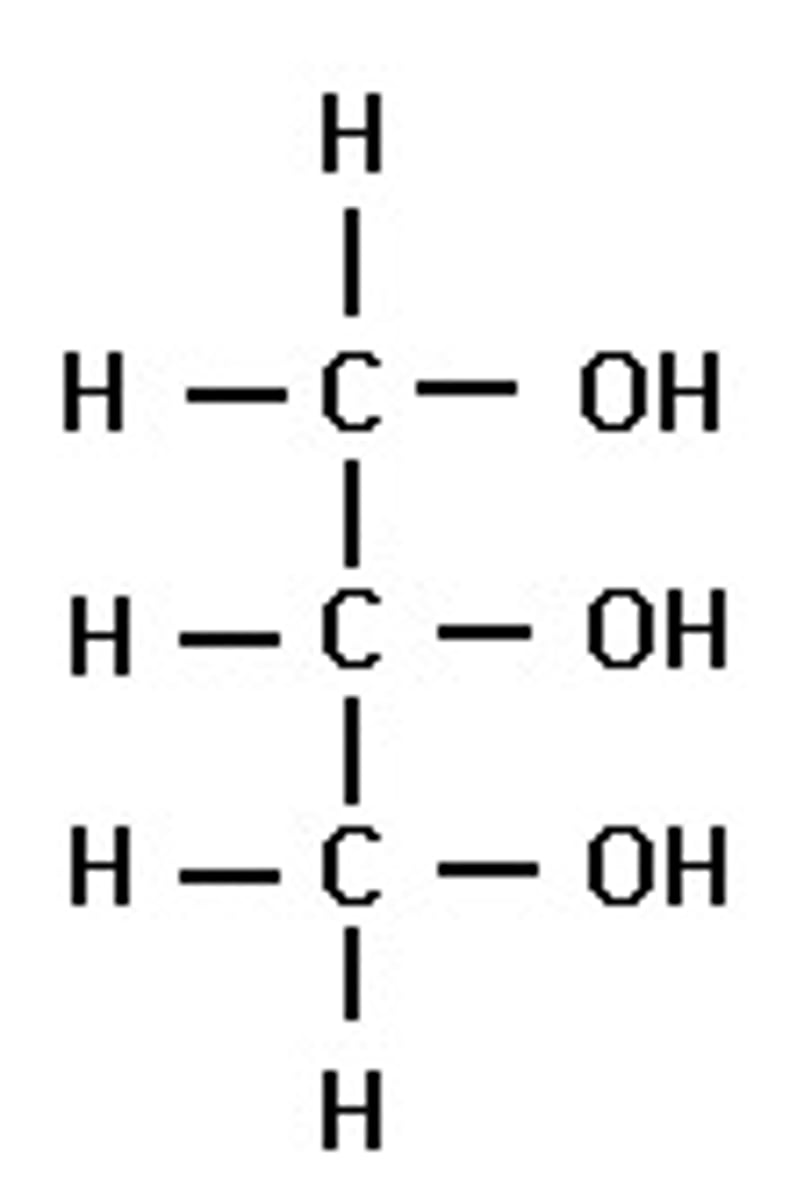
Glycerol
A molecule which combines with three fatty acids to form triglycerides. It is 3 carbon chain with 3 hydroxyl groups.
Saturated fatty acid
A fatty acid in which there are no double bonds between the carbon atoms
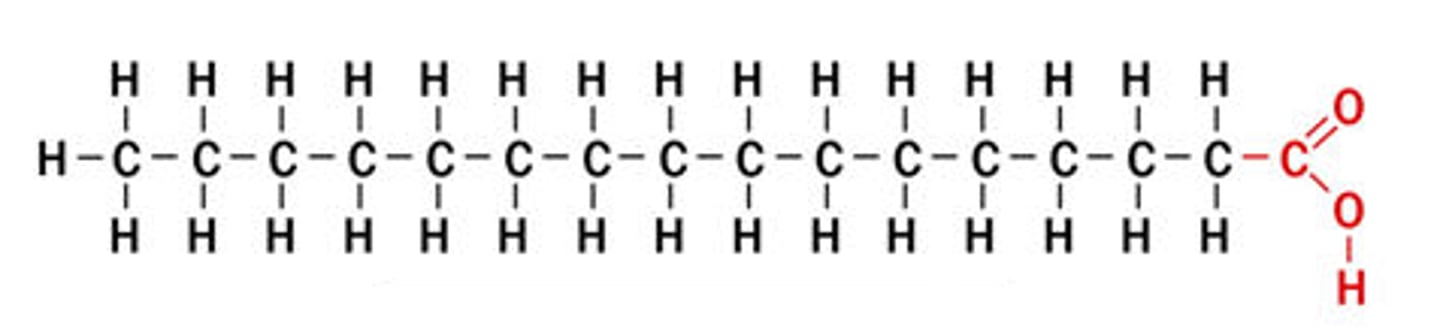
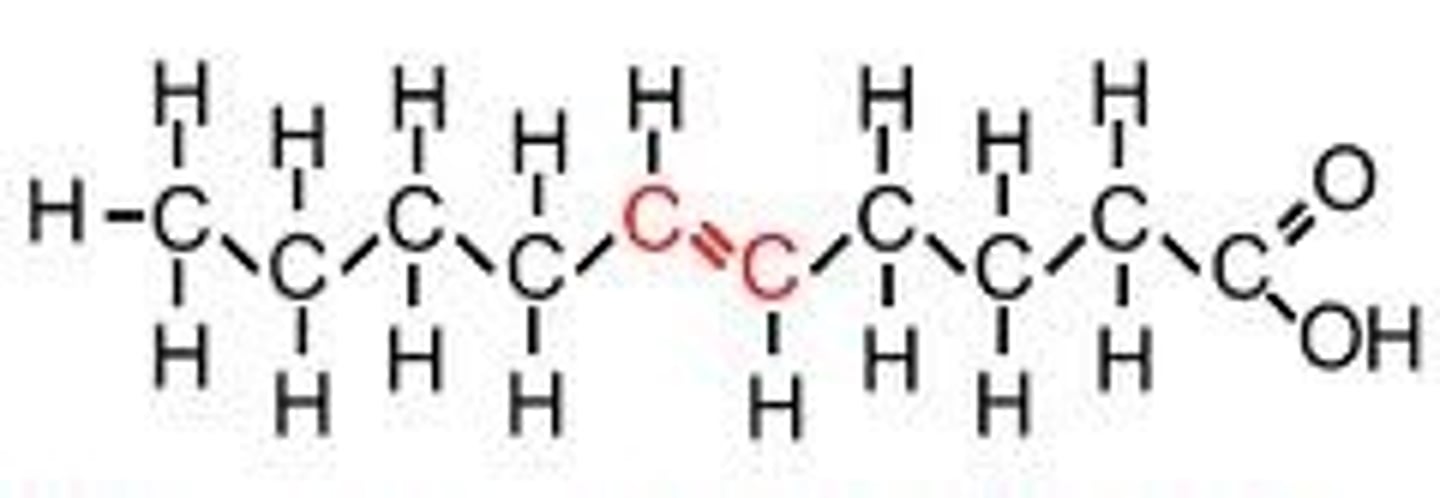
Mono-unsaturated fatty acid
Fatty acid which possesses a carbon chain with a single double bond between carbon atoms.
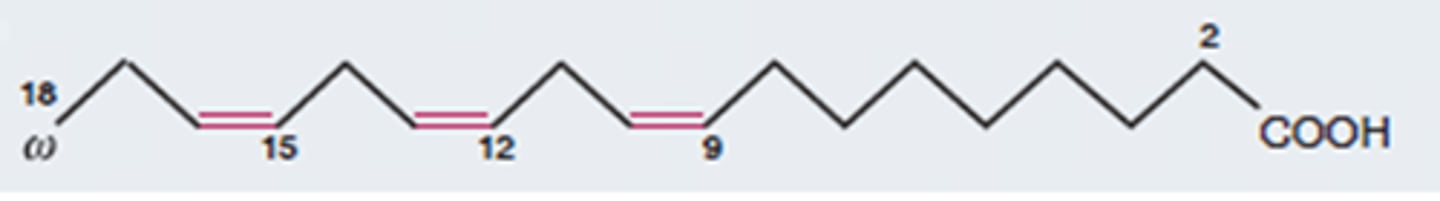
Poly-unsaturated fatty acid
Fatty acid which possesses a carbon chain with many double bonds between carbon atoms.
