GCSE Computer Science Complete
1/362
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
363 Terms
Describe the process for a linear search
Go through each value in the list until the value matches the given input
Describe the process of binary search
If the input is greater than the middle element, everything below the middle element is removed, and vice versa. This repeats until the middle element matches the input.
Describe the process of bubble sort
An element is swapped with the next if it is larger. This repeats throughout the list - a pass. Passes repeat until the list is sorted.
State the time complexity
n²
State the number of passes needed for a list of length n
n - 1
State the number of checks per pass for a list of length n
n - 1
Describe the process of merge sort
The list is being divided into shorter lists, being split at the middle item. Each sublist is half the length of the list it was created from. The subdivision process terminates when each sublist is of length 1. The lists are being merged together. When two lists are merged, the items in them are put into the new list in order. Eventually one list is produced - which is the sorted list.
Compare binary and linear search
Binary is more time-efficient for larger datasets but it is harder to program, and the list must be sorted. Linear search can be used for multi-dimensional arrays, but binary search can only be used for one-dimensional arrays. Binary search can only search for numbers but linear search can search for anything.
Compare merge and bubble sort
Merge sort is more time-efficient but is harder to program, but bubble sort is better in a best-case scenario. Bubble sort uses less memory
Define algorithm
An algorithm is a sequence of steps that can be followed to complete a task.
Distinguish between algorithm and program
A program is an implementation of an algorithm.
Define decomposition
Decomposition means breaking a problem into a number of sub-problems, so that each sub-problem accomplishes an identifiable task.
Define abstraction
Abstraction is the process of removing unnecessary detail from a problem.
What is pseudocode?
A fake language, not a programming language with syntax, that should have some consistency and relation to a language.
Convert this python syntax into pseudocode: name = input("Enter name"). print ("Hello", name). if name == "James": elif name == "Sid": else:.
OUTPUT "Enter name"
name <- USERINPUT
OUTPUT "Hello ", name
IF name = "James" THEN
ELSE IF name = "Sid" THEN
ENDIF
State the pseudocode syntax for while, for, and repeat until loops.
WHILE running = True
ENDWHILE
FOR i <- 0 to 10 STEP 2
ENDFOR
FOR char IN string
ENDFOR
REPEAT
UNTIL running = False
State the pseudocode syntax for a subroutine
SUBROUTINE function (num1)
ENDSUBROUTINE
OUTPUT function (1)
State the pseudocode syntax for creating an array
array <- ["A", "B", "C"]
OUTPUT array[2]
OUTPUT LEN(array)
State the pseudocode syntax for creating a record
RECORD Dog
name : string
age : integer
ENDRECORD
myDog <- Dog ("John", 3)
OUTPUT myDog.name
mydog.age <- 4
State the pseudocode syntax for locating the position of a character in a string
string <- "example"
OUTPUT POSITION (string, "e")
OUTPUT SUBSTRING (0, 5, string)
State the pseudocode syntax for conversion between characters and their ASCII values
CODE_TO_CHAR
CHAR_TO_CODE
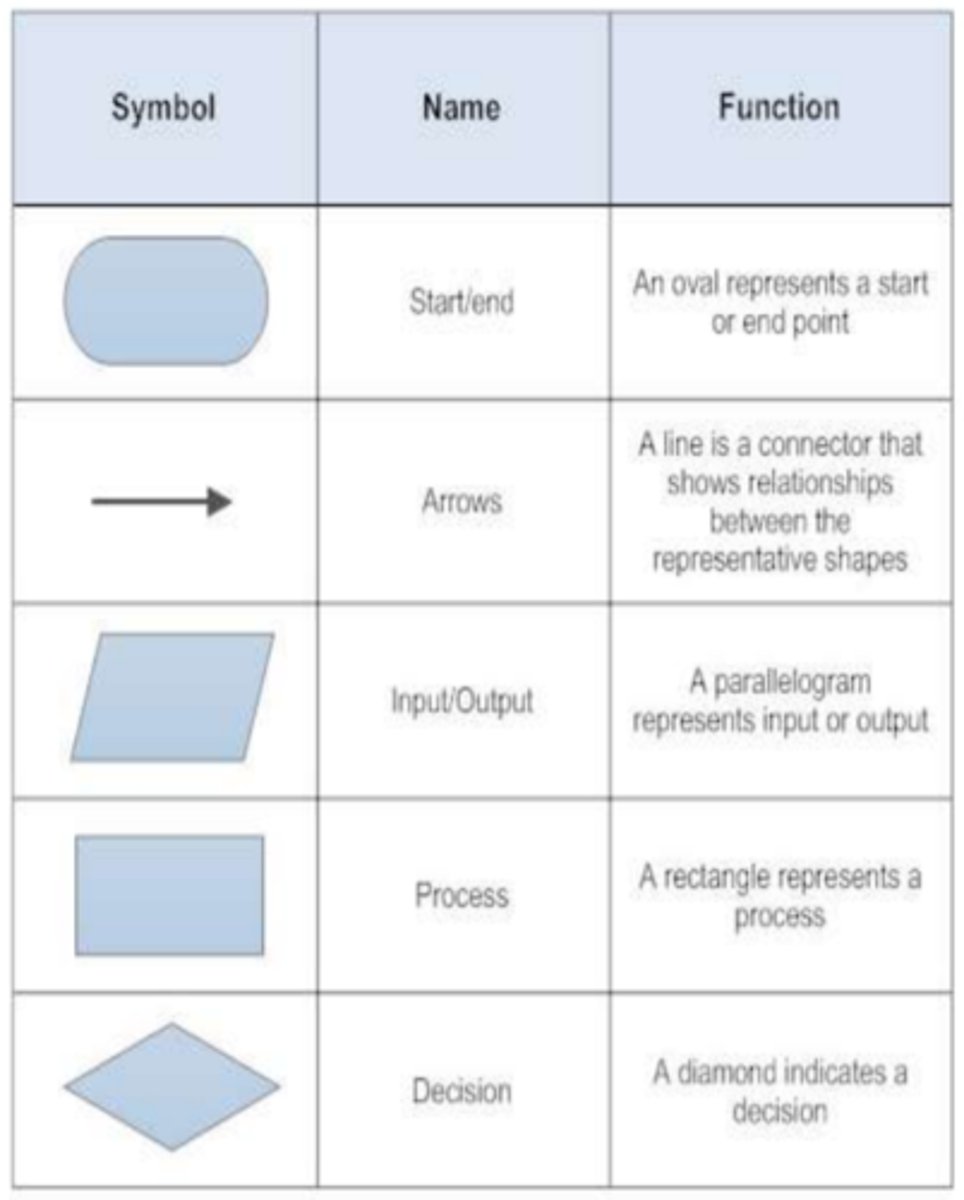
What does each flowchart symbol represent?
Rounded box - start or stop. Diamond - selection. Rectangle - process. Parallelogram - input. Arrow - progression of code.
What is a variable?
A location of memory that stores data.
How should you design variable names?
