Biology - Cell Divison
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Define cell continuity
When cells develop from other existing cells
State the composition of a chromosome
DNA and protein
State the location of chromosomes in a cell
Nucleus
Define the term haploid cell and name an example
Has one set of chromosomes (e.g. sperm and eggs)
Define the term diploid cell and name an example
Has two sets of chromosomes (e.g. skin cells)
Define the term homologous pair
Two chromosomes with similar genes
List the two stages of the cell cycle and which one is shorter
Interphase and mitosis, mitosis is shorter
Define mitosis
When one nucleus divides into two identical nuclei
Function of mitosis in a single celled organism
asexual reproduction
Function of mitosis in a multi cellular organism
Growth and repair of cells
List the four stages of mitosis in order
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
prophase
chromosomes are double stranded. spindle fibres start to move to the poles stage 1. 30m

metaphase
chromosomes line up in the equator. spindle fibres attach to the chromosome. membrane of nucleus is broken down. 30m stage 2,

Define centromere
The point at which chromosomes are attached together in a double stranded structure
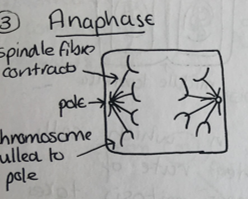
anaphase
stage 3. spindle fibres contract chromosomes pulled apart chromosomes move towards the poles. about 10m
telophase
stage 4, chromosomes change back into chromatin. membrane of the nucleus is reformed. takes about 30m.

Name the feature that allows animal cells to split in two
Cleavage furrow
Name the feature that allows plant cells to split in two
Cell plate
Define cancer
when a cell loses the ability to control the rate of mitosis. This forms a mass of cells called a tumour
Define carcinogen
Cancer causing agent
Define oncogene
Cancer causing genes
Distinguish between a benign and malignant tumor
A benign tumour does not invade other cells and stops dividing after some time, a malignant tumour invaded other cells and is an uncontrolled division of tumours
Define meiosis
Where a nucleus divides into four new nuclei that are not identical and contain only half the number of chromosomes as the parent nucleus
State two functions of meiosis
Allows sexual reproduction/ allows for greater variation within a species
Where does meiosis occur in males
Testes
Where does meiosis occur in females
Ovaries
chromatin
Long thin threads of DNA which is found in the nucleus of cells that are not dividing.
gene
section of dna that contains the structure for the formation of a protein.