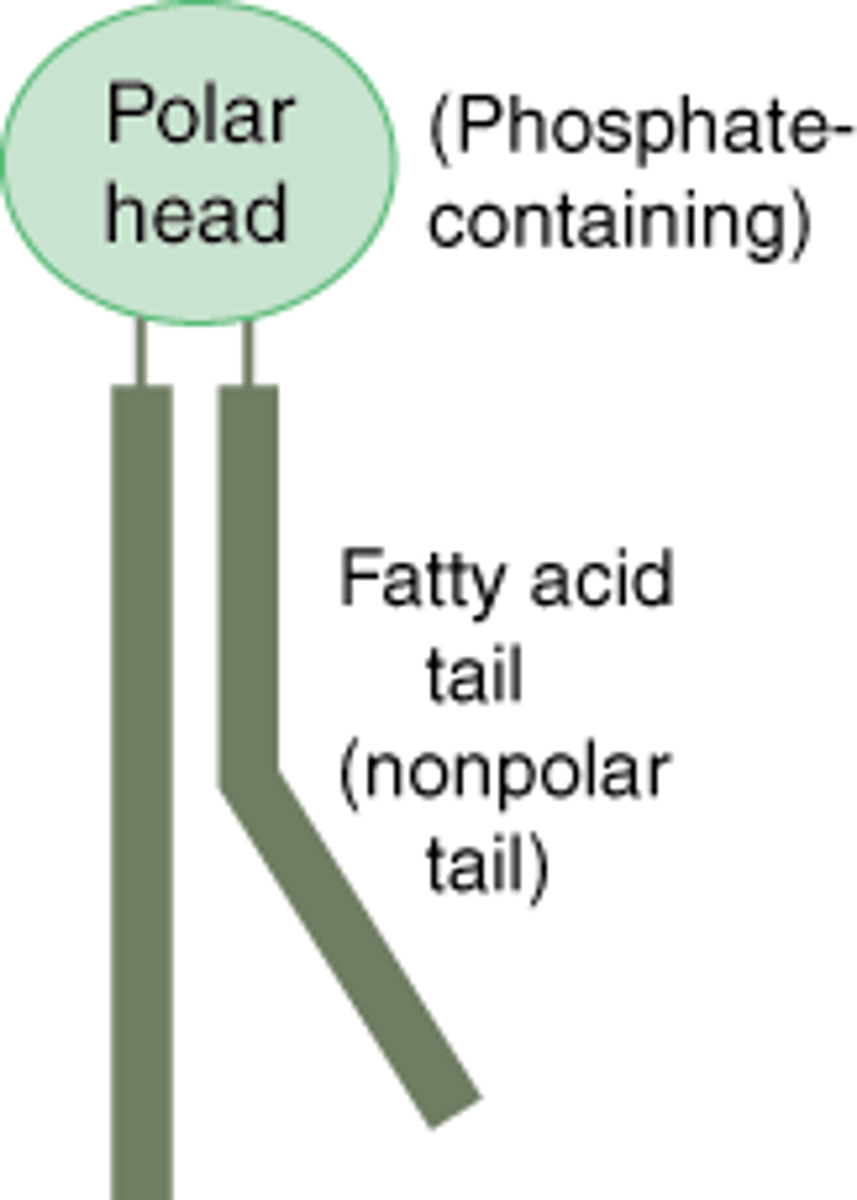
Phospholipid
Triglyceride in which one of the three fatty acid molecules is replaced by a phosphate molecule. Phospholipids are important in the structure and functioning of plasma membranes.
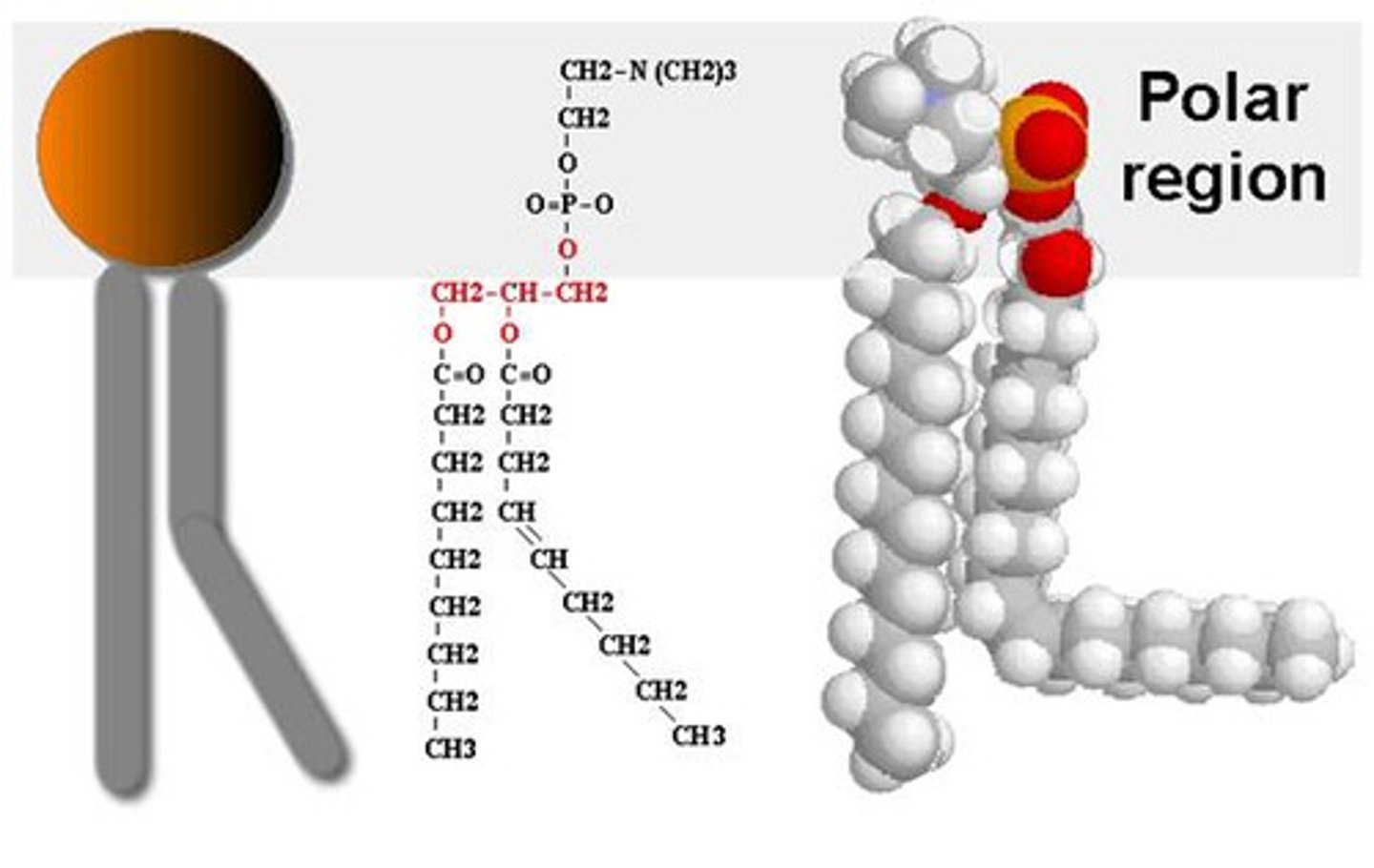
Hydrophilic
Section of a molecule which is attracted to water.
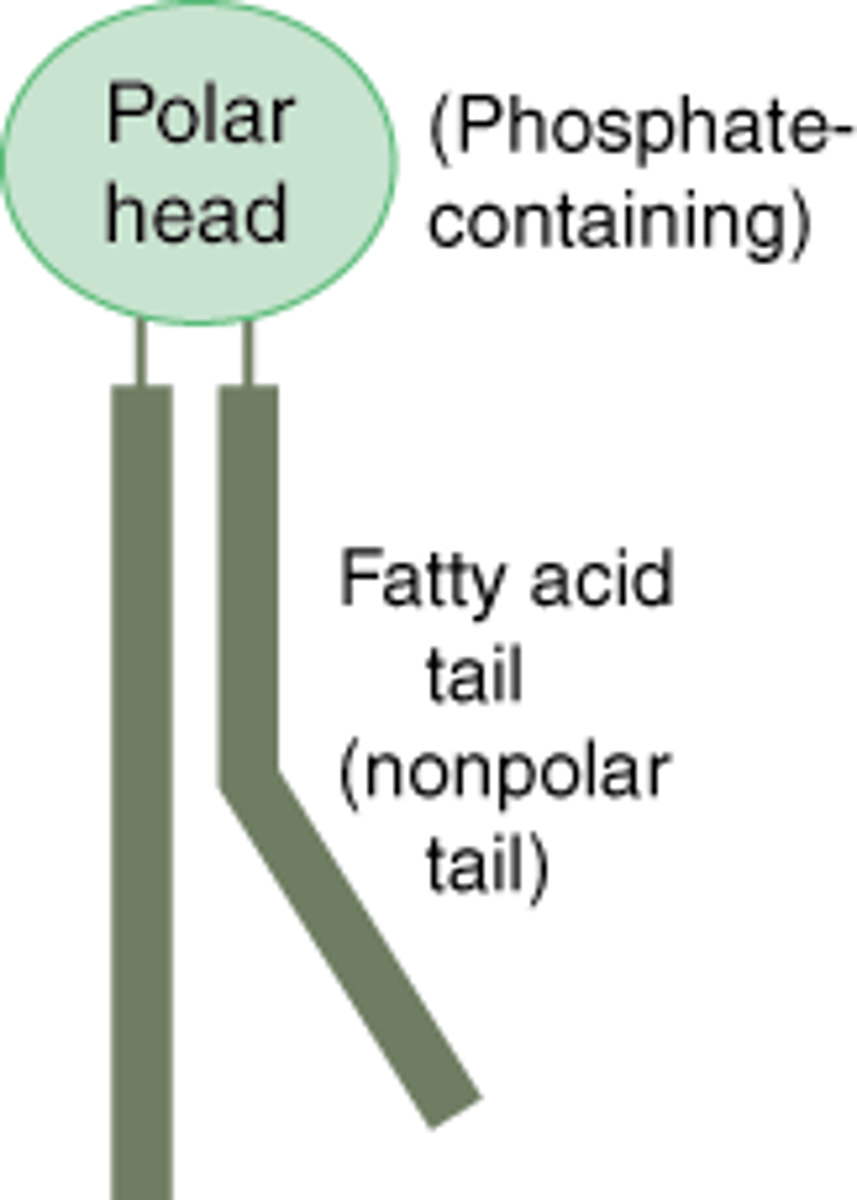
Hydrophobic
Section of a molecule which is repulsed by water.
Emulsion test
Test for lipids. Mix your sample with ethanol and then add water. If a white cloudy emulsion forms then a lipid is present.

Protein
A polymer which is made up of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. May also contain prosthetic groups as part of its quaternary structure.
Amino acid
A monomer which makes up proteins. Has a central carbon atom which is bonded to: a carboxylic acid group, an amino group, a hydrogen atom and a R group.
