BIO SET 2 - Enviormental Science
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Who was Charles Dickens and what did he discover?
Charles Dickens was the father of evolution and discovered the theory of evolution, which said that species change over time, divergent species share a common ancestor, and natural selection produces change
Jean Baptiste Lamarck’s Theory
Theory of Use &Disuse, which states that organisms changed body parts to adapt to their environment and passed on the changes in their offspring. He used giraffe necks as an example. This theory is incorrect
Thomas Malthus’s Theory
Malthus argued that population was growing faster than the resources being produced and would outgrow them. A catastrophe like an asteroid or pandemic would return the population to normal.
What is evolution?
Evolution is the genetic change in a population of organisms over time
What is natural selection?
Natural Selection is the process by which organisms with variations most suited for their environment survive and have more offspring. It occurs due to variation and adaptation, a struggle for existence, survival of the fittest, & common descent
Variation of Traits
The difference in observable or measurable characteristics among individuals in a population. An example is the size and shape of finch beaks.
Adaptations in Elephants
Elephants have a trunk that is used to reach water, large fan-like ears to lower blood temperature, tusks for self defense, wrinkled skin to retain moisture, and strong legs to move long distances
Struggle for existence/Survival of the Fittest
Species must struggle for existence to wean out the weak genes and have strong traits. Survival of the fittest are the species with the highest fitness
High vs. Low Fitness in Animals
High fitness is a strong animal who frequently reproduces and low fitness are weak animals who reproduce very infrequently
What is adaptive advantage?
A beneficial trait that increases an organisms chance of survival or reproduction. Ex: Spikes, Long claws, Waterproof fur, herding behavior
Coevolution
The change in two or more species in close association. EX- Bees get nectar to drink from flowers, and in the process, cross pollinate flowers allowing them to have offspring
Convergent Evolution
Organisms that appear similar but are not. Ex- Sharks and Porpoises (dolphins) look similar, but are not related
Divergent evolution
Two or more closely related organisms that become more and more dissimilar. Example - The red fox and kit fox are the same species but look very different. They are also found in different biomes.
Adaptive Radiation
A type of divergent evolution where many species evolve from a single ancestor. Example - 1 of Darwin’s Finches evolved into 13 different species with different beaks
Analogous and Homologous Structures
Analogous Structures are structures in two different organisms bodies that have the same function but different structure with no common ancestor. An example would be the fin in penguins, sharks, and dolphins. Homologous structures are structures in two different organisms bodies with different functions but the same structure with a common ancestor. The pentadactyl limbs of animals like humans and cats would be an example.
Did all life originate from one ancestor?
Yes. We know because one single called organism evolved from non living things and became alive.
What is an extinct species?
Species with no living population
How do extinctions occur?
Naturally over time as a result from a change in the environment. Climate change, changes in sea level or currents, asteroids, cosmic radiation, or genetics.
What happened to the dinosaurs?
A giant asteroid hit Mexico. This asteroid formed a huge dust cloud that blocked the sun and sunlight from penetrating the earths surface. With no sunlights, plants couldn’t photosynthesize, and they died. With no plants, herbivore plants died. With no herbivores to eat, primary consumer dinosaurs died. A chain reaction occurred, killing everything.
Why does variation occur in a population?
Mutations occur during changes in DNA sequences affecting proteins, in sexual reproduction alleles combine differently creating new traits, & the gene flow, the movement of new individuals from one population to another
Gene Flow
Gene flow is the exchange of genes through populations through sexual reproduction. It helps maintain a species, & without it, populations would be genetically isolated.
What is a species?
Species is a group of similar organisms that can reproduce. Species must be able to mate and have fertile offspring to classify as such
Microevolution vs Macroevolution
Microevolution is short term change, such as spontaneous mutations that change the fur color of a fox. Macroevolution is large scale evolutionary change over long periods of time such as speciation & extinction.
Speciation
The formation of new species from an existing species
Reproductive Isolation
Reproductive Isolation is when two groups of organisms can no longer exchange genes due to geological, temporal, mechanical, or behavioral differences
Allopathic speciation
Allopathic speciation is speciation occurred due to geological conflicts. Sympatric speciation is speciation occurred by anything not geography related
Sympatric Speciation
Speciation occurred by anything not geography related. Temporal, Behavioral, and Mechanical.
Temporal Speciation
Not being able to breed due to timing differences like different feeding/mating times
Mechanical Speciation
Not being able to breed due to incompatible reproductive organs
Behavioral Speciation
Not being able to breed due to different behavioral patterns such as different mating rituals.
How old is the Earth and how long ago did life originate?
The earth is 4.5 billion years old and life originated 3.5 billion years ago
How did life originate on earth?
Spontaneous abiotic origin. Life evolved spontaneously from inorganic molecules
Why are hydrothermal vents so incredible?
