Kidney - Selective Reabsorption
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What substances are removed from the blood during ultrafiltration, and why must some of them be reabsorbed?
Ultrafiltration removes urea from the blood, but it also removes a lot of water along with glucose, salt, and more.
Many of these substances are needed by the body, like glucose, which is used in cellular respiration.
How does the concentration of the ultrafiltrate compare to blood plasma, and what must happen after filtration?
The ultrafiltrate is also hypotonic (less concentrated) than the blood plasma.
After the Bowman's capsule, the nephron needs to return most of the filtered substances back to the blood.
Selective Reabsorption
All glucose, amino acids, vitamins, and many Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions are reabsorbed out of the proximal convoluted tubule and back into the blood via facilitated diffusion
Where does selective reabsorption occur?
In the proximal convoluted tubule
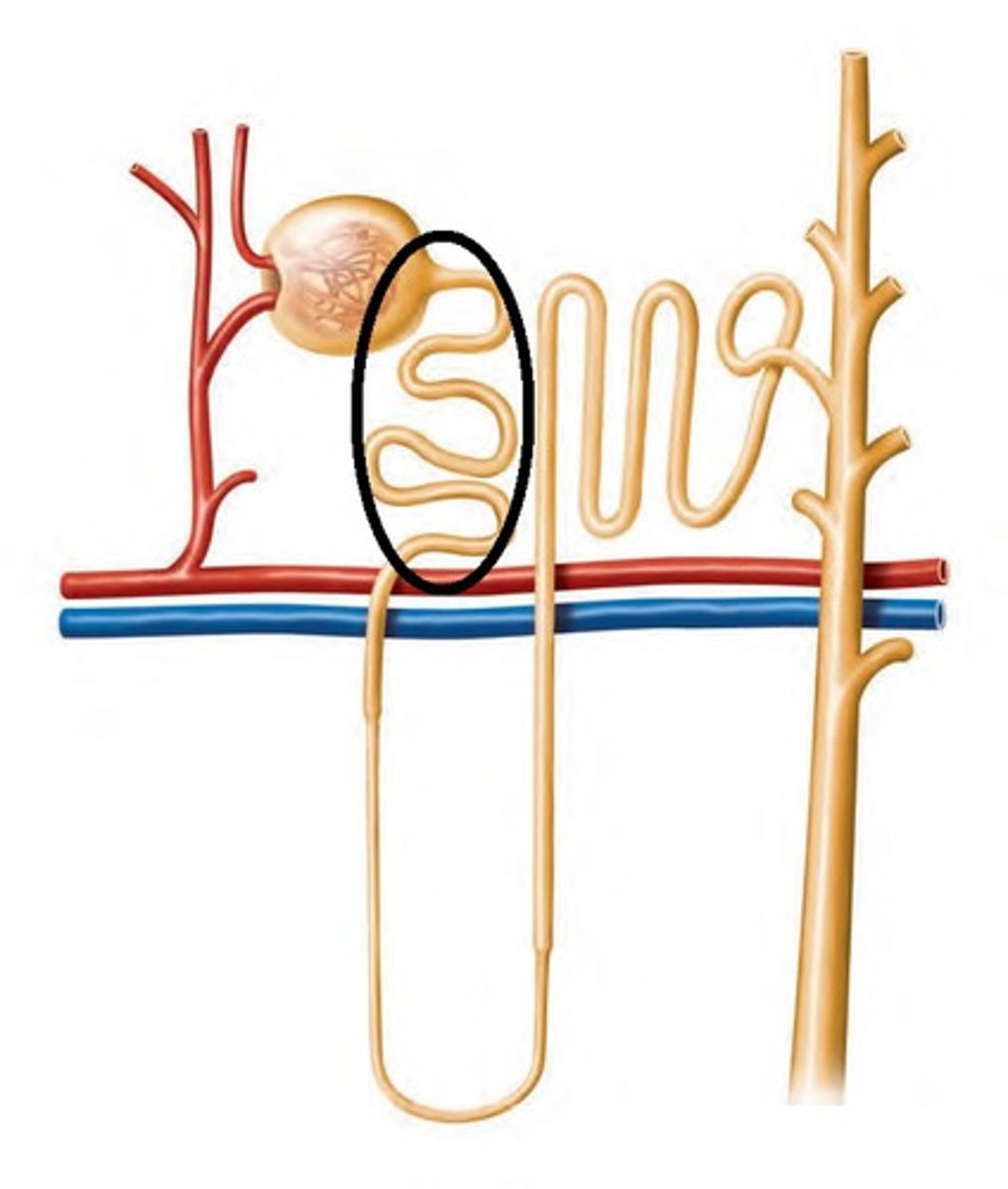
What type of cell lines the proximal convoluted tubule?
Cuboidal epithelium
Why do cuboidal epithelium have microvilli?
To give a large surface area over which substances can be reabsorbed
Where do blood capillaries lie?