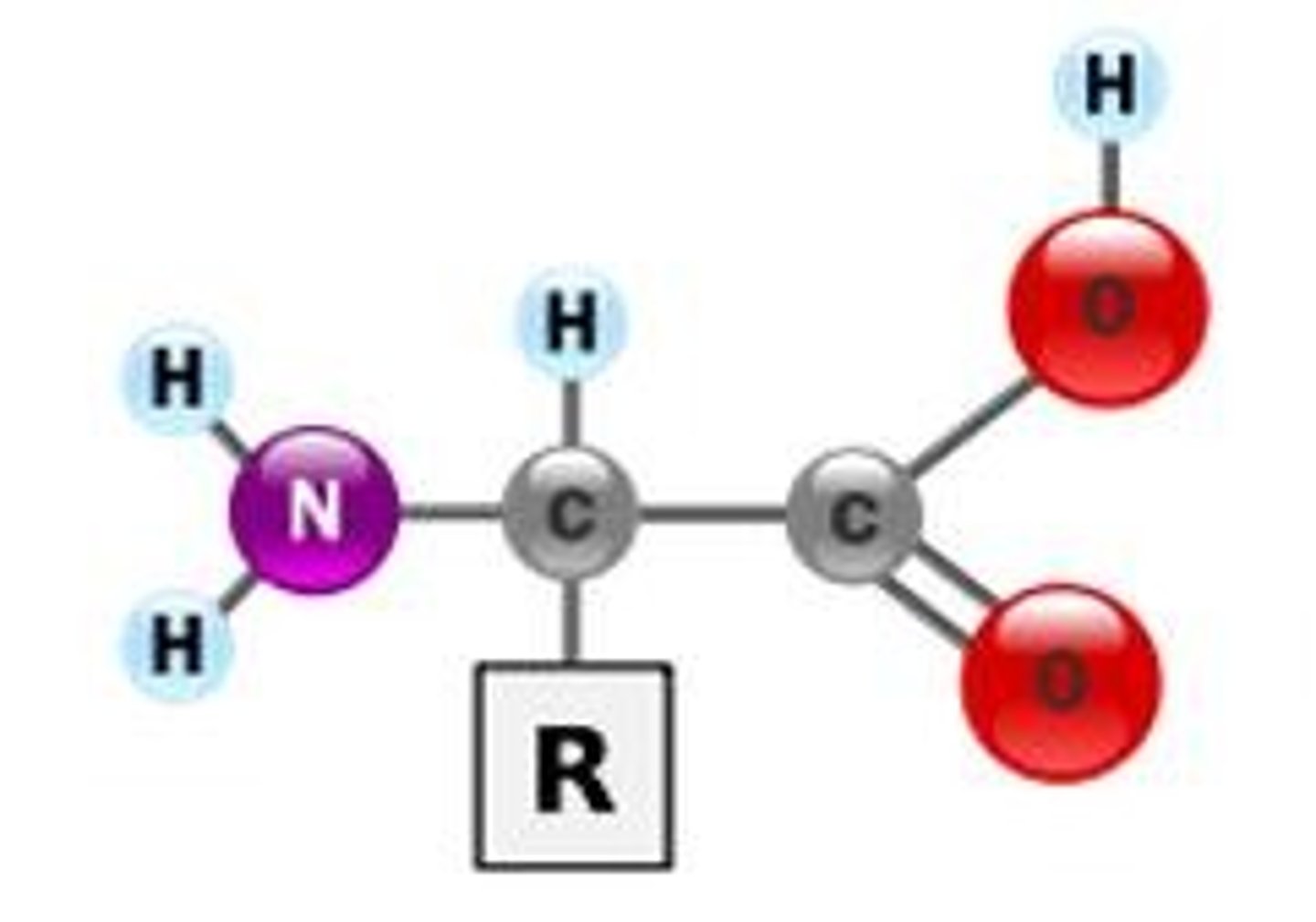
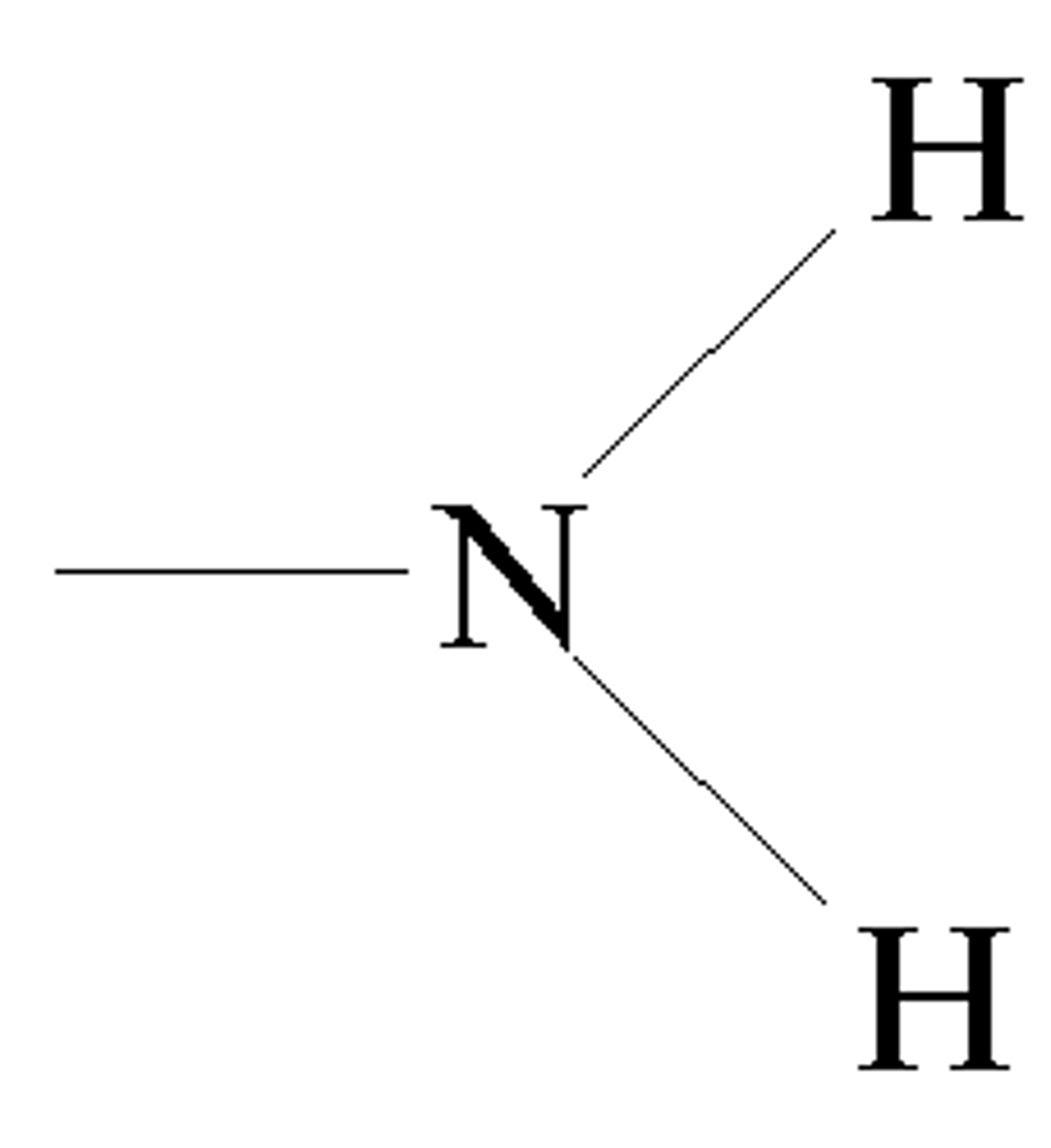
Amino group
The -NH2 group of an amino acid.
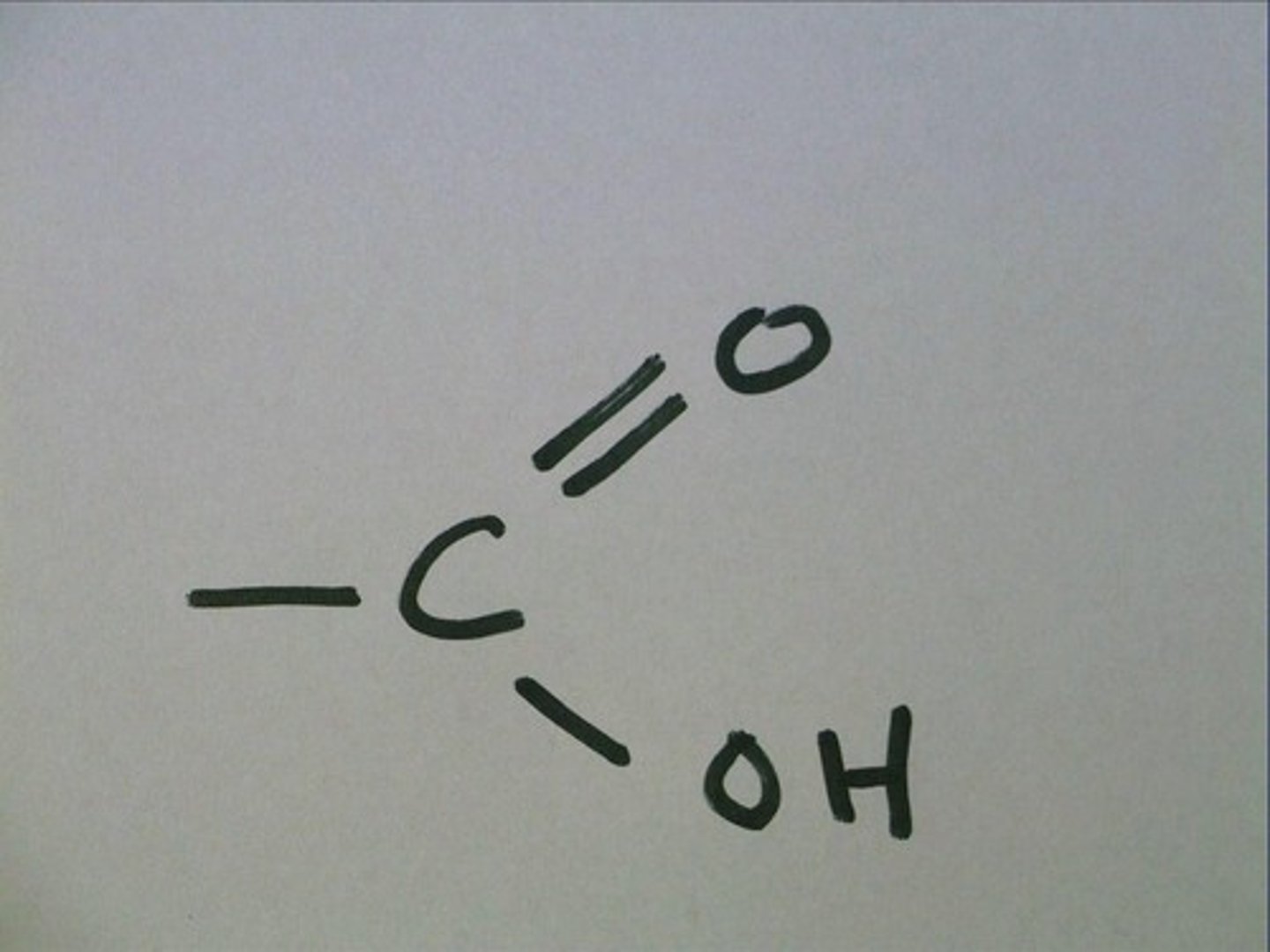
Carboxyl group
The -COOH group of an amino acid.
