Science 9: Work-Energy-and-Power
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Work
It represents a measurable change in a system, caused by a force. It is defined as a force acting upon an object to cause a displacement.
F
It is used to represent Force.
d
It is used to represent displacement.
angle (theta)
It is defined as the angle between the force and the displacement vector.
Joule or kg times m/s²
SI Unit for Work
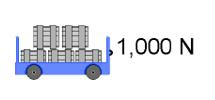
W = Fd
This formula is used when force is parallel to distance.
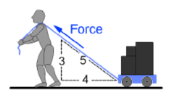
W = Fd cos(theta)
This formula is used when force is at angle to distance.
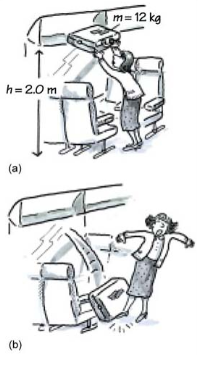
W = mgh
This formula is used when force is done against gravity.
Power
It is is defined as this rate of energy transfer. It s simply energy exchanged per unit time, or how fast you get work done.

Watts or Joules/sec
SI Unit of Power
P = W/t
Formula of Power
Energy
It is the ability to do work.
Work
It is the energy transferred to or from a system by a force that acts on it.
Mechanical Energy
It is the energy which is possessed by an object due to its motion or its stored energy of position.
Kinetic energy
It is the energy of motion.
Potential Energy
An object can store energy as the result of its position or elastic source.
Scalar
(Scalar or Vector): Kinetic Energy
KE = 1/2mv²
Formula of Kinetic Energy
KE
It represents the kinetic energy of an object.
Gravitational Potential Energy
It is associated with an object at a given location above the surface of the earth.
PE(G) = mgh
It is the formula for the gravitational potential energy.
PE(G)
Used to represent Gravitational Potential Energy.
9.8 m/s²
It is the value of gravitation due to acceleration.
Elastic Potential Energy
It can be thought of as the energy stored in the deformed spring (one that is either compressed or stretched from its equilibrium position).
PE(E) = 1/2kx²
The formula used for Elastic Potential Energy
PE(E)
Used to represent Elastic Potential Energy.
Conservation of Energy
It states that the sum of kinetic energy and potential energy in a system is constant, in absence of friction.
Energy
It cannot be created or destroyed; it may be transformed from one form to another, but the total amount of energy in a system remains constant.
Conservation of Energy
This formula is aka: KEi + PEi = KEf + PEf
W
used to represent Work
m
used to represent mass
g
used to represent gravitational acceleration
h
used to represent the height of the object raised
t
used to represent time
v
used to represent velocity or speed
k
used to represent the spring force constant
x
used to represent the extension of the spring