Ankle and Foot
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
complaint, mechanism, weight bear, description, claudication, neurologic, occupation, recreational, skin temperature, vascular
history should include chief _____, _____ of injury, ability to _____ following injury, pain _____ (cramping/aching may accompany _____, numbness/tingling may indicate _____), _____ and _____ activities, change in _____ (potential _____)
swelling, discoloration, nail, condition, callus, posture, height, alignment, deformities, weight bearing, footwear, wear
observation should include _____, skin _____, _____ and skin _____, _____ formation, foot _____ and arch _____, toe _____ or _____, _____ status, _____ with _____ pattern
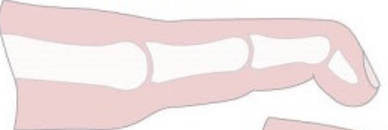
hammer toe
PIP flexion, MTP and DIP hyperextension
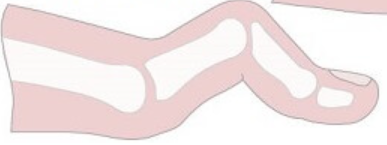
mallet toe
DIP flexion
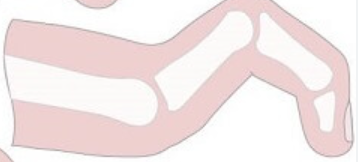
claw toe
PIP and DIP flexion, MTP hyperextension
hallux valgus
proximal phalanx deviates laterally, first metatarsal drifts medially, increased prominence of first metatarsal head
laterally, progressive, deformities, overlapping
hallux valgus will cause WB to shift _____, may contribute to _____ gait deviations and further toe _____ (_____ toes)
morton’s toe
longer second toe
metatarsus adductus
metatarsal bones deviated inward
dynamic, double, single, squats, gait, jumping, landing, running
movement analysis allows _____ assessment, may include _____/_____ leg _____, strength/ROM, _____ examination, _____ and _____ mechanics, and _____
lateral ankle sprain
most common foot/ankle injury, most common sports injury
inversion, plantarflexion, anterior tibiofibular ligament, plantarflexion, inversion, calcaneofibular ligament, dorsiflexion, inversion, posterior tibiofibular ligament
lateral ankle sprain MOI is _____ usually with _____, sequence of injury is _____ (_____ and _____) then _____ (_____ and _____), and _____
bruising, proprioceptive, ROM, impingement, chronic ankle instability, fracture, osteochondral, altered, cartilage, osteoarthritis
lateral ankle sprain secondary complications include bone _____, _____/_____ deficits, ankle _____, _____ (CAI), _____, _____ defect, _____ kinematics causing _____ stress causing _____
lateral ankle sprain, women, dorsiflexion, hip abductor, extensor, asymmetry, functional, court, prophylactic bracing
lateral ankle sprain risk factors include history of _____, more _____, limited _____, decreased _____/_____ strength, _____ or poor performance on _____ outcome measures, participating in _____ sports without _____
grading, extent, number, presentation, functional
no universal _____ system on ankle sprain severity, may be based on _____ of damage to single ligament, _____ of ligaments injured, _____ and _____ impairments
stretched, ATFL, mild, tenderness, limited, no, full, normal, little
West Point ankle sprain grading system grade I is _____ ligament (_____), _____ point _____, _____ dysfunction, _____ laxity, _____ WB, _____ gait, _____ edema
partially torn, ATFL/CFL, diffuse, tenderness, moderate, slight, painful, antalgic, moderate local
West Point ankle sprain grading system grade II is _____ ligament (_____), _____ and point _____, _____ dysfunction, _____ laxity, _____ WB, _____ gait, _____ edema
substantially torn, ATFL/CFL/PTFL, diffuse, tenderness, significant, definite, severe pain, AD, significant diffuse
West Point ankle sprain grading system grade III is _____ ligament (_____), _____ and point _____, _____ dysfunction, _____ laxity, _____ WB, needs _____, _____ edema
trauma, malleolar zone pain, posterior lateral malleolus tenderness, posterior medial malleolus tenderness, inability to weight bear immediately and in ED
ottawa ankle rule radiograph ordered after _____ with _____ and _____/_____/_____
trauma, midfoot zone pain, metatarsal base tenderness, navicular bone tenderness, inability to weight bear immediately and in ED
ottawa foot rule radiograph ordered after _____ with _____ and _____/_____/_____
figure 8 edema measurement, anterior drawer, medial talar tilt, weight bearing lunge
lateral ankle sprain special tests (4)
sensorimotor, ROM, strength, fibularis, reaction time, dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, mobility
