Peripheral Nervous System
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
The peripheral nervous system
the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord
PNS relation with CNS
nerves allow the CNS to receive information and initiate action
Attach to the brain
cranial nerves
numbered from I to XII
cranial nerves
Where do cranial nerves I and II attach to
the forebrain
Where do all other cranial nerves attach
the brain stem
cranial nerves primarily serve what 2 structures
head and neck structures
Vagus nerve X
the only cranial nerve that extends into the abdomen
The Olfactory nerve function
sensory
Olfaction (smell)
Anosmia
the lost of smell (partial or permanent)
The sensory nerves of smell
olfactory nerves cranial I
CN II: the optic nerve function
sensory
vision
Anopsia in optic nerves
vision loss or defect in the vision field
the sensory nerve of vision
Optic nerves cranial II
CN III: the oculomotor nerve function
motor function
How many extra ocular eye muscles does the oculomotor nerve control
4 of the 6
oculomotor nerve responsibility
moving the eye superiorly, inferiorly, medially
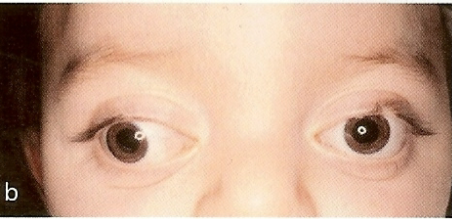
What is happening in the picture?
external strabismus
the two extraocular eye muscles not served by CN III are unopposed and move the eye laterally + inferiorly. The patient experiences double vision
innervates 4 of the 6 extrinsic eye muscles
Oculomotor nerves cranial III
the superior oblique muscle
moves eye inferolaterally (below and to one side)
what is happening in this picture?
trochlear nerve palsy
inferior oblique muscle is unopposed and moves the eye superomedially (up and towards the middle). The patient experiences double vision
innervates the superior oblique muscle (an extrinsic eye muscle)
trochlear nerves of the IV cranial nerve
CN V: the trigeminal nerve function
mixed (sensory and motor) function in 3 branches
Ophthalmic (v1)
sensory from the forehead, eyelids, and nose
Maxillary (V2)
sensory from lower eyelid, upper lip, and cheek
Mandibular (V3)
sensory to the lower jaw; motor to the muscles of mastication
CN V: the trigeminal nerve example
dental anesthesia
CN VI: the abducens nerve function
motor funcition
How many extra-ocular eye muscles does the abducens nerve control?
1 of the 6
Lateral rectus muscle in the abducens nerve function
moves eye laterally
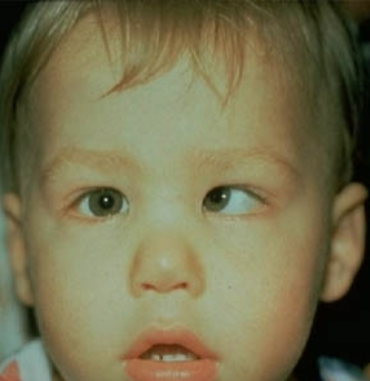
What is happening in this picture?
internal strabismus
medial rectus muscle is unopposed and moves the eye medially. The patient experiences double vision.
Abducts the eyeball—innervates the lateral rectus muscle
VI (#6) abducen nerves
CN VII: the facial nerve function
mixed (sensory and motor) function
Sensory in the VII facial nerve
gustation (taste) from anterior 2/3 of tongue
Motor in the VII facial nerve
controls muscles of the face (facial expression)
innervates muscles of facial expression+taste on anterior (2/3 of the tongue)
CN VII facial nerves
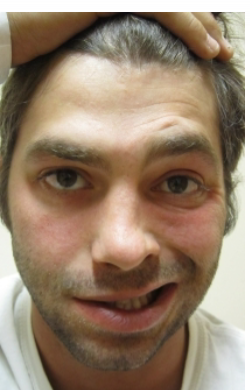
What is happening in this picture?