Meaningful and specific to the topic. Shouldn't have keywords like print or if. Constants should be uppercase and always remain the same.
Distinguish between real division and integer division
Real division returns a float, but integer division returns a (rounded down) whole number. Real division in python is /. Integer division in python is //.
What is the modulo?
The remainder after division, which is % in python.
How is exponentiation written in python?
** or pow(num1, num2)
State the relational operators in python
< > <= >= == !=
State the arithmetic operators in python
+ - / % += -= = /= //
What can cause a value error?
When you try to cast a variable into a different datatype.
What is type casting?
Changing a data type to a different type?
What are the main data types?
Integer, string, boolean, float.
How can you convert characters and ASCII values in python?
ord() converts characters to the ASCII value and chr() converts ASCII values into characters.
How do you convert a string into a float?
Using float()
What is sequence?
The order in which instructions are executed.
What is selection?
Conditions that change the program's direction, determining whether code should be executed.
What is definite and indefinite iteration?
Definite iteration finishes at a defined time, and indefinite iteration finished until a condition is met.
What is nested selection / iteration?
When loops / conditions are used inside other loops / conditions.
What is assignment?
Giving a variable a value.
What's the difference between arrays and lists?
Arrays are a fixed length data structure of one data type. Lists are variable length data structures of varying data types.
What are 2D arrays?
Arrays containing arrays. Individual elements can be abstracted by array[num1][num2]
What are records?
Any number of data items (fields) of any data type.
What are the uses of subroutines?
Keeping code neat, helping abstraction, and you can test each function separately.
What are the differences between functions and procedures?
Functions return values unlike procedures, where it is optional. Functions can only have input parameters but procedures can have input and output parameters. Functions must have an input parameter but procedures can take zero or any input parameters. Functions can be called from a procedure but procedures cannot be called from a function.
How are functions written in python?
def function (num1, num2):
return (num1, num2)
print (function(3, 5))
What is verification?
Checking that a software achieves its goal without any bugs (e.g. that my age is 15).
What is validation?
Checking that a software has correct requirements (e.g. that my age is an integer).
What type of validation checks are there?
Range check, type check, presence check, format check, length check
What is a local variable?
A variable in a function that will not be passed to the main program.
What is the advantage of local variables?
They do not have to be deleted after the subroutine has run.
What is the difference between global and local variables?
Global variables are accessible anywhere in the program and local variables are only accessible in their scope, such as in subroutines.
What does the structure approach involve?
Modularised programming, appropriately named variables, subroutines, code comments, well-documented interfaces.
What are the advantages of the structured approach?
Multiple programmers can work on different functions at a time, pre-tested subroutines can be used again or in different programs, easier maintenance and debugging, other people can understand your intentions.
What is try except?
The code under try is run, and if there is an error the code under except will run.