They support unique and thriving ecosystems
Eukaryotes
Organisms with cells that have a nucleus
Endosymbiosis
When an organism lives within the body or cells of another organism and usually have a mutualistic relationship. EX - Organelles in Eukaryotic cells
Modern Extinction
Extinction tied to human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing grasslands, drained wetlands, and pollution
Endangered species
Species whose population size is so low that it is at risk for extinction.
Vulnerable species
Vulnerable species are species that face a high risk of endangerment
Threatened Species
Species that may not be endangered yet, but could be threatened without intervention
Ecology
The study of interactions that take place between organisms and their environment
Organism
An individual of a species that occupies a habitat where they share food and shelter with other organisms. Has a niche, or a specific job for their environment
Population
A group of organisms of the same species that interbreed and live togetehr
Community
Interacting populations in certain areas at a certain time
Ecosystem
Interacting populations in a biological community with abiotic factors. Either terrestrial or aquatic.
Biotic and Abiotic Factors
Biotic factors are factors that are alive or were once alive like squirrels and fish while abiotic factors are factors that never lived like rocks and soil
What do we look for when determining what type of biome a piece of land is?
Variety of unique characteristics, average temperature, and average amount of water
Mutualism
A relationship where both species benefit from the relationship. An example is the clownfish and the anemone
Commensalism
A relationship between two species where one benefits and the other neither benefits or is harmed. An example is the shark and the remora
Parasitism
A relationship between two species where one is benefited and the other is harmed. An example is ticks and humans
Why is competition important
Weeds out the weaklings and creates stronger species. Also prevents two species from occupying the same niche in the same habitat at the same time through the Competitive Exclusion Principle
Levels of Organization
Organism, Species, Population, Community, Ecosystem, Biome, Biosphere
Example of a predator/prey relationship
A spider eating a trapped fly
Primary Producers
Make their own food from the sun. As the base of the ecological pyramid, they make the energy that we use in our bodies that is passed down from one consumer to the next
Carbon Cycle
The taking of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to be utilized in photosynthesis. Also called carbon fixation
Nitrogen Cycle
Bacteria takes nitrogen out of the atmosphere and converts it into a usable form. Occurs in three steps, Nitrogen Fixation, Nirtufication, Denitrification.
Nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen gas is converted into ammonia, useful for plants
Nitrification
Ammonia is converted into nitrite and nitrate. Nitrite is useful for plants
Denitrification
Nitrate is converted back to nitrogen gas and put back into the air
Ecological Pyramid
The loss of energy modeled in the food chain over time. The food groups with the most energy are on the bottom of the pyramid while the top layer consists of the highest ranking consumers who get very little of the initial energy
Food Chain vs Food Web
A food chain is only one flow of nutrients while a food web showcases multiple flows at once
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants and other organisms make their own food using energy from sunlight. It is important as it’s the way autotrophs make food
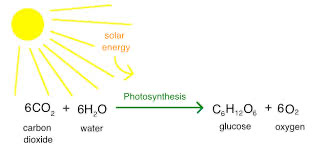
Equation for photosynthesis
Three ecological roles of photosynthesis
Conversion of solar energy into chemical energy, fixing of inorganic carbon into organic carbon, and production of oxygen
What do plants need to thrive and survive?
Water, soil, Carbon Dioxide, & Sunlight
What is created in the Calvin cycle?
Glucose from Carbon Dioxide
Light vs Dark reactions in photosynthesis
In light, chloroplasts absorb sunlight and convert the sunlight into glucose, releasing oxygen. In the dark, the Calvin cycle occurs, carbon dioxide from the atmosphere joins with Hydrogen from water to make glucose
Taxonomy
The branch of science concerned with the classification of animals. It uses a hierarchy system to group animals based on shared characteristics
Levels of taxonomy from biggest to smallest
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Tiktaalik
Transitional fossil showcasing the ancestors of tetrapods. It was the first animal to be able to walk on land
Parts of ocean
Photic - enough light for photosynthesis, Aphotic - not enough light for photosynthesis, Intertidal - high to low tide, Neritic - shallow water over continental shelf, Oceanic - open ocean, Pelagic - open ocean without sea floor, Benthic - sea floor, Abyssal - part of benthic with no light
Primary Succession
When a community arises in a lifeless area with no soil. Autotrophic microorganisms are the first to appear. Eventually, when soil arises, the area bursts with life, Takes hundreds to thousands of years
Pioneer species
The first species to populate a lifeless area. Usually lichens or moss
Secondary succession
When a disturbance damages the area but keeps the soil intact. New vegetation regrows rapidly since the soil survives, making it faster than primary succession.
Climax community
The return to the natural and healthy state of the environment after secondary succession is complete