Neurological System
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Year 2 Cycle 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
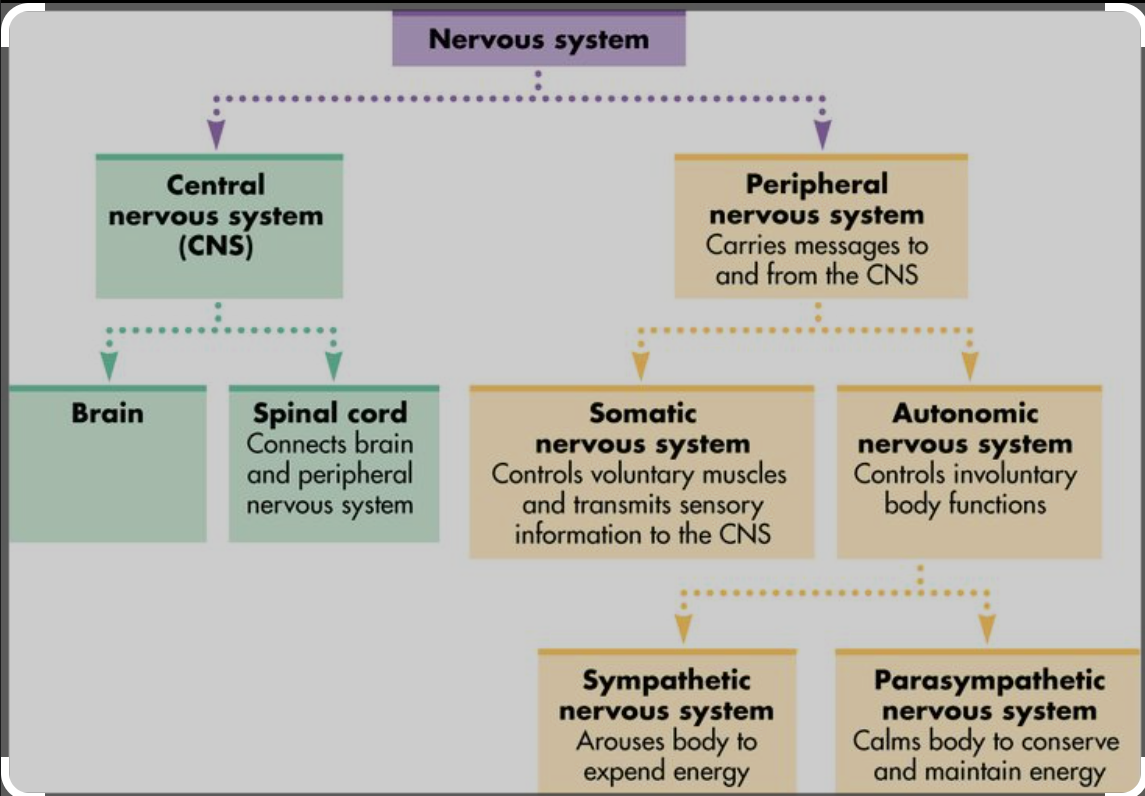
What is the organisation of the Nervous system?
see image
What are meninges?
Three protective layers that surround the bone that encases the brain and spinal cord
What is grey matter?
It is principally formed of cell bodies and unmyelinated interneurons, forms inner H shaped core
What is white matter?
Principally myelinated axons, contains ascending and descending tracts
What is the function of the Medulla Oblongata?
It is responsible for involuntary functions like swallowing, breathing, coughing, sneezing and heart rate
What is the function of the Cerebellum?
It coordinates voluntary movements and helps maintain balance and posture, sense of equilibrium
What is the function of the Cerebrum?
Largest part of the brain divided into 4 parts:
Frontal lobe: Responsible for planning, reasoning, problem solving and voluntary movement
Parietal lobe: Responsible for sensory information e.g. pain, touch
Temporal lobe: Responsible for auditory and memory processing
Occipital lobe: Responsible for visual processing
What is the function of the Basal Ganglia?
Part of the telencephalon, involved in voluntary motor control, procedural learning and habitual behaviours
What is the function of the limbic system?
Behavioural and emotional responses?