R group
Each of the 20 amino acids has a different R group - determines the bonding that the amino acid can carry out.
Peptide bond
The type of bond that is formed between two amino acids.
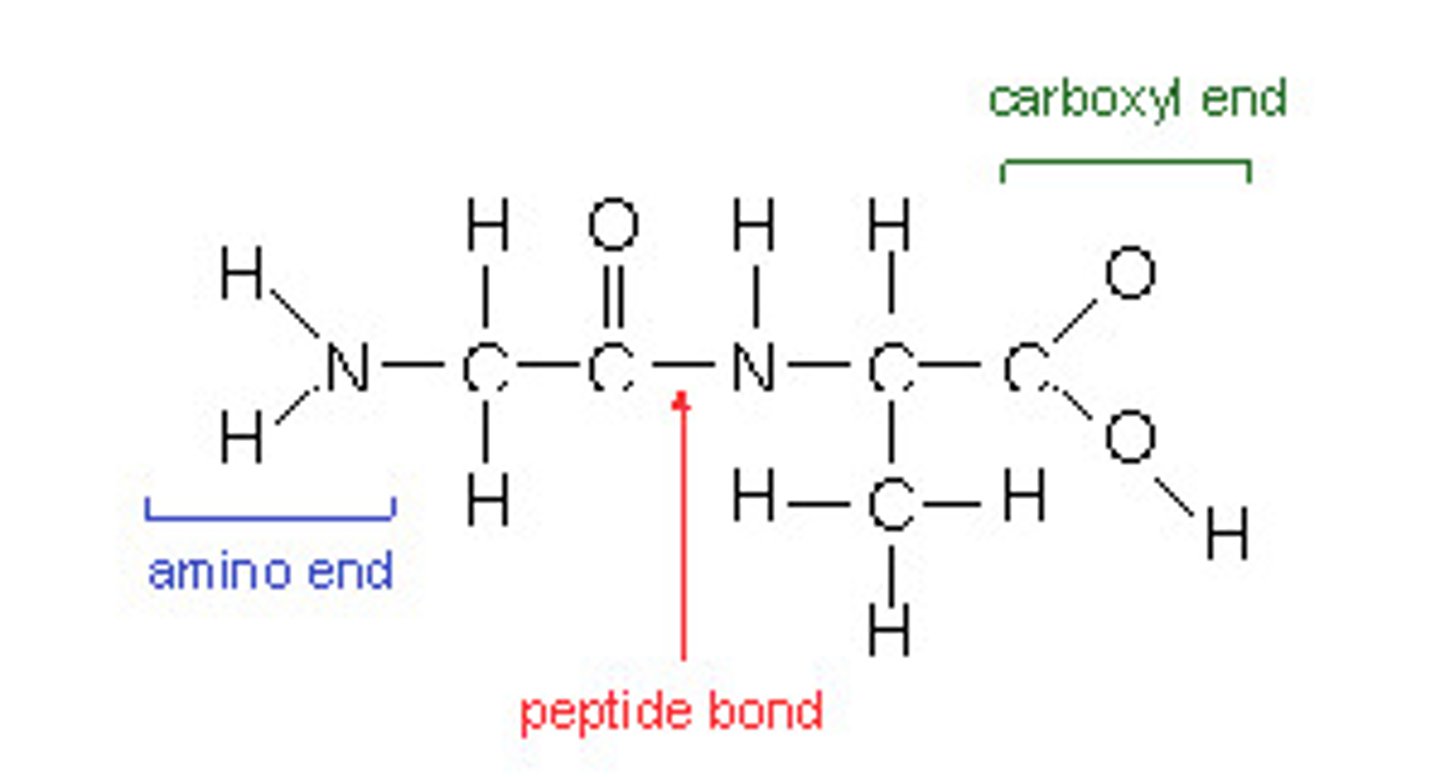
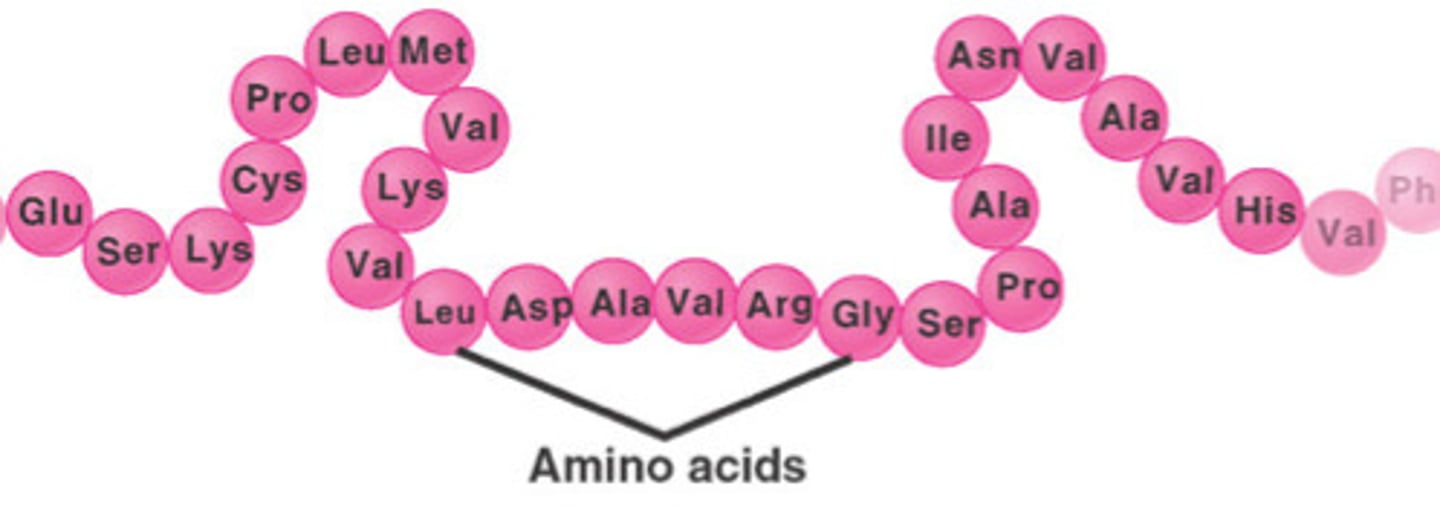
Polypeptide
Many amino acids joined together by peptide bonds.
