Microbio Lab Quiz 5
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Alexander Fleming
- Father of antibiotics
- Discovered penicillin on accident
Paul Ehlrich
- "Magic Bullet" Hypothesis
- Chemicals can be designed to bind to and kill specific microbes or tumor cells without harming the host itself
Selman Waksman
- Coined the term "antibiotic"
- He discovered and developed the antibiotic streptomycin, produced by Streptomyces griseus
- Streptomycin was the cure for tuberculosis
Alma Whiffen
- Mycologist
- Discovered the antifungal agent cycloheximide
Antagonism
an interaction between organisms where one organism benefits at the expense of another
How do you detect antagonism?
Zone of inhibition
How and why is antibiotic resistance a concern?
- Occurs spontaneous mutations, horizontal gene transfer via conjugation
- Concern: The effect of the over use of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in the environment
Antibiotic Characteristics
1. They are therapeutic agents
2. They are selectively toxic towards microorganisms
3. They kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria
4. These are small secondary metabolites
5. The term "antibiotics" is used for either antibiotics produced by microbes or for synthetic antibiotic
Targets of antibiotics
- Narrow-spectrum antibiotics: target a few types of bacteria
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics: target many types of bacteria.
- Metabolic enzymes, Cell wall synthesis, Ribosomes, Cell membrane, DNA synthesis
What are the steps of PCR?
1. Denaturation
2. Annealing
3. Extension
What happens in the denaturation step of PCR?
The DNA strands are separate
What happens in the annealing step of PCR?
Primers adhere to the DNA strands
What happens in the extension step of PCR?
Taq polymerase builds complementary strands
What is PCR?
A laboratory technique for rapidly amplifying millions to billions of copies of a specific segment of DNA
What is the purpose of PCR?
to amplify a specific desired fragment of DNA
What is a thermal cycler?
Used to amplify DNA sequence by increasing and decreasing temperature
What is Thermus aquaticus?
the organism that is thermophile whose enzymes are stable at high temperature
Taq polymerase
DNA polymerase which is heat stable; taken from Thermus aquaticus
What are primers?
small nucleotide sequence
What are the PCR components?
- Taq Polymerase
- dNTP's
- Polymerase Buffer
- Primers
- di water
What is the function of Taq polymerase?
polymerization of dNTP into a DNA strand
What is the function of dNTP's?
mix of nucleotides building blocks of new DNA strand
What is the function of Polymerase Buffer?
creates optimum activity of Taq polymerase
What is the function of Primers?
locate target DNA fragments
Tris-HCl
maintain pH
What are the Buffer compositions?
- Tris-HCl
- EDTA
- MgCl2
- KCl
- Triton
EDTA
chelating agent, keep DNA intact
MgCl2
cofactor for Taq polymerase
KCl
neutralizes charges in DNA template
Triton
stabilizes DNA
What are the PCR applications?
Bacterial identification, DNA fingerprinting, bioengineering
What is the principle and purpose of Gel electrophoresis?
- Analysis of nucleic acids (DNA /RNA) and proteins
- A procedure that separatesmolecules on the basis of their rate of movementthrough a gel under the influence of an electricalfield, their charge, shape and size
How does DNA migrate?
From cathode (positive) to anode (negative)
What dictates how far a fragment will travel?
size, the smallest fragments will travel the greater distance
What is agarose?
a linear polymer extracted from seaweed
What is the use of TBE (Tris/Borate/EDTA) and/or TAE (Tris/Acetate/EDTA buffer?
used for analyzing DNA products from PCRs by using agarose gel electrophoresis or polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
What is the function of Gel Green Stain and Staining dye?
binds to DNA and fluoresces under UV light, allowing the visualization of DNA on a Gel
Loading and Tracking buffer
- Bromophenol Blue (for color)
- Glycerol (for weight)
What is the purpose of Loading and Tracking buffer?
this allows the samples to be seen when loading onto the gel, and increases the density of the samples, causing them to sink into the gel wells
What is the DNA ladder? (1 Kb-1.5Kb ladder)
- DNAs of known sizes
- Makes it easy to determine the sizes of unknown DNAs.
How do we "read" the DNA migration?
DNA ladder
What are plaques?
clear zones that develop on lawns of host cells
What is coliphage?
virus that infects certain bacteria called coliforms
What is bacteriophage?
A virus that infects bacteria
What are obligate intracellular parasites?
viruses that depend on the host cell for replication
What is titer?
Amount of bacteriophage present in a sample
What is the Coliphage used in lab?
T4 phage
What is the bacteria used in lab?
E. coli
What is the Lytic cycle?
- clear plaques
- involves the reproduction of viruses using a host cell to manufacture more viruses; the viruses then burst out of the cell
What is the lysogenic cycle?