What is normal, erroneous, and boundary data?
Normal data is the expected data. Erroneous data falls outside of what is acceptable and should be rejected by the system. Boundary data falls outside the expected range. If your expected range is 0 < x < 101, boundary data includes 0, 1, 100, and 101, but erroneous data includes 102.
What is the purpose of testing?
To ensure a program works as intended under good conditions and copes with errors when given bad data.
How can we conduct testing?
With trace tables and test plans.
What is a trace table?
A table that records the variables in a programs as they change, used to check that they are correct at the end of an algorithm.
What format is data on computers stored in?
Binary
What are the names for bit storage quantities?
Bit, Byte, Kilobyte, Megabyte, Gigabyte, Terabyte. b, B, KB, MB, GB, TB.
What are the typical files with each of these sizes?
b - single boolean. B - ASCII character. KB - text file. MB - photos and MP3 files. GB - videos and software applications. TB - backups of whole systems.
What is the typical file size for a compressed HD movie?
8 GB
What is the typical file size for a MP3 file?
4 MB
What is the typical file size for a photo?
10 MB
What is the typical file size for a word document of a few pages?
50 KB
Why do computers use binary?
Binary numbers represent the flow of electricity through transistors and logic circuits. Secondary storage devices may represent the binary data in other forms, such as positively or negatively charged magnetic particles or transitions between pits and lands.
How is binary data transmitted across networks?
As electrical pulses, light, or encoded radio waves.
What is a number system?
A mechanism for representing a number using a set of symbols or digits.
e.g. Convert 33 into binary
100001
e.g. Convert 1010101 into decimal
89
How do we add binary numbers?
Through column additions, where 0 + 0 = 0, 0 + 1 = 1, 1 + 1 = 0 (carry 0), and 1 + 1 + 1 = 1 (carry 1).
What is an overflow error?
An error that occurs when the result of binary addition is too large to represent the number of bits available within the system. It can lead to inaccurate results or software crashes if not handled correctly.
How can we deal with an overflow error?
By storing the overflow bits in another memory location or set a special flag bit to indicate that the error has occurred. The CPU, OS, or application can detect the status of this flag and respond accordingly, e.g. by breaking the sum down into two smaller sums that can be computed and combined together.
How does character encoding work?
Each character in a character set is given a unique number.
What ASCII value is A?
65
What ASCII value is a?
97
Why is ASCII an impractical character set today?
It cannot represent non-English characters.
What other character sets have more characters?
The extended ASCII set uses 8 bits, providing up to 256 characters. Unicode aims to represent every possible character (including emojis), using between 8 and 48 bits per character.
How do you enter a hexadecimal number in python?
Prefix it with 0x.
e.g. What is 30 in hexadecimal?
1E
e.g. What is 11101010 in hexadecimal?
EA
e.g. What is F5 in binary?
11110101
e.g. What is CB in decimal?
203
How are images represented?
By bitmap pixels (pixel = picture element) where each pixel has a single colour assigned to it, stored as a binary value.
What is colour depth?
The number of bits used per pixel to represent the colour.
How can you calculate the number of colours possible?
2ᶜᵒˡᵒᵘʳ⁻ᵈᵉᵖᵗʰ
How can the colours be stored?
You could use a colour palette with a binary number for every colour, or combining amounts of red, green, and blue out of 255.
What is the formula for image file size?
File size = image height X image width X colour-depth
What is analogue and digital information?
Analogue information is continuous values that can be measured with theoretically infinite position. Digital information is discrete / finite values.
How can you convert between the two?
ADC (analogue-to-digital converter) or DAC (digital-to-analogue converter).
Describe the process of recording digital audio
The air around an object is compressed when something produces sound. The resulting pressure waves travel through the air and cause the diaphragm of a microphone to oscillate at the same frequency at the original sound, producing an electrical current. An ADC in a sound card samples the amplitude (voltage) of the electrical current produced by the microphone and converts this value into binary, which is sent to a computer for storing and processing.
Describe the process of playing back digital audio
The data in a sound file is passed to a DAC within a digital device, which produces an analogue signal by producing voltages based on the binary values captured at each sample within the file. These voltages travel as electrical signals to speakers, where they cause magnetic drivers to oscillate, producing compressions in the air that travel to the ear.
What determines the volume and pitch of the sound?
Amplitude - volume. Frequency - pitch.
What is a sample?
A measure of the amplitude at a point in time (stored as a binary value).
What is the sampling rate?
The number of samples captured per second, measured in Hz.
What is the sampling interval?
The time between two samples.
What is the sample resolution?
The number of bits used to store each sample.
What is the bit-rate?
The number of bits needed to store one second of audio, calculated by sampling frequency X sample resolution.
How do you calculate the file size?
Bit-rate X duration of recording (s)
What is the difference between lossless and lossy compression?
Lossy compression involves the loss of data, but lossless compression preserves all original data.