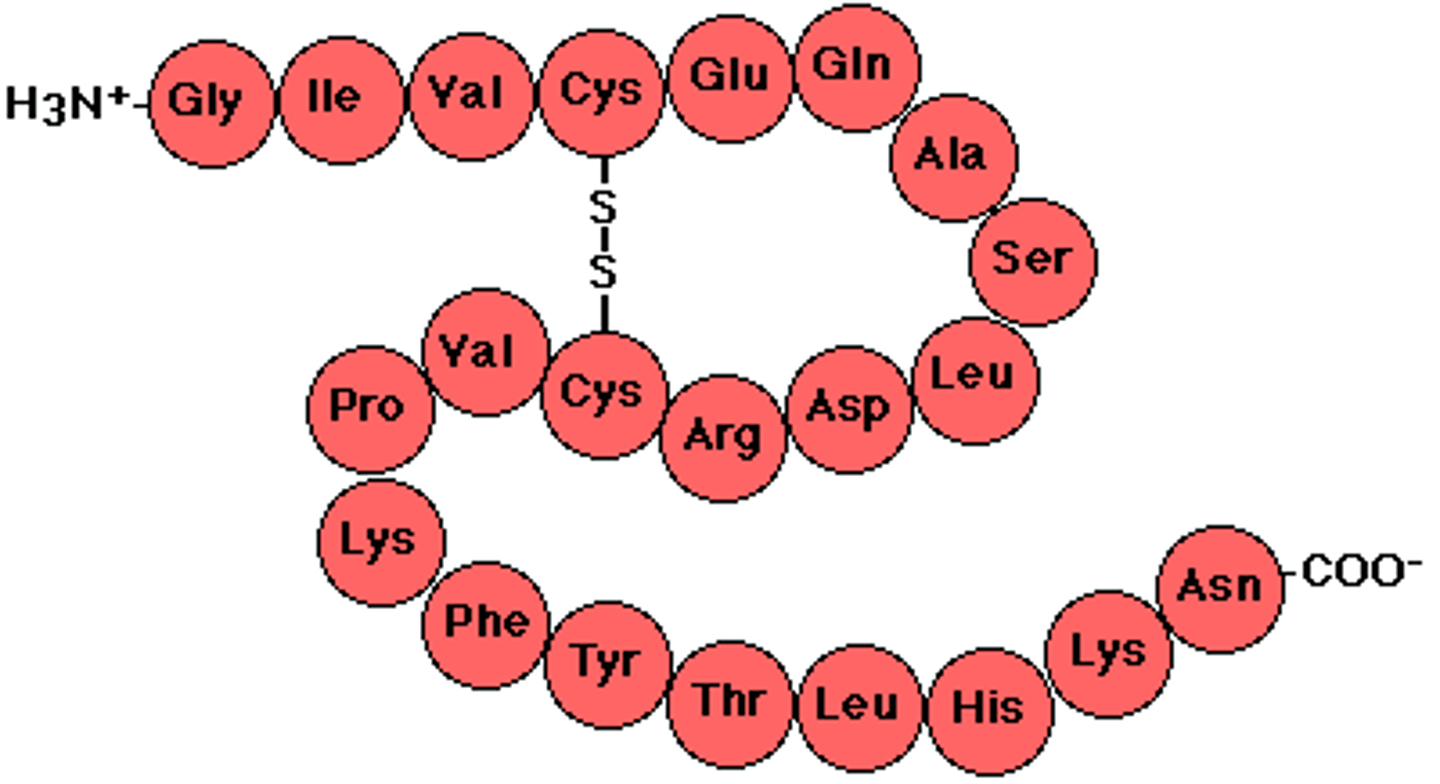
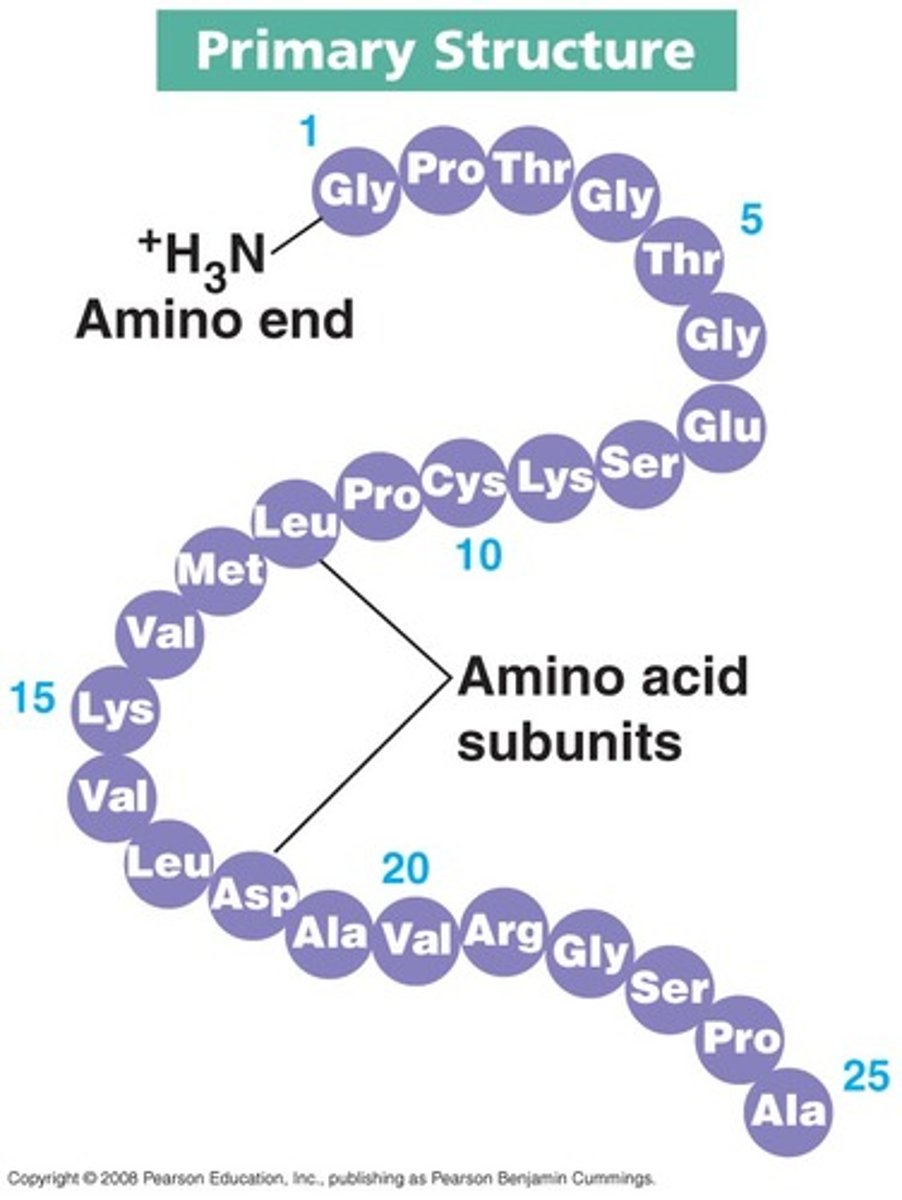
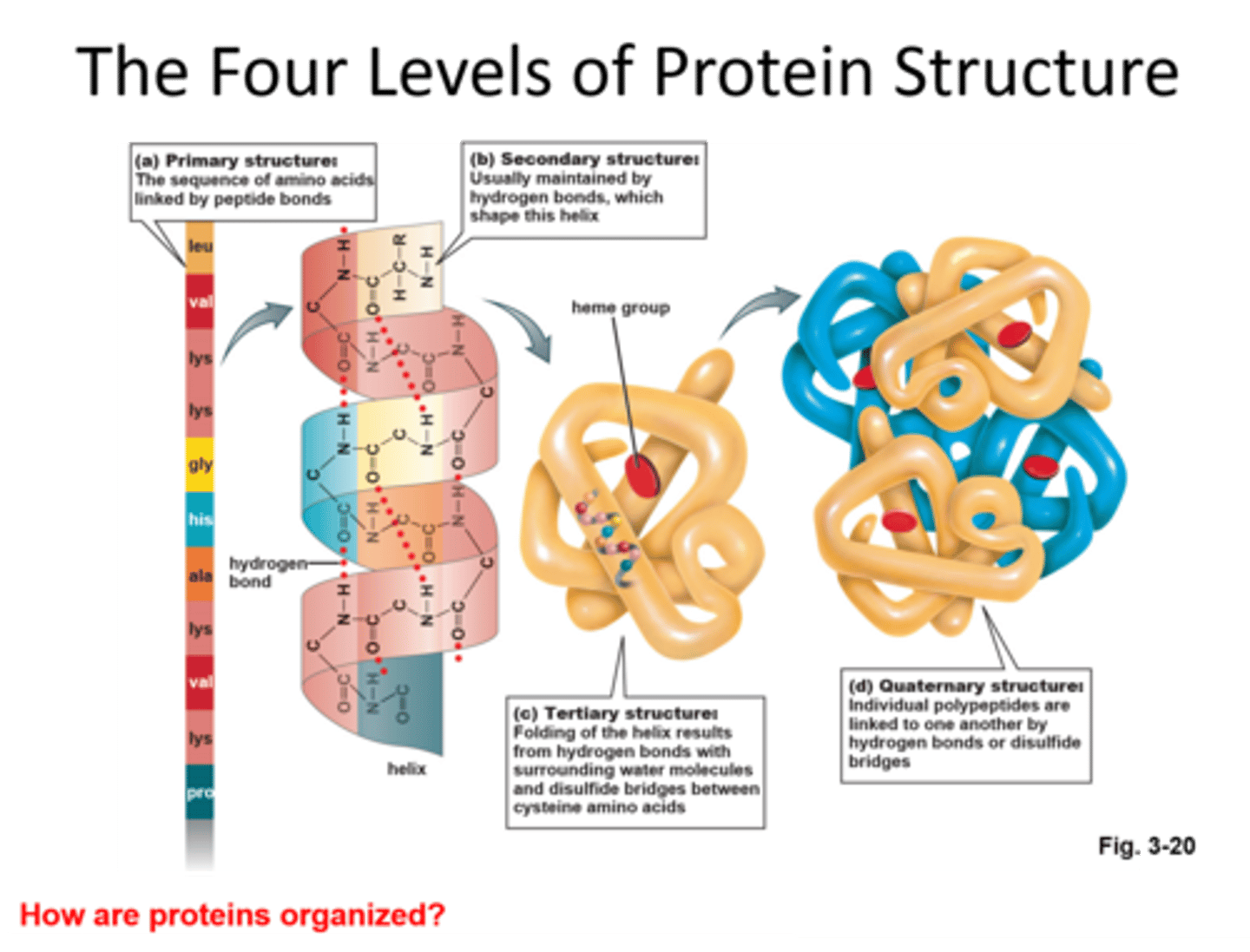
Primary protein structure
The sequence of amino acids that makes up the polypeptides of a protein.
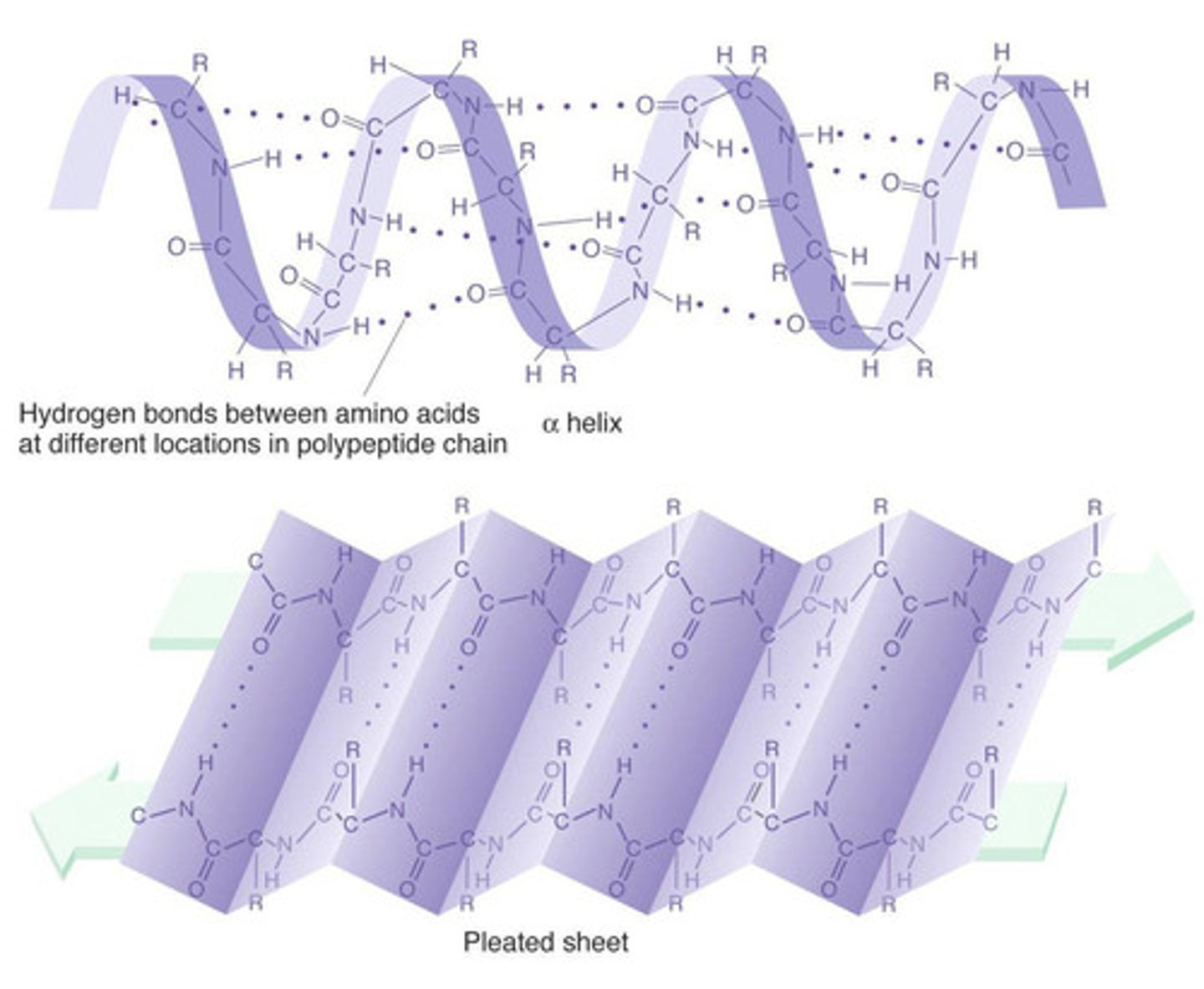
Secondary protein structure
The way in which the chain of amino acids of the polypeptides of a protein is folded. This occurs due to the formation of Hydrogen bonds and can form an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet.
