systems path 2 exam 3 - ureter, bladder and urethra (pg 78-97)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
dilation of the renal pelvis/calyces due to obstruction
hydroneophrosis (swollen kidney)
cause of congenital hydronephrosis
atresia of ureter or urethra
congenital hydronephrosis is found in who?
male infants
causes of acquired hydronephrosis
stone, BPH, prostate CA
is hydronephrosis unilateral or bilateral
both
bilateral hydronephrosis symptoms
polyuria (incomplete) or anuria (complete
untreated hydrocephalus leads to
progressive renal atrophy
concretion formed in any part of the body, most commonly in the passages of the biliary and urinary tracts ; usually composed of salts of inorganic or organic acids or other material such as cholesterol
calculus
signs/symptoms of a renal calculus (kidney stone)
pain (renal colic ; flank pain-> groin), usually unilateral
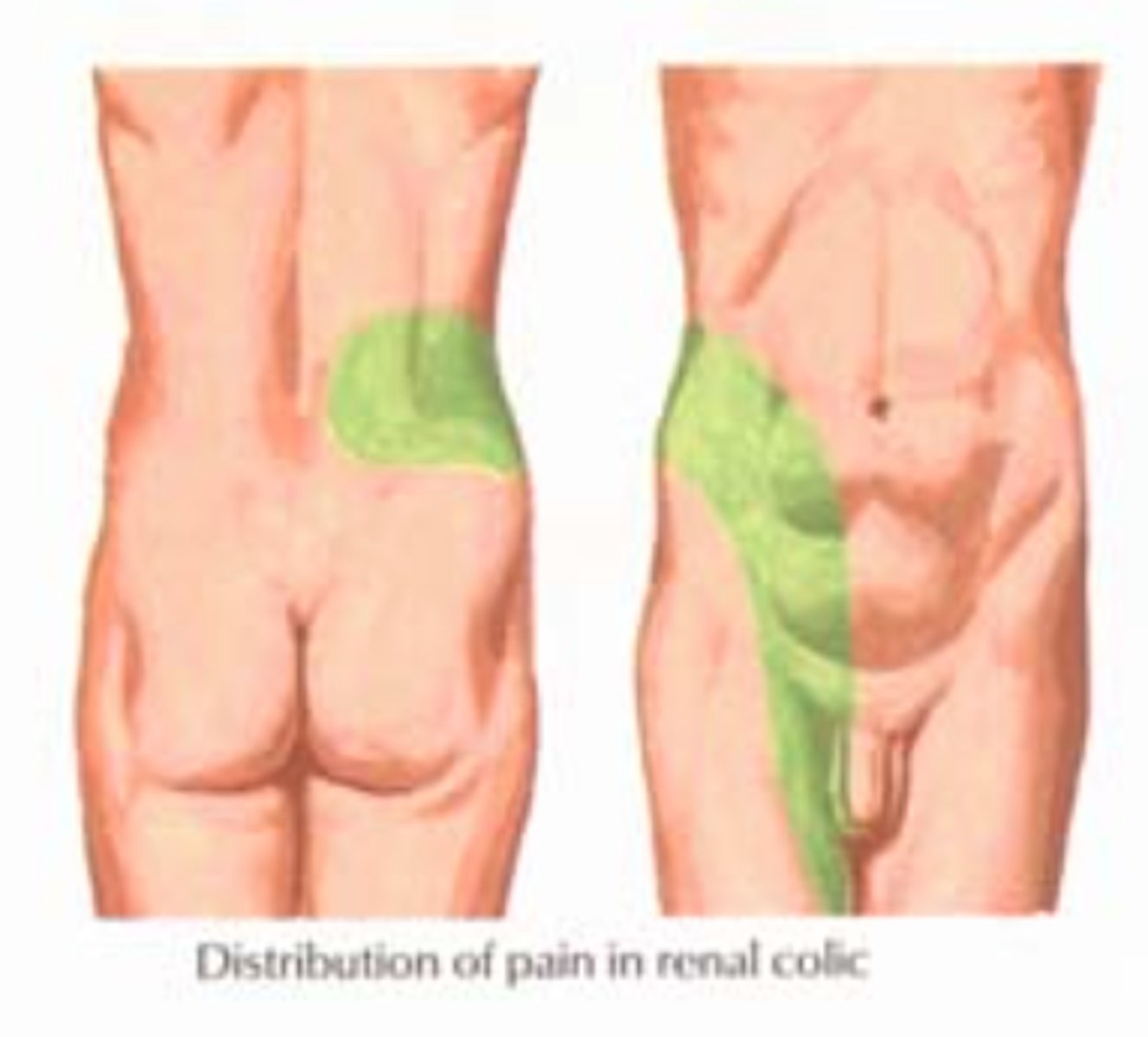
what are kidney stones MC composed of?
Calcium oxalate
risks for developing a kidney stone
males, family hx, dehydration, UTI's, low vitamin A, gout
how long until you pass a kidney stone?
4 weeks (lithotripsy if big)
upper urinary tract stone which forms a cast of the renal pelvis
staghorn calculus
What are stag-horn calculi normally composed of?
magnesium ammonium phosphate
staghorn calculi are linked to recurrent ______ with urease-producing bacteria
UTIs
vitamin A deficiency causes....
kidney stones, bitot spots
vitamin A overdose/toxicity causes....
vomiting/weight loss, arthritis, HA, dizziness, diplopia
evagination of the bladder wall which is MC small, asymptomatic, and has an infection risk
diverticulum
what causes a urinary bladder diverticulum?
acquired : urethral obstruction (BPH)
inflammation of the urinary bladder due to bacterial infection (E. coli), chemo/radiation, trauma, poor hygiene, etc.
cystitis
signs/symptoms of cystitis
suprapubic pain, dysuria/frequency, hematuria, painful sex
risks for cystitis
sexual intercourse, female, elderly/impaired bladder emptying, diabetes
4th most common cancer in men
bladder cancer
Who does bladder cancer MC affect?
50-80 year old males
causes of bladder cancer?
bladder irritation, smoking, industrialized/urban environments, occupational carcinogens (acquired)
what type of acquired mutations are associated with developing bladder cancer?
TP53 or Rb
what type of bladder cancer subtype grows in slender, finger-like projections from the inner surface of the bladder toward the hollow center, often without growing into the deeper bladder layers?
papillary carcinomas
what type of cancer only affects inner layer/cells (transitional epithelium)
non-invasive
what type of cancer grows into deeper layers of the bladder wall, is MC to spread and harder to treat
invasive
what describes bladder cancer that has not grown into the main muscle layer/bladder that is both invasive and non-invasive?
superficial (non-muscle invasive)
most common type of bladder cancer
Urothelial (transitional cell) carcinoma
papillary tumor that doesn't grown into deeper bladder layers
non-invasive papillary carcinoma
very low-grade (slow growing) non-invasive papillary cancer which tends to have a very good outcome
PUNLMP (papillary urothelial neoplasm of low-malignant potential)
what is it called when a papillary or flat tumor grows into deeper layers of the bladder?
invasive urothelial (transitional cell) carcinoma
tumor that does not grow toward the hollow part of the bladder
flat carcinoma
flat tumor that is only in the inner layer of the bladder cells
non-invasive flat cell carcinoma (flat carcinoma in situ)
signs/symptoms of bladder cancer
painless hematuria, changes in bladder habits
diagnosis for bladder cancer
cystoscopy
treatment for bladder cancer
chemo/radiation, cystectomy
how does smoking cessation affect bladder cancer?
decrease risk of progression and recurrence