Close to the outer surface of proximal convoluted tubule
Selective reabsorption diagram
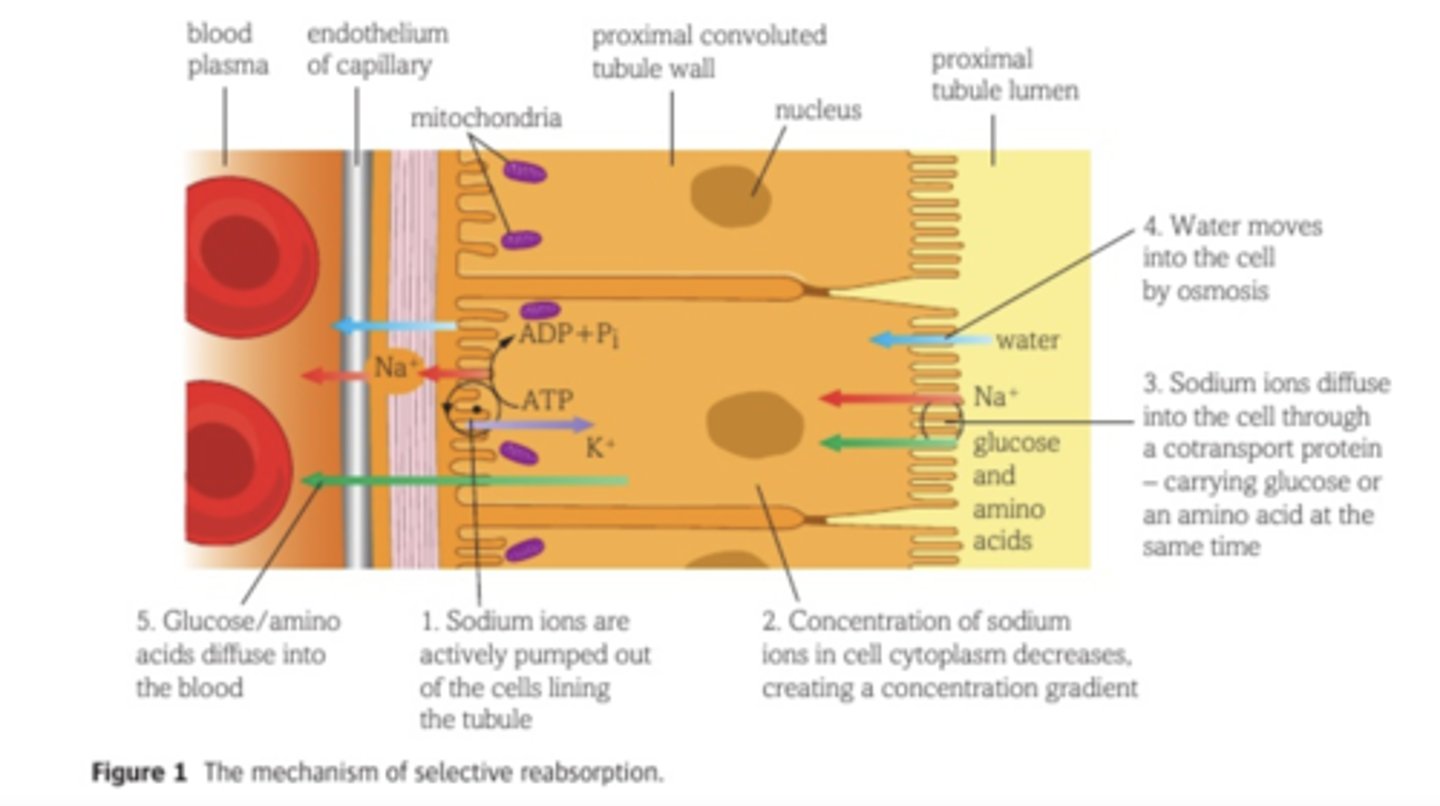
1)
Na⁺ are actively transported out of outer membranes of cuboidal epithelial cells from the cytoplasm, into tissue fluid, using a SOPI pump.
Because Na⁺ is being actively transported into the blood, water will also move out of the cuboidal epithelium via osmosis into the bloodstream
(because Na⁺ lowers the water potential in the blood, so water enters the blood down the water potential gradient)
The Na⁺ that has been actively transported into the blood will then be replaced by Na⁺ that diffuse down the concentration gradient, from the glomerular filtrate (in the PCT) into the cuboidal epithelium cells (which line the PCT) via facilitated diffusion with co-transporter proteins (along with glucose or amino acid).
The water potential inside the cuboidal epithelium will be lowered, so water will be drawn in from the PCT lumen via osmosis down the water potential gradient.
Once glucose and amino acids have entered the cuboidal epithelial cells that line the PCT via facilitated diffusion using co-transport, glucose or amino acid will then enter the bloodstream via facilitated diffusion.
Why are there lots of mitochondria present in the cuboidal epithelium?
Active transport requires ATP, so a lot of mitochondria are present in the cuboidal epithelium.
What will facilitated diffusion of Na⁺ require?
It will require a glucose or amino acid in the process of co-transport.
Why is it co-transport during selective reabsorption?
Because Na⁺ will enter the cuboidal epithelial cells at the same time with either a glucose or an amino acids
Why is it facilitated diffusion in selective reabsorption?
Because it uses a protein to move into the cuboidal epithelial cell
Why do glucose and/or amino acids enter the bloodstream via facilitated diffusion?
Glucose and amino acids are too big to pass through the phospholipid bilayer, therefore will have to use a transport protein.
Summary of Selective Reabsorption
Na⁺ are actively transported out of cells into the tissue fluid
Glucose or amino acids enter cells alongside Na⁺ via facilitated diffusion
Glucose and amino acids diffuse into the blood capillary
What does the selective reabsorption of salts, glucose, and amino acids do to the cells?
It increases the water potential in the proximal convoluted tubule, and reduces the water potential in the cuboidal epithelial cells.
How is water reabsorbed into the blood?
Via osmosis
Which one of the following is normally completely reabsorbed by the nephron from the fluid passing through it?
Sodium
Glucose
Water
Urea
Glucose
All valuable glucose that has passed into the filtrate is reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule.
The body may choose not to recover water or sodium from the urine if too much is present in the body.
Some urea returns to the body to aid water recovery.
Which substance is lost from the body of a healthy person by the kidneys, but not by the lungs?
Carbon dioxide
Water
Glucose
Urea
Urea
Water and carbon dioxide are lost from the body as air is exhaled from the lungs.
No glucose is lost from the kidney as it is all recovered by selective reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule. Urea is lost from the kidneys, but not by the lungs