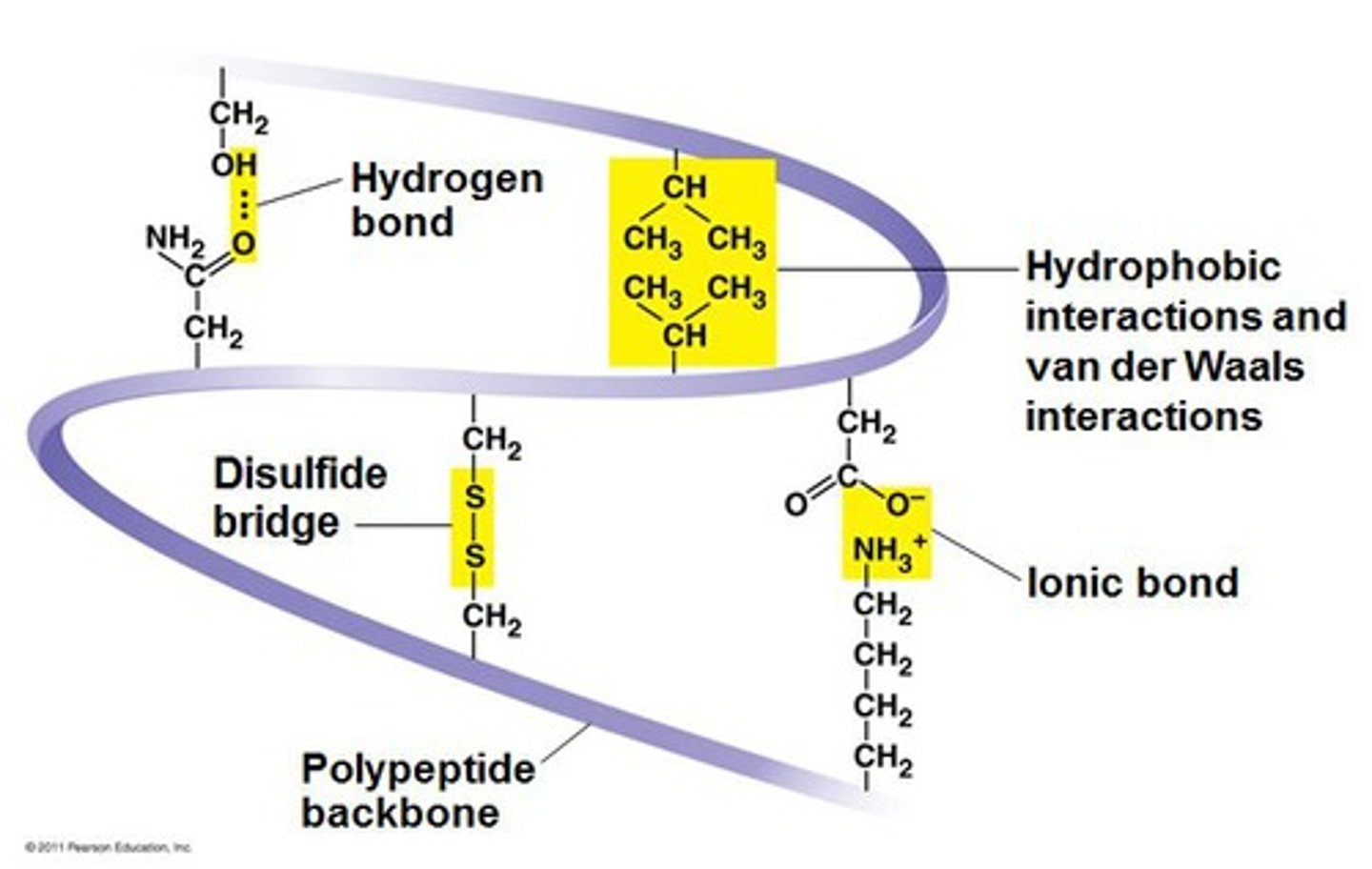
Tertiary protein structure
The folding of a whole polypeptide chain in a precise way, as determined by the R groups of the amino acids of which it is composed. Formed by more H bonds, Ionic bonds, Disulfide bonds and Hydrophobic interactions.
Disulphide bridge
Bond formed between Sulphur atoms in R groups of amino acids.
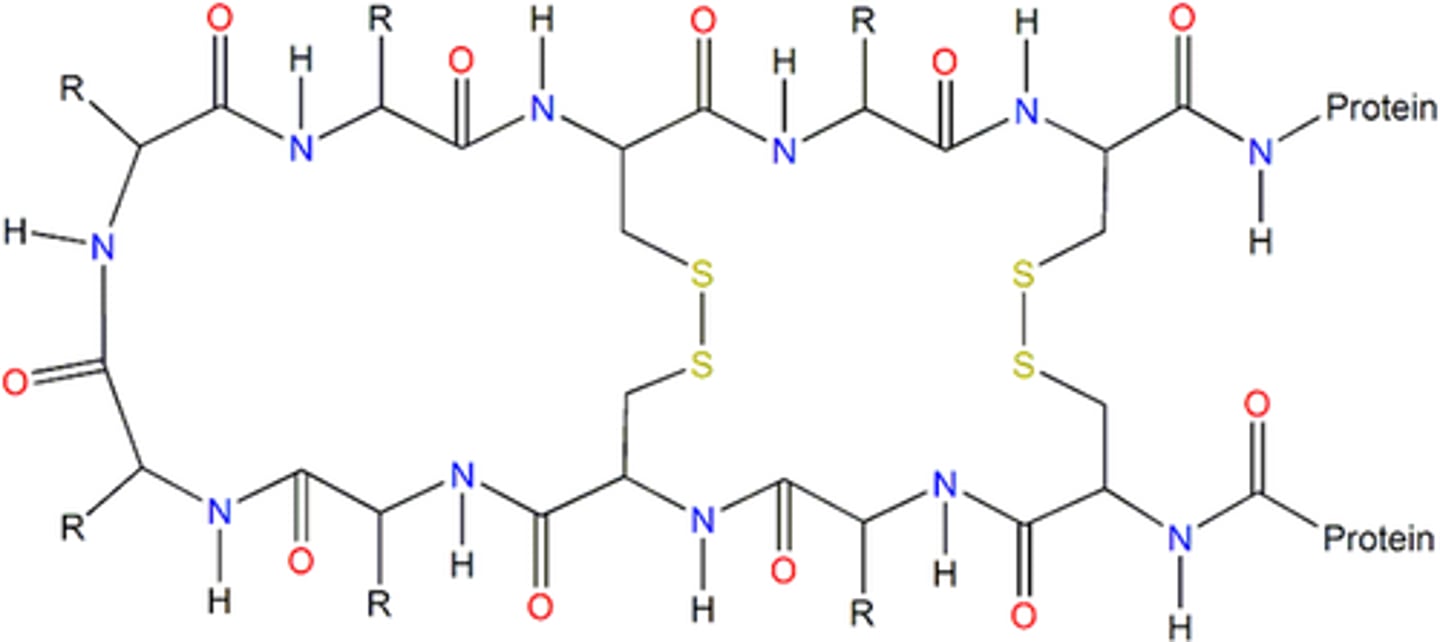
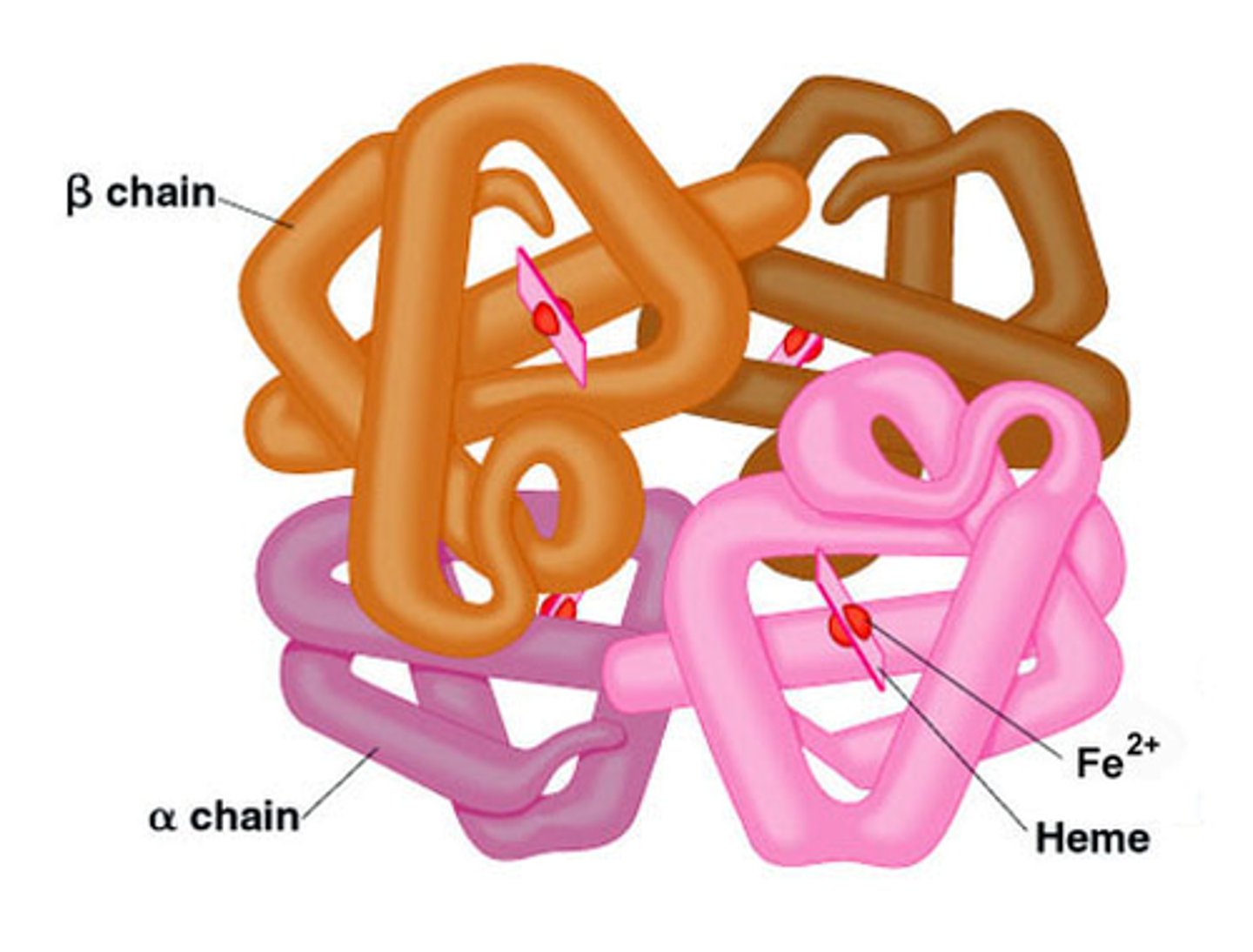
Quarternary protein structure
More than one polypeptide chain linked together, and sometimes associated with prosthetic groups (non-protein groups) to form a protein e.g. Iron in Haemoglobin.