CN VII: the facial nerve: bell’s palsy
CN VIII: the vestibulocochlear nerve function
sensory function
two types of sensory function in CN VIII: the vestibulocochlear nerve
Audition (hearing)
equilibrium (balance)
Example of CN VIII: the vestibulocochlear nerve
nerve deafness and vertigo
if the cochlear branch is damaged=
nerve deafness can occur
if the vestibular branch is damaged=
vertigo (dizziness, loss of balance, nausea, rapid eye movement) can occur
Sensory nerve of hearing and balance
CN VIII: the vestibulocochlear nerve
CN IX: the glossopharyngeal nerve function
mixed (sensory and motor) function
Sensory function in CN IX: the glossopharyngeal nerve
gustation (taste) from posterior 1/3 of tongue
Motor function in CN IX: the glossopharyngeal nerve
pharyngeal muscles (swallowing)
motor control of pharynx elevation (swallow reflex) + taste on posterior 1/3 of tongue
CN IX: the glossopharyngeal nerve
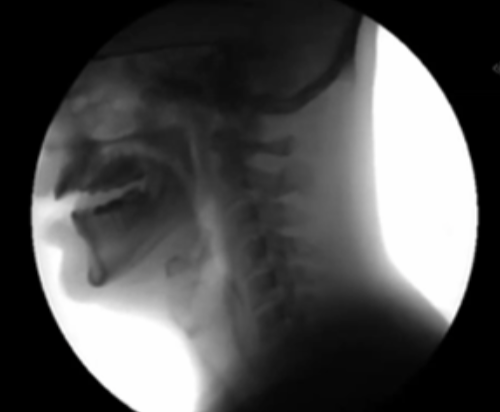
What is happening in this picture?
impaired swallowing (IX: the glossopharyngeal nerve)
another example of the glossopharyngeal nerve
loss of taste (ageusia) in posterior tongue
CN X: the Vagus nerve sensory function
sensation from organs (visceral sensory)
CN X: the Vagus nerve motor function
primary parasympathetic (“rest and digest”) nerve to the internal organs (visceral motor division)
Example of CN X: the Vagus nerve
death
complete damage of the vagus nerve is incompatible with life
Slight damage symptoms of the Vagus nerve sensory function
impairments to digestion or leading to hoarseness + loss of voice
A mixed sensory and motor nerve
X Vagus Nerves
“Wanders” into thorax and abdomen
X Vagus nerves
Parasympathetic innervation of organs
X Vagus nerves
CN XI: the accessory nerve function
motor function
What 2 muscles does the XI: the accessory nerve control
sternocleidomastoid muscle
trapezius muscle

what is happening in this picture?
damage of XI: the accessory nerve
accessory nerve damage
CN XII: the hypoglossal nerve function
motor function
controls tongue movement
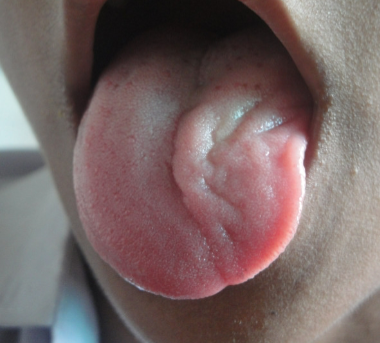
What is happening in this picture?
Tongue deviation of the hypoglossal nerve
unilateral nerve damage leads to tongue deviation
bilateral damage of the tongue leads to what?
tongue paralysis
Runs inferior to the tongue
XII hypoglossal nerve
innervates the tongue muscles
XII hypoglossal nerve
how many pairs of spinal nerves and what do they contain?
31 pairs; contain thousands of nerve fibers
Connect to the spinal cord
spinal nerves
named for point of issue from the spinal cord
spinal nerves
C1-C8
8 pairs of cervical nerves
T1-T12
12 pairs of thoracic nerves
L1-L5
5 pairs of lumbar nerves
S1-S5
5 pairs of sacral nerves
CO1
1 pair of coccygeal nerves