lateral ankle sprain presents with _____ and _____ deficits including decreased leg/ankle _____, decreased _____ muscle _____, decreased _____/_____, increased forefoot and midfoot _____
movement, ankle, knee, hip, both, balance, gait, jumping
lateral ankle sprain presents with altered _____ strategies, in _____/_____/_____, in _____ extremities, occur during _____/_____/_____
pain, edema, POLICE, external support, gait, sagittal, AROM, pain free, isometrics, low, joint mobilizations, estim
lateral ankle sprain acute phase protection interventions should control _____ and _____, use _____, _____ as needed, _____ training, gentle _____ plane _____ in _____ range, gentle _____, _____ grade _____, _____ as needed
brace, gait, mobilizations, resistance, intensity
lateral ankle sprain subacute phase controlled motion interventions include _____ to provide stability, _____ training, joint _____, progress therex _____ and _____
strengthening, neuro reed, external support, functional
lateral ankle sprain chronic phase return to function interventions should progress _____ and _____, no _____ during training, use _____ movement patterns
running, surface, plyometrics, sport specific, prophylactic bracing
lateral ankle sprain return to sport interventions include _____ progression considering _____, _____, _____ training, use _____ and appropriate footwear
chronic ankle instability
long term complication of lateral ankle sprain
one year, giving way, pain, weakness, ROM, self reported function, ankle sprains
CAI symptoms persist for more than _____ after initial injury, repetitive episodes of ankle _____, ongoing _____/_____/reduced _____, diminished _____, recurrent _____
single leg drop landing, double leg drop landing to vertical jump, dynamic control, SEBT, ADL
predictors of CAI is 2 weeks is inability to complete _____ and _____, 6 months poor _____ of hip/knee/ankle with _____ in posteromedial and posterolateral directions and lower scores on _____ subscale of FAAM
primary tissue injury, pathomechanical, sensory perceptual, motor behavioral, personal, environmental, outcome, CAI, coper
components of CAI include _____ (ankle sprain), _____ impairments, _____ impairments, _____ impairments, _____ and _____ factors, leading to continuum of _____ from _____ to _____
both, muscle activation, strength, force, proprioception, dorsiflexion, motion, spinal, reflex, supraspinal corticomotor, movement
CAI sensorimotor findings in _____ limbs include abnormal timing of _____, decreased _____, impaired _____ and _____, decreased ankle _____, increased subtalar/midfoot _____, impaired _____ level control and _____ inhibition, abnormalities of _____, affects _____ system
strength, dynamic balance, postural stability, joint mobilizations, dry needling, fibularis
CAI interventions include neuro reed and therex to improve _____/_____/_____, manual therapy including _____, and _____ to _____ muscle group
5, 24, 11
CAI patient report outcome cut offs include ankle instability instrument yes to at least _____ questions, cumberland ankle instability tool score equal to of less than _____, identification of functional ankle instability score of equal to or greater than _____
hop, lift, balance, sls, posteromedial, SEBT, barefoot, correlate
CAI functional outcome measures include _____ tests, foot _____/time in _____/_____ of BESS, _____ of _____, all tests performed _____, _____ with other symptoms
high ankle sprain/syndesmotic injury
injury to distal tibiofibular joint or syndesmosis
interosseous membrane, anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament, fracture, widening
high ankle sprain injury may include _____ and _____, may have concurrent _____, excessive _____ between tibia and fibula during dorsiflexion
external rotation, dorsiflexion
high ankle sprain MOI is excessive _____ with possible _____
anterolateral pain, AITFL, weight bear, swelling, bruising
high ankle sprain presents with _____ proximal to _____, difficulty/inability to _____, less _____ and _____ than lateral ankle sprain
dorsiflexion external rotation, syndesmosis squeeze
high ankle sprain special tests (2)
NWB, pain free, brace, external rotation, lateral ankle sprain, delayed
high ankle sprain interventions include _____ in cast for 2-3 weeks, delayed WB until _____, use _____ that limits _____, similar treatment to _____ but _____
deltoid ligament, rare, fracture, excessive eversion, lateral talar tilt