What is the function of the primary motor cortex?
Frontal lobes specialised for control of movement
What is the function of the primary somatic cortex?
Posterior lobes specialised for perception, receives information (pain, touch, pressure, temperature)
What is the function of the Thalamus?
Acts as a relay station for sensory information to the cerebral cortex (except smell)
What is the function of the Hypothalamus?
Regulates body temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep and the release of hormones from the pituitary gland
What are some examples of small molecule transmitters in the CNS?
Monoamines, acetylcholine, amino acids
What is an example of a large molecule transmitters in the CNS?
Neuropeptides
What are the effects of acetylcholine both peripherally and centrally?
Excitatory on skeletal muscle, inhibitory on cardiac muscle
Opposing effects due to receptor subtypes: nicotinic receptors found on muscle fibres, muscarinic receptors found peripherally and in CNS
Name a subtype of Monoamines, give examples and state and what they are produced from?
Catecholamines
Adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine
Produced from tyrosine
Name another subtype of Monoamines and give examples
Indolamines
Melatonin, 5HT
Which nervous systems do adrenaline and noradrenaline work in and what are their roles?
Both peripheral and CNS
Adrenaline in the CNS has minor importance but helps your brain stay alert and focused, it kicks the body into action when needed in the PNS
Noradrenergic neurones in the brain primarily involved in control of wakefulness and alertness
Which nervous system is Dopamine in and why is it important?
It is an important CNS neurotransmitter
It controls movement, attention and learning
Degeneration of dopaminergic neurones of nigrostriatal tract leads to Parkinsonism
D2 receptors implicated in schizophrenia
Where is Serotonin found and what its role?
It regulates mood, there are many 5-HT subtypes and 5-HT2 is exclusively found postsynaptically
What are some Amino acid transmitters?
Glutamic acid, GABA, Glycine. These are the most common CNS transmitters
What is the role and importance of Glutamic acid?
Its role is in synaptic plasticity and has a range of excitatory effects. Its linked to inhibition of cAMP and has three receptor subtypes, based on affinity of binding of agonists: (ion channel receptors)
NMDA
AMPA
Kainste
What are NMDA receptors?
They are ionotropic receptors
Agonist binding causes depolarisation so channels blocked by magnesium ions in resting state are opened so that sodium and potassium ions can enter
Low concentrations of glycine are needed as a co-agonist
What is GABA?
An inhibitory amino acid produced from glutamic acid decarboxylase. Its receptors are associated with Cl- ion channel. GABA mediated effects are throughout spinal cord
GABA is divided into Type A and B, what are the differences?
Type A: Similar structure to nicotinic receptor
binding results in Cl- channel opening
inhibitory influence important in control of neural activity and prevention of seizures
Benzodiazepines and barbiturates bind allosterically to the receptor and augment channel opening
Type B: receptor recognises different agonists/antagonists
GPCR linked to inhibition of cAMP
What is Glycine?
It is an inhibitory transmitter in spinal cord and lower brain, it binds allosterically to glutamate receptor. Its receptor is similar to GABA-A receptor
What do Neuropeptides do?
They bind to receptors in the brain and activate systems associated with analgesia and and experience of pleasure
What are the two types of pain?
Nociceptive (sharp) pain- from pain receptors, carried by myelinated A-delta fibres
Neuropathic (slow) pain- from nerve damage with gradual intensity increase, carried by unmyelniated C fibres
How do local anaesthetics work for pain relief?
They reversibly block the conduction of action potential carried along the nerves
the molecules are more likely to to enter into open NA+ VOCs
they have a lipid-soluble hydrophobic aromatic group and a charged hydrophilic amide group, the bond between these 2 groups determines the class of the drug (amide or ester)
The ester linkage is more easily broken than amide bond so ester drugs are less stable in solution and cannot be stored for as long as amides
What are some side effects of opioid analgesics?
Respiratory depression (due to respiratory centre losing sensitivity to the CO2 in the blood)
Nausea and vomiting (due to stimulation of the chemoreceptor trigger zone)
Pupillary constriction
Constipation
Histamine released resulting in itching, bronchoconstriction, vasodilation and hypotension
Sedation
Euphoria