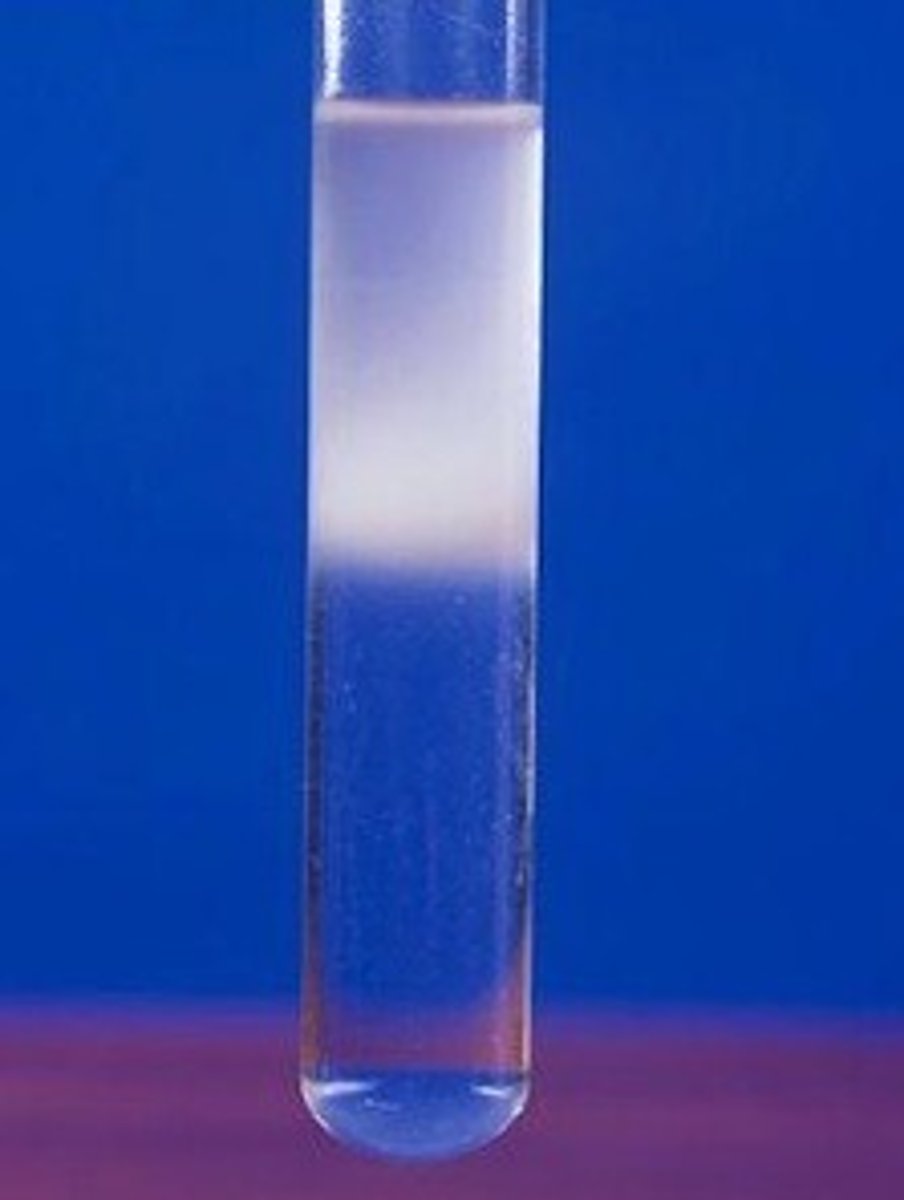
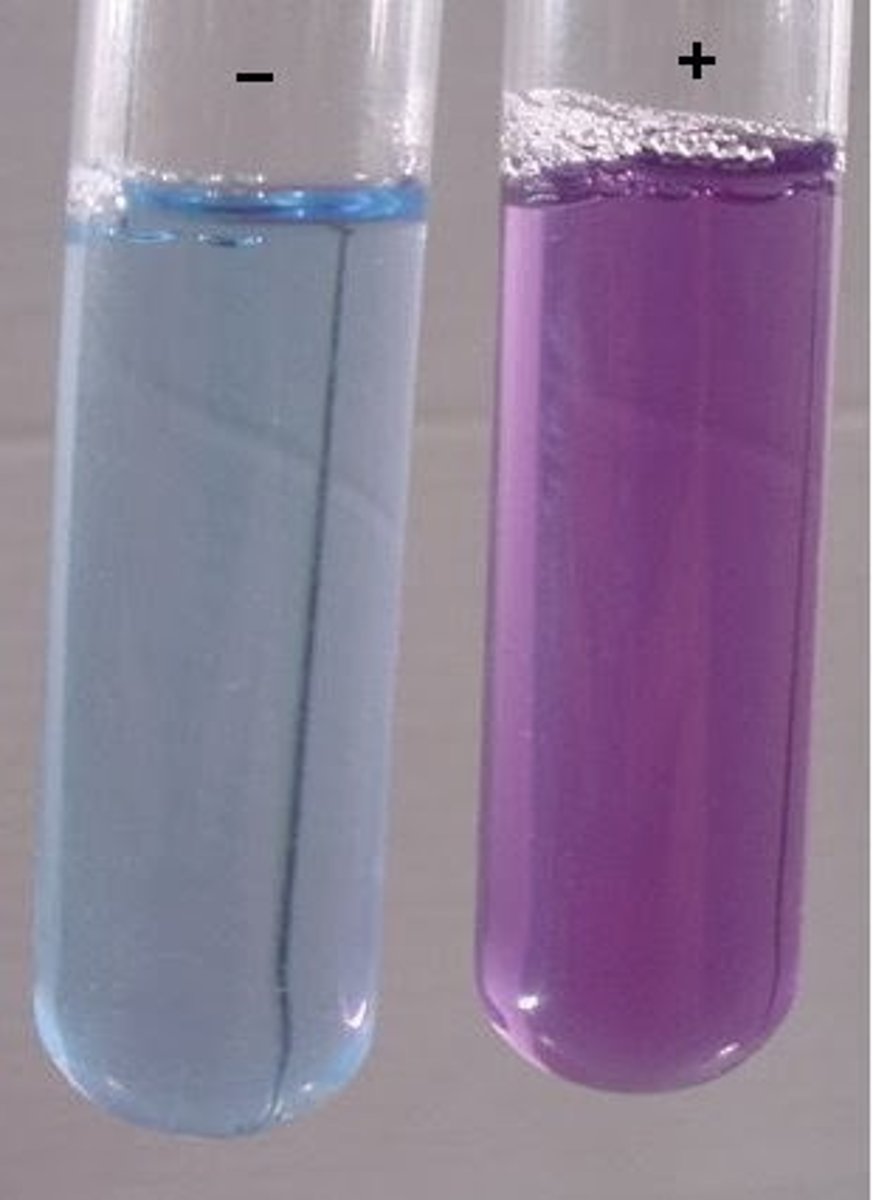
Biuret test
A simple biochemical reaction to detect the presence of protein, if the Biuret's solution turns purple then protein is present.

Latent heat of vaporisation
The heat energy needed to change the substance from a liquid at its boiling point into gas at the same temperature.
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same type. Hydrogen bonds form between water molecules. It is important in the movement of water up a plant.