medial ankle sprain is sprain of _____, very _____, usually with ankle _____, MOI is _____, special test is _____
overuse, eccentric
achilles tendinopathy is most common _____ syndrome of the leg from extreme/rapid/repetitive _____ loading
midportion, insertion
achilles tendinopathy may occur at _____ (more common) or at tendon _____
age, anatomic, systemic, collagen, extrinsic, fluoroquinolone
tendinopathy risk factors include _____ related, _____ causes, _____ disease, (decrease _____ quality) and _____ factors such as _____ use
biomechanical, pronation, lateral, concentric/eccentric, gait, propulsion
achilles tendinopathy risk factors include _____ causes such as excessive _____, more pressure on _____ side during running, rapid alternating _____, altered _____ with decreased _____
eccentric, plantarflexion, weakness, motor control, cold, alcohol, obesity, footwear, age, men, genetics, fluoroquinolone, tendinopathy, fracture
other risk factors for achilles tendinopathy include decreased _____ and _____ strength, proximal muscle _____/_____, training during _____ weather, moderate _____ use, _____, _____ with rigid insoles, increasing _____, _____ sex, _____, _____ use, prior LE _____/_____
gradual, stiffness, inactivity, loading, tenderness on palpation, thickening, crepitus
achilles tendinopathy has _____ onset, _____ following _____, pain provoked with _____, _____ with possible tendon _____ and _____
arc sign, royal london hospital, thompson
achilles special tests (3)
dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, arch height, alignment, weight bearing
other considerations for achilles tendinopathy include _____ ROM, _____ strength/endurance, static _____, forefoot _____, _____ testing
education, modification, risk factors, complete rest, stretch plantarflexors, motor control
achilles tendinopathy treatment includes patient _____ for activity _____ or modifiable _____, _____ not recommended, follow tendinopathy progression, _____ if DF ROM is limited, neuro reed for _____
manual, dry needling, heel lift, taping, iontophoresis, not
achilles tendinopathy treatment may include _____ therapy and _____, temporary _____, _____ if patient prefers, and _____ if acute, night splints _____ recommended
fibularis longus, fibularis brevis, avascular zones, lateral malleolus, cuboid
peroneal tendinopathy is acute or chronic overuse to _____/_____, _____ are contributing factor (tendons run around _____/curve around _____)
direction change, jumping, training, footwear, growth, tightness, CAI, subluxing tendons, varus, forefoot
fibularis tendinopathy risk factors include sports with frequent _____/_____, abrupt change in _____, inappropriate _____, recent _____ spurt, _____ in gastrocnemius/soleus, history of _____ or _____, excessive hindfoot _____, _____ strike pattern
gradual, tendon sheath, mechanical, subluxation, eversion, plantarflexion, stretch, rest
fibularis tendinopathy presents with _____ onset, fluid may be palpable in _____, may report _____ symptoms, _____ may occur in eversion, pain/weakness with resisted _____/_____, pain exacerbated with _____, running/cutting/uneven surface, activity after _____
palpation, MMT, pain, subluxation, anterior drawer, swelling, posture
fibularis tendinopathy testing includes _____ and _____ of fibularis longus and brevis for _____ or _____, _____ for CAI concerns, _____ assessment, and foot _____ in weight bearing
tendinopathy, motor control, manual, restrictions, education, training, footwear
tendinopathy treatment follows _____ progression, _____ for biomechanical issues, _____ for soft tissue _____, and patient _____ for _____/_____ modifications
posterior, tibia, fibula, interosseous membrane, tarsal tunnel, navicular tuberosity, supinate, plantarflex, stabilize, medial longitudinal arch, concentric, eccentric
tibialis posterior is in _____ compartment, origin is proximal/posterior _____/_____/_____, passes through _____, inserts on _____, acts to _____/_____, functions to _____ foot/ankle, support _____, _____ (supination)/_____ (control pronation) during gait
microtrauma, overuse, medial malleolus, vascularity, tarsal tunnel, direction, friction
tibialis posterior tendinopathy is from chronic repetitive _____ from _____, pain posterior/slightly proximal to _____, decreased _____ in this region, in _____, change in tendon _____ causes increased _____