- The lysogenic cycle is a viral replication cycle
that does not kill the host immediately.
- Cloudy plaques
What is the purpose of Nutrient agar?
supports the growth of a wide range of non-fibrous organisms
What supplement is used in the bacteriophage experiment?
Na +supplement
What is the calculation of titer?
# of plaques times 1 over the dilution factor
What is the unit of titer?
PFU/mL
What does PFU stand for?
plaque forming units
What is the principle of the starch test?
to test the presence of carbohydrates
What is the developer of the starch test?
Iodine
How do you read the starch test? (positive and negative)
- Positive: produce brown-black color
- Negative: no brown-black color produced
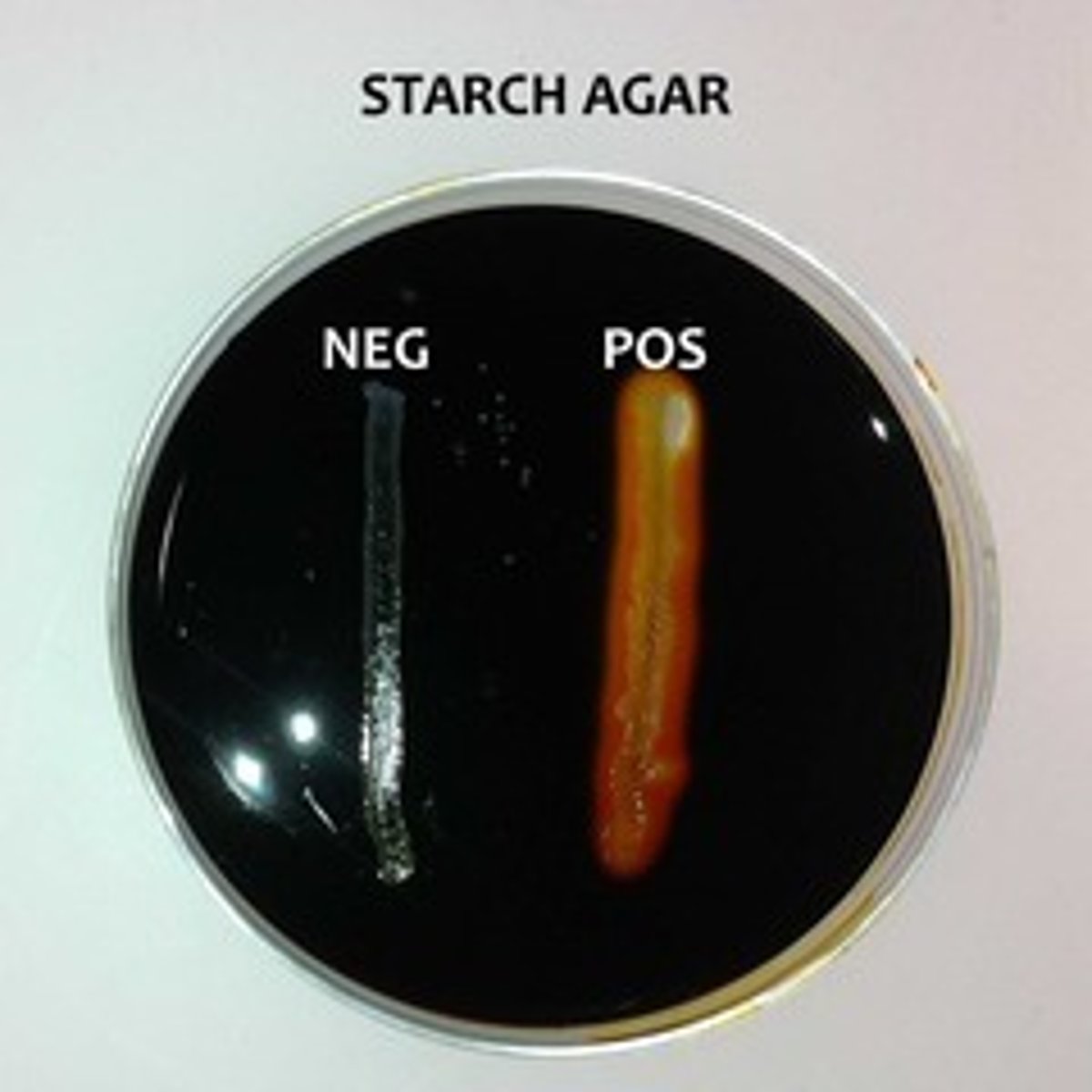
Which organisms are positive and negative for the starch hydrolysis?
- Positive: B. megaterium
- Negative: E. coli
Which primers were used for the 16S rRNA?
27F and 1492R
How did we test for the production of antibiotics by our isolates?
Zone of inhibition