Surface tension
The tension of the surface film of a liquid caused by the attraction of the particles in the surface layer by the bulk of the liquid.

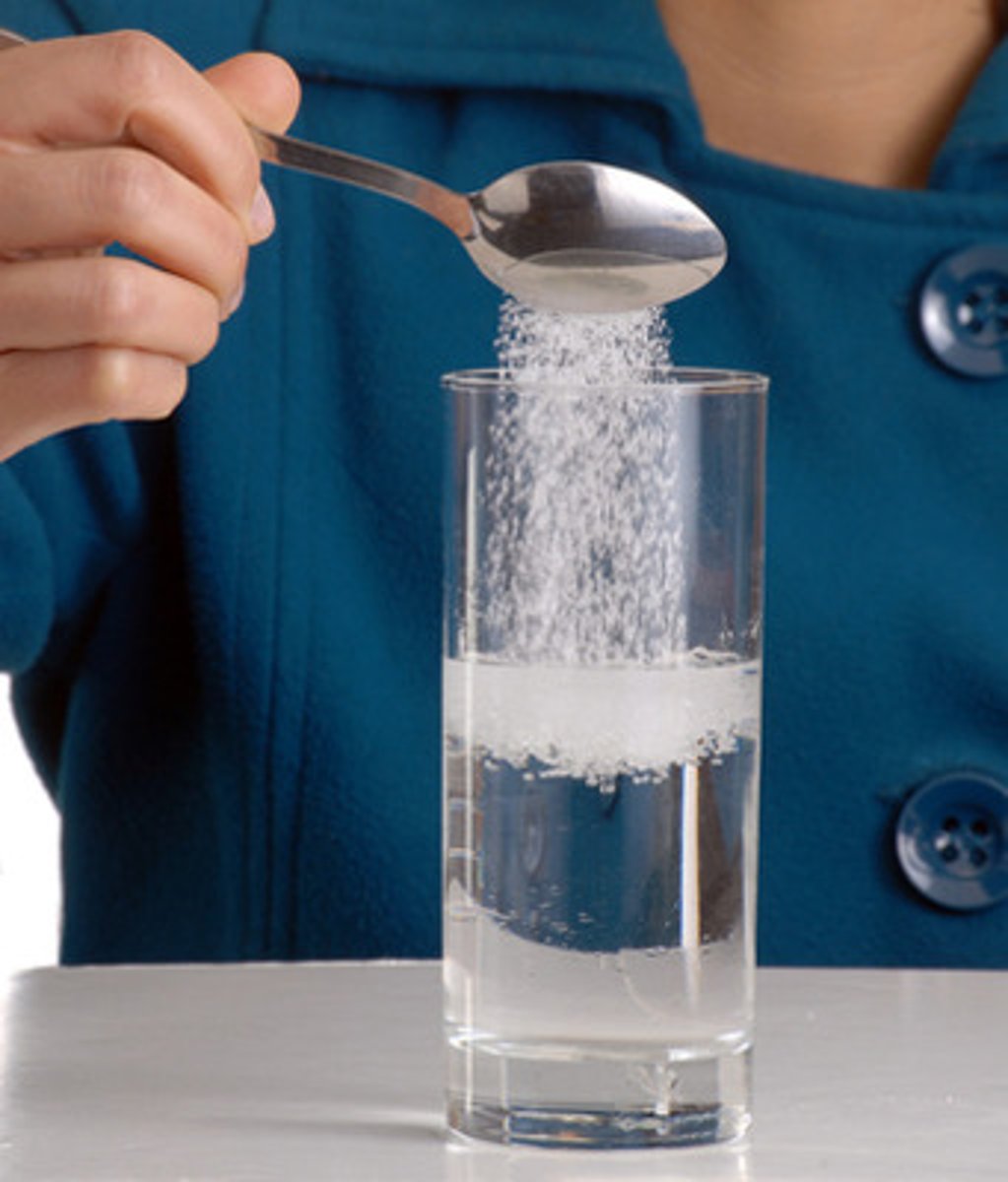
Solvent
The liquid in which a solute is dissolved to form a solution.

Inorganic ions
Formed when an element or compound, that does not contain carbon, gains or looses electrons to become negatively or positively charged, for example: hydrogen ions, phosphate ions, iron ions and sodium ions.
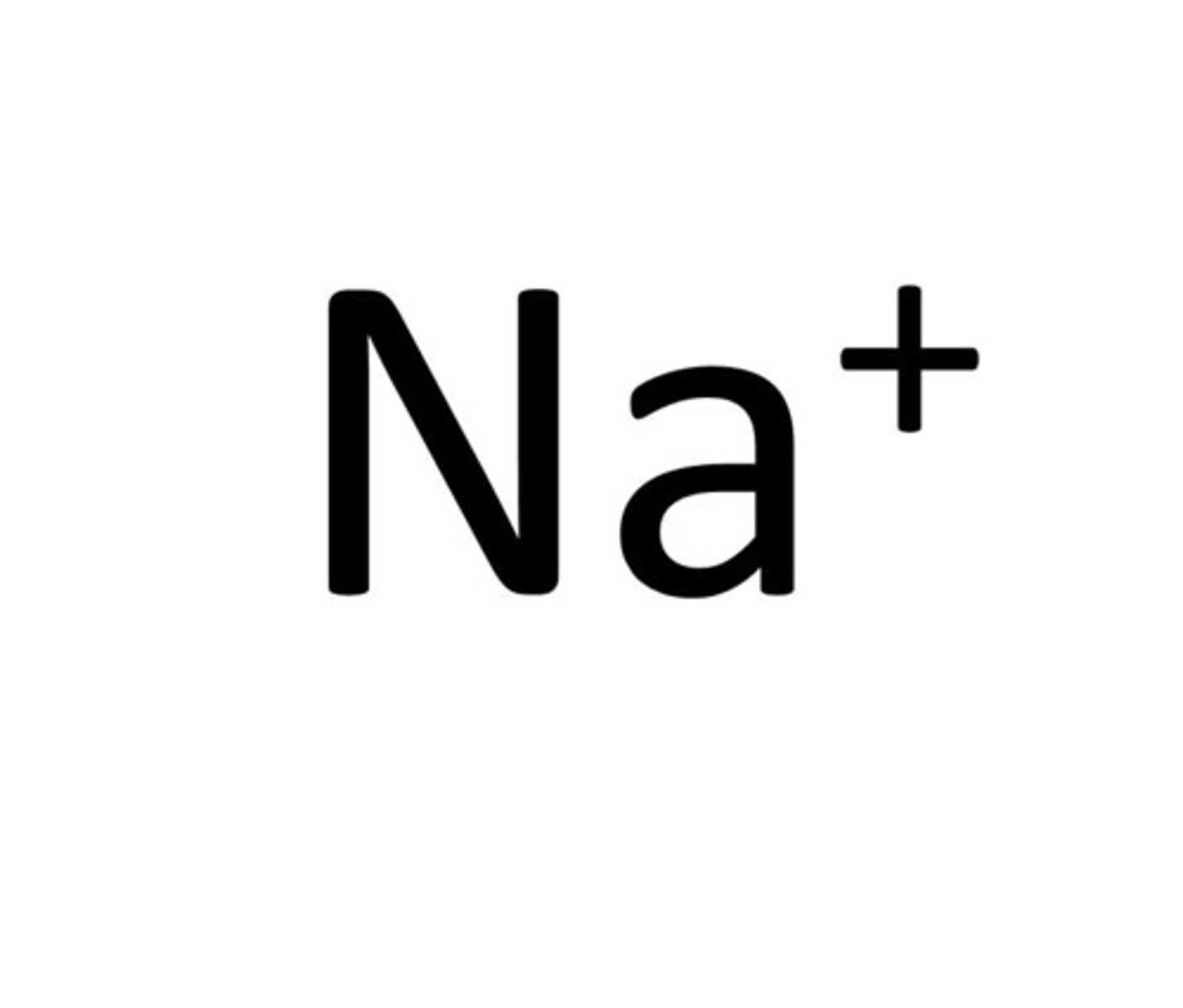
Transparent
A material that allows light to pass through so that objects behind can be distinctly seen. This allows light to pass through water, so that plants can photosynthesise.
Inorganic Ions
Important in cellular processes e.g: muscle contraction, nervous coordination and osmotic pressure in cells and blood. For example potassium ions, sodium ions, magnesium ions
Macronutrients
Needed in small concentrations. Four of these include - Magnesium ions, Iron ions, Phosphate ions, Calcium ions.
Micronutrients
Needed in small concentrations
Magnesium Ion (Macronutrients)
Necessary for chlorophyll, and thus needed for photosynthesis. Lack of magnesium causes yellow leaves, as the plant cannot make chlorophyll. This is known as Chlorosis. Growth is stunted, due to lack of glucose production. Animals need magnesium for bones.
Iron Ion (Macronutrients)
Necessary for Haemoglobin, which transports oxygen in red blood cells. Lack of Iron in the diet causes anaemia.
Phosphate ion (Macronutrients)
Used to make nucleotides including ATP. These are also found in phospholipids, which are a molecule that makes up membranes. Also important constituent in bones and teeth.
Calcium Ions (Macronutrients)
Important mineral in bones, teeth and a component in making cell walls. Provides strength.
High specific heat capacity
A large amount of energy is needed to raise the temperature of water, due many hydrogen bonds between water molecules restricting their movement. This prevents large fluctuations in water temperature.
Pentose
A sugar with 5 carbons
Triose
sugar with 3 carbons
isomer
Alpha and Beta glucose. Resulting in formation of structurally different molecules. Such as Starch (alpha) and Cellulose (beta)
Uses of triglycerides
Energy reserve, thermal insulation, protection of organs, metabolic water released when fat is oxidised
Uses of waxes
Waterproofing in terrestrial organisms, plants and insects have a hydrophobic cuticle.
Implications of saturated fats
High levels of Low Density Lipoproteins. this can lead to fatty material called atheroma being deposited in her arteries. This build up can lead to a heart attack.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
Carry harmful fats away to the liver for disposal
Atherosclerosis
Condition in which fatty deposits called plaque build up on the inner walls of the arteries, due to a high level of HDLs