>50, men, systemic, medial ankle trauma, steroid injections, pronation, repetitive
tibialis posterior tendinopathy risk factors include age _____, _____ sex, _____ disease, history of _____, local _____, biomechanical factors including excessive _____, _____ loading
gradual, insidious, lateral, impingement, loading, plantarflexion, inversion, on toes, tenderness on palpation
tibialis posterior has _____ and _____ onset, _____ ankle pain possible with _____ later, pain worse with _____ (WB, resisted _____/_____, difficulty standing _____), _____
swelling, pronation, too many toes, pain, plantarflexion, everted
tibialis posterior tendinopathy inspection may include _____, excessive _____, and _____ sign, gait may have _____ with _____, and an _____ foot
single leg heel raise, maximum height, inability to perform, pain reproduction
tibialis posterior special test is _____ compare _____ to uninvolved side or NWB, positive is _____ or _____
intrinsics, proximal, orthoses, motor control, nsaids
tibialis posterior tendinopathy treatment follows tendinopathy progression, also strengthen _____ and _____ muscles, may use _____ to support medial arch and reduce tendon stretch, address faulty _____, use _____
tibial nerve, medial malleolus, talus/calcaneus, flexor retinaculum, FDL, FHL
tarsal tunnel syndrome is entrapment of _____, tarsal tunnel is formed by _____/_____/_____, passes between _____/_____ and then divides
footwear, trauma, sprain, biomechanical, scar, systemic, edema
tarsal tunnel syndrome extrinsic risk factors include poorly fitting _____, _____ (ankle _____), _____ faults, _____ tissue, _____ disease, generalized _____
tendinopathy, osteo, retinaculum, masses, arterial
tarsal tunnel syndrome intrinsic risk factors include _____, _____phytes, hypertrophic _____, any _____, _____ insufficiency
sharp, numbness, tingling, plantar, light touch, radiation, paresthesia, eversion, dorsiflexion, night, pronation, tenderness on palpation, gait, motor
tarsal tunnel syndrome presents with ____ pain, _____/_____/burning on _____ surface, diminished _____, _____ of pain and _____ along distribution, symptoms worsen at extreme _____/_____, with activity, or at _____, increased _____, _____, _____ abnormalities, and _____ symptoms if chronic
tinel’s sign, dorsiflexion eversion
tarsal tunnel syndrome special tests (2)
strengthening, tibialis posterior, stretching, nerve glides, manual, motor control, modalities
tarsal tunnel syndrome treatment includes therex (_____ of _____, _____, and _____), _____ therapy, neuro reed for _____, _____ for pain relief
medial tibial stress syndrome, fascial insertion, medial soleus, tibia, periosteum inflammation, bone overload
_____ AKA shin splints occur at _____ of _____ on _____ due to _____ and _____
runners, military, women, BMI, smaller, pronation, plantarflexion, external rotation, training, uneven, overuse, weakness, vitamin D
medial tibial stress syndrome risk factors include _____ and _____ recruits, _____ sex, greater _____, _____ q angle, excessive _____, increased ankle _____ and hip _____ ROM, sudden increase in _____, training on _____ ground, _____/_____ of tibialis anterior/EDL/EDB, _____ deficiency
exercise, aching, tibia, palpation, 5 cm, tendinopathy
medial tibial stress syndrome presents with _____ induced _____ pain on _____, produced by _____ over length of _____, follows _____ pain behaviors
pain, 5 cm, absence
medial tibial stress syndrome is diagnosed with _____ with palpation over _____ length and _____ of other findings
reducing, gradual, 9-12 months, low impact, graded, manual, motor control
medial tibial stress syndrome treatment includes education on _____ training and _____ return up to _____, _____ stretching/_____ strengthening, _____ therapy, neuro reed _____
plantar, medial heel, fascia insertion, calcaneus, heel spur, healthcare, chronic
plantar fasciitis causes _____/_____ pain at _____ on ____ with/without _____, often _____ workers, becomes _____ prior to treatment
dorsiflexion, BMI, running, prolonged standing, noncompliant, footwear, hamstring, leg length
plantar fasciitis risk factors include limited _____, high _____, _____ athletes, work related _____ especially on _____ surface, _____ worn, _____ tightness, _____ discrepancy (longer)
plantar medial heel, initial steps, NWB, prolonged, increase, tenderness on palpation
plantar fasciitis presents with pain in _____ region, worst with _____ after period of _____ or _____ WB, or recent _____ in activity, _____
windlass test
plantar fasciitis special test is _____
DF ROM, tenderness on palpation, posture, hamstring, length, gait
plantar fasciitis can also be tested using _____ and _____, foot _____ index, _____ muscle _____, and _____ assessment
heel center, progressively worse, barefoot, bilateral, night
heel fat pad syndrome presents with pain at _____, _____ pain, worse pain when _____, more likely to be _____ or at _____ pain
loads, footwear, BMI, stretching, strengthening, kinetic chain, manual
plantar fasciitis treatment includes education on modifying _____, _____ recommendations, maintaining optimal _____, therex for gastrocnemius/soleus _____, foot/ankle _____, any _____ deficits with neuro reed, _____ therapy
antipronation taping, are, orthoses, ultrasound
plantar fasciitis treatment may include _____, night splints _____ recommended, dry needling, foot _____, no _____ with biophysical agents
metatarsal heads, plantar, description
metatarsalgia is pain under _____ on _____ foot surface, _____ of symptoms rater than true diagnosis
anatomic, first ray, second metatarsal, plantarflexion
primary metatarsalgia is due to _____ abnormalities such as _____ insufficiency, long _____, or excessive metatarsal _____
indirect overloading, trauma, metabolic
secondary metatarsalgia is due to _____ such as _____, _____ disorders, or other syndromes
training, fat pad, tightness, arch, deformities, hyper, dorsiflexion, footwear, shorter, inflammatory, metabolic
metatarsalgia risk factors include over_____, submetatarsal _____ atrophy, _____ in toe extensors, _____ posture, toe _____, _____mobile first ray, limited _____, _____ worn, leg length discrepancy _____ leg, _____/_____ disorders
weight bearing, terminal stance, callous, pressure
metatarsalgia pain worsens with _____ especially in _____, _____ formation is possible with pain and _____ sensitivity
ROM, palpation, posture, gait
metatarsalgia special tests include thoroughly examining _____, _____, foot ____ in NWB/WB, and _____ analysis
orthotics, footwear, dorsiflexion, plantarflexor, kinetic chain, motor control
metatarsalgia treatments include foot _____, education on _____, therex for _____ ROM and _____ stretching, strengthen weakness from _____, neuro reed for _____
compressive, interdigital, third and fourth, narrow, thicker
morton’s neuroma is _____ neuropathy of _____ nerve, specifically between _____ metatarsals (space is more _____ and nerve is _____)
unknown, microtrauma, compression, ligament, soft tissue, bursa, ischemia
morton’s neuroma etiology is _____, possibly chronic _____, _____ between _____/_____ or _____, _____
women, middle, footwear, trauma, deviation, bursitis, impact, MTP, thickening
morton’s neuroma risk factors include _____ sex especially _____ age, _____ worn, history of _____, _____ of toes, intermetatarsal _____, high _____ sports, _____ pathology, _____ of ligament
between, burning, tingling, weight bearing, radiate
morton’s neuroma presents with pain _____ metatarsal heads, _____/_____ sensation, aggravated in _____, pain may _____
web space tenderness, squeeze
morton’s neuroma special tests (2)
orthotics, activity, footwear, biomechanical, pain
morton’s neuroma treatment includes foot _____, education on _____/_____ modification, correction of _____ faults and _____ management
degenerative arthritis, limited dorsiflexion, first MTP
hallux limitus/rigidus is progressive _____ resulting in _____ of _____
tenderness on palpation, lost joint space, osteophytes, gait
hallux limitus/rigidus causes _____, radiographs demonstrate _____ with _____, alters _____ mechanics
footwear, NSAIDs, corticosteroids, joint mobilizations, mobility
hallux limitus/rigidus conservative interventions include _____ modifications to limit DF, _____/_____ for pain, _____, ROM/stretching/strengthening to maintain _____
cheilectomy, dorsal metatarsal head, articular cartilage, moberg, proximal phalanx
hallux limitus/rigidus surgical interventions include _____ (excision of _____ to remove osteophytes, improve DF ROM, preserves _____) or _____ procedure (dorsiflexion osteotomy of _____ to